The
World
Wide
Web
is
a
network-spanning
information
space
of
resources
interconnected
by
links.
interrelated
resources.
This
information
space
is
the
basis
of,
and
is
shared
by,
a
number
of
information
systems.
Within
each
of
these
systems,
agents
(people
people
and
software)
software
retrieve,
create,
display,
analyze,
relate,
and
reason
about
resources.
Web
architecture
includes
the
definition
of
the
information
space
in
terms
of
identification
and
representation
of
its
contents,
and
of
the
protocols
that
support
the
interaction
of
agents
in
an
information
system
making
use
of
the
space.
Web
architecture
is
influenced
by
social
requirements
and
software
engineering
principles
.
These
lead
to
design
choices
and
constraints
on
the
behavior
of
systems
that
use
the
Web
in
order
to
achieve
desired
properties
of
the
shared
information
space:
efficiency,
scalability,
and
the
potential
for
indefinite
growth
across
languages,
cultures,
and
media.
Good
practice
by
agents
in
the
system
is
also
important
to
the
success
of
the
system.
This
document
reflects
the
three
bases
of
Web
architecture:
identification,
interaction,
and
representation.
This
section
describes
the
status
of
this
document
at
the
time
of
its
publication.
Other
documents
may
supersede
this
document.
A
list
of
current
W3C
publications
and
the
latest
revision
of
this
technical
report
can
be
found
in
the
W3C
technical
reports
index
at
http://www.w3.org/TR/.
This
is
the
8
June
5
July
2004
Editor's
Draft
of
"Architecture
of
the
World
Wide
Web,
First
Edition."
This
draft
takes
into
account
TAG
deleted text:
decisions
at
the
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2004/05/14-tag-summary.html" shape="rect">
12-14
May
2004
face-to-face
meeting
</a>
and
the
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2004/06/07-tag-summary.html" shape="rect">
7
June
2004
teleconference
</a>,
as
well
as
reviewer
comments
on
the
10
May
8
June
2004
draft.
Editor's
Draft
.
It
includes
a
number
of
changes
that
take
into
account
TAG
decisions
to
issues
raised
about
the
9
December
2003
Last
Call
Working
Draft.
However,
it
does
not
address
all
last
call
issues
.
The
TAG
expects
this
document
to
become
a
W3C
Recommendation.
Please
comments
about
this
document
to
the
TAG
mailing
list
public-webarch-comments@w3.org
(
public
archive
).
This
document
has
been
developed
by
W3C's
Technical
Architecture
Group
(TAG)
(
charter
).
A
complete
list
of
changes
to
this
document
since
the
first
public
Working
Draft
is
available
on
the
Web.
The
TAG
charter
describes
a
process
for
issue
resolution
by
the
TAG.
In
accordance
with
those
provisions,
the
TAG
maintains
a
running
issues
list
.
The
First
Edition
of
"Architecture
of
the
World
Wide
Web"
does
not
address
every
issue
that
the
TAG
has
accepted
since
it
began
work
in
January
2002.
The
TAG
has
selected
a
subset
of
issues
that
the
First
Edition
does
address
to
the
satisfaction
of
the
TAG;
those
issues
are
identified
in
the
TAG's
issues
list.
The
TAG
intends
to
address
the
remaining
(and
future)
issues
after
publication
of
the
First
Edition
as
a
Recommendation.
This
document
uses
the
concepts
and
terms
regarding
URIs
as
defined
in
draft-fielding-uri-rfc2396bis-0x,
preferring
them
to
those
defined
in
RFC
2396.
The
IETF
Internet
Draft
draft-fieldi
ng-uri-rfc2396bis-0x
is
expected
to
obsolete
RFC
2396
,
which
is
the
current
URI
standard.
The
TAG
is
tracking
the
evolution
of
draft-fielding-uri-rfc2396bis-0x.
Publication
as
a
Working
Draft
does
not
imply
endorsement
by
the
W3C
Membership.
This
is
a
draft
document
and
may
be
updated,
replaced
or
obsoleted
by
other
documents
at
any
time.
It
is
inappropriate
to
cite
this
document
as
other
than
"work
in
progress."
The
latest
information
regarding
patent
disclosures
related
to
this
document
is
available
on
the
Web.
This
document
is
not
yet
covered
by
any
W3C
Patent
Policy.
deleted text:
World
Wide
Web
(
WWW
,
or
simply
Web
)
is
an
information
space
in
which
the
items
of
interest,
referred
to
as
resources
,
are
identified
by
global
identifiers
called
Uniform
Resource
Identifiers
(
URI
).
A
Examples
such
as
the
following
travel
scenario
is
are
used
throughout
this
document
to
illustrate
typical
behavior
of
Web
agents
—
—
people
or
software
(on
behalf
of
a
person,
entity,
or
process)
acting
on
this
information
space.
A
user
agent
acts
on
behalf
of
a
user.
Software
agents
include
servers,
proxies,
spiders,
browsers,
and
multimedia
players.
Story
While
planning
a
trip
to
Mexico,
Nadia
reads
"Oaxaca
weather
information:
'http://weather.example.com/oaxaca'"
in
a
glossy
travel
magazine.
Nadia
has
enough
experience
with
the
Web
to
recognize
that
"http://weather.example.com/oaxaca"
is
a
deleted text:
URI.
Given
the
context
in
which
the
URI
appears,
she
expects
and
that
it
allows
her
she
is
likely
to
access
weather
information.
be
able
to
use
software
to
retrieve
associated
information
(in
this
case,
about
the
weather,
as
advertised).
When
Nadia
enters
the
URI
into
her
browser:
-
The
browser
performs
an
information
retrieval
action
in
accordance
with
its
configured
behavior
for
resources
identified
via
the
"http"
URI
scheme.
-
The
authority
responsible
for
"weather.example.com"
provides
information
in
a
response
to
the
retrieval
request.
-
The
browser
displays
the
retrieved
information,
which
includes
hypertext
links
to
other
information.
Nadia
can
follow
these
hypertext
links
to
retrieve
additional
information.
This
scenario
illustrates
the
three
architectural
bases
of
the
Web
that
are
discussed
in
this
document:
-
Identification
.
Each
resource
is
identified
by
a
URI.
In
this
travel
scenario,
the
resource
is
a
periodically
updated
report
on
the
weather
in
Oaxaca,
and
the
URI
is
"http://weather.example.com/oaxaca".
-
Interaction
.
Protocols
define
the
syntax
and
semantics
of
messages
exchanged
by
agents
over
a
network.
Through
protocols,
Web
agents
communicate
the
information
state
of
a
resource
through
the
exchange
of
<a href="#def-representation" shape="rect">
representations
</a>.
In
the
travel
scenario,
resource.
Nadia
(by
clicking
on
a
hypertext
link
)
tells
her
browser
to
request
a
representation
the
information
state
of
the
resource
identified
by
the
URI
in
the
hypertext
link.
The
In
this
example,
the
browser
sends
an
HTTP
GET
request
to
the
server
at
"weather.example.com".
The
"weather.example.com"
and
the
server
responds
with
sends
back
a
representation
of
the
information
state.
In
this
example,
the
representation
deleted text:
that
includes
XHTML
data
and
metadata
such
as
the
Internet
media
type
of
the
data,
"application/xhtml+xml".
Note:
In
this
document,
the
noun
"representation"
means
"octets
that
encode
resource
state
information".
These
octets
do
not
necessarily
describe
the
resource,
or
portray
a
likeness
of
the
resource,
or
represent
the
resource
in
other
senses
of
the
word
"represent".
-
Formats
.
Representations
are
built
from
a
non-exclusive
set
of
data
formats,
used
separately
or
in
combination
(including
XHTML,
CSS,
PNG,
XLink,
RDF/XML,
SVG,
and
SMIL
animation).
In
this
scenario,
the
representation
deleted text:
data
format
is
built
primarily
in
XHTML.
While
interpreting
the
XHTML
representation
data,
the
browser
retrieves
and
displays
weather
maps
identified
by
URIs
within
the
XHTML.
Some
of
those
maps
are
built
in
SVG.
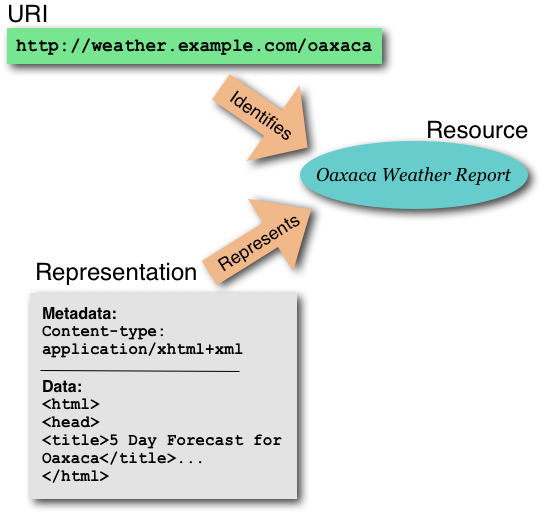
The
following
illustration
shows
the
relationship
between
identifier,
resource,
and
representation.
In
the
remainder
of
this
document,
we
highlight
important
architectural
points
regarding
Web
identifiers,
protocols,
and
formats.
We
also
discuss
some
important
general
architectural
principles
in
the
context
of
the
Web.
This
document
describes
the
properties
we
desire
of
the
Web
and
the
design
choices
that
have
been
made
to
achieve
them.
It
promotes
re-use
of
existing
standards
when
suitable,
and
gives
guidance
on
how
to
innovate
in
a
manner
consistent
with
the
Web
architecture.
The
terms
MUST,
MUST
NOT,
SHOULD,
SHOULD
NOT,
and
MAY
are
used
in
the
principles,
constraints,
and
good
practice
notes
in
accordance
with
RFC
2119
[
RFC2119
].
However,
this
document
does
not
include
conformance
provisions
for
these
reasons:
-
Conforming
software
is
expected
to
be
so
diverse
that
it
would
not
be
useful
to
be
able
to
refer
to
the
class
of
conforming
software
agents.
-
Some
of
the
good
practice
notes
concern
people;
specifications
generally
define
conformance
for
software,
not
people.
-
The
addition
of
a
conformance
section
is
not
likely
to
increase
the
utility
of
the
document.
This
document
is
intended
to
inform
discussions
about
issues
of
Web
architecture.
The
intended
audience
for
this
document
includes:
-
Participants
in
W3C
Activities
-
Other
groups
and
individuals
designing
technologies
to
be
integrated
into
the
Web
-
Implementers
of
W3C
specifications
-
Web
content
authors
and
publishers
Readers
will
benefit
from
familiarity
with
the
Requests
for
Comments
(
RFC
)
series
from
the
IETF
,
some
of
which
define
pieces
of
the
architecture
discussed
in
this
document.
Note:
This
document
does
not
distinguish
in
any
formal
way
the
terms
"language"
and
"format."
Context
determines
which
term
is
used.
The
phrase
"specification
designer"
encompasses
language,
format,
and
protocol
designers.
This
document
presents
the
general
architecture
of
the
Web.
Other
groups
inside
and
outside
W3C
also
address
specialized
aspects
of
Web
architecture,
including
accessibility,
internationalization,
device
independence,
and
Web
Services.
The
section
on
Architectural
Specifications
includes
references.
This
document
strikes
a
balance
between
brevity
and
precision
while
including
illustrative
examples.
TAG
findings
are
informational
documents
that
complement
the
current
document
by
providing
more
detail
about
selected
topics.
This
document
includes
some
excerpts
from
the
findings.
Since
the
findings
evolve
independently,
this
document
also
includes
references
to
approved
TAG
findings.
For
other
TAG
issues
covered
by
this
document
but
without
an
approved
finding,
references
are
to
entries
in
the
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist" shape="rect">
TAG
issues
list
.
Many
of
the
examples
in
this
document
that
involve
human
activity
suppose
the
familiar
Web
interaction
model
where
a
person
follows
a
link
via
a
user
agent,
the
user
agent
retrieves
and
presents
data,
the
user
follows
another
link,
etc.
This
document
does
not
discuss
in
any
detail
other
interaction
models
such
as
voice
browsing
(see,
for
example,
[
VOICEXML2
]).
For
instance,
when
a
graphical
user
agent
running
on
a
laptop
computer
or
hand-held
device
encounters
an
error,
the
user
agent
can
report
errors
directly
to
the
user
through
visual
and
audio
cues,
and
present
the
user
with
options
for
resolving
the
errors.
On
the
other
hand,
when
someone
is
browsing
the
Web
through
voice
input
and
audio-only
output,
stopping
the
dialog
to
wait
for
user
input
may
reduce
usability
since
it
is
so
easy
to
"lose
one's
place"
when
browsing
with
only
audio-output.
This
document
does
not
discuss
how
the
principles,
constraints,
and
good
practices
identified
here
apply
in
all
interaction
contexts.
The
important
points
of
this
document
are
categorized
as
follows:
-
Principle
-
An
architectural
principle
is
a
fundamental
rule
that
applies
to
a
large
number
of
situations
and
variables.
Architectural
principles
include
"separation
of
concerns",
"generic
interface",
"self-descriptive
syntax,"
"visible
semantics,"
"network
effect"
(Metcalfe's
Law),
and
Amdahl's
Law:
"The
speed
of
a
system
is
limited
by
its
slowest
component."
-
Constraint
-
In
the
design
of
the
Web,
some
design
choices,
like
the
names
of
the
p
and
li
elements
in
HTML,
or
the
choice
of
the
colon
(:)
character
in
URIs,
are
somewhat
arbitrary;
if
paragraph
had
been
chosen
instead
of
p
or
asterisk
(*)
instead
of
colon,
the
large-scale
result
would,
most
likely,
have
been
the
same.
Other
design
choices
are
more
fundamental;
these
are
the
focus
of
this
document.
Design
choices
can
lead
to
constraints,
i.e.,
restrictions
in
behavior
or
interaction
within
the
system.
Constraints
may
be
imposed
for
technical,
policy,
or
other
reasons
to
achieve
certain
properties
of
the
system,
such
as
accessibility
and
global
scope,
and
non-functional
properties,
such
as
relative
ease
of
evolution,
re-usability
of
components,
efficiency,
and
dynamic
extensibility.
