Outline
- Web's Success and the Role of Standards
- World Wide Web Consortium
- Web for Everyone
- Web on Everything
- Rich Web (Web 2.0), Voice, Mobile Web
- Web of Data and Services
- Questions
Web's Success
and the
Role of Standards
What Led to the Web's Success?

- Simple architecture - HTML, URI, HTTP
- Networked - value grows with data, services, users
- Extensible - from Web of documents to ...
- Tolerant - even w/ imperfect mark-up, data, links, software
- Universal - independent of systems and people
- Free / cheap - browsers, information, services
- Simple / powerful / fun for users - text, graphics, links
- Open standards ...
Why are Open Standards Important?

- Broad industry agreement (if done right)
- Interoperability ... cross-application, -organization, -data
- Avoids vendor lock-in ... for providers and users
- Open access = no black boxes
- Mandated ... by customers, government
- Open, royalty-free standards = good business
sense
World Wide Web Consortium
Founded by Tim Berners-Lee in 1994, W3C is:
- Providing the Vision to Lead
- Engineering the Open Standards that
Make the Web Work ...
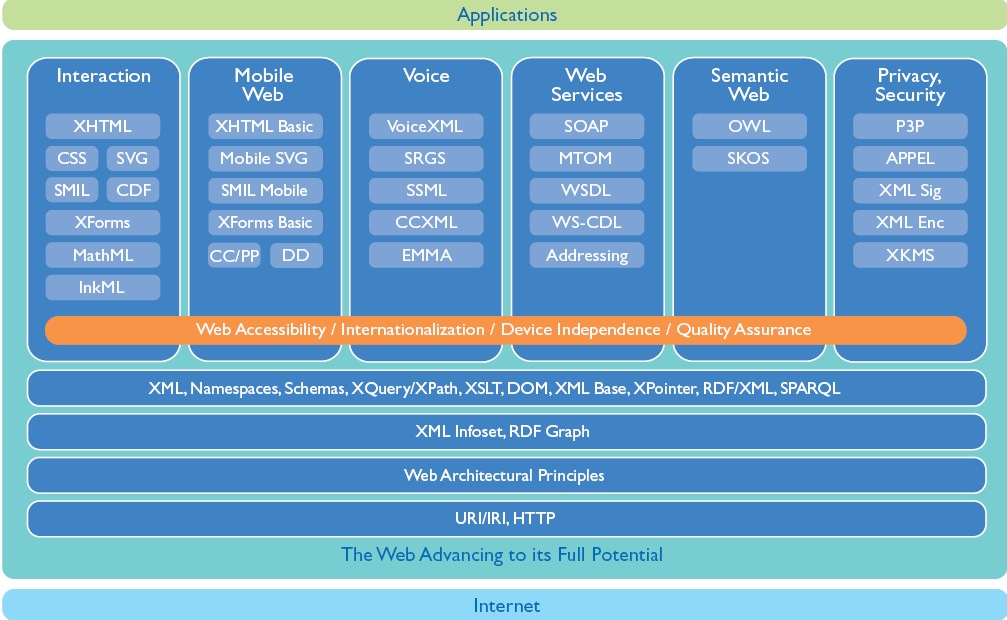
... expanding ...
- From a Web of Documents ...
- Toward One Web ...
- ... of Data and Services
- ... on Everything
- ... for Everyone
- -- think Web 3.0

Why Participate in W3C?
Saying in China*: "Third-class companies make products;
second-class companies develop technology; first-class companies set
standards."

