Abstract
This document describes CCXML, or the Call Control eXtensible
Markup Language. CCXML is designed to provide telephony call
control support for dialog systems, such as VoiceXML [
VOICEXML ].
While CCXML can be used with any dialog systems capable of handling
media, CCXML has been designed to complement and integrate with a
VoiceXML interpreter. Because of this there are many references to
VoiceXML's capabilities and limitations. There are also details on
how VoiceXML and CCXML can be integrated. However, it should be
noted that the two languages are separate and are not required in
an implementation of either language. For example, CCXML could be
integrated with a more traditional Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
system or a 3GPP Media Resource Function (MRF), and VoiceXML or
other dialog systems could be integrated with other call control
systems.
Status of this Document
This section describes the status of this document at the
time of its publication. Other documents may supersede this
document. A list of current W3C publications and the latest
revision of this technical report can be found in the W3C technical reports
index at http://www.w3.org/TR/.
This is the 4 May 2011 XXXXXXX
1 April 2010 Candidate
Proposed Recommendation of "Call
Control eXtensible Markup Language (CCXML) Version 1.0". Changes
from the Last Call Working Draft
Candidate Recommendation can be found
in Appendix F - Changes
- Proposed Recommendation . A
diff-marked version of this
document is also available for comparison purposes.
This specification describes the Call Control XML (CCXML) markup
language that is designed to provide telephony call control support
for VoiceXML or other dialog systems.
This document has been produced as part of the Voice Browser
Activity . The authors of this document are participants in the
Voice Browser
Working Group . For more information see the Voice Browser FAQ .
The Working Group expects to advance this document to
Recommendation status.
This is a W3C Candidate Recommendation for review by W3C Members
and other interested parties. W3C publishes a technical
report as a Candidate Recommendation to indicate that the document
is believed to be stable, and to encourage implementation by the
developer community.
The entrance criteria to the Proposed Recommendation phase
require required at least two independently developed
interoperable implementations of each required feature, and at
least one or two implementations of each optional feature depending
on whether the feature's conformance requirements have an impact on
interoperability. Detailed
implementation These requirements
and the invitation were met for participation
in the Implementation Report are provided in all features. For further detail and complete results
please see section 7 of the detailed
Implementation Report Plan .
We expect to meet all requirements of that
report within the Candidate Recommendation period closing 28 May
2010 . The Voice Browser Working Group will advance CCXML 1.0 to
Proposed Recommendation no sooner than 28 May 2010 .
Several of the features in the current
draft specification are considered to be at risk of removal due to
potential lack of implementations. <move> - Section 9.2.4
Advanced <join> use cases (dialog to dialog, conf to conf) -
Section 7 , combined with Section 10.4 Advanced entertone /
exittone (URI) - Section 10.5.7 dialog.transfer eventing and use
case - Section 7.3.5 and Appendix D.9 Comments are welcome on
www-voice@w3.org
( archive ). See W3C mailing list and archive usage guidelines .
Please check the disposition of comments received during the Last Call Candidate
Recommendation period.
Publication as a Candidate
Proposed Recommendation does not imply
endorsement by the W3C Membership. This is a draft document and may
be updated, replaced or obsoleted by other documents at any time.
It is inappropriate to cite this document as other than work in
progress.
This document was produced by a group operating under the
5 February 2004 W3C Patent Policy . W3C maintains
a public list of any patent disclosures made in connection
with the deliverables of the group; that page also includes
instructions for disclosing a patent. An individual who has actual
knowledge of a patent which the individual believes contains
Essential Claim(s) must disclose the information
in accordance with section 6 of the W3C Patent Policy .
Conventions of this Document
In this document, the key words "must", "must not", "required",
"shall", "shall not", "should", "should not", "recommended", "may",
and "optional" are to be interpreted as described in [RFC2119] and indicate requirement
levels for compliant CCXML implementations.
Table of Contents
1: Introduction
This document describes CCXML, the Call Control eXtensible
Markup Language. CCXML provides declarative markup to describe
telephony call control. CCXML is a language that can be used with a
dialog system such as VoiceXML [ VOICEXML ].
CCXML can provide a complete telephony service application,
comprised of Web server CGI compliant application
logic, one or more CCXML documents to declare and perform call
control actions, and to control one or more dialog applications
that perform user media interactions
Since platforms implementing CCXML may choose to use one of many
telephony call control definitions (JAIN Call Control [
JSR021 ], ECMA
CSTA [ CSTA ],
S.100 [ S.100 ],
etc.), the call control model in CCXML has been designed to be
sufficiently abstract so that it can accommodate all major
definitions. For relatively simple types of call control, this
abstraction is straightforward. The philosophy in this regard has
been to "make simple things simple to do." Outdial, transfer
(redirect), two-party bridging, and many forms of multi-party
conferences fall within this classification.
Figure 1 shows the architecture of a telephony implementation
consisting of four primary components:
- a caller (along with the telephone network),
- a dialog system (e.g. a VoiceXML implementation),
- a conference server used to mix media streams,
- and the CCXML implementation which manages the Connections
between the first two components.
The Telephony Web Application may or may not be integrated with
the Voice Web Application.
The Telephony Control and Dialog Control Interfaces may be
implemented as an API or protocol.
The components as shown in the figure below represent logical
functions, and are not meant to imply any particular
architecture.