-
Good
practice
-
Good
practice
—
—
by
software
developers,
content
authors,
site
managers,
users,
and
specification
designers
—
—
increases
the
value
of
the
Web.
In
order
to
communicate
internally,
a
community
agrees
(to
a
reasonable
extent)
on
a
set
of
terms
and
their
meanings.
One
design
goal
for
the
Web,
from
its
inception,
has
been
to
create
build
a
global
community
in
which
any
party
can
share
information
with
any
other
party
party.
To
achieve
this
goal,
the
Web
makes
use
of
a
single
global
identification
mechanism.
system.
The
global
scope
promotes
large-scale
"network
effects":
the
value
of
an
identifier
increases
the
more
it
is
used
(e.g.,
consistently
(for
example,
the
more
it
is
used
in
<a href="#hypertext" shape="rect">
hypertext
links
[section
4.4]
).
Principle:
Global
Identifiers
Global
naming
leads
to
global
network
effects.
This
principle
dates
back
at
least
as
far
as
Douglas
Engelbart's
seminal
work
on
open
hypertext
systems;
see
section
Every
Object
Addressable
in
[
Eng90
].
The
choice
of
syntax
for
global
identifiers
is
somewhat
arbitrary;
what
is
important
is
their
global
scope.
The
Uniform
Resource
Identifier
([
URI
],
currently
being
revised)
deleted text:
mechanism
has
been
successfully
deployed
since
the
creation
of
the
Web.
There
are
substantial
benefits
to
participating
in
the
existing
network
of
URIs,
including
linking,
bookmarking,
caching,
and
indexing
by
search
engines.
A
resource
should
be
assigned
a
have
an
associated
URI
if
another
party
might
reasonably
want
to
create
a
hypertext
link
to
it,
make
or
refute
assertions
about
it,
retrieve
or
cache
a
representation
of
it,
include
all
or
part
of
it
by
reference
into
another
representation,
annotate
it,
or
perform
other
operations
on
it.
Software
developers
should
expect
that
it
will
prove
useful
to
be
able
to
share
sharing
a
URI
across
applications,
applications
will
be
useful,
even
if
that
utility
is
not
initially
evident.
The
TAG
finding
"
URIs,
Addressability,
and
the
use
of
HTTP
GET
and
POST
"
discusses
additional
benefits
and
considerations
of
URI
addressability.
Good
practice:
Identify
with
URIs
To
benefit
from
and
increase
the
value
of
the
World
Wide
Web,
agents
should
provide
URIs
as
identifiers
for
resources.
Other
mechanisms
for
identifying
resources
resource
identification
systems
(see
the
section
on
future
directions
for
identifiers
)
may
expand
the
Web
as
we
know
it
today.
However,
there
are
substantial
costs
to
creating
a
new
identification
mechanism
system
that
has
the
same
properties
as
URIs.
To
keep
communication
costs
down,
by
design
a
URI
identifies
one
resource.
resource
.
Since
the
scope
of
a
URI
is
global,
the
resource
identified
by
a
URI
does
not
depend
on
the
context
in
which
the
URI
appears
(see
also
the
section
about
indirect
identification
).
Just
as
one
might
wish
to
refer
to
a
person
by
different
names
(by
full
name,
first
name
only,
sports
nickname,
romantic
nickname,
and
so
forth),
Web
architecture
allows
the
assignment
association
of
more
than
one
URI
to
with
a
resource.
URIs
that
identify
the
same
resource
are
called
URI
aliases
</a>
.
The
section
on
URI
aliases
discusses
some
of
the
potential
costs
of
creating
multiple
URIs
for
the
same
resource.
The
following
sections
address
other
questions
about
the
relationship
between
URIs
and
resources,
including:
-
How
much
can
I
tell
about
a
resource
by
inspection
of
a
URI
that
identifies
it?
See
in
particular
the
sections
on
URI
schemes
and
Information
Resources
.
-
Who
determines
what
resource
a
URI
identifies?
See
the
section
on
URI
ownership
.
-
Can
the
resource
identified
by
a
URI
change
over
time?
See
in
particular
the
sections
on
URI
persistence
and
representation
management
.
-
Since
more
than
one
URI
can
identify
the
same
resource,
how
do
I
know
which
URIs
identify
the
same
resource?
See
in
particular
the
sections
on
URI
comparison
and
assertions
that
two
URIs
identify
the
same
resource
.
deleted text:
<li>
Are
there
resources
that
are
not
identified
by
any
URI?
In
a
system
where
the
only
resource
identification
mechanism
is
the
URI,
the
question
is
only
of
philosophical
interest
(similarly,
if
a
tree
falls
in
the
forest
and
nobody
is
around
to
hear
it,
does
it
make
a
sound?).
The
advent
of
other
resource
identification
mechanisms
may
change
the
nature
of
this
question
and
answer.
</li>
The
most
straightforward
way
of
establishing
that
two
parties
are
referring
to
the
same
resource
is
to
compare,
character-by-character,
the
URIs
they
are
using.
Two
used
in
making
the
reference;
two
URIs
that
are
identical
deleted text:
(character
for
character)
refer
to
the
same
resource.
Because
Web
architecture
allows
the
assignment
association
of
more
than
one
URI
to
with
a
resource,
two
URIs
that
are
not
character
for
character
character-by-character
identical
can
still
refer
to
the
same
resource
(i.e.,
they
do
not
necessarily
refer
to
different
resources).
There
is
generally
a
higher
computational
cost
to
determine
that
two
different
URIs
refer
to
the
same
resource.
To
reduce
the
risk
of
a
false
negative
(i.e.,
an
incorrect
conclusion
that
two
URIs
do
not
refer
to
the
same
resource)
or
a
false
positive
(i.e.,
an
incorrect
conclusion
that
two
URIs
do
refer
to
the
same
resource),
certain
specifications
license
applications
to
apply
specify
equivalence
tests
in
addition
to
character-by-character
comparison.
For
example,
for
"http"
URIs,
the
authority
component
(the
part
after
"//"
and
before
the
next
"/")
is
defined
to
be
case-insensitive.
Thus,
the
"http"
URI
specification
licenses
applications
allows
agents
to
conclude
that
authority
components
in
two
"http"
URIs
are
equivalent
identify
the
same
resource
when
those
strings
are
character-by-character
equivalent
or
differ
only
by
case.
Agents
that
reach
conclusions
based
on
comparisons
that
are
not
licensed
specified
by
relevant
specifications
take
responsibility
for
any
problems
that
result.
result;
see
the
section
on
error
handling
[section
5.3]
for
more
information
about
responsible
behavior
when
reaching
unlicensed
conclusions.
Section
6
of
[
URI
]
provides
more
information
about
comparing
URIs
and
reducing
the
risk
of
false
negatives
and
positives.
See
the
section
below
on
approaches
other
than
string
comparison
that
allow
different
parties
agents
to
<a href="#future-comparison" shape="rect">
assert
conclude
that
two
URIs
identify
the
same
resource
[section
2.9.2]
.
Although
there
are
benefits
(such
as
naming
flexibility)
to
URI
aliases,
there
are
also
costs.
For
example,
the
assignment
association
of
more
than
one
URI
for
with
a
resource
undermines
the
network
effect.
URI
aliases
can
also
raise
the
cost
or
may
even
make
it
impossible
for
software
to
determine
by
following
specifications
that
the
URIs
identify
the
same
resource.
URI
producers
should
thus
be
conservative
about
the
number
of
different
URIs
they
produce
for
associate
with
the
same
resource.
Good
practice:
Avoiding
URI
aliases
A
URI
owner
SHOULD
NOT
create
associate
arbitrarily
different
URIs
for
with
the
same
resource.
URI
consumers
also
have
a
role
in
ensuring
URI
consistency.
For
instance,
when
transcribing
a
URI,
agents
should
not
gratuitously
percent-encode
characters.
The
term
"character"
refers
to
URI
characters
as
defined
in
section
2
of
[
URI
];
percent-encoding
is
discussed
in
section
2.1
of
that
specification.
Good
practice:
Consistent
URI
usage
If
An
agent
that
receives
a
URI
deleted text:
has
been
assigned
to
a
resource,
agents
SHOULD
refer
to
the
associated
resource
using
the
same
URI,
character
for
character.
character-by-character.
When
a
URI
alias
does
become
common
currency,
the
URI
owner
should
use
protocol
techniques
such
as
server-side
redirects
to
connect
relate
the
two
resources.
The
community
benefits
when
the
URI
owner
supports
both
the
"official"
URI
and
the
alias.
As
discussed
above,
a
URI
identifies
one
resource.
At
times,
agents
may
intentionally
or
unintentionally
use
a
URI
to
identify
different
resources.
URI
overloading
refers
to
the
use
of
one
URI
to
refer
directly
to
more
than
one
resource.
Overloading
often
imposes
a
cost
in
communication
due
to
the
effort
required
to
resolve
ambiguities.
Suppose,
for
example,
that
one
organization
makes
use
of
a
URI
to
refer
to
the
movie
"The
Sting",
and
another
organization
uses
the
same
URI
to
refer
to
a
discussion
forum
about
"The
Sting."
This
overloading
can
create
confusion
about
what
the
URI
identifies,
undermining
the
value
of
the
URI.
If
one
wanted
to
talk
about
the
creation
date
of
the
resource
identified
by
the
URI,
for
instance,
it
would
not
be
clear
whether
this
meant
"when
the
movie
created"
or
"when
the
discussion
forum
about
the
movie
was
created."
Good
practice:
Avoiding
URI
Overloading
Agents
SHOULD
find
out
what
resource
a
URI
identifies
before
using
creating
references
with
that
URI.
The
section
below
on
<a href="#uri-ownership" shape="rect">
URI
ownership
[section
2.5]
examines
approaches
for
establishing
the
authoritative
source
of
information
about
what
resource
a
URI
identifies.
Listening
to
a
news
broadcast,
one
might
hear
a
report
on
Britain
that
begins,
"Today,
10
Downing
Street
announced
a
series
of
new
economic
measures."
Generally,
"10
Downing
Street"
identifies
the
official
residence
of
Britain's
Prime
Minister.
In
this
context,
the
news
reporter
is
using
it
(as
English
rhetoric
allows)
to
indirectly
identify
the
British
government.
Similarly,
URIs
identify
resources,
but
they
can
also
be
used
in
many
constructs
to
indirectly
identify
arbitrary
entities.
Certain
properties
of
URIs
Globally
adopted
assignment
policies
make
them
some
URIs
appealing
as
general-purpose
identifiers.
Local
policy
establishes
what
they
indirectly
identify.
For
example,
the
URI
"mailto:nadia@example.com"
identifies
an
Internet
mailbox
(as
licensed
specified
by
the
"mailto"
URI
scheme).
Suppose
this
particular
URI
identifies
Nadia's
Internet
mailbox.
The
organizers
of
a
conference
attended
by
Nadia
might
use
"mailto:nadia@example.com"
to
refer
indirectly
to
her
(e.g.,
using
the
URI
as
a
database
key
in
their
database
of
conference
participants).
To
avoid
URI
overloading
,
it
is
important
to
reduce
the
risk
that
different
agents
will
unintentionally
(or
intentionally)
create
use
the
same
URI
(i.e.,
sequence
of
characters).
URI
scheme
specifications
can
help
reduce
this
risk,
and
commonly
do
so
through
the
hierarchical
delegation
of
authority.
This
approach,
exemplified
by
the
"http"
and
"mailto"
schemes,
allows
the
assignment
of
a
part
of
URI
space
to
one
party,
who
may,
in
turn,
delegate
management
of
pieces
of
that
space
to
other
parties.
It
is
thus
useful
for
a
URI
scheme
to
establish
a
unique
relationship
between
a
social
entity
and
a
URI;
this
is
the
case
for
the
"http",
"mailto",
"mid",
and
"cid"
schemes,
for
example.
This
relationship
is
called
URI
ownership
.
In
this
document,
the
phrase
"authority
responsible
for
domain
X"
indicates
that
the
same
entity
owns
those
URIs
where
the
authority
component
is
domain
X.
This
document
does
not
address
how
the
benefits
and
responsibilities
of
URI
ownership
may
be
delegated
to
other
parties,
such
as
to
a
server
manager
or
to
someone
who
has
been
delegated
part
of
the
URI
space
on
a
given
Web
server.
The
approach
taken
for
the
"http"
URI
scheme
follows
the
pattern
whereby
the
Internet
community
delegates
authority,
via
the
IANA
URI
scheme
registry
[
IANASchemes
]
and
the
DNS,
over
a
set
of
URIs
with
a
common
prefix
to
one
particular
owner.
One
consequence
of
this
approach
is
the
Web's
heavy
reliance
on
the
central
DNS
registry.
A
URI
owner
may,
upon
request,
provide
representations
of
the
resource
identified
by
the
URI.
For
example,
when
a
URI
owner
uses
the
HTTP
protocol
to
provide
those
representations,
the
HTTP
origin
server
(defined
in
[
RFC2616
])
is
the
software
agent
acting
on
behalf
of
the
URI
owner
to
provide
the
authoritative
representations
for
the
resource
identified
by
that
URI.
The
owner
is
also
responsible
for
accepting
or
rejecting
requests
to
modify
the
resource
identified
by
that
URI,
for
example,
by
configuring
a
server
to
accept
or
reject
HTTP
PUT
data
based
on
Internet
media
type,
validity
constraints,
or
other
constraints.
Recall
that
the
Web
architecture
allows
different
URI
owners
to
create
URI
aliases
.
This
means
that
multiple
parties
may
provide
representations
of
the
same
resource,
depending
on
which
URI
is
used
for
interaction.
A
URI
owner's
rights
extend
only
to
the
representations
served
for
requests
given
that
URI.
There
are
social
expectations
for
responsible
<a href="#representation-management" shape="rect">
representation
management
[section
3.6]
by
URI
owners,
discussed
below.
Additional
social
implications
of
URI
ownership
are
not
discussed
here.
However,
the
success
or
failure
of
these
different
approaches
depends
on
the
extent
to
which
there
is
consensus
in
the
Internet
community
on
abiding
by
the
defining
specifications.
