What is the World Wide Web Consortium?
- W3C as an International Organization
- Mission
- Structure
- Process
- People
- Web Technologies
Leading the Web to its Full Potential
Founded by Tim Berners-Lee in 1994, W3C is:
- Providing the Vision to Lead
- Engineering the Open Standards that
Make the Web Work ...
... expanding ...
- From a Web of Documents ...
- Toward One Web ...
- ... of Creators and Consumers
- ... of Data and Services
- ... on Everything
- ... for Everyone

Organization: International Web Standards Body
Expanding base of international operations
Process: Developing Standards
- Clear and effective Process: Coordination, consensus,
interoperability
- Member-neutrality: All Members have
equal rights
- Engineer dependencies (within W3C, and with 40+ Liaisons with SDOs)
- Consistent architectural framework:
- Industry-leading Patent Policy
- Royalty-free licensing commitment
- Incubator Activity launched in 2006
- Quicker, lighter process for innovative efforts led by Members
(Views of the Process: Life of Working Group, Recommendation Track)
People: International Leadership and Cooperation
Expanding base of the world's leading technology organizations and
technologists

W3C Membership by Country (Apr
2007)
Who are W3C's Members?
"Third-class companies make products; second-class companies
develop technology; first-class companies set standards."
- W3C's Members includes
...
- most of the world's leading IT companies
- other large and small companies
- academic and research institutions
- gov't, non-profit and standards organizations
- ... which are ...
- developing Web-based products
- using Web technologies
- conducting research on the Web
- developing specifications built upon W3C's work
* popular saying in Chinese business and
government, from "China’s Post-WTO
Technology Policy: Standards, Software and the Changing Nature of
Techno-Nationalism", by Richard P.
Suttmeier and Yao Xiangkui.
Full-fee Members (27 May
2007)
W3C Engineers the Foundation of the Web
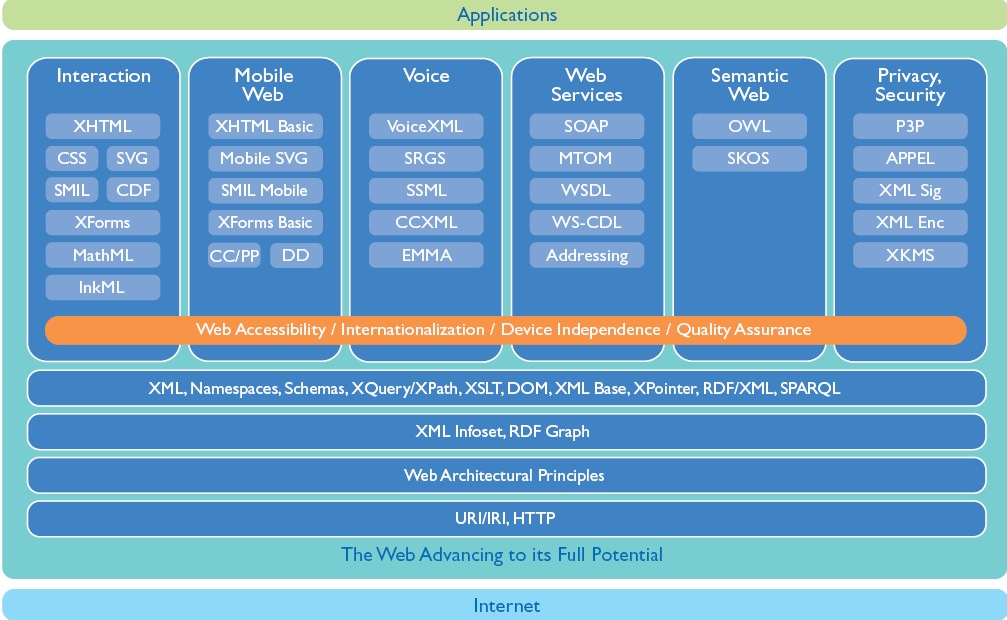
Web of Data & Services

Interoperable information and programs ...
- XML: Binary, Processing Model
- Web of
Services: Performance, Addressing, SemWeb Services, Policy (overview
slides)
- Web of Data = Semantic Web: Deployment, Query, Rules, Health Care/Life Sciences, Content Labeling, Geospatial, Multimedia Semantics
Web on Everything

*The* User Interface, everywhere ...
- Interaction Technologies: HTML, XForms, CSS, MathML, Voice,
Graphics, Multimedia, Multimodal
- Web 2.0 = Rich Web Clients: Compound Doc Formats, Web Apps
APIs
(e.g., AJAX) and Formats (e.g., Widgets)
- Mobile Web Initiative
- Device Independence
- Ubiquitous Web
Applications
Web for Everyone

Universal Access ...
Summary























![]()