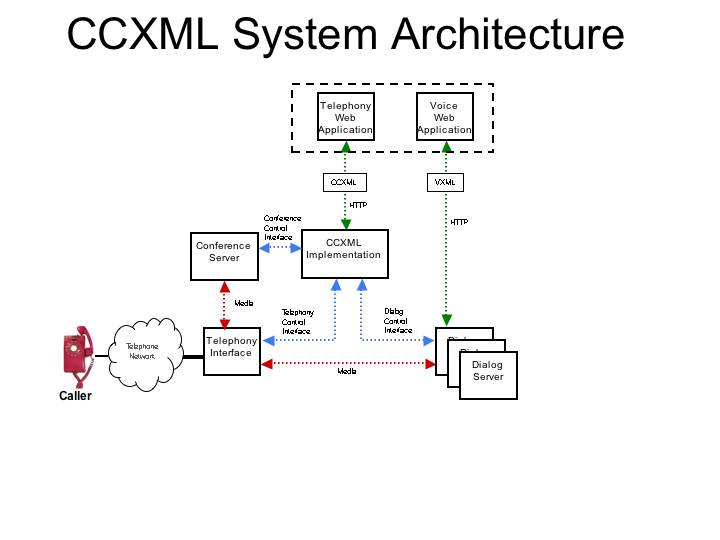
Figure 1
2: Motivation (Informative)
CCXML is designed to complement dialog systems such as VoiceXML
by providing advanced telephony functions. It also can be used as a
third-party call control manager in any telephony system. This
document contains references to VoiceXML's capabilities and
limitations, as well as details on how VoiceXML and CCXML can be
integrated.
The CCXML specification originated from the desire to handle
call control requirements that were beyond the scope of the
VoiceXML specification. The following requirements are addressed by
this specification:
- Support for multi-party conferencing, with advanced conference
and audio control. A conferencing application involves multiple
participants, and is dependent upon call control to establish
relationships between those participants.
- The ability to give each active call leg its own dedicated
VoiceXML interpreter. For example, in VoiceXML, the second leg of a
transferred call lacks a VoiceXML interpreter of its own, limiting
the scope of possible applications.
- Sophisticated multiple-call handling and control, including the
ability to place outgoing calls.
- Handling for a richer class of asynchronous events. Advanced
telephony operations involve substantial amounts of signals, status
events, and message-passing. VoiceXML 2.0 does not integrate
asynchronous "external" events into its event-processing
model.
- VoiceXML lacks the external interfaces required to interact
with an outside call queue, or place calls on behalf of an external
document server
CCXML and VoiceXML implementations are not mutually dependent. A
CCXML implementation may or may not support voice dialogs, or may
support dialog languages other than VoiceXML.
3: Concepts and Architecture
A CCXML
application consists of a collection of CCXML documents that
control and manage the objects listed below:
- CCXML Session: A CCXML session is comprised of an executing CCXML
document, or sequence of CCXML documents; each concurrently
executing CCXML document is a separate session, and can be uniquely
identified and referenced.
- Connection: Connections can be "call legs" (real-world phone
connections) or system resources to facilitate interaction with a
voice dialog . Media streams
between Connections , or
between Connections and
Conference objects ,
need to be tracked by the CCXML interpreter and will take real system resources,
but do not need a dedicated identifier because they are identified
by their endpoints. Ownership of Connections can be moved from one session to another
using
<move> .
- Conference object: A Conference Object models a
resource for mixing media streams. In order to accommodate the
widest range of underlying telephony call control definitions,
CCXML assumes a separate Conference Object , realizing that this abstraction may
not have a direct counterpart in all telephony platforms. See
<createconference> and
<destroyconference> for further
information.
- Dialog: When active, a Dialog may interact with
other Connections or Conferences using one-way or two-way media
streams, often under the control of dialog environment such as
VoiceXML.
CCXML programs manipulate these entities through elements
defined in the CCXML language. They can also send and/or receive
asynchronous events associated with these entities.
CCXML programs directly manipulate Connection Objects and Conference Objects with various elements in the
language, such as <accept> ,
<createconference> , and
<join> . CCXML may also receive events from
Connection and Conference Objects , in the case
of line signaling, line-status informational messages, or error and
failure scenarios.
CCXML programs can start and kill Voice Dialogs using language elements. It can receive
events from Voice Dialogs ,
which may be standardized events such as dialog.exit ,
or application-specific ones. CCXML can support sending of an event
to a Voice Dialog .
CCXML programs can create other CCXML sessions using <createccxml> .
This is the only guaranteed control mechanism a CCXML Session ever wields over
another. Any other interaction takes place through the event
mechanism. CCXML Sessions
can both send and receive events between one another.
3.1: Event Processing
Telephone applications need to receive and process large numbers
of events in real-time. These events arrive from outside the
program itself - either the underlying telephony platform, or from
other sources of events.
A CCXML program includes event handlers which are executed when
certain events arrive. There are mechanisms for passing information
back and forth between Voice
Dialogs (such as VoiceXML) and CCXML, but the important points
are that CCXML:
- lives on its own thread, and
- carries the burden of rapid asynchronous event handling
Note: References to threads are meant as logical threads and do
not imply any specific platform implementation.
3.2: Conferencing
CCXML provides a powerful and flexible method of creating
multi-party calls based on the following concepts:
- Call legs are audio sinks and sources which can be combined to
form arbitrary networks.
- A conference is an audio stream that mixes together all the
speakers' audio outputs. CCXML conference networks allow for
conference objects ,
which mix inputs into a single output channel.
- A conference's architecture may be modified dynamically, thus
allowing for moderation, floor control, mute, etc.
- Media splitters, which take a single input channel and emit it
over several outputs, may be used by an implementation to realize
the CCXML model in a given network environment.
- Conferencing technology is implementation-dependent. CCXML
implementations may not support all conferencing features mentioned
above.
3.3: Scripting
The computational semantics of CCXML language is based on the
ECMAScript Compact Profile (ES-CP, also known as ECMA-327) [
ECMA327 ].
ES-CP is a strict subset of the third edition of ECMA-262 [
ECMASCRIPT
]. Execution efficiency is a primary goal of CCXML implementations,
and ES-CP was chosen to ensure that CCXML implementations can
operate in a variety of execution environments and without
excessive execution overhead.