- Early insight into market trends
- Promoting image as innovator
(Membership / Benefits / How to
join W3C / "At a Glance" brochure)
* from "China’s Post-WTO Technology Policy: Standards,
Software and the Changing Nature of Techno-Nationalism", by Richard P. Suttmeier and Yao Xiangkui.
Increasing Focus on Needs of Industries

- Why?
- Supports application of standards to real, important problem
- Improves standards: Use cases, reqs, implementation, testing
- Health Care and Life
Sciences - launched November 2005
- "use of Semantic Web technologies ... to improve collaboration,
research and development, and innovation adoption"
- Agfa, AstraZeneca, Cleveland Clinic, HL7, Merck, Partners, Pfizer
(66 participants)
- Financial Services - under consideration
- American Express, Citigroup, Dow Jones joined in 2006 (many others
considering)
What We Hear from Financial Services

- Customer (+employee) relationship management
- Security
- Legacy systems and data
- Interfacing and interoperability
- Transaction speed and reliability
- Mergers and acquisitions
- Risk management
- Corporate governance
- Competition and efficiency
- Globalization
- Leveraging IT -- a challenge in itself!
- XML, SOA, WS, mobile, and more ...
The Real Question
- Q: Which of these are relevant to you?
- A: All of them…

- ... but let's look at a subset of W3C's
emerging technologies
Web for Everyone

Universal Access ...
Web Security @ W3C
- W3C's Security Activity
- Seeking practical standards to address most pressing problems
- New Web Security Context Working
Group
- Planned during workshop
w/ major browser, security, financial services companies
- Usable, mutual authentication
- ... e.g., "secure
letterhead", "petname",
padlock use, certificates, etc.
- Forms annotation (in HTML WG) = important complement
- Starting to gather use cases
- New Maintenance Group?
- for core Web security standards for signature, encryption, key
management
- More about Web 2.0 security later ...
Web on Everything

*The* User Interface, everywhere ...
Web 2.0
- HTML, as an application platform
- Finally, the "Read-Write" Web
- Powerful apps emerging, e.g.
- Compact, interactive, efficient updating
- Tools: Gmail, Google Maps, Basecamp
- Blogs, wikis, social sites, etc.
- Dashboards: e.g. ⇨
- More scripting, more security concerns
- Exposure of user and server data and systems
- Browser safeguards limit potential
W3C Rich Web Clients @ W3C

- Mature W3C standards (plus javascript) enable Web 2.0
- HTML WG bringing most
important spec up to date
- DOM, CSS, SVG, etc.
- New Rich Web Clients
Activity, is standardizing:
- Coordinating with browser developers to enable more secure application
environment
- e.g., standard
for site to declare that its data are available to any javascript
application (or not)
(little AJAX/SVG-based demos: XMLHTTPRequest
playlist, fatcats, cubes)
Voice @ W3C
- Why?
- Companies provide interactive voice response (IVR)
- Companies use Web technologies (e.g., XML) to manage data
- Similarities between voice- and screen-browsing
- What does the Voice Browser
Working Group do?
- Standards for vocal interaction with Web applications
- Convergence with other Web technologies
- How important is this?
- One of the largest W3C Working Groups
- VoiceXML leads the voice markup market ... and growing
Voice: Architecture
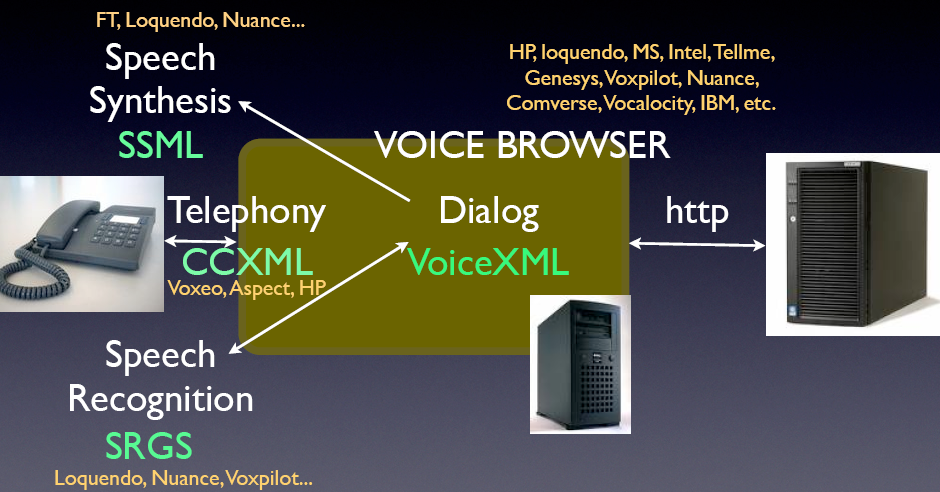
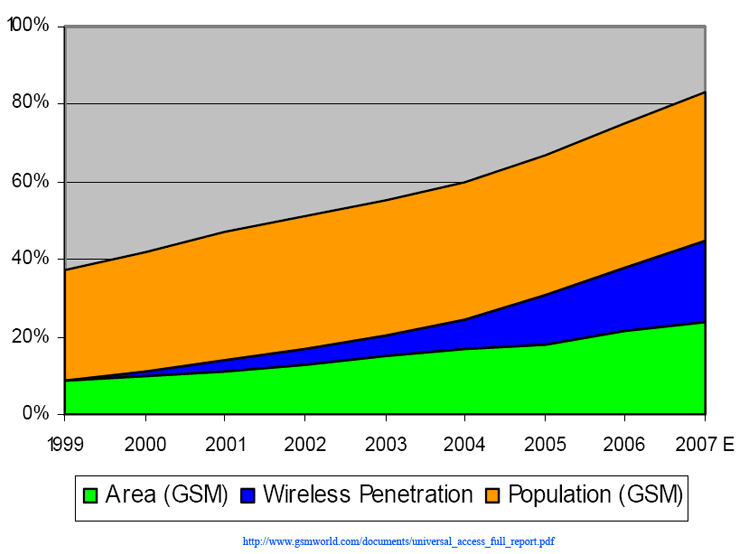
Mobile Web: The Next "Thing"
- 2+ billion connected. ~2/3 Web-capable. +1 million more/day.