See
TAG
issue
siteData-36
,
which
concerns
the
expropriation
of
naming
authority.
In
the
URI
"http://weather.example.com/",
the
"http"
that
appears
before
the
colon
(":")
names
a
URI
scheme.
Each
URI
scheme
has
a
specification
that
explains
how
identifiers
are
assigned
within
that
scheme.
The
URI
syntax
is
thus
a
federated
and
extensible
naming
mechanism
system
wherein
each
scheme's
specification
may
further
restrict
the
syntax
and
semantics
of
identifiers
within
that
scheme.
Examples
of
URIs
from
various
schemes
include:
-
mailto:joe@example.org
-
ftp://example.org/aDirectory/aFile
-
news:comp.infosystems.www
-
tel:+1-816-555-1212
-
ldap://ldap.example.org/c=GB?objectClass?one
-
urn:oasis:names:tc:entity:xmlns:xml:catalog
While
the
Web
architecture
allows
the
definition
of
new
schemes,
introducing
a
new
scheme
is
costly.
Many
aspects
of
URI
processing
are
scheme-dependent,
and
a
significant
amount
of
deployed
software
already
processes
URIs
of
well-known
schemes.
Introducing
a
new
URI
scheme
requires
the
development
and
deployment
not
only
of
client
software
to
handle
the
scheme,
but
also
of
ancillary
agents
such
as
gateways,
proxies,
and
caches.
See
[
RFC2718
]
for
other
considerations
and
costs
related
to
URI
scheme
design.
Because
of
these
costs,
if
a
URI
scheme
exists
that
meets
the
needs
of
an
application,
designers
should
use
it
rather
than
invent
one.
Good
practice:
<a name="pr-new-scheme-expensive" id="pr-new-scheme-expensive" shape="rect">
New
Reuse
URI
schemes
A
specification
SHOULD
NOT
introduce
a
new
URI
scheme
when
reuse
an
existing
URI
scheme
(rather
than
create
a
new
one)
when
it
provides
the
desired
properties
of
identifiers
and
their
relation
to
resources.
Consider
our
travel
scenario
:
should
the
agent
providing
information
about
the
weather
in
Oaxaca
register
a
new
URI
scheme
"weather"
for
the
identification
of
resources
related
to
the
weather?
They
might
then
publish
URIs
such
as
"weather://travel.example.com/oaxaca".
When
a
software
agent
dereferences
such
a
URI,
if
what
really
happens
is
that
HTTP
GET
is
invoked
to
retrieve
a
representation
of
the
resource,
then
an
"http"
URI
would
have
sufficed.
If
the
motivation
behind
registering
a
new
scheme
is
to
allow
a
software
agent
to
launch
a
particular
application
when
retrieving
a
representation,
such
dispatching
can
be
accomplished
at
lower
expense
via
Internet
media
types.
When
designing
a
new
data
format,
the
appropriate
mechanism
to
promote
its
deployment
on
the
Web
is
the
Internet
media
type.
Media
types
also
provide
a
means
for
<a href="#media-types-infospace" shape="rect">
building
new
information
space
applications
[section
4.6]
,
described
below.
Note
that
even
if
an
agent
cannot
process
representation
data
in
an
unknown
format,
it
can
at
least
retrieve
it.
The
data
may
contain
enough
information
to
allow
a
user
or
user
agent
to
make
some
use
of
it.
When
an
agent
does
not
handle
a
new
URI
scheme,
it
cannot
retrieve
a
representation.
The
Internet
Assigned
Numbers
Authority
(
IANA
)
maintains
a
registry
[
IANASchemes
]
of
mappings
between
URI
scheme
names
and
scheme
specifications.
For
instance,
the
IANA
registry
indicates
that
the
"http"
scheme
is
defined
in
[
RFC2616
].
The
process
for
registering
a
new
URI
scheme
is
defined
in
[
RFC2717
].
The
use
of
unregistered
URI
schemes
is
discouraged
for
a
number
of
reasons:
-
There
is
no
generally
accepted
way
to
locate
the
scheme
specification.
-
Someone
else
may
be
using
the
scheme
for
other
purposes.
-
One
should
not
expect
that
general-purpose
software
will
do
anything
useful
with
URIs
of
this
scheme
beyond
URI
comparison;
the
network
effect
is
lost.
Note:
Some
URI
scheme
specifications
(such
as
the
"ftp"
URI
scheme
specification)
use
the
term
"designate"
where
the
current
document
uses
"identify."
deleted text:
<p>
TAG
issue
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/issues.html#siteData-36" shape="rect">
siteData-36
</a>
is
about
expropriation
of
naming
authority.
</p>
It
is
tempting
to
guess
the
nature
of
a
resource
by
inspection
of
a
URI
that
identifies
it.
However,
the
Web
is
designed
so
that
agents
communicate
resource
information
state
through
representations
,
not
identifiers.
In
general,
one
cannot
determine
the
Internet
media
type
of
representations
of
a
resource
by
inspecting
a
URI
for
that
resource.
For
example,
the
".html"
at
the
end
of
"http://example.com/page.html"
provides
no
guarantee
that
representations
of
the
identified
resource
will
be
served
with
the
Internet
media
type
"text/html".
The
HTTP
protocol
does
not
constrain
the
Internet
media
type
based
on
the
path
component
of
the
URI;
the
URI
owner
is
free
to
configure
the
server
to
return
a
representation
using
PNG
or
any
other
data
format.
Resource
state
may
evolve
over
time.
Requiring
a
URI
owner
to
publish
a
new
URI
for
each
change
in
resource
state
would
lead
to
a
significant
number
of
broken
links.
references.
For
robustness,
Web
architecture
promotes
independence
between
an
identifier
and
the
identified
resource.
Good
practice:
URI
opacity
Agents
making
use
of
URIs
MUST
SHOULD
NOT
attempt
to
infer
properties
of
the
referenced
resource
except
as
licensed
specified
by
relevant
specifications.
The
example
URI
used
in
the
travel
scenario
("http://weather.example.com/oaxaca")
suggests
that
the
identified
resource
has
something
to
do
with
the
weather
in
Oaxaca.
A
site
reporting
the
weather
in
Oaxaca
could
just
as
easily
be
identified
by
the
URI
"http://vjc.example.com/315".
And
the
URI
"http://weather.example.com/vancouver"
might
identify
the
resource
"my
photo
album."
On
the
other
hand,
the
URI
"mailto:joe@example.com"
indicates
that
the
URI
refers
to
a
mailbox.
The
"mailto"
URI
scheme
specification
authorizes
agents
to
infer
that
URIs
of
this
form
identify
Internet
mailboxes.
In
some
cases,
relevant
technical
specifications
license
allow
URI
assignment
authorities
to
publish
assignment
policies.
For
more
information
about
URI
opacity,
see
TAG
issue
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#metadataInURI-31" shape="rect">
metaDataInURI-31
.
Story
When
navigating
within
the
XHTML
data
that
Nadia
receives
as
a
representation
of
the
resource
identified
by
"http://weather.example.com/oaxaca",
Nadia
finds
that
the
URI
"http://weather.example.com/oaxaca#tom"
refers
to
the
part
of
the
representation
that
conveys
information
about
tomorrow's
weather
in
Oaxaca.
This
URI
includes
the
fragment
identifier
"tom"
(the
string
after
the
"#").
The
fragment
identifier
component
of
a
URI
allows
indirect
identification
of
a
secondary
resource
by
reference
to
a
primary
resource
and
additional
identifying
information.
The
secondary
resource
may
be
some
portion
or
subset
of
the
primary
resource,
some
view
on
representations
of
the
primary
resource,
or
some
other
resource
defined
or
described
by
those
representations.
The
terms
"primary
resource"
and
"secondary
resource"
are
defined
in
section
3.5
of
[
URI
].
The
interpretation
of
fragment
identifiers
is
discussed
in
the
section
on
media
types
and
fragment
identifier
semantics
.
See
TAG
issues
issue
abstractComponentRefs-37
</a>
and
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/issues.html#DerivedResources-43" shape="rect">
DerivedResources-43
</a>.
,
which
concerns
the
use
of
fragment
identifiers
with
namespace
names
to
identify
abstract
components.
There
remain
open
questions
regarding
identifiers
on
the
Web.
The
following
sections
identify
a
few
areas
of
future
work
in
the
Web
community.
The
integration
of
internationalized
identifiers
(i.e.,
composed
of
characters
beyond
those
allowed
by
[
URI
])
into
the
Web
architecture
is
an
important
and
open
issue.
See
TAG
issue
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#IRIEverywhere-27" shape="rect">
IRIEverywhere-27
for
discussion
about
work
going
on
in
this
area.
Emerging
Semantic
Web
technologies,
including
the
"Web
Ontology
Language
(OWL)"
[
OWL10
],
define
RDF
properties
such
as
sameAs
to
assert
that
two
URIs
identify
the
same
resource
or
functionalProperty
to
imply
it.
Communication
between
agents
over
a
network
about
resources
involves
URIs,
messages,
and
data.
The
Web's
protocols
(including
HTTP,
FTP,
SOAP,
NNTP,
and
SMTP)
are
based
on
the
exchange
of
messages.
A
message
may
include
data
as
well
as
metadata
about
the
resource
(such
as
the
"Alternates"
and
"Vary"
HTTP
headers),
the
message
data,
and
the
message
itself
(such
as
the
"Transfer-encoding"
HTTP
header).
A
message
may
even
include
metadata
about
the
message
metadata
(for
message-integrity
checks,
for
instance).
Two
important
classes
of
message
are
those
that
request
a
representation
of
an
Information
Resource
,
and
those
that
return
the
result
of
such
a
request.
Story
Nadia
follows
a
hypertext
link
labeled
"satellite
image"
expecting
to
retrieve
a
satellite
photo
of
the
Oaxaca
region.
The
link
to
the
satellite
image
is
an
XHTML
link
encoded
as
<a href="http://example.com/satimage/oaxaca">satellite image</a>
<a
href="http://example.com/satimage/oaxaca">satellite
image</a>
.
Nadia's
browser
analyzes
the
URI
and
determines
that
its
scheme
is
"http".
The
browser
configuration
determines
how
it
locates
the
identified
information,
which
might
be
via
a
cache
of
prior
retrieval
actions,
by
contacting
an
intermediary
(such
as
a
proxy
server),
or
by
direct
access
to
the
server
identified
by
a
portion
of
the
URI.
In
this
example,
the
browser
opens
a
network
connection
to
port
80
on
the
server
at
"example.com"
and
sends
a
"GET"
message
as
specified
by
the
HTTP
protocol,
requesting
a
representation
of
the
resource.
The
server
sends
a
response
message
to
the
browser,
once
again
according
to
the
HTTP
protocol.
The
message
consists
of
several
headers
and
a
JPEG
image.
The
browser
reads
the
headers,
learns
from
the
"Content-Type"
field
that
the
Internet
media
type
of
the
representation
is
"image/jpeg",
reads
the
sequence
of
octets
that
make
up
the
representation
data,
and
renders
the
image.
This
section
describes
the
architectural
principles
and
constraints
regarding
interactions
between
agents,
including
such
topics
as
network
protocols
and
interaction
styles,
along
with
interactions
between
the
Web
as
a
system
and
the
people
that
make
use
of
it.
The
fact
that
the
Web
is
a
highly
distributed
system
affects
architectural
constraints
and
assumptions
about
interactions.
The
term
Information
Resource
refers
to
the
class
of
resources
having
information
state
—
—
state
that
can
be
represented
as
octets.
A
representation
of
information
state
consists
logically
of
two
parts:
data
(expressed
in
one
or
more
formats
used
separately
or
in
combination)
and
metadata
(such
as
the
Internet
media
type
of
the
data).
The
Information
Resource
provides
the
foundation
for
the
familiar
hypertext
Web,
where
agents
use
representations
to
modify
as
well
as
retrieve
information
state.
Much
of
this
document
describes
architecture
specific
to
Information
Resources.
For
instance,
the
techniques
of
caching
and
content
negotiation
,
and
the
social
processes
of
publishing,
apply
to
Information
Resources.
Agents
may
use
a
URI
to
access
the
referenced
resource;
this
is
called
dereferencing
the
URI
.
Access
may
take
many
forms,
including
retrieving
a
representation
of
the
resource
(for
instance,
by
using
HTTP
GET
or
HEAD),
adding
or
modifying
a
representation
of
the
resource
(for
instance,
by
using
HTTP
POST
or
PUT,
which
in
some
cases
may
change
the
actual
state
of
the
resource
if
the
submitted
representations
are
interpreted
as
instructions
to
that
end),
and
deleting
some
or
all
representations
of
the
resource
(for
instance,
by
using
HTTP
DELETE,
which
in
some
cases
may
result
in
the
deletion
of
the
resource
itself).
There
may
be
more
than
one
way
to
access
a
resource
for
a
given
URI;
application
context
determines
which
access
mechanism
method
an
agent
uses.
For
instance,
a
browser
might
use
HTTP
GET
to
retrieve
a
representation
of
a
resource,
whereas
a
hypertext
link
checker
might
use
HTTP
HEAD
on
the
same
URI
simply
to
establish
whether
a
representation
is
available.
Some
URI
schemes
set
expectations
about
available
access
mechanisms,
methods,
others
(such
as
the
URN
scheme
[
RFC
2141
])
do
not.
Section
1.2.2
of
[
URI
]
discusses
the
separation
of
identification
and
interaction
in
more
detail.
For
more
information
about
relationships
between
multiple
access
mechanisms
methods
and
URI
addressability,
see
the
TAG
finding
"
URIs,
Addressability,
and
the
use
of
HTTP
GET
and
POST
"
.
Although
many
URI
schemes
are
named
after
protocols,
this
does
not
imply
that
use
of
such
a
URI
will
necessarily
result
in
access
to
the
resource
via
the
named
protocol.
Even
when
an
agent
uses
a
URI
to
retrieve
a
representation,
that
access
might
be
through
gateways,
proxies,
caches,
and
name
resolution
services
that
are
independent
of
the
protocol
associated
with
the
scheme
name.