The ES-CP document specification states:
'ECMAScript Compact Profile is a subset of ECMAScript
3rd Edition tailored to resource-constrained devices such as
battery powered embedded devices. Therefore, special attention is
paid to constraining ECMAScript features that require
proportionately large amounts of system memory (both for storing
and executing the ECMAScript language features) and continuous or
proportionately large amounts of processing power.'
While CCXML implementations are not necessarily intended for
battery powered embedded devices, it is intended to be used in
large, real-time telephony platforms managing thousands of lines.
The constraints of ES-CP emphasize CCXML's ongoing concern for
execution efficiency.
Even though ES-CP tends to be implemented using interpreters,
CCXML does not require an interpretive implementation. ES-CP can be
compiled to a target language such as C, and thus in turn to
machine code, so that CCXML documents which are static can be
rendered once in machine code. For example, a CCXML implementation,
for optimization purposes, could translate and compile frequently
used CCXML documents on their way from the document server to the
CCXML execution environment in order to avoid multiplying
interpretive overhead by the number of lines that execute the same
document.
The emphasis on efficiency in CCXML language is also shown by
the avoidance of requirements which can only be implemented either
by interpretation or by run-time evaluation.
The choice of an implementation strategy is up to the CCXML
implementer and CCXML language is aimed to allow a range of design
choices in order to accommodate implementations on a wide variety
of platforms.
A CCXML implementation MUST support the
ECMAScript Compact Profile.
3.3.1: Implementation Note:
Line by line vs Batch ECMAScript execution
CCXML implementations MAY provide different levels of optimization in their
ECMAScript interpreters and are expected to be deployed in
performance critical environments. One such level of optimization
could be a decision to execute all the executable items in a
<transition>
as if they were a single script instead of
processing them line by line as is the normal mode of execution. An
example of this is the following bit of CCXML Code:
<assign name="x" expr="3"/>
<var
name="x"/>
In the case where the platform executes
CCXML line by line the <assign> statement will fail with an error.semantic event
due to trying to assign to an undefined variable.
However on a platform where the actions are optimized into a single
ECMAScript execution block something like the following code would
actually be executed instead:
x=3;
var
x;
Due to how ECMAScript
var statements work, declarations are applied before
assignments no matter where they are placed in the code. This
script is actually allowed and the assignment to
x will be completed without error.
Due to this difference in behavior between
line by line vs batch execution application developers
SHOULD NOT
depend on the ability to declare variables
out of document order and SHOULD write code such
that its behavior is the same whether executed line by line or in a
batch.
A more complex situation can arise if you
use the <var>
element to declare transition scoped
variables by the same name as session or
application scoped variables inside of an <if> statement.
An example of this would be:
<if cond="id==session.id">
<var name="id" expr="'2'"/>
</if>
If executed line by line this would end up
executing every line in the script and declaring a transition
scoped variable named id with a value of 2.
The <if>
statement would evaluate to
true due to auto scope searching when resolving the
id reference into a session scoped variable and the next
line would assign a new transition scoped variable by the
name id .However, if the CCXML implementation were to optimize
this into a single ecmascript chunk you may get something like the
following scriptlet:
if(id==session.id) {
var id = '2';
}
Due to the way ECMAScript treats var
declarations the initial ID will evaluate as
undefined as ECMAScript adds a implicit var declaration to
the top of the script and changes the var to an assignment
leaving you with something that is executed as if it was written
like this:
var id;
if(id==session.id) {
id = '2';
}
This causes a different flow of execution
and could cause unexpected program behavior as
id in the if
statement will now be undefined instead of
being equal to session.id .Application developers SHOULD consider this bad programing practice and avoid creating
scenarios where applications create and depend on ambiguously
scoped variables that use assignments inside conditional blocks
with variable names that are already in use by parent
scopes.
Based on years of implementation
experience the CCXML working group believes that CCXML application
code that would be affected by these scenarios is very rare. Any
such code likely relies on unusual ordering of variable
declarations and assignment statements or the use of confusing
variable names and scopes; such code is discouraged due to its
potential for producing unintended results.
3.4: Definitions
The following terms, which are used throughout this
specification, are defined as:
-
ECMAScript left-hand-side expression - defined
in ECMA-262 [ ECMASCRIPT ] 11.2; this is an expression which
produces a result to which a value can be assigned; an expression
which is valid as the left hand operand of an assignment (=)
operator;
Several examples of left-hand-side expressions are as follows
(left-hand-side expression in red):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<script>
var simpleVar;
var aaVar = Object();
simpleVar = 'Simple Expr';
aaVar[0] = 'Simple Expr';
aaVar['arrayKey'] = 'Simple Expr';
aaVar = {callingDevice: 'notSpecified', callCharacteristics: 'voiceUnitCall'};
</script>
</ccxml>
-
ECMAScript expression - defined in ECMA-262 [
ECMASCRIPT
] 11.1; this is an expression which produces a value; an expression
which is valid on the right hand side of an assignment
operator;
Several examples of ECMAScript expressions are as follows
(ECMAScript expression in red):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<script>
var simpleVar;
var aaVar = Object();
simpleVar = 'hello world'; // simple string expression
simpleVar = 'hello world'.length; // Calling a method that returns a
// number on the simple string object
simpleVar = 5; // Simple number expression
simpleVar = aaVar[0]; // Associative Array position expression
simpleVar = aaVar['key']; // Associative Array named value expression
simpleVar = myCoolFunction(); // Function return expression
</script>
</ccxml>
-
ECMAScript variable name - defined in ECMA-262
[ ECMASCRIPT ] 7.6; this is any valid sequence of
characters, known as an identifier, which can be used as a variable
name, a property name, or a function name; this does not include
any qualifiers, such as array or property accessors;
Several examples of ECMAScript variable names are as follows
(ECMAScript variable name in red):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<script>
var simpleVar;
var arrayVar = Object();
simpleVar = 'Simple Expr';
arrayVar[0] = 'Simple Expr';
arrayVar['arrayKey'] = 'Simple Expr';
arrayVar = {callingDevice: 'notSpecified', callCharacteristics: 'voiceUnitCall'};
</script>
</ccxml>
- Empty ECMAScript object - an object returned
by the
new Object() ECMAScript expression; an object
with no properties.