(Source: Steven Pemberton)
Today, Mobile Web is Inconvenient, Inefficient
- Operators/phones require custom Web authoring for acceptable
usability

(Source: RusselBeattie.com)
Mobile Web Initiative @ W3C
Goal: Make Web access on phones as seamless, reliable,
cost-effective and useful on on desktops and laptops
(MWI Overview
slides)
MWI: Best Practices Guidelines Focus on Usability
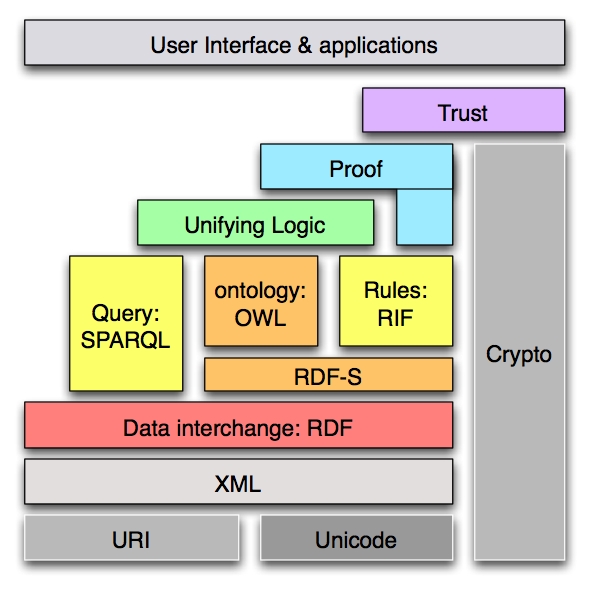
Web of Data & Services
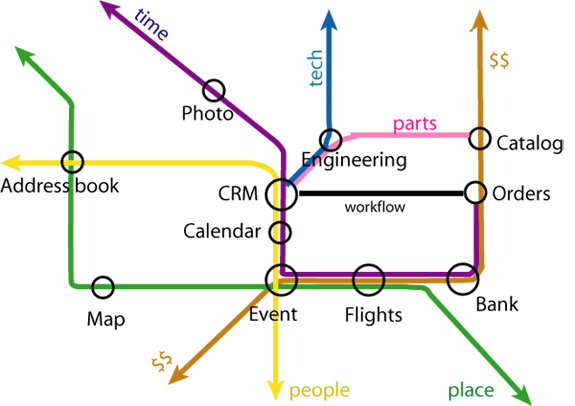
Interoperable information and programs ...
- XML: Binary, Processing Model
- Web of
Services: Performance, Addressing, SemWeb Services, Policy (overview
slides)
- Web of Data = Semantic Web: Deployment, Query, Rules, Health Care/Life Sciences, Content Labeling, Geospatial, Multimedia Semantics