Dereferencing
a
URI
generally
involves
a
succession
of
steps
as
described
in
multiple
specifications
and
implemented
by
the
agent.
The
following
example
illustrates
the
series
of
specifications
that
are
involved
when
a
user
instructs
a
user
agent
to
follow
a
hypertext
link
that
is
part
of
an
SVG
document.
In
this
example,
the
URI
is
"http://weather.example.com/oaxaca"
and
the
application
context
calls
for
the
user
agent
to
retrieve
and
render
a
representation
of
the
identified
resource.
-
Since
the
URI
is
part
of
a
hypertext
link
in
an
SVG
document,
the
first
relevant
specification
is
the
SVG
1.1
Recommendation
[
SVG11
].
Section
17.1
of
this
specification
imports
the
link
semantics
defined
in
XLink
1.0
[
XLink10
]:
"The
remote
resource
(the
destination
for
the
link)
is
defined
by
a
URI
specified
by
the
XLink
href
attribute
on
the
'
a
'
element."
The
SVG
specification
goes
on
to
state
that
interpretation
of
an
a
element
involves
retrieving
a
representation
of
a
resource,
identified
by
the
href
attribute
in
the
XLink
namespace:
"By
activating
these
links
(by
clicking
with
the
mouse,
through
keyboard
input,
voice
commands,
etc.),
users
may
visit
these
resources."
-
The
XLink
1.0
[
XLink10
]
specification,
which
defines
the
href
attribute
in
section
5.4,
states
that
"The
value
of
the
href
attribute
must
be
a
URI
reference
as
defined
in
[IETF
RFC
2396],
or
must
result
in
a
URI
reference
after
the
escaping
procedure
described
below
is
applied."
-
The
URI
specification
[
URI
]
states
that
"Each
URI
begins
with
a
scheme
name
that
refers
to
a
specification
for
assigning
identifiers
within
that
scheme."
The
URI
scheme
name
in
this
example
is
"http".
-
[
IANASchemes
]
states
that
the
"http"
scheme
is
defined
by
the
HTTP/1.1
specification
(RFC
2616
[
RFC2616
],
section
3.2.2).
-
In
this
SVG
context,
the
agent
constructs
an
HTTP
GET
request
(per
section
9.3
of
[
RFC2616
])
to
retrieve
the
representation.
-
Section
6
of
[
RFC2616
]
defines
how
the
server
constructs
a
corresponding
response
message,
including
the
'Content-Type'
field.
-
Section
1.4
of
[
RFC2616
]
states
"HTTP
communication
usually
takes
place
over
TCP/IP
connections."
This
example
does
not
address
that
step
in
the
process,
or
other
steps
such
as
Domain
Name
System
(
DNS
)
resolution.
-
The
agent
interprets
the
returned
representation
according
to
the
data
format
specification
that
corresponds
to
the
representation's
Internet
Media
Type
(the
value
of
the
HTTP
'Content-Type')
in
the
relevant
IANA
registry
[
MEDIATYPEREG
].
Precisely
which
representation(s)
are
retrieved
depends
on
a
number
of
factors,
including:
-
Whether
the
URI
owner
makes
available
any
representations
at
all;
-
Whether
the
agent
making
the
request
has
access
privileges
for
those
representations
(see
the
section
on
linking
and
access
control
);
-
If
the
URI
owner
has
provided
more
than
one
representation
(in
different
formats
such
as
HTML,
PNG,
or
RDF;
in
different
languages
such
as
English
and
Spanish;
or
transformed
dynamically
according
to
the
hardware
or
software
capabilities
of
the
recipient),
the
resulting
representation
may
depend
on
negotiation
between
the
user
agent
and
server.
-
The
time
of
the
request;
information
changes
over
time,
and
so
representations
of
that
information
are
also
likely
to
change.
Note
also
that
the
choice
and
expressive
power
of
a
format
can
affect
how
precisely
a
representation
provider
communicates
resource
state.
The
use
of
natural
language
to
communicate
information
may
lead
to
ambiguity
about
what
the
associated
resource
is,
which
in
turn
can
lead
to
URI
overloading
.
The
Internet
media
type
[
RFC2046
])
of
a
representation
determines
which
data
format
specification(s)
provide
the
authoritative
interpretation
of
the
representation
data
(including
fragment
identifier
syntax
and
semantics
,
if
any).
The
IANA
registry
[
MEDIATYPEREG
]
maps
media
types
to
data
formats
.
The
TAG
finding
"
Internet
media
type
registration,
consistency
of
use
"
provides
more
information
to
W3C
groups
about
media
type
registration.
Internet
media
type
mechanism
does
have
its
limitations.
For
instance,
media
type
strings
do
not
support
versioning
or
other
parameters.
The
See
TAG
issue
mediaTypeManagement-45
</a>
concerns
,
which
concern
the
appropriate
level
of
granularity
of
the
media
type
mechanism.
Story
In
one
of
his
XHTML
pages,
Dirk
links
creates
a
hypertext
link
to
an
image
that
Nadia
has
published
on
the
Web.
He
creates
a
hypertext
link
with
<a
href="http://www.example.com/images/nadia#hat">Nadia's
hat</a>
.
Nadia
serves
an
SVG
representation
of
the
image
(with
Internet
media
type
"image/svg+xml"),
so
the
authoritative
interpretation
of
the
fragment
identifier
"hat"
depends
on
the
SVG
specification.
Per
[
URI
],
given
a
URI
"U#F",
and
a
representation
retrieved
by
dereferencing
URI
"U"
(which
is
authoritative),
the
(
secondary
)
resource
identified
by
"U#F"
is
determined
by
interpreting
"F"
according
to
the
specification
associated
with
the
Internet
media
type
of
the
representation
data.
Thus,
in
the
case
of
Dirk
and
Nadia,
the
authoritative
interpretation
of
the
fragment
identifier
is
given
by
the
SVG
specification,
not
the
XHTML
specification
(i.e.,
the
context
where
the
URI
appears).
The
semantics
of
a
fragment
identifier
are
defined
by
the
set
of
representations
that
might
result
from
a
retrieval
action
on
the
primary
resource.
The
fragment's
format
and
resolution
is
therefore
dependent
on
the
media
type
[
RFC2046
]
of
a
potentially
retrieved
representation,
even
though
such
a
retrieval
is
only
performed
if
the
URI
is
dereferenced.
If
no
such
representation
exists,
then
the
semantics
of
the
fragment
are
considered
unknown
and,
effectively,
unconstrained.
Fragment
identifier
semantics
are
orthogonal
to
URI
schemes
and
thus
cannot
be
redefined
by
URI
scheme
specifications.
Interpretation
of
the
fragment
identifier
is
performed
solely
by
the
agent;
the
fragment
identifier
is
not
passed
to
other
systems
during
the
process
of
retrieval.
This
means
that
some
intermediaries
in
the
Web
architecture
(such
as
proxies)
have
no
interaction
with
fragment
identifiers
and
that
redirection
(in
HTTP
[
RFC2616
],
for
example)
does
not
account
for
them.
As
with
any
URI,
use
of
a
fragment
identifier
component
does
not
imply
that
a
retrieval
action
will
take
place.
A
URI
with
a
fragment
identifier
may
be
used
to
refer
to
the
secondary
resource
without
any
implication
that
the
primary
resource
is
accessible
or
will
ever
be
accessed.
One
may
compare
URIs
with
fragment
identifiers
without
a
retrieval
action.
Parties
that
draw
conclusions
about
the
interpretation
of
a
fragment
identifier
based
solely
on
a
syntactic
analysis
of
all
or
part
of
a
URI
do
so
at
their
own
risk;
such
interpretations
are
not
authoritative
because
they
are
not
licensed
by
specification
(specifically
[
URI
]).
Please
note
the
following
about
primary
and
secondary
resources:
-
A
resource
may
be
both
a
primary
and
secondary
resource
since
more
than
one
URI
may
identify
the
resource.
-
One
cannot
carry
out
an
HTTP
POST
operation
using
a
URI
that
identifies
a
secondary
resource.
Content
negotiation
refers
to
the
practice
of
making
available
multiple
representations
via
the
same
URI.
Negotiation
between
the
requesting
agent
and
the
server
determines
which
representation
is
served
(usually
with
the
goal
of
serving
the
"best"
representation
a
receiving
agent
can
process).
HTTP
is
an
example
of
a
protocol
that
enables
representation
providers
to
use
content
negotiation.
Individual
data
formats
may
define
their
own
restrictions
on,
or
structure
within,
the
fragment
identifier
syntax
for
specifying
different
types
of
subsets,
views,
or
external
references
that
are
identifiable
as
secondary
resources
by
that
media
type.
Therefore,
representation
providers
must
manage
content
negotiation
carefully
when
used
with
a
URI
that
contains
a
fragment
identifier.
Consider
an
example
where
the
owner
of
the
URI
"http://weather.example.com/oaxaca/map#zicatela"
uses
content
negotiation
to
serve
two
representations
of
the
identified
resource.
Three
situations
can
arise:
-
The
interpretation
of
"zicatela"
is
defined
consistently
by
both
data
format
specifications.
The
representation
provider
decides
when
definitions
of
fragment
identifier
semantics
are
are
sufficiently
consistent.
-
The
interpretation
of
"zicatela"
is
defined
inconsistently
by
the
data
format
specifications.
-
The
interpretation
of
"zicatela"
is
defined
in
one
data
format
specification
but
not
the
other.
The
first
situation
—
—
consistent
semantics
—
—
poses
no
problem.
The
second
case
is
a
server
management
error:
representation
providers
must
not
use
content
negotiation
to
serve
representation
formats
that
have
inconsistent
fragment
identifier
semantics.
This
situation
also
leads
to
URI
overloading
.
The
third
case
is
not
a
server
management
error.
It
is
a
means
by
which
the
Web
can
grow.
Because
the
Web
is
a
distributed
system
in
which
formats
and
agents
are
deployed
in
a
non-uniform
manner,
Web
architecture
does
not
constrain
authors
to
only
use
"lowest
common
denominator"
formats.
Content
authors
may
take
advantage
of
new
data
formats
while
still
ensuring
reasonable
backward-compatibility
for
agents
that
do
not
yet
implement
them.
In
case
three,
behavior
by
the
receiving
agent
should
vary
depending
on
whether
the
negotiated
format
defines
fragment
identifier
semantics.
When
a
received
data
format
does
not
define
fragment
identifier
semantics,
the
agent
should
not
perform
silent
error
recovery
unless
the
user
has
given
consent;
see
[
CUAP
]
for
additional
suggested
agent
behavior
in
this
case.
See
related
TAG
issue
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist.html#RDFinXHTML-35" shape="rect">
RDFinXHTML-35
.
Successful
communication
between
two
parties
depends
on
a
reasonably
shared
understanding
of
the
semantics
of
exchanged
messages,
both
data
and
metadata.
At
times,
there
may
be
inconsistencies
between
a
message
sender's
data
and
metadata.
For
instance,
examples
that
have
been
observed
in
practice
of
inconsistencies
between
representation
data
and
metadata
include:
-
The
actual
character
encoding
of
a
representation
(e.g.,
"iso-8859-1",
specified
by
the
encoding
attribute
in
an
XML
declaration)
is
inconsistent
with
the
charset
parameter
in
the
representation
metadata
(e.g.,
"utf-8",
specified
by
the
'Content-Type'
field
in
an
HTTP
header).
-
The
namespace
of
the
root
element
of
XML
representation
data
(e.g.,
as
specified
by
the
"xmlns"
attribute)
is
inconsistent
with
the
value
of
the
'Content-Type'
field
in
an
HTTP
header.
On
the
other
hand,
there
is
no
inconsistency
in
serving
HTML
content
with
the
media
type
"text/plain",
for
example,
as
this
combination
is
licensed
by
specification.
Receiving
agents
should
detect
protocol
inconsistencies
and
perform
proper
error
recovery
.
Principle:
Data-metadata
inconsistency
Agents
MUST
NOT
ignore
message
metadata
without
the
consent
of
the
user.
Thus,
for
example,
if
the
parties
responsible
for
"weather.example.com"
mistakenly
label
the
satellite
photo
of
Oaxaca
as
"image/gif"
instead
of
"image/jpeg",
and
if
Nadia's
browser
detects
a
problem,
Nadia's
browser
must
not
ignore
the
problem
(e.g.,
by
simply
rendering
the
JPEG
image)
without
Nadia's
consent.
Nadia's
browser
can
notify
Nadia
of
the
problem
or
notify
Nadia
and
take
corrective
action.
Furthermore,
representation
providers
can
help
reduce
the
risk
of
inconsistencies
through
careful
assignment
of
representation
metadata
(especially
that
which
applies
across
representations).
The
section
on
media
types
for
XML
presents
an
example
of
reducing
the
risk
of
error
by
providing
no
metadata
about
character
encoding
when
serving
XML.
The
TAG
finding
"
Client
handling
of
MIME
headers
"
discusses
in
more
detail
the
handling
of
this
type
of
inconsistency.
Nadia's
retrieval
of
weather
information
(an
example
of
a
read-only
query
or
lookup)
qualifies
as
a
"safe"
interaction;
a
safe
interaction
is
one
where
the
agent
does
not
incur
any
obligation
beyond
the
interaction.
An
agent
may
incur
an
obligation
through
other
means
(such
as
by
signing
a
contract).
If
an
agent
does
not
have
an
obligation
before
a
safe
interaction,
it
does
not
have
that
obligation
afterwards.
Other
Web
interactions
resemble
orders
more
than
queries.
These
unsafe
interactions
may
cause
a
change
to
the
state
of
a
resource
and
the
user
may
be
held
responsible
for
the
consequences
of
these
interactions.
Unsafe
interactions
include
subscribing
to
a
newsletter,
posting
to
a
list,
or
modifying
a
database.
Note:
In
this
context,
the
word
"unsafe"
does
not
necessarily
mean
"dangerous";
the
term
"safe"
is
used
in
section
9.1.1
of
[
RFC2616
]
and
"unsafe"
is
the
natural
opposite.
Story
Nadia
decides
to
book
a
vacation
to
Oaxaca
at
"booking.example.com."