- CCXML variable name - a variable name, with
optional dot separated qualification, declared in a CCXML
<var> element or defined within ECMAScript code
using the var keyword.
- Scope element - a CCXML element which defines
a variable scope;
<ccxml> and
<transition> are CCXML scope elements. Variables
which are defined within a scope element are not visible to
variables defined in other scope elements.
- Time interval - CCXML uses the Cascading Style
Sheets, Level 2 [ CSS2 ] time format. Time designations consist of
a non-negative real number followed by a time unit identifier. The
time unit identifiers are:
- ms : milliseconds
- s : seconds
Examples include: "3s", "850ms", "0.7s", ".5s" and "+1.5s".
- CCXML
Application/Program - A collection of CCXML documents that
together create a complete application/program.
- CCXML Interpreter -
The software that processes CCXML documents, executes commands and
dispatches events. Also referred to as the "CCXML Platform".
- CCXML Platform - An
implementation of CCXML for a specific network and environment,
generally including a CCXML Interpreter as a component.
- CCXML Session - A single instance of a CCXML
application. It can span multiple documents and phone calls. See
Section 3.5 Session
Life-Cycle for details.
- CCXML Parent Session - The CCXML session that
created the currently running session using the <createccxml>
element.
- Event - An action or occurrence to which an
application can respond. Examples of events are incoming phone
calls, dialog actions or user defined events. Events in CCXML are
modeled as ECMAScript objects and can contain complex values. All
events in CCXML have a standard set of properties as defined in
section 9.4.2: Standard Event Attributes
.
- Associative array - An associative array (also
known as a map, lookup table, or dictionary) is an abstract data
type composed of a collection of keys and a collection of values,
where each key is associated with one value. Associative arrays in
ECMAScript are implemented using an Object with sub
properties.
- Class - CCXML Classes are ECMAScript
Constructor objects (see section 4.2.1 of the ECMAScript
specification for more information) to help in creating the
appropriate type of object instances (such as connection,
conference and dialog). The Constructor object may contain
properties that are not inherited by children objects (such as
Connection.states). The constructor object MAY also contain a Prototype property to allow
properties that are inherited. Platforms MAY choose to add properties to classes. By
convention, the properties MUST begin with
an underscore, "_", to identify them as platform-dependent. All
defined objects in this specification must be initiated via one of
these classes. An example would be
'MyConnection = new
Connection()'. Reserved ECMAScript
property ' prototype.constructor ' MUST reference the class
constructor object, so in the example above,
'MyConnection.prototype.constructor == Connection'. The
Connection class MUST initiate connection
objects, the Dialog class MUST initiate
dialog objects and the Conference class MUST initiate conference objects.
3.5: Session Life-Cycle
3.5.1: Startup
A CCXML session can be started for the following reasons:
- A new incoming phone call coming into the platform.
- A CCXML application executing a
<createccxml> .
- An external session launch request coming into the
platform.
To create a CCXML session, the URI for the initial CCXML
document must be known, along with any fetching parameters
affecting how that CCXML document is retrieved. For incoming calls,
the selection of the initial URI and fetching parameters is
platform-dependent, and MAY be based on
information from the incoming call. Sessions created via
<createccxml> and the session creation event I/O
processor determine the initial URI and fetching parameters as
stated in this specification.
When a session is started due to an incoming call it has
ownership of the new Connection that caused it to be created. The
new CCXML session will be responsible for processing the Connection
state events and performing the Connection actions. If the session
was started because of a <createccxml> , it will
start without ownership of any event endpoints. In the case of an
external session launch the session will not own any event
endpoints.
A CCXML application can determine the reason its session was
started by evaluating the contents of the
session.startupmode session variable that is defined
in the Session
Variables section.
3.5.2: Shutdown
A CCXML session can end in one of the following ways:
- The CCXML application executes an
<exit>
.
- An unhandled
"error.*" event.
- An unhandled
"ccxml.kill" event.
- A
"ccxml.kill.unconditional" event.
When a CCXML session ends, all active connections, conferences
and dialogs that are owned by that session are automatically
terminated by the platform.
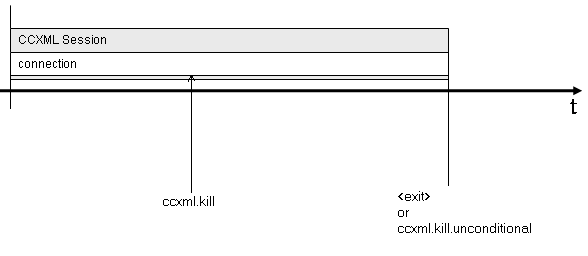
3.5.3: Session Life-Cycle
Diagrams
The following diagrams illustrate the session life-cycle of
several different scenarios. These diagrams do not show all
possible scenarios but rather show some of the most common ones
that CCXML applications may encounter.
3.5.3.1: session can live before
and after active connections (or no connections at all)
A CCXML session does not necessarily need to have any
connections associated with it. After starting, a session may
acquire connections as a result of <createcall>
or <move> requests.

3.5.3.2: connection life shorter
than session
In this example, the session is started due to an incoming call.
A connection is typically shorter than a session. A session does
not end when a connection terminates.