Semantic Web: Why?
- Tasks often require combining data across the Internet, e.g.:
- Integrating data across the enterprise
- Hotel, transport, meeting, personal info come from different
sites
- Mining data from biochemical, genetic, pharmaceutical, patient
databases
- Cross-referencing disparate digital libraries
- Humans understand how to combine this information ...
- Not always easy (different vocabularies, languages, formats)
- Machines aren't smart enough :-)
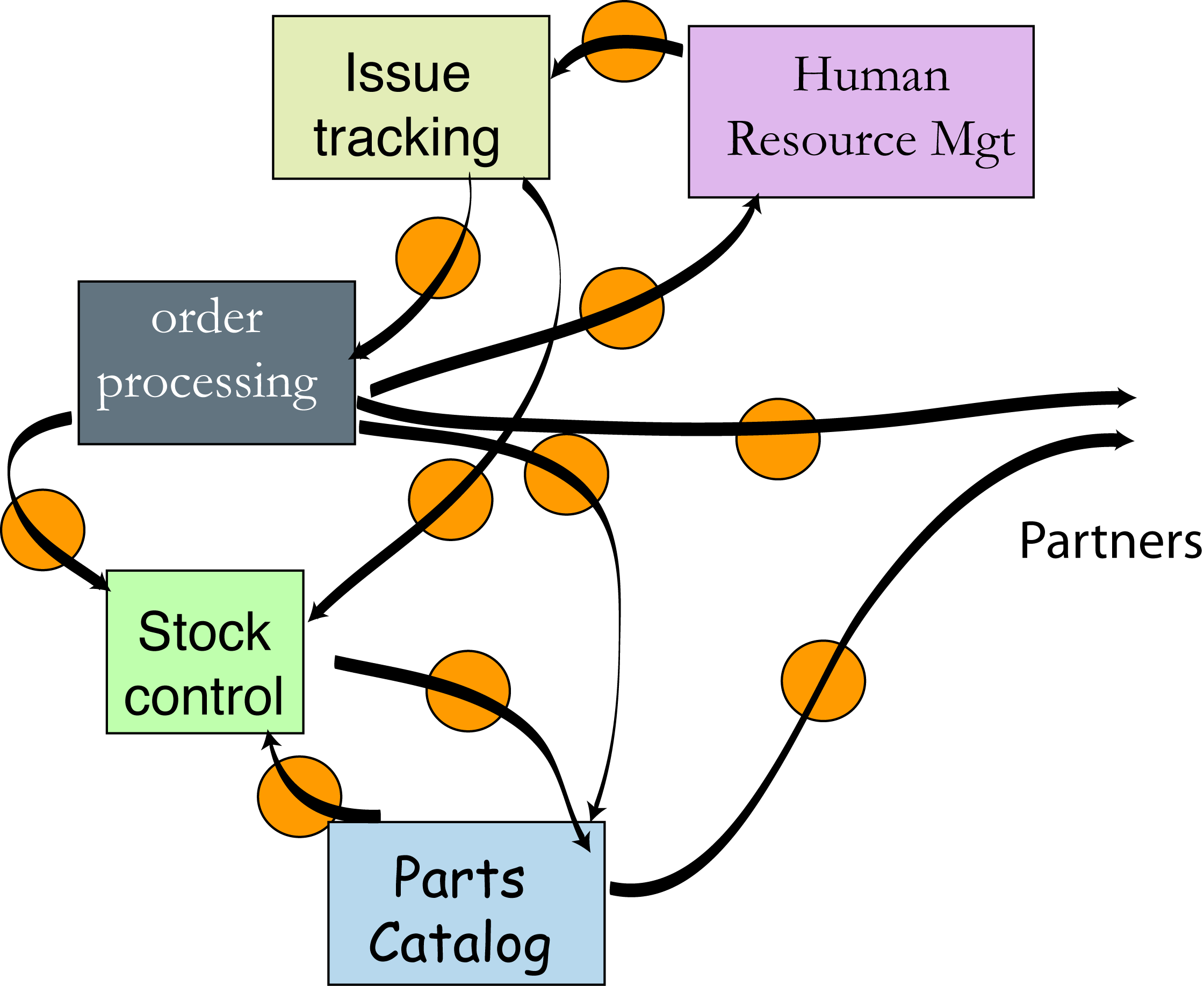
Enterprise Integration Today
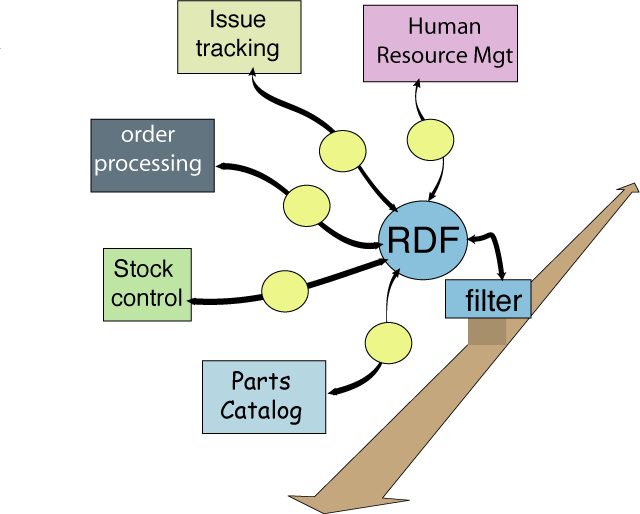
Enterprise Integration on the "Semantic Bus"
Summary




