She
enters
data
into
a
series
of
online
forms
and
is
ultimately
asked
for
credit
card
information
to
purchase
the
airline
tickets.
She
provides
this
information
in
another
form.
When
she
presses
the
"Purchase"
button,
her
browser
opens
another
network
connection
to
the
server
at
"booking.example.com"
and
sends
a
message
composed
of
form
data
using
the
POST
method.
This
is
an
unsafe
interaction
;
Nadia
wishes
to
change
the
state
of
the
system
by
exchanging
money
for
airline
tickets.
The
server
reads
the
POST
request,
and
after
performing
the
booking
transaction
returns
a
message
to
Nadia's
browser
that
contains
a
representation
of
the
results
of
Nadia's
request.
The
representation
data
is
in
XHTML
so
that
it
can
be
saved
or
printed
out
for
Nadia's
records.
Note
that
neither
the
data
transmitted
with
the
POST
nor
the
data
received
in
the
response
necessarily
correspond
to
any
resource
identified
by
a
URI.
Safe
interactions
are
important
because
these
are
interactions
where
users
can
browse
with
confidence
and
where
agents
(including
search
engines
and
browsers
that
pre-cache
data
for
the
user)
can
follow
hypertext
links
safely.
Users
(or
agents
acting
on
their
behalf)
do
not
commit
themselves
to
anything
by
querying
a
resource
or
following
a
hypertext
link.
Principle:
Safe
retrieval
Agents
do
not
incur
obligations
by
retrieving
a
representation.
For
instance,
it
is
incorrect
to
publish
a
link
URI
that,
when
followed,
followed
as
part
of
a
hypertext
link,
subscribes
a
user
to
a
mailing
list.
Remember
that
search
engines
may
follow
such
hypertext
links.
For
more
information
about
safe
and
unsafe
operations
using
HTTP
GET
and
POST,
and
handling
security
concerns
around
the
use
of
HTTP
GET,
see
the
TAG
finding
"
URIs,
Addressability,
and
the
use
of
HTTP
GET
and
POST
"
.
Story
Nadia
pays
for
her
airline
tickets
online
(through
a
POST
interaction
as
described
above).
She
receives
a
Web
page
with
confirmation
information
and
wishes
to
bookmark
it
so
that
she
can
refer
to
it
when
she
calculates
her
expenses.
Although
Nadia
can
print
out
the
results,
or
save
them
to
a
file,
she
would
also
like
to
bookmark
them.
Transaction
requests
and
results
are
valuable
resources,
and
like
all
valuable
resources,
it
is
useful
to
be
able
to
refer
to
them
with
a
persistent
URI
.
However,
in
practice,
Nadia
cannot
bookmark
her
commitment
to
pay
(expressed
via
the
POST
request)
or
the
airline
company's
acknowledgment
and
commitment
to
provide
her
with
a
flight
(expressed
via
the
response
to
the
POST).
There
are
ways
to
improve
the
situation.
For
transaction
requests,
user
agents
can
provide
an
interface
for
managing
transactions
where
the
user
agent
has
incurred
an
obligation
on
behalf
of
the
user.
For
transaction
results,
HTTP
allows
representation
providers
to
assign
associate
a
URI
to
with
the
results
of
an
HTTP
POST
request
using
the
"Content-Location"
header
(described
in
section
14.14
of
[
RFC2616
]).
Story
Since
Nadia
finds
the
Oaxaca
weather
site
useful,
she
emails
a
review
to
her
friend
Dirk
recommending
that
he
check
out
'http://weather.example.com/oaxaca'.
Dirk
clicks
on
the
resulting
hypertext
link
in
the
email
he
receives
and
is
frustrated
by
a
404
(not
found).
Dirk
tries
again
the
next
day
and
receives
a
representation
with
"news"
that
is
two-weeks
old.
He
tries
one
more
time
the
next
day
only
to
receive
a
representation
that
claims
that
the
weather
in
Oaxaca
is
sunny,
even
though
his
friends
in
Oaxaca
tell
him
by
phone
that
it
in
fact
it
is
raining
(and
he
trusts
them
more
than
he
trusts
the
Web
site
in
question).
Dirk
and
Nadia
conclude
that
the
URI
owners
are
unreliable
or
unpredictable.
Although
the
URI
owner
has
chosen
the
Web
as
a
communication
medium,
they
have
lost
two
customers
due
to
ineffective
resource
management.
A
URI
owner
may
supply
zero
or
more
authoritative
representations
of
the
resource
identified
by
that
URI.
There
is
a
benefit
to
the
community
in
providing
representations.
Good
practice:
Available
representation
A
URI
owner
SHOULD
provide
representations
of
the
identified
resource.
For
example,
owners
of
XML
namespace
URIs
should
use
them
to
identify
a
namespace
document
.
The
following
sections
discuss
some
aspects
of
representation
management,
including
promoting
URI
persistence
and
managing
access
to
resources
.
As
is
the
case
with
many
human
interactions,
confidence
in
interactions
via
the
Web
depends
on
stability
and
predictability.
For
an
Information
Resource
,
persistence
generally
depends
directly
on
the
consistency
of
information
conveyed
by
a
series
of
representations.
The
representation
provider
decides
when
representations
are
sufficiently
consistent
(although
that
determination
generally
takes
user
expectations
into
account).
Although
persistence
in
this
case
is
observable
as
a
result
of
representation
retrieval,
the
term
URI
persistence
is
used
to
describe
the
desirable
property
that,
once
assigned
to
associated
with
a
resource,
a
URI
should
continue
indefinitely
to
refer
to
that
resource.
Good
practice:
Consistent
representation
A
URI
owner
SHOULD
provide
representations
of
the
identified
resource
consistently
and
predictably.
URI
persistence
is
a
matter
of
policy
and
commitment
on
the
part
of
the
URI
owner
.
The
choice
of
a
particular
URI
scheme
provides
no
guarantee
that
those
URIs
will
be
persistent
or
that
they
will
not
be
persistent.
HTTP
[
RFC2616
]
has
been
designed
to
help
manage
URI
persistence.
For
example,
HTTP
redirection
(using
the
3xx
response
codes)
permits
servers
to
tell
an
agent
that
further
action
needs
to
be
taken
by
the
agent
in
order
to
fulfill
the
request
(for
example,
deleted text:
the
resource
has
been
assigned
a
new
URI).
URI
is
associated
with
the
resource).
In
addition,
content
negotiation
also
promotes
consistency,
as
a
site
manager
is
not
required
to
define
new
URIs
when
adding
support
for
a
new
format
specification.
Protocols
that
do
not
support
content
negotiation
(such
as
FTP)
require
a
new
identifier
when
a
new
data
format
is
introduced.
Improper
use
of
content
negotiation
can
lead
to
inconsistent
representations.
For
more
discussion
about
URI
persistence,
see
[
Cool
].
It
is
reasonable
to
limit
access
to
a
resource
(for
commercial
or
security
reasons,
for
example),
but
it
is
unreasonable
to
prohibit
others
from
merely
identifying
the
resource.
As
an
analogy:
The
owners
of
a
building
might
have
a
policy
that
the
public
may
only
enter
the
building
via
the
main
front
door,
and
only
during
business
hours.
People
who
work
in
the
building
and
who
make
deliveries
to
it
might
use
other
doors
as
appropriate.
Such
a
policy
would
be
enforced
by
a
combination
of
security
personnel
and
mechanical
devices
such
as
locks
and
pass-cards.
One
would
not
enforce
this
policy
by
hiding
some
of
the
building
entrances,
nor
by
requesting
legislation
requiring
the
use
of
the
front
door
and
forbidding
anyone
to
reveal
the
fact
that
there
are
other
doors
to
the
building.
Story
Nadia
sends
to
Dirk
the
URI
of
the
current
article
she
is
reading.
With
his
browser,
Dirk
follows
the
hypertext
link
and
is
asked
to
enter
his
subscriber
username
and
password.
Since
Dirk
is
also
a
subscriber
to
services
provided
by
weather.example.com,
he
can
access
the
same
information
as
Nadia.
Thus,
the
authority
for
weather.example.com
can
limit
access
to
authorized
parties
and
still
provide
the
benefits
of
URIs.
The
Web
provides
several
mechanisms
to
control
access
to
resources;
these
mechanisms
do
not
rely
on
hiding
or
suppressing
URIs
for
those
resources.
For
more
information,
see
the
TAG
finding
"
'Deep
Linking'
in
the
World
Wide
Web
"
.
There
remain
open
questions
regarding
Web
interactions.
The
TAG
expects
future
versions
of
this
document
to
address
in
more
detail
the
relationship
between
the
architecture
described
herein,
Web
Services
,
peer-to-peer
systems,
instant
messaging
systems
(such
as
[
XMPP
]),
and
voice-over-IP
(such
as
RTSP
[
RFC2326
]).
A
data
format
(including
XHTML,
RDF/XML,
SMIL,
XLink,
CSS,
and
PNG)
specifies
the
interpretation
of
representation
data.
The
first
data
format
used
on
the
Web
was
HTML.
Since
then,
data
formats
have
grown
in
number.
The
Web
architecture
does
not
constrain
which
data
formats
content
providers
can
use.
This
flexibility
is
important
because
there
is
constant
evolution
in
applications,
resulting
in
new
data
formats
and
refinements
of
existing
formats.
Although
the
Web
architecture
allows
for
the
deployment
of
new
data
formats,
the
creation
and
deployment
of
new
formats
(and
agents
able
to
handle
them)
is
expensive.
Thus,
before
inventing
a
new
data
format
(or
"meta"
format
such
as
XML),
designers
should
carefully
consider
re-using
one
that
is
already
available.
For
a
data
format
to
be
usefully
interoperable
between
two
parties,
the
parties
must
agree
(to
a
reasonable
extent)
about
its
syntax
and
semantics.
Shared
understanding
of
a
data
format
promotes
interoperability
but
does
not
imply
constraints
on
usage;
for
instance,
a
data
sender
cannot
count
on
being
able
to
constrain
the
behavior
of
a
data
receiver.
Below
we
describe
some
characteristics
of
a
data
format
that
facilitate
integration
into
the
Web
architecture.
This
document
does
not
address
generally
beneficial
characteristics
of
a
specification
such
as
readability,
simplicity,
attention
to
programmer
goals,
attention
to
user
needs,
accessibility,
nor
internationalization.
The
section
on
architectural
specifications
includes
references
to
additional
format
specification
guidelines.
Binary
data
formats
are
those
in
which
portions
of
the
data
are
encoded
for
direct
use
by
computer
processors,
for
example
thirty-two
bit
little-endian
two's-complement
and
sixty-four
bit
IEEE
double-precision
floating-point.
The
portions
of
data
so
represented
include
numeric
values,
pointers,
and
compressed
data
of
all
sorts.
A
textual
data
format
is
one
in
which
the
data
is
specified
as
a
sequence
of
characters.
HTML,
Internet
e-mail,
and
all
XML-based
formats
are
textual.
Increasingly,
internationalized
textual
data
formats
refer
to
the
Unicode
repertoire
[
UNICODE
]
for
character
definitions.
Text
(i.e.,
a
sequence
of
characters
from
a
repertoire)
is
distinct
from
serving
data
with
a
media
type
beginning
with
"text/".
Although
XML-based
formats
are
textual,
many
XML-based
formats
do
not
consist
primarily
of
phrases
in
natural
language.
See
the
section
on
media
types
for
XML
for
issues
that
arise
when
"text/"
is
used
in
conjunction
with
an
XML-based
format.
In
principle,
all
data
can
be
represented
using
textual
formats.
In
practice,
some
types
of
content
(e.g.,
audio
and
video)
are
generally
represented
using
binary
formats.
The
trade-offs
between
binary
and
textual
data
formats
are
complex
and
application-dependent.
Binary
formats
can
be
substantially
more
compact,
particularly
for
complex
pointer-rich
data
structures.
Also,
they
can
be
consumed
more
rapidly
by
agents
in
those
cases
where
they
can
be
loaded
into
memory
and
used
with
little
or
no
conversion.
Textual
formats
are
usually
more
portable
and
interoperable.
Textual
formats
also
have
the
considerable
advantage
that
they
can
be
directly
read
by
human
beings
(and
understood,
given
sufficient
documentation).
This
can
simplify
the
tasks
of
creating
and
maintaining
software,
and
allow
the
direct
intervention
of
humans
in
the
processing
chain
without
recourse
to
tools
more
complex
than
the
ubiquitous
text
editor.
Finally,
it
simplifies
the
necessary
human
task
of
learning
about
new
data
formats;
this
is
called
the
"view
source"
effect
.
It
is
important
to
emphasize
that
intuition
as
to
such
matters
as
data
size
and
processing
speed
is
not
a
reliable
guide
in
data
format
design;
quantitative
studies
are
essential
to
a
correct
understanding
of
the
trade-offs.
Therefore,
designers
of
a
data
format
specification
should
make
a
considered
choice
between
binary
and
textual
format
design.
deleted text:
<strong>
Note:
</strong>
Text
(i.e.,
a
sequence
of
characters
from
a
repertoire)
is
distinct
from
serving
data
with
a
media
type
beginning
with
"text/".
Although
XML-based
formats
are
textual,
many
XML-based
formats
do
not
consist
primarily
of
phrases
in
natural
language.
See
the
section
on
<a href="#xml-media-types" shape="rect">
media
types
for
XML
</a>
for
issues
that
arise
when
"text/"
is
used
in
conjunction
with
an
XML-based
format.
</p>
<p>
See
TAG
issue
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#binaryXML-30" shape="rect">
binaryXML-30
.
Extensibility
and
versioning
are
strategies
to
help
manage
the
natural
evolution
of
information
on
the
Web
and
technologies
used
to
represent
that
information.
For
more
information
about
versioning
strategies
and
agent
behavior
in
the
face
of
unrecognized
extensions,
see
See
TAG
issue
XMLVersioning-41
</a>
,
which
concerns
good
practices
for
designing
extensible
XML
languages
and
for
handling
versioning.
See
also
"Web
Architecture:
Extensible
Languages"
[
EXTLANG
].
There
is
typically
a
(long)
transition
period
during
which
multiple
versions
of
a
format,
protocol,
or
agent
are
simultaneously
in
use.