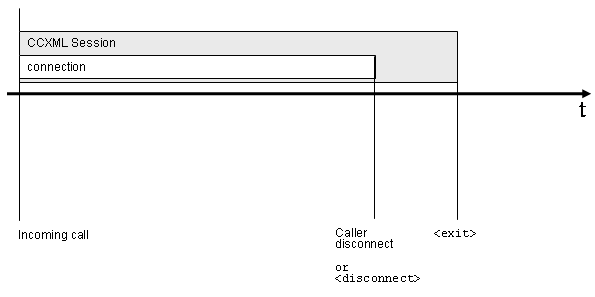
3.5.3.3: session ends, kills all
active connections
When a session ends, any resources, including connections owned
by that session are terminated.

3.5.3.4: session can have
multiple sequential connections
A session can have multiple sequential connections
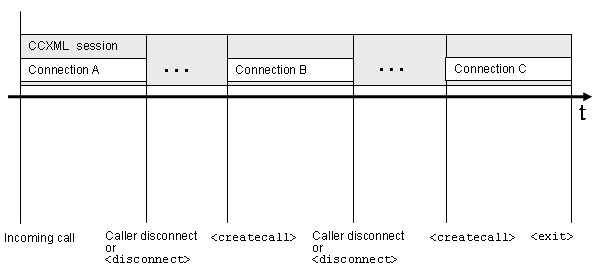
3.5.3.5: session can have
multiple sequential connections and multiple concurrent
connections
In addition to having multiple sequential connections, a session
can have multiple concurrent connections.
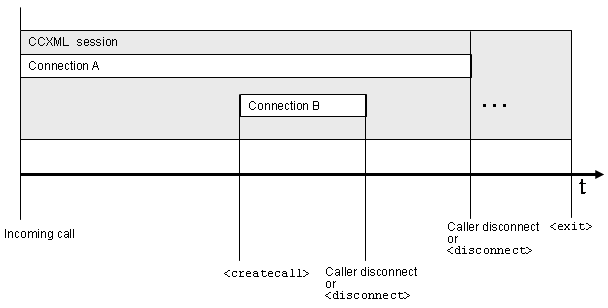
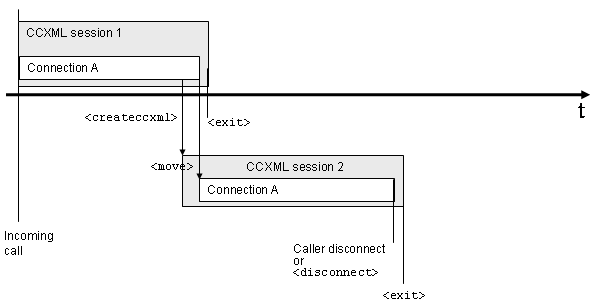
3.5.3.5: move a connection to a
newly created session
A connection can be moved from one CCXML session to another
session. In the figure below, CCXML session (1) creates a new CCXML
session (2) via <createccxml> . Then, the
connection is moved from the original CCXML session to the new
session.
3.5.3.7: move a connection to a
"master" session
A connection can be moved from one CCXML session to another
session, such as a "master" session.
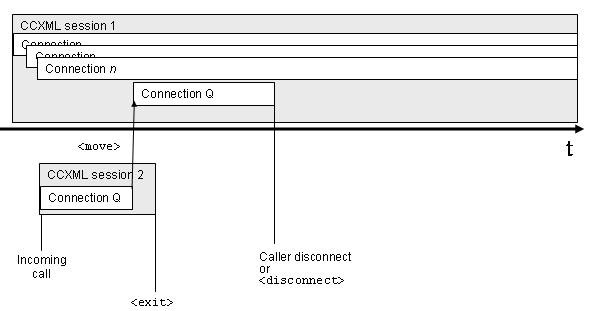
3.5.3.8: optional "master"
session for inbound call handling
Implementations MAY , as a
platform-specific optimization, choose to deliver more than one
inbound call to a single "master" session. This can be viewed as
equivalent to sessions handling incoming calls performing a
<move> , as described in 3.5.3.7, of the new
Connection (including the connection.alerting event)
to the single "master" CCXML session.
The default inbound call handling behavior for CCXML
implementations is to create a new CCXML session and deliver the
connection.alerting event to it. If a platform
supports delivery of multiple inbound calls to a single session,
the way this is configured is implementation specific.
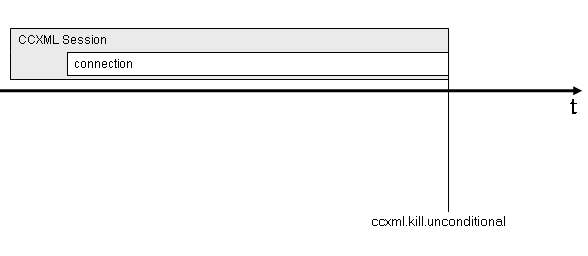
3.5.3.9:
ccxml.kill.unconditional event raised
If at anytime a ccxml.kill.unconditional event is
raised by the underlying implementation, the CCXML session is
immediately terminated and all active connections, conferences and
dialogs that are owned by that session are automatically terminated
by the platform.
3.5.3.10: Normal session
shutdown requested by the platform
If at anytime the platform wishes to terminate a CCXML session
it MUST raise a ccxml.kill
event to inform the CCXML application. The normal response to this
event is for the CCXML application to perform any clean up and
termination of current active connections, conferences or dialogs
and then execute an <exit> element.
If the CCXML application does not respond to the
ccml.kill event in a timely manner the platform
MAY then raise a
ccxml.kill.unconditional event to immediately
terminate the CCXML session and all active connections,
conferences, and dialogs that are owned by the session.