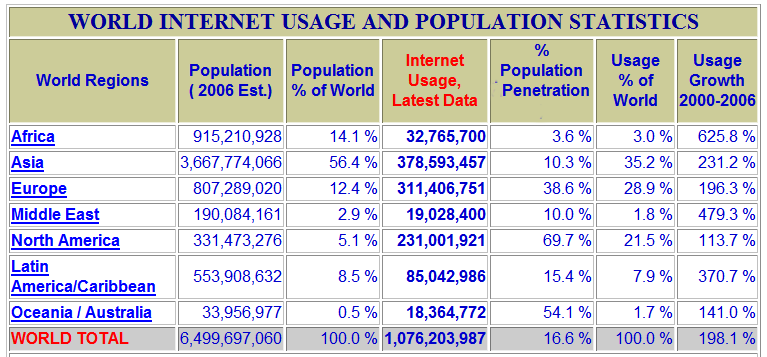
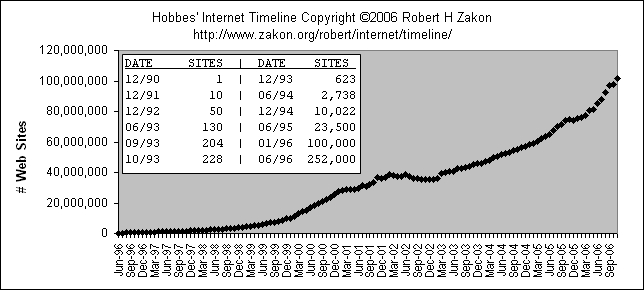



![]()
![]()