Good
practice:
Version
information
A
data
format
specification
SHOULD
provide
for
version
information.
Story
Nadia
and
Dirk
are
designing
an
XML
data
format
to
encode
data
about
the
film
industry.
They
provide
for
extensibility
by
using
XML
namespaces
and
creating
a
schema
that
allows
the
inclusion,
in
certain
places,
of
elements
from
any
namespace.
When
they
revise
their
format,
Nadia
proposes
a
new
optional
lang
attribute
on
the
film
element.
Dirk
feels
that
such
a
change
requires
them
to
assign
a
new
namespace
name,
which
might
require
changes
to
deployed
software.
Nadia
explains
to
Dirk
that
their
choice
of
extensibility
strategy
in
conjunction
with
their
namespace
policy
allows
certain
changes
that
do
not
affect
conformance
of
existing
content
and
software,
and
thus
no
change
to
the
namespace
identifier
is
required.
They
choose
this
policy
to
help
them
meet
their
goals
of
reducing
the
cost
of
change.
Dirk
and
Nadia
have
chosen
a
particular
namespace
change
policy
that
allows
them
to
avoid
changing
the
namespace
name
whenever
they
make
changes
that
do
not
affect
conformance
of
deployed
content
and
software.
They
might
have
chosen
a
different
policy,
for
example
that
any
new
element
or
attribute
has
to
belong
to
a
namespace
other
than
the
original
one.
Whatever
the
chosen
policy,
it
should
set
clear
expectations
for
users
of
the
format.
For
almost
all
applications,
changing
the
namespace
name
of
an
element
completely
changes
the
element
name.
If
"a"
and
"b"
are
bound
to
two
different
URIs,
a:element
and
b:element
are
as
distinct
as
a:eieio
and
a:xyzzy.
Practically
speaking,
this
means
that
deployed
applications
will
have
to
be
upgraded
in
order
to
recognize
the
new
language;
the
cost
of
this
upgrade
may
be
very
high.
It
follows
that
there
are
significant
tradeoffs
to
be
considered
when
deciding
on
a
namespace
change
policy.
If
a
vocabulary
has
no
extensibility
points
(that
is,
if
it
does
not
allow
elements
or
attributes
from
foreign
namespaces
or
have
a
mechanism
for
dealing
with
unrecognized
names
from
the
same
namespace),
it
may
be
absolutely
necessary
to
change
the
namespace
name.
Languages
that
allow
some
form
of
extensibility
without
requiring
a
change
to
the
namespace
name
are
more
likely
to
evolve
gracefully.
Good
practice:
Namespace
policy
A
format
specification
SHOULD
include
information
about
change
policies
for
XML
namespaces.
As
an
example
of
a
change
policy
designed
to
reflect
the
variable
stability
of
a
namespace,
consider
the
W3C
namespace
policy
for
documents
on
the
W3C
Recommendation
track.
The
policy
sets
expectations
that
the
Working
Group
responsible
for
the
namespace
may
modify
it
in
any
way
until
a
certain
point
in
the
process
("Candidate
Recommendation")
at
which
point
W3C
constrains
the
set
of
possible
changes
to
the
namespace
in
order
to
promote
stable
implementations.
Note
that
since
namespace
names
are
URIs,
the
owner
of
a
namespace
URI
has
the
authority
to
decide
the
namespace
change
policy.
Designers
can
facilitate
the
transition
process
by
making
careful
choices
about
extensibility
during
the
design
of
a
language
or
protocol
specification.
Good
practice:
Extensibility
mechanisms
A
specification
SHOULD
provide
mechanisms
that
allow
any
party
to
create
extensions
that
do
not
interfere
with
conformance
to
the
original
specification.
Application
needs
determine
the
most
appropriate
extension
strategy
for
a
specification.
For
example,
applications
designed
to
operate
in
closed
environments
may
allow
specification
designers
to
define
a
versioning
strategy
that
would
be
impractical
at
the
scale
of
the
Web.
Good
practice:
Unknown
extensions
A
specification
SHOULD
specify
agent
behavior
in
the
face
of
unrecognized
extensions.
Two
strategies
have
emerged
as
being
particularly
useful:
-
"Must
ignore":
The
agent
ignores
any
content
it
does
not
recognize.
-
"Must
understand":
The
agent
treats
unrecognized
markup
as
an
error
condition.
A
powerful
design
approach
is
for
the
language
to
allow
either
form
of
extension,
but
to
distinguish
explicitly
between
them
in
the
syntax.
Additional
strategies
include
prompting
the
user
for
more
input
and
automatically
retrieving
data
from
available
hypertext
links.
More
complex
strategies
are
also
possible,
including
mixing
strategies.
For
instance,
a
language
can
include
mechanisms
for
overriding
standard
behavior.
Thus,
a
data
format
can
specify
"must
ignore"
semantics
but
also
allow
for
extensions
that
override
that
semantics
in
light
of
application
needs
(for
instance,
with
"must
understand"
semantics
for
a
particular
extension).
Extensibility
is
not
free.
Providing
hooks
for
extensibility
is
one
of
many
requirements
to
be
factored
into
the
costs
of
language
design.
Experience
suggests
that
the
long
term
benefits
of
extensibility
generally
outweigh
the
costs.
Many
modern
data
format
include
mechanisms
for
composition.
For
example:
-
It
is
possible
to
embed
text
comments
in
some
image
formats,
such
as
JPEG/JFIF.
Although
these
comments
are
embedded
in
the
containing
data,
they
have
little
or
no
effect
on
the
display
of
the
image.
-
There
are
container
formats
such
as
SOAP
which
fully
expect
to
be
composed
from
multiple
namespaces
but
which
provide
an
overall
semantic
relationship
of
message
envelope
and
payload.
-
The
semantics
of
combining
RDF
documents
containing
multiple
vocabularies
is
well-defined.
These
relationships
can
be
mixed
and
nested
arbitrarily.
In
principle,
a
SOAP
message
can
contain
an
SVG
image
that
contains
an
RDF
comment
which
refers
to
a
vocabulary
of
terms
for
describing
the
image.
Note
however,
that
for
general
XML
there
is
no
semantic
model
that
defines
the
interactions
within
XML
documents
with
elements
and/or
attributes
from
a
variety
of
namespaces.
Each
application
must
define
how
namespaces
interact
and
what
effect
the
namespace
of
an
element
has
on
the
element's
ancestors,
siblings,
and
descendants.
See
TAG
issues
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#mixedUIXMLNamespace-33" shape="rect">
mixedUIXMLNamespace-33
</a>,
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#xmlFunctions-34" shape="rect">
(concerning
the
meaning
of
a
document
composed
of
content
in
multiple
namespaces),
xmlFunctions-34
</a>,
(concerning
one
approach
for
managing
XML
transformation
and
composability),
and
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#RDFinXHTML-35" shape="rect">
RDFinXHTML-35
</a>.
(concerning
the
interpretation
of
RDF
when
embedded
in
an
XHTML
document).
The
Web
is
a
heterogeneous
environment
where
a
wide
variety
of
agents
provide
access
to
content
to
users
with
a
wide
variety
of
capabilities.
It
is
good
practice
for
authors
to
create
content
that
can
reach
the
widest
possible
audience,
including
users
with
graphical
desktop
computers,
hand-held
devices
and
mobile
phones,
users
with
disabilities
who
may
require
speech
synthesizers,
and
devices
not
yet
imagined.
Furthermore,
authors
cannot
predict
in
some
cases
how
an
agent
will
display
or
process
their
content.
Experience
shows
that
the
separation
of
content,
presentation,
and
interaction
promotes
the
reuse
and
device-independence
of
content;
his
follows
from
the
principle
of
orthogonal
specifications
.
For
more
information
about
principles
of
device-independence,
see
[
DIPRINCIPLES
].
Good
practice:
Separation
of
content,
presentation,
interaction
A
specification
SHOULD
allow
authors
to
separate
content
from
both
presentation
and
interaction
concerns.
Note
that
when
content,
presentation,
and
interaction
are
separated
by
design,
agents
need
to
recombine
them.
There
is
a
recombination
spectrum,
with
"client
does
all"
at
one
end
and
"server
does
all"
at
the
other.
There
are
advantages
to
each:
recombination
on
the
server
allows
the
server
to
send
out
generally
smaller
amounts
of
data
that
can
be
tailored
to
specific
devices
(such
as
mobile
phones).
However,
such
data
will
not
be
readily
reusable
by
other
clients
and
may
not
allow
client-side
agents
to
perform
useful
tasks
unanticipated
by
the
author.
When
a
client
does
the
work
of
recombination,
content
is
likely
to
be
more
reusable
by
a
broader
audience
and
more
robust.
However,
such
data
may
be
of
greater
size
and
may
require
more
computation
by
the
client.
Of
course,
it
may
not
always
be
desirable
to
reach
the
widest
possible
audience.
Designers
should
consider
appropriate
technologies
for
limiting
the
audience.
For
instance
digital
signature
technology,
access
control
,
and
other
technologies
are
appropriate
for
controlling
access
to
content.
Some
data
formats
are
designed
to
describe
presentation
(including
SVG
and
XSL
Formatting
Objects).
Data
formats
such
as
these
demonstrate
that
one
can
only
separate
content
from
presentation
(or
interaction)
so
far;
at
some
point
it
becomes
necessary
to
talk
about
presentation.
Per
the
principle
of
orthogonal
specifications
these
data
formats
should
only
address
presentation
issues.
See
the
TAG
issues
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#formattingProperties-19" shape="rect">
formattingProperties-19
(concerning
interoperability
in
the
case
of
formatting
properties
and
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#contentPresentation-26" shape="rect">
names)
and
contentPresentation-26
</a>.
(concerning
the
separation
of
semantic
and
presentational
markup).
A
defining
characteristic
of
the
Web
is
that
it
allows
embedded
references
to
other
resources
via
URIs.
The
simplicity
of
creating
hypertext
links
using
absolute
URIs
(
<a
href="http://www.example.com/foo">
)
and
relative
URI
references
(
<a
href="foo">
and
<a
href="foo#anchor">
)
is
partly
(perhaps
largely)
responsible
for
the
birth
of
the
hypertext
Web
as
we
know
it
today.
When
one
resource
(representation)
refers
to
another
resource
with
a
URI,
this
constitutes
a
link
between
the
two
resources.
Additional
metadata
may
also
form
part
of
the
link
(see
[
XLink10
],
for
example).
Note:
In
this
document,
the
term
"link"
generally
means
"relationship",
not
"physical
connection".
Good
practice:
Link
mechanisms
identification
A
specification
SHOULD
provide
mechanisms
for
identifying
ways
to
identify
links
to
other
resources
and
to
portions
of
representation
data
(via
fragment
identifiers).
Formats
that
allow
content
authors
to
use
URIs
instead
of
local
identifiers
promote
the
network
effect:
the
value
of
these
formats
grows
with
the
size
of
the
deployed
Web.
Good
practice:
Web
linking
A
specification
SHOULD
deleted text:
provide
mechanisms
that
allow
Web-wide
linking,
not
just
internal
document
linking.
Good
practice:
Generic
URIs
A
specification
SHOULD
allow
content
authors
to
use
URIs
without
constraining
them
to
a
limited
set
of
URI
schemes.
What
agents
do
with
a
hypertext
link
is
not
constrained
by
Web
architecture
and
may
depend
on
application
context.
Users
of
hypertext
links
expect
to
be
able
to
navigate
links
among
representations.
Good
practice:
Hypertext
links
A
data
format
SHOULD
incorporate
hypertext
links
if
hypertext
is
the
expected
user
interface
paradigm.
Data
formats
that
do
not
allow
content
authors
to
create
hypertext
links
lead
to
the
creation
of
"terminal
nodes"
on
the
Web.
Links
are
commonly
expressed
using
URI
references
(defined
in
section
4.2
of
[
URI
]),
which
may
be
combined
with
a
base
URI
to
yield
a
usable
URI.
Section
5.1
of
[
URI
]
explains
different
mechanisms
for
establishing
ways
to
establish
a
base
URI
for
a
resource
and
establishes
a
precedence
among
the
various
mechanisms.
them.
For
instance,
the
base
URI
may
be
a
URI
for
the
resource,
or
specified
in
a
representation
(see
the
base
elements
provided
by
HTML
and
XML,
and
the
HTTP
'Content-Location'
header).
See
also
the
section
on
<a href="#xml-links" shape="rect">
links
in
XML
[section
4.5.2]
.
Agents
resolve
a
URI
reference
before
using
the
resulting
URI
to
interact
with
another
agent.
URI
references
help
in
content
management
by
allowing
content
authors
to
design
a
representation
locally,
i.e.,
without
concern
for
which
global
identifier
may
later
be
used
to
refer
to
the
associated
resource.
Many
data
formats
are
XML-based
,
that
is
to
say
they
conform
to
the
syntax
rules
defined
in
the
XML
specification
[XML10]
.
This
section
discusses
issues
that
are
specific
to
such
formats.
Anyone
seeking
guidance
in
this
area
is
urged
to
consult
the
"Guidelines
For
the
Use
of
XML
in
IETF
Protocols"
[IETFXML]
,
which
contains
a
thorough
discussion
of
the
considerations
that
govern
whether
or
not
XML
ought
to
be
used,
as
well
as
specific
guidelines
on
how
it
ought
to
be
used.
While
it
is
directed
at
Internet
applications
with
specific
reference
to
protocols,
the
discussion
is
generally
applicable
to
Web
scenarios
as
well.
The
discussion
here
should
be
seen
as
ancillary
to
the
content
of
[IETFXML]
.
Refer
also
to
"XML
Accessibility
Guidelines"
[XAG]
for
help
designing
XML
formats
that
lower
barriers
to
Web
accessibility
for
people
with
disabilities.
XML
defines
textual
data
formats
that
are
naturally
suited
to
describing
data
objects
which
are
hierarchical
and
processed
in
a
chosen
sequence.
It
is
widely,
but
not
universally,
applicable
for
data
formats;
an
audio
or
video
format,
for
example,
is
unlikely
to
be
well
suited
to
expression
in
XML.