4: Simple Examples
4.1: Hello World
This simple CCXML document shows an example of a "hello world"
application that is started due to an incoming call where the
application simply assigns a value to a variable, prints a message
to the platform log and exits:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<eventprocessor>
<transition event="connection.alerting">
<var name="MyVariable" expr="'This is a CCXML Variable'"/>
<log expr="'Hello World. I just made a variable: ' + MyVariable"/>
<log expr="'Lets hang up on this incoming call.'"/>
<exit/>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
4.2: Accept or Reject a
Call
This CCXML document shows an example of how to process a
incoming call event and answer or reject the call based on the
phone number of the calling party:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<eventprocessor>
<transition event="connection.alerting">
<log expr="'The number called is' + event$.connection.remote + '.'"/>
<if cond="event$.connection.remote == 'tel:+18315551234'">
<log expr="'Go away! we do not want to answer the phone.'"/>
<reject/>
<else/>
<log expr="'We like you! We are going to answer the call.'"/>
<accept/>
</if>
</transition>
<transition event="connection.connected">
<log expr="'Call was answered,Time to disconnect it.'"/>
<disconnect/>
</transition>
<transition event="connection.disconnected">
<log expr="'Call has been disconnected. Ending CCXML Session.'"/>
<exit/>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
4.3: Simple Dialog
This is an example of running a simple VoiceXML dialog from
CCXML. The application answers an incoming phone call and then
connects it to a VoiceXML dialog that returns a value that is then
logged to the platform:
dialog.ccxml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<!-- Lets declare our state var -->
<var name="state0" expr="'init'"/>
<eventprocessor statevariable="state0">
<!-- Process the incoming call -->
<transition state="init" event="connection.alerting">
<accept/>
</transition>
<!-- Call has been answered -->
<transition state="init" event="connection.connected">
<log expr="'Houston, we have liftoff.'"/>
<dialogstart src="'dialog.vxml'"/>
<assign name="state0" expr="'dialogActive'" />
</transition>
<!-- Process the incoming call -->
<transition state="dialogActive" event="dialog.exit">
<log expr="'Houston, the dialog returned [' + event$.values.input + ']'" />
<exit />
</transition>
<!-- Caller hung up. Lets just go on and end the session -->
<transition event="connection.disconnected">
<exit/>
</transition>
<!-- Something went wrong. Lets go on and log some info and end the call -->
<transition event="error.*" >
<log expr="'Houston, we have a problem: (' + event$.reason + ')'"/>
<exit/>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
dialog.vxml:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form id="Form">
<field name="input" type="digits">
<prompt>
Please say some numbers ...
</prompt>
<filled>
<exit namelist="input"/>
</filled>
</field>
</form>
</vxml>
5: CCXML Elements Listing
6: Document Control Flow and Execution
6.1: Overview
A CCXML session begins with the execution of a CCXML document.
The flow of the execution can be changed with the help of
<if> , <elseif> ,
<else> , <fetch> , and
<goto> . Most of a CCXML session's execution
will take place within an <eventprocessor> ,
which processes a stream of incoming events.
A CCXML session can consist of multiple CCXML documents,
traversed by use of <goto> and
<fetch> .
A new CCXML session has a new session object (
session.* ). A CCXML session can contain multiple
active connections.
A CCXML session may launch a new CCXML session using
<createccxml> . The new CCXML session executes
in an independent context and variable space from the original
CCXML session, completely independent of the lifetime of the
original session. Sessions can communicate by sending messages via
<send> .
This media type should be used for a
XML document containing CCXML content, see Appendix M.
6.2: Elements
This section details the CCXML elements for control flow and
execution.
6.2.1: <ccxml>
6.2.1.1: Overview
This is the parent element of a CCXML document and encloses the
entire CCXML script in a document. When a
<ccxml> is executed, its child elements are
collected logically together at the beginning of the document and
executed in document order before the target
<eventprocessor> . This is called document
initialization.
The <ccxml> can designate the CCXML
namespace. This can be achieved by declaring an xmlns
attribute or an attribute with an " xmlns " prefix.
See [XMLNS] for details. Note
that when the xmlns attribute is used alone, it sets
the default namespace for the element on which it appears and for
any child elements. The namespace URI for CCXML is
"http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml".
6.2.1.2: <ccxml> Attribute
Details
| version |
true |
|
string |
none |
1.0 |
The version of this CCXML
document. The initial version number must be 1.0. |
| xml:base |
false |
|
valid URI |
none |
A valid URI |
The base URI for this document as
defined in [XML-BASE] . As in [HTML] , a URI which all relative references
within the document take as their base. |
6.2.2.1: Overview
The <metadata> and <meta> are
containers in which information about the document can be placed.
The <metadata> provides more general and
powerful treatment of metadata information than <meta> by using a metadata
schema.
A <meta> declaration associates a
string to a declared meta property or declares " http-equiv " content. Either a name or http-equiv attribute
is REQUIRED . It is an error to provide
both name and http-equiv attributes. A content attribute is REQUIRED
. The http-equiv attribute has a special
significance when documents are retrieved via HTTP . Although the
preferred method of providing HTTP header information is
by using HTTP header fields, the "
http-equiv " content MAY be used in situations where the CCXML document
author is unable to configure HTTP header fields
associated with their document on the origin server, for example,
cache control information. Note that, as with
<meta> in HTML documents [HTML] , HTTP servers and caches
are not NOT REQUIRED to introspect the contents of
<meta> in CCXML documents and thereby
override the header values they would send otherwise.
Informative: This is an example of how <meta> can be
included in a CCXML document to specify a resource that provides
additional metadata information and also indicate that the document
MUST NOT be cached.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<meta http-equiv="Cache-Control" content="no-cache"/>
</ccxml>
<meta> is an empty element.
6.2.2.2: <meta> Attribute
Details
| name |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the http-equiv
attribute |
NMTOKEN |
none |
|
The NAME of the metadata
property. |
| http-equiv |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the name attribute |
NMTOKEN |
none |
A valid HTTP header |
The NAME of an HTTP response
header.
This attribute has special significance when documents are
retrieved via HTTP. The http-equiv content may be
used in situations where the CCXML document author is unable to
configure HTTP header fields associated with their document on the
origin server. |
| content |
true |
|
string |
none |
|
The value of the metadata
property. |
6.2.3.1: Overview
<metadata> is a container in which
information about the document can be placed using a metadata
language. Although any metadata language can be used within
<metadata> , it is recommended that the Resource Description Format
[RDF] be used in conjunction with the general metadata properties
defined by the Dublin Core Metadata Initiative [DC] .