Design
constraints
that
would
suggest
the
use
of
XML
include:
-
Requirement
for
a
hierarchical
structure.
-
The
data's
usefulness
should
outlive
the
tools
currently
used
to
process
it
(though
obviously
XML
can
be
used
for
short-term
needs
as
well).
-
Ability
to
support
internationalization
in
a
self-describing
way
that
makes
confusion
over
coding
options
unlikely.
-
Early
detection
of
encoding
errors
with
no
requirement
to
"work
around"
such
errors.
-
A
high
proportion
of
human-readable
textual
content.
-
Potential
composition
of
the
data
format
with
other
XML-encoded
formats.
Sophisticated
linking
mechanisms
have
been
invented
for
XML
formats.
XPointer
allows
links
to
address
content
that
does
not
have
an
explicit,
named
anchor.
XLink
is
an
appropriate
specification
for
representing
links
in
hypertext
XML
applications.
XLink
allows
links
to
have
multiple
ends
and
to
be
expressed
either
inline
or
in
"link
bases"
stored
external
to
any
or
all
of
the
resources
identified
by
the
links
it
contains.
Designers
of
XML-based
formats
should
consider
using
XLink
and,
for
defining
fragment
identifier
syntax,
using
the
XPointer
framework
and
XPointer
element()
Schemes.
See
TAG
issue
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#xlinkScope-23" shape="rect">
xlinkScope-23
.
The
purpose
of
an
XML
namespace
(defined
in
[
XMLNS
])
is
to
allow
the
deployment
of
XML
vocabularies
(in
which
element
and
attribute
names
are
defined)
in
a
global
environment
and
to
reduce
the
risk
of
name
collisions
in
a
given
document
when
vocabularies
are
combined.
For
example,
the
MathML
and
SVG
specifications
both
define
the
set
element.
Although
XML
data
from
different
formats
such
as
MathML
and
SVG
can
be
combined
in
a
single
document,
in
this
case
there
could
be
ambiguity
about
which
set
element
was
intended.
XML
namespaces
reduce
the
risk
of
name
collisions
by
taking
advantage
of
existing
mechanisms
systems
for
allocating
globally
scoped
names:
the
URI
system
(see
also
the
section
on
<a href="#uri-ownership" shape="rect">
URI
ownership
[section
2.5]
).
When
using
XML
namespaces,
each
local
name
in
an
XML
vocabulary
is
paired
with
a
URI
(called
the
namespace
URI)
to
distinguish
the
local
name
from
local
names
in
other
vocabularies.
All
of
the
globally
grounded
terms
in
an
XML
namespace
share
the
same
syntactic
prefix:
the
namespace
URI.
The
use
of
URIs
confers
additional
benefits.
First,
each
local
name
/
URI
pair
can
be
mapped
to
another
URI,
grounding
the
terms
of
the
vocabulary
in
the
Web.
These
terms
may
be
important
resources
and
thus
it
is
appropriate
to
be
able
to
assign
associate
URIs
to
with
them.
One
particularly
useful
mapping
in
the
case
of
flat
namespaces
(specified,
for
example,
in
[
RDF10
])
is
to
combine
the
namespace
URI,
a
hash
("#"),
and
the
local
name,
thus
creating
a
URI
for
a
secondary
resource
(the
identified
term).
Other
mappings
are
likely
to
be
more
suitable
for
hierarchical
namespaces;
see
the
related
TAG
issue
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist.html#abstractComponentRefs-37" shape="rect">
abstractComponentRefs-37
.
Designers
of
XML-based
data
formats
who
declare
namespaces
thus
make
it
possible
to
reuse
those
data
formats
and
combine
them
in
novel
ways
not
yet
imagined.
Failure
to
declare
namespaces
makes
such
re-use
more
difficult,
even
impractical
in
some
cases.
Good
practice:
Namespace
adoption
A
specification
that
establishes
an
XML
vocabulary
SHOULD
place
all
element
names
and
global
attribute
names
in
a
namespace.
Attributes
are
always
scoped
by
the
element
on
which
they
appear.
An
attribute
that
is
"global,"
that
is,
one
that
might
meaningfully
appear
on
elements
of
any
type,
including
elements
in
other
namespaces,
should
be
explicitly
placed
in
a
namespace.
Local
attributes,
ones
associated
with
only
a
particular
element
type,
need
not
be
included
in
a
namespace
since
their
meaning
will
always
be
clear
from
the
context
provided
by
that
element.
The
type
attribute
from
the
W3C
XML
Schema
Instance
namespace
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
([
XMLSCHEMA
],
section
4.3.2)
is
an
example
of
a
global
attribute.
It
can
be
used
by
authors
of
any
vocabulary
to
make
an
assertion
in
instance
data
about
the
type
of
the
element
on
which
it
appears.
As
a
global
attribute,
it
must
always
be
qualified.
The
frame
attribute
on
an
HTML
table
is
an
example
of
a
local
attribute.
There
is
no
value
in
placing
that
attribute
in
a
namespace
since
the
attribute
is
unlikely
to
be
useful
on
an
element
other
than
an
HTML
table.
Applications
that
rely
on
DTD
processing
must
impose
additional
constraints
on
the
use
of
namespaces.
DTDs
perform
validation
based
on
the
lexical
form
of
the
element
and
attribute
names
in
the
document.
This
makes
prefixes
syntactically
significant
in
ways
that
are
not
anticipated
by
[
XMLNS
].
Story
Nadia
receives
representation
data
from
"weather.example.com"
in
an
unfamiliar
data
format.
She
knows
enough
about
XML
to
recognize
which
XML
namespace
the
elements
belong
to.
Since
the
namespace
is
identified
by
the
URI
"http://weather.example.com/2003/format",
she
asks
her
browser
to
retrieve
a
representation
of
the
identified
resource.
She
gets
back
some
useful
data
that
allows
her
to
learn
more
about
the
data
format.
Nadia's
browser
may
also
be
able
to
perform
some
operations
automatically
(i.e.,
unattended
by
a
human
overseer)
given
data
that
has
been
optimized
for
software
agents.
For
example,
her
browser
might,
on
Nadia's
behalf,
download
additional
agents
to
process
and
render
the
format.
Another
benefit
of
using
URIs
to
build
XML
namespaces
is
that
the
namespace
URI
can
be
used
to
identify
an
Information
Resource
that
contains
useful
information,
machine-usable
and/or
human-usable,
about
terms
in
the
namespace.
This
type
of
Information
Resource
is
called
a
namespace
document
.
When
a
namespace
URI
owner
provides
a
namespace
document,
it
is
authoritative
for
the
namespace.
There
are
many
reasons
to
provide
a
namespace
document.
A
person
might
want
to:
-
understand
the
purpose
of
the
namespace,
-
learn
how
to
use
the
markup
vocabulary
in
the
namespace,
-
find
out
who
controls
it
and
associated
policies,
-
request
authority
to
access
schemas
or
collateral
material
about
it,
or
-
report
a
bug
or
situation
that
could
be
considered
an
error
in
some
collateral
material.
A
processor
might
want
to:
-
retrieve
a
schema,
for
validation,
-
retrieve
a
style
sheet,
for
presentation,
or
-
retrieve
ontologies,
for
making
inferences.
In
general,
there
is
no
established
best
practice
for
creating
representations
of
a
namespace
document;
application
expectations
will
influence
what
data
format
or
formats
are
used.
Application
expectations
will
also
influence
whether
relevant
information
appears
directly
in
a
representation
or
is
referenced
from
it.
Good
practice:
Namespace
documents
The
owner
of
an
XML
namespace
name
SHOULD
make
available
material
intended
for
people
to
read
and
material
optimized
for
software
agents
in
order
to
meet
the
needs
of
those
who
will
use
the
namespace
vocabulary.
For
example,
the
following
are
examples
of
data
formats
for
namespace
documents:
[
OWL10
],
[
RDDL
],
[
XMLSCHEMA
],
and
[
XHTML11
].
Each
of
these
formats
meets
different
requirements
described
above
for
satisfying
the
needs
of
an
agent
that
wants
more
information
about
the
namespace.
Note,
however,
issues
related
to
fragment
identifiers
and
content
negotiation
if
content
negotiation
is
used.
See
TAG
issues
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#namespaceDocument-8" shape="rect">
namespaceDocument-8
(concerning
desired
characteristics
of
namespace
documents)
and
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist.html#abstractComponentRefs-37" shape="rect">
abstractComponentRefs-37
</a>.
(concerning
the
use
of
fragment
identifiers
with
namespace
names
to
identify
abstract
components).
Section
3
of
"Namespaces
in
XML"
[
XMLNS
]
provides
a
syntactic
construct
known
as
a
QName
for
the
compact
expression
of
qualified
names
in
XML
documents.
A
qualified
name
is
a
pair
consisting
of
a
URI,
which
names
a
namespace,
and
a
local
name
placed
within
that
namespace.
"Namespaces
in
XML"
provides
for
the
use
of
QNames
as
names
for
XML
elements
and
attributes.
Other
specifications,
starting
with
[
XSLT10
],
have
employed
the
idea
of
using
QNames
in
contexts
other
than
element
and
attribute
names,
for
example
in
attribute
values
and
in
element
content.
However,
general
XML
processors
cannot
reliably
recognize
QNames
as
such
when
they
are
used
in
attribute
values
and
in
element
content;
for
example,
the
syntax
of
QNames
overlaps
with
that
of
URIs.
Experience
has
also
revealed
other
limitations
to
QNames,
such
as
losing
namespace
bindings
after
XML
canonicalization.
Good
practice:
QNames
Indistinguishable
from
URIs
A
specification
in
which
QNames
represent
URI/local-name
pairs
SHOULD
NOT
allow
both
Qnames
and
URIs
in
attribute
values
or
element
content,
where
they
would
be
indistinguishable.
For
more
information,
see
the
TAG
finding
"
Using
QNames
as
Identifiers
in
Content
"
.
Because
QNames
are
compact,
some
specification
designers
have
adopted
the
same
syntax
as
a
means
of
identifying
resources.
Though
convenient
as
a
shorthand
notation,
this
usage
has
a
cost.
There
is
no
single,
accepted
way
to
convert
a
QName
into
a
URI
or
vice
versa.
Although
QNames
are
convenient,
they
do
not
replace
the
URI
as
the
identification
mechanism
system
of
the
Web.
The
use
of
QNames
to
identify
Web
resources
without
providing
a
mapping
to
URIs
is
inconsistent
with
Web
architecture.
Good
practice:
QName
Mapping
A
specification
in
which
QNames
serve
as
resource
identifiers
MUST
provide
a
mapping
to
URIs.
One
particularly
useful
mapping
in
the
case
of
flat
namespaces
is
to
combine
the
namespace
URI,
a
hash
("#"),
and
the
local
name;
see
the
section
on
XML
namespaces
for
more
examples.
See
also
TAG
issues
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist" shape="rect">
rdfmsQnameUriMapping-6
</a>,
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#qnameAsId-18" shape="rect">
(concerning
the
mapping
of
QNames
to
URIs),
qnameAsId-18
</a>,
(concerning
the
use
of
QNames
as
identifiers
in
XML
content),
and
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist.html#abstractComponentRefs-37" shape="rect">
abstractComponentRefs-37
</a>.
(concerning
the
use
of
fragment
identifiers
with
namespace
names
to
identify
abstract
components).
Consider
the
following
fragment
of
XML:
<section
name="foo">
.
Does
the
section
element
have
what
the
XML
Recommendation
refers
to
as
the
ID
foo
(i.e.,
"foo"
must
not
appear
in
the
surrounding
XML
document
more
than
once)?
One
cannot
answer
this
question
by
examining
the
element
and
its
attributes
alone.
In
XML,
the
quality
of
"being
an
ID"
is
associated
with
the
type
of
an
attribute,
not
its
name.
Finding
the
IDs
in
a
document
requires
additional
processing.
-
Processing
the
document
with
a
processor
that
recognizes
DTD
attribute
list
declarations
(in
the
external
or
internal
subset)
might
reveal
a
declaration
that
identifies
the
name
attribute
as
an
ID.
Note:
This
processing
is
not
necessarily
part
of
validation.
A
non-validating,
DTD-aware
processor
can
perform
ID
assignment.
-
Processing
the
document
with
a
W3C
XML
schema
might
reveal
an
element
declaration
that
identifies
the
name
attribute
as
an
W3C
XML
Schema
ID
.
-
In
practice,
processing
the
document
with
another
schema
language,
such
as
RELAX
NG
[
RELAXNG
],
might
reveal
the
attributes
declared
to
be
of
ID
in
the
XML
Schema
sense.
Many
modern
specifications
begin
processing
XML
at
the
Infoset
[
INFOSET
]
level
and
do
not
specify
normatively
how
an
Infoset
is
constructed.
For
those
specifications,
any
process
that
establishes
the
ID
type
in
the
Infoset
(and
Post
Schema
Validation
Infoset
(
PSVI
)
defined
in
[
XMLSCHEMA
])
may
usefully
identify
the
attributes
of
type
ID.
-
In
practice,
applications
may
have
independent
means
(such
as
those
defined
in
the
XPointer
specification,
[
XPTRFR
]
section
3.2
)
of
locating
identifiers
inside
a
document.
To
further
complicate
matters,
DTDs
establish
the
ID
type
in
the
Infoset
whereas
W3C
XML
Schema
produces
a
PSVI
but
does
not
modify
the
original
Infoset.
This
leaves
open
the
possibility
that
a
processor
might
only
look
in
the
Infoset
and
consequently
would
fail
to
recognize
schema-assigned
IDs.
The
TAG
expects
to
continue
to
work
with
other
groups
to
help
resolve
open
questions
about
establishing
"ID-ness"
in
XML
formats.
See
formats;
this
is
the
subject
of
TAG
issue
xmlIDSemantics-32
.
RFC
3023
defines
the
Internet
media
types
"application/xml"
and
"text/xml",
and
describes
a
convention
whereby
XML-based
data
formats
use
Internet
media
types
with
a
"+xml"
suffix,
for
example
"image/svg+xml".
These
Internet
media
types
create
two
problems:
First,
for
data
identified
as
"text/*",
Web
intermediaries
are
allowed
to
"transcode",
i.e.,
convert
one
character
encoding
to
another.