RDF [RDF-SYNTAX] is a
declarative language and provides a standard way for using XML to
represent metadata in the form of statements about properties and
relationships of items on the Web. A recommended set of generally applicable metadata
properties (e.g., " title ", " creator ",
" subject ", " description ", "
copyrights ", etc.) is the Dublin Core Metadata
Element Set [DC] , used in the
example below.
Document properties declared with <metadata> can use
any metadata schema.
Informative: This is an example of how <metadata> can be
included in a CCXML document using the Dublin Core version 1.0 RDF
schema [DC] describing general
document information such as title, description, date, and so
on:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<metadata>
<rdf:RDF
xmlns:rdf = "http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:dc = "http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/">
<!-- Metadata about CCXML document -->
<rdf:Description rdf:about="http://www.example.com/meta.ccxml"
dc:title="Hamlet-like Soliloquy"
dc:description="Aldine's Soliloquy in the style of Hamlet"
dc:publisher="W3C"
dc:language="en"
dc:date="2002-11-29"
dc:rights="Copyright 2002 Aldine Turnbet"
dc:format="application/ccxml+xml" >
<dc:creator>William Shakespeare</dc:creator>
<dc:creator>Aldine Turnbet</dc:creator>
</rdf:Description>
</rdf:RDF>
</metadata>
</ccxml>
The following CCXML elements can occur within the content of
<metadata> : none .
6.2.3.2: <metadata> Attribute
Details
6.2.4: <if>
6.2.4.1: Overview
<if> is a container for conditionally
executed elements. <else> and
<elseif> can optionally appear within an
<if> as immediate children, and serve to
partition the elements within an <if> .
<else> and <elseif> have no
content. <else/> is a synonym for
<elseif cond="true"/> .
Each partition within an <if> is preceded by
an element having a cond attribute. The initial
partition is preceded by the <if> and subsequent
partitions by <elseif> s (or
<else> s). The first partition in document order
with a cond that evaluates to true is
selected. <else> always evaluate to
true . A partition MAY be
empty.
If an <if> has no immediate
<elseif> or <else> children,
the full contents of the <if> will be selected
when the cond attribute is true .
<else> was chosen to match similar concepts
in other languages, and supports examples such as
<if cond="...">
<!-- selected when <if cond> is true -->
<else/>
<!-- selected when <if cond> is false -->
</if>
However, <else> is a synonym for
<elseif cond="true"/> , so an example such
as
<if cond="...">
<!-- selected when <if cond> is true -->
<else/>
<!-- selected when <if cond> is false -->
<else/>
<!-- never selected -->
</if>
is also possible and MUST be interpreted
as
<if cond="...">
<!-- selected when <if cond> is true -->
<elseif cond="true"/>
<!-- selected when <if cond> is false -->
<elseif cond="true"/>
<!-- never selected -->
</if>
With this definition for <else> , CCXML
provides familiar if/elseif/else semantics, but conforms to the
rules of valid XML [XML]
documents.
6.2.4.2: <if> Attribute
Details
| cond |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A valid ECMAScript
expression |
An ECMAScript expression which
can be evaluated to true or false. |
6.2.5: <elseif>
6.2.5.1: Overview
An <elseif> partitions the content of an
<if> , and provides a condition that determines
the selection of the partition it begins.
<elseif> can appear optionally as an immediate
child of an <if> .
6.2.5.2: <elseif>
Attribute Details
| cond |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A valid ECMAScript
expression |
An ECMAScript expression which
can be evaluated to true or false. |
6.2.6: <else>
6.2.6.1: Overview
<else> is a synonym for <elseif
cond="true"/> .
6.2.6.2: <else> Attribute
Details
| none |
|
|
|
none |
|
else is a synonym for elseif
cond="true". |
6.2.7: <fetch>
6.2.7.1: Overview
<fetch> is used to asynchronously fetch
content identified by the attributes of the
<fetch> . The fetched content may be a CCXML
document, script content or other document types supported by the
CCXML platform. Content that has been acquired using
<fetch> is accessible through other elements
defined by CCXML and via the content attribute of the
fetch.done event. Execution returns from the element
immediately, and the CCXML application can continue on while the
platform works to fetch the identified resource. When the fetch
request has been completed, an event is generated against the
session that initiated the fetch. If the requested content was
fetched successfully, and in the case of CCXML content, was
successfully parsed and validated, a fetch.done
MUST be generated. If the requested
content failed to be fetched, an error.fetch
MUST be generated. Note that even if
content is successfully fetched, errors in processing fetched
content (for instance, a CCXML document with a syntax error) may
result in an error.fetch being thrown.
The fetch request is local to the session that initiated the
<fetch> , and is referenced through a unique
identifier generated by the CCXML platform. The application may
obtain the unique identifier for a fetch request by providing an
ECMAScript left-hand-side expression in the fetchid
attribute when the fetch is performed. The fetch identifier can
also be obtained as a property of the fetch.done
event. The application uses the fetch identifier in any CCXML
elements that reference fetched content, currently
<goto> and <script> .
Fetched content that could be referenced via a
fetchid (eg, a CCXML or ECMAScript Document) that was
fetched in processed mode has a lifetime that is
limited to that of the document in which it is fetched. Therefore,
following a transition to a new CCXML document using
<goto> , content fetched in the scope of the
current document is no longer accessible. Note that this should not
be taken to preclude platform-level optimizations or caching of
resources that are fetched multiple times.
All other content is only accessible via the content attribute
of the fetch.done event. If the application needs
access to the content outside of the fetch.done event
transition it is the responsibility of the application to save a
reference in an appropriately scoped variable.