Transcoding
may
make
the
self-description
false
or
may
cause
the
document
to
be
not
well-formed.
Good
practice:
XML
and
"text/*"
In
general,
a
representation
provider
SHOULD
NOT
assign
Internet
media
types
beginning
with
"text/"
to
XML
representations.
Second,
representations
whose
Internet
media
types
begin
with
"text/"
are
required,
unless
the
charset
parameter
is
specified,
to
be
considered
to
be
encoded
in
US-ASCII.
Since
the
syntax
of
XML
is
designed
to
make
documents
self-describing,
it
is
good
practice
to
omit
the
charset
parameter,
and
since
XML
is
very
often
not
encoded
in
US-ASCII,
the
use
of
"text/"
Internet
media
types
effectively
precludes
this
good
practice.
Good
practice:
XML
and
character
encodings
In
general,
a
representation
provider
SHOULD
NOT
specify
the
character
encoding
for
XML
data
in
protocol
headers
since
the
data
is
self-describing.
The
section
on
media
types
and
fragment
identifier
semantics
discusses
the
interpretation
of
fragment
identifiers.
Designers
of
an
XML-based
data
format
specification
should
define
the
semantics
of
fragment
identifiers
in
that
format.
The
XPointer
Framework
[
XPTRFR
]
provides
an
interoperable
starting
point.
When
the
media
type
assigned
to
representation
data
is
"application/xml",
there
are
no
semantics
defined
for
fragment
identifiers,
and
authors
should
not
make
use
of
fragment
identifiers
in
such
data.
The
same
is
true
if
the
assigned
media
type
has
the
suffix
"+xml"
(defined
in
"XML
Media
Types"
[
RFC3023
]),
and
the
data
format
specification
does
not
specify
fragment
identifier
semantics.
In
short,
just
knowing
that
content
is
XML
does
not
provide
information
about
fragment
identifier
semantics.
Many
people
assume
that
the
fragment
identifier
#abc
,
when
referring
to
XML
data,
identifies
the
element
in
the
document
with
the
ID
"abc".
However,
there
is
no
normative
support
for
this
assumption.
See
TAG
issue
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#fragmentInXML-28" shape="rect">
fragmentInXML-28
.
Because
of
their
role
in
defining
fragment
identifier
semantics,
data
formats
enable
the
creation
of
new
applications
to
make
use
of
the
information
space
infrastructure.
The
Semantic
Web
is
one
such
application,
built
on
top
of
RDF
[
RDF10
].
This
document
does
not
discuss
the
Semantic
Web
in
detail;
the
TAG
expects
that
future
editions
of
this
document
will.
See
the
related
TAG
issue
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist.html#httpRange-14" shape="rect">
httpRange-14
.
<h3>
1.2.
A
number
of
general
architecture
principles
apply
to
all
three
bases
of
Web
architecture.
<h4>
1.2.1.
Identification,
interaction,
and
representation
are
orthogonal
concepts,
meaning
that
technologies
used
for
identification,
interaction,
and
representation
may
evolve
independently.
For
instance:
-
One
identifies
a
resource
with
a
URI.
One
may
assign
and
publish
then
use
a
URI
without
building
any
representations
of
the
resource
or
determining
whether
any
representations
are
available.
-
A
generic
URI
syntax
allows
agents
to
function
in
many
cases
without
knowing
specifics
of
URI
schemes.
-
In
many
cases
one
may
change
the
representation
of
a
resource
without
disrupting
references
to
the
resource.
resource
(for
example,
by
using
content
negotiation
).
When
two
specifications
are
orthogonal,
one
may
change
one
without
requiring
changes
to
the
other,
even
if
one
has
dependencies
on
the
other.
For
example,
although
the
HTTP
specification
depends
on
the
URI
specification,
the
two
may
evolve
independently.
This
orthogonality
increases
the
flexibility
and
robustness
of
the
Web.
For
example,
one
may
refer
by
URI
to
an
image
without
knowing
anything
about
the
format
chosen
to
represent
the
image.
This
has
facilitated
the
introduction
of
image
formats
such
as
PNG
and
SVG
without
disrupting
existing
references
to
image
resources.
Orthogonal
abstractions
benefit
from
orthogonal
specifications.
deleted text:
Specifications
should
clearly
indicate
those
features
that
simultaneously
access
information
from
otherwise
orthogonal
abstractions.
For
example
a
specification
should
draw
attention
to
a
feature
that
requires
information
from
both
the
header
and
the
body
of
a
message.
</p>
<p>
Although
the
HTTP,
HTML,
and
URI
specifications
are
orthogonal
for
the
most
part,
they
are
not
entirely
so.
Experience
demonstrates
that
where
they
are
not,
problems
have
arisen:
-
The
HTML
specification
—
—
a
data
format
specification
—
—
includes
a
protocol
extension
of
sorts:
it
specifies
how
a
user
agent
sends
HTML
form
data
to
a
server
(as
a
URI
query
string).
The
design
works
reasonably
well,
although
there
are
limitations
related
to
internationalization
(see
the
TAG
finding
"
URIs,
Addressability,
and
the
use
of
HTTP
GET
and
POST
"
)
and
the
query
string
design
impinges
on
the
server
design.
Software
developers
(for
example,
of
[
CGI
]
applications)
might
have
an
easier
time
finding
the
specification
if
it
were
published
separately
and
then
cited
from
the
HTTP,
URI,
and
HTML
specifications.
-
The
HTML
specification
allows
content
providers
to
instruct
HTTP
servers
to
build
response
headers
from
META
element
instances.
This
is
an
abstraction
violation;
the
software
developer
community
would
benefit
from
being
able
to
find
all
HTTP
headers
from
the
HTTP
specification
(including
any
associated
extension
registries
and
specification
updates
per
IETF
process).
Perhaps
as
a
result,
this
feature
of
the
HTML
specification
is
not
widely
deployed.
Furthermore,
this
design
has
led
to
confusion
in
user
agent
development.
The
HTML
specification
states
that
META
in
conjunction
with
http-equiv
is
intended
for
HTTP
servers,
but
many
HTML
user
agents
interpret
http-equiv='refresh'
as
a
client-side
instruction.
-
Some
content
authors
use
the
META
/
http-equiv
approach
to
declare
the
character
encoding
scheme
of
an
HTML
document.
By
design,
this
is
a
hint
that
an
HTTP
server
should
emit
a
corresponding
"Content-Type"
header
field.
In
practice,
the
use
of
the
hint
in
servers
is
not
widely
deployed.
Furthermore,
many
user
agents
use
this
information
to
override
the
"Content-Type"
header
sent
by
the
server,
violating
protocol
semantics.
A
specification
should
clearly
indicate
which
features
advance
into
abstraction
territory
rightfully
governed
by
another
specification.
<h4>
1.2.2.
The
information
in
the
Web
and
the
technologies
used
to
represent
that
information
change
over
time.
Extensibility
describes
the
property
of
a
technology
that
promotes
both
evolution
and
interoperability.
Some
examples
of
successful
technologies
designed
to
allow
change
while
minimizing
disruption
include:
-
the
fact
that
URI
schemes
are
orthogonally
specified;
-
the
use
of
an
open
set
of
Internet
media
types
in
mail
and
HTTP
to
specify
document
interpretation;
-
the
separation
of
the
generic
XML
grammar
and
the
open
set
of
XML
namespaces
for
element
and
attribute
names;
-
extensibility
models
in
Cascading
Style
Sheets
(CSS),
XSLT
1.0,
and
SOAP;
-
user
agent
plug-ins.
An
example
of
an
unsuccessful
extension
mechanism
is
HTTP
mandatory
extensions.
extensions
[
HTTPEXT
].
The
community
has
sought
mechanisms
to
extend
HTTP,
but
apparently
the
costs
of
the
mandatory
extension
proposal
(notably
in
complexity)
outweighed
the
benefits
and
thus
hampered
adoption.
Below
we
discuss
the
property
of
"extensibility,"
exhibited
by
URIs,
some
data
formats,
and
some
protocols
(through
the
incorporation
of
new
messages).
Subset
language
:
one
language
is
a
subset
(or,
"profile")
of
a
second
language
if
any
document
in
the
first
language
is
also
a
valid
document
in
the
second
language
and
has
the
same
interpretation
in
the
second
language.
Extended
language
:
If
one
language
is
a
subset
of
another,
the
latter
superset
is
called
an
extended
language;
the
difference
between
the
languages
is
called
the
extension.
Clearly,
extending
a
language
is
better
for
interoperability
than
creating
an
incompatible
language.
Ideally,
many
instances
of
a
superset
language
can
be
safely
and
usefully
processed
as
though
they
were
in
the
language
subset.
Languages
that
exhibit
this
property
are
said
to
be
"extensible."
Language
designers
can
facilitate
extensibility
by
defining
how
implementations
must
handle
unknown
extensions
—
—
for
example,
that
they
be
ignored
(in
some
way)
or
should
be
considered
errors.
For
example,
from
early
on
in
the
Web,
HTML
agents
followed
the
convention
of
ignoring
unknown
elements.
This
choice
left
room
for
innovation
(i.e.,
non-standard
elements)
and
encouraged
the
deployment
of
HTML.
However,
interoperability
problems
arose
as
well.
In
this
type
of
environment,
there
is
an
inevitable
tension
between
interoperability
in
the
short
term
and
the
desire
for
extensibility.
Experience
shows
that
designs
that
strike
the
right
balance
between
allowing
change
and
preserving
interoperability
are
more
likely
to
thrive
and
are
less
likely
to
disrupt
the
Web
community.
Orthogonal
specifications
help
reduce
the
risk
of
disruption.
For
further
discussion,
see
the
section
on
versioning
and
extensibility
.
See
also
TAG
issue
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#xmlProfiles-29" shape="rect">
xmlProfiles-29
.
<h4>
1.2.3.
Errors
occur
in
networked
information
systems.
An
error
condition
can
be
well-specified
(e.g.,
well-formedness
errors
in
XML
or
4xx
client
errors
in
HTTP)
or
arise
unpredictably.
Error
correction
means
that
an
agent
repairs
an
condition
so
that
within
the
system,
it
is
as
though
the
error
never
occurred.
One
example
of
error
correction
involves
data
retransmission
in
response
to
a
temporary
hardware
failure.
Error
recovery
means
that
an
agent
does
not
repair
an
error
condition
but
continues
processing.
processing
by
addressing
the
fact
that
the
error
has
occurred.
Agents
frequently
correct
errors
without
user
awareness,
sparing
users
the
details
of
complex
network
communications.
On
the
other
hand,
it
is
important
that
agents
recover
from
error
in
a
way
that
is
transparent
evident
to
users,
since
the
agents
are
acting
on
their
behalf.
Principle:
Error
recovery
Agents
that
recover
from
error
by
making
a
choice
without
the
user's
consent
are
not
acting
on
the
user's
behalf.
An
agent
is
not
required
to
interrupt
the
user
(e.g.,
by
popping
up
a
confirmation
box)
to
obtain
consent.
The
user
may
indicate
consent
through
pre-selected
configuration
options,
modes,
or
selectable
user
interface
toggles,
with
appropriate
reporting
to
the
user
when
the
agent
detects
an
error.
Agent
developers
should
not
ignore
usability
issues
when
designing
error
recovery
behavior.
To
promote
interoperability,
specification
designers
should
identify
predictable
error
conditions.
Experience
has
led
to
the
following
observations
about
error-handling
approaches.
-
Protocol
designers
should
provide
enough
information
about
an
error
condition
so
that
an
agent
can
address
the
error
condition.
For
instance,
an
HTTP
404
message
status
code
(not
found)
is
useful
because
it
allows
user
agents
to
present
relevant
information
to
users,
enabling
them
to
contact
the
representation
provider
in
case
of
problems.
-
Experience
with
the
cost
of
building
a
user
agent
to
handle
the
diverse
forms
of
ill-formed
HTML
content
convinced
the
designers
of
the
XML
specification
to
require
that
agents
fail
upon
encountering
ill-formed
content.
Because
users
are
unlikely
to
tolerate
such
failures,
this
design
choice
has
pressured
all
parties
into
respecting
XML's
constraints,
to
the
benefit
of
all.
-
An
agent
that
encounters
unrecognized
content
may
handle
it
in
a
number
of
ways,
including
by
considering
it
an
error;
see
also
the
section
on
<a href="#ext-version" shape="rect">
extensibility
and
versioning
[section
4.2]
.
-
Error
behavior
that
is
appropriate
for
a
person
may
not
be
appropriate
for
software.
People
are
capable
of
exercising
judgement
in
ways
that
software
applications
generally
cannot.
An
informal
error
response
may
suffice
for
a
person
but
not
for
a
processor.
See
the
TAG
issues
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#contentTypeOverride-24" shape="rect">
issue
contentTypeOverride-24
</a>
and
<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/ilist#errorHandling-20" shape="rect">
errorHandling-20
</a>.
,
which
concerns
the
source
of
authoritative
metadata.
<h4>
1.2.4.
The
Web
follows
Internet
tradition
in
that
its
important
interfaces
are
defined
in
terms
of
protocols,
by
specifying
the
syntax,
semantics,
and
sequence
sequencing
constraints
of
the
messages
interchanged.
Protocols
designed
to
be
resilient
in
the
face
of
widely
varying
environments
have
helped
the
Web
scale
and
have
facilitated
communication
across
multiple
trust
boundaries.
Traditional
application
programming
interfaces
(
APIs
)
do
not
always
take
these
constraints
into
account,
nor
should
they
be
required
to.
One
effect
of
protocol-based
design
is
that
the
technology
shared
among
agents
often
lasts
longer
than
the
agents
themselves.
It
is
common
for
programmers
working
with
the
Web
to
write
code
that
generates
and
parses
these
messages
directly.
It
is
less
common,
but
not
unusual,
for
end
users
to
have
direct
exposure
to
these
messages.
It
is
often
desirable
to
provide
users
with
access
to
format
and
protocol
details:
allowing
them
to
"
view
source
,"
whereby
they
may
gain
expertise
in
the
workings
of
the
underlying
system.