Content referenced via fetchid (for example via
<script> or <goto> )
MUST be fetched using
processed mode.
The use of <fetch> to obtain content does not
compel the application to make use of that content. However, it is
wasteful of system resources to fetch resources that are not used.
Platforms are responsible for clearing out unused fetch resources,
and may impose limits on the resources that can be fetched by a
single session.
The "http" URI scheme MUST be supported
by CCXML platforms, the "https" protocol should be supported and other URI protocols
may be supported.
If the platform does not support the content type returned from
a <fetch> request but the fetch does
successfully complete (for example HTTP 2xx response code) the
platform MUST still throw a
fetch.done event for the fetchid .
If the platform implements a security model (such as Access
Control for Cross-site Requests [ACCESS-CONTROL] ) and the request is denied due
to the security model an error.notallowed event
MUST be thrown.
INFORMATIVE NOTE: It is expected in future versions of CCXML
additional forms of processed fetch modes will be added. Examples
of these could be dom or e4x mappings of raw XML content.
6.2.7.2: <fetch> Attribute
Details
| next |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
must evaluate to a valid URI |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns the URI of the resource to be fetched. |
| type |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
In processed mode
"application/ccxml+xml". In raw mode "*/*". |
MIME Types formatted as per HTTP
Accept header [RFC2616] |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string setting the value of the HTTP Accept
header to tell the application server what content type the
application wishes to have returned. |
| namelist |
false |
|
Var List |
none |
List of ECMAScript Variable
names |
A list of zero or more whitespace
separated CCXML variable names. These variables must be submitted
to the web server, with the same qualification as used in the
namelist. When an ECMAScript variable is submitted to the web
server, its value must be first converted into a string before
being submitted.
If the variable is an ECMAScript Object, the mechanism by which it
must be submitted is not currently defined. Instead of submitting
ECMAScript Objects directly, the application developer may
explicitly submit the properties of an Object. e.g. "date.month
date.year". |
| method |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
get |
get
post |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that indicates the HTTP method to use.
Values defined by the specification are:
- get
- This indicates that the "GET" method must be used to fetch the
URI
- post
- This indicates that the "POST" method must be used while
submitting the URI to the web server.
|
| fetchid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Left Hand Side
Expression |
none |
ECMAScript Variable |
An ECMAScript left hand side
expression evaluating to a previously defined variable. The value
of the attribute must receive an internally generated unique string
identifier to be associated with the completion event. This
identifier can be tested by the fetch completion event handler to
distinguish among several outstanding fetch requests.
If this attribute is not specified, the fetch identifier can be
acquired from the fetch completion event. Every fetch request must
receive a unique fetch identifier, even if the request is for the
same URI |
| timeout |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string in CSS2 [CSS2]
format |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. This interval begins when
the fetch is executed. The fetch must fail if not completed at the
end of this interval. A failed fetch must return the
error.fetch event. |
| maxage |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a valid time value for the HTTP 1.1 request [RFC2616] |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. This indicates that the
document is willing to use content whose age must be no greater
than the specified time in seconds (cf. 'max-age' in HTTP 1.1
[RFC2616] ). The document is not willing
to use stale content, unless maxstale is also provided. |
| maxstale |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a valid time value for the HTTP 1.1 request [RFC2616] |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. This indicates that the
document is willing to use content that has exceeded its expiration
time (cf. 'max-age' in HTTP 1.1 [RFC2616] ). If maxstale is assigned a value,
then the document is willing to accept content that has exceeded
its expiration time by no more than the specified number of
seconds. |
| enctype |
false |
Valid only when the
value of the method is "post" , otherwise ignored. |
ECMAScript Expression |
application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
valid media encoding type |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that indicates the media encoding type
of the submitted document (when the value of the method is "post").
Values defined by the specification are:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- This indicates that the ccxml variables specified in the
namelist must be url encoded.
|
| mode |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
processed |
processed, raw |
Controls what the CCXML platform
should do with fetched content. If set to processed
(the default) the CCXML platform MUST
attempt to parse and validate the returned content. If set to
raw the platform MUST NOT
attempt to process the data and MUST leave
processing of the content to the application who can do what it
wishes with the content via the content attribute of
the fetch.done event |
6.2.8: <goto>
6.2.8.1: Overview
<fetch> , in conjunction with
<goto> , is used to transfer execution to a
different CCXML document in a multi-document CCXML application. The
<fetch> tells the platform to find, load, and
parse a given CCXML document. After the fetch completes, the CCXML
application can then issue a <goto> to execute
the now-fetched document.
Below is a small snippet of code from the CCXML application's
event handler. We execute a <fetch> operation,
and continue on to assign to a state variable, and maybe handle
more events. Eventually, the fetch completes, the CCXML platform
services the event, and the application performs the
<goto> .
<fetch next="'http://www.example.com/control.ccxml'"/>
<--control continues here->
<assign name="state_var" expr="'fetch_wait'"/>
</transition>
<!-- ……… -->
<transition state="fetch_wait" event="fetch.done"/>
<goto fetchid="event$.fetchid"/>
</transition>
A <goto> transfers control to the document
obtained through a fetch request, using the platform-generated
unique identifier associated with that fetch request. The fetch
completion event MUST have arrived before
the <goto> is executed, otherwise, an
error.semantic event is generated. If the fetched
content referenced by the fetch identifier is not a CCXML document,
or the fetch identifier is invalid and does not correspond to any
fetch request, this also results in an error.semantic
event.
When a <goto> is executed, the target
document replaces the current document in its session. Event
sources associated with this session are inherited by the target
document. Execution of the current document terminates.
6.2.8.2: <goto> Attribute
Details
| fetchid |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A valid fetch id |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns the fetch identifier of a completed fetch request acquired
either in a fetch with the fetchid attribute, or from the fetchid
attribute of a fetch.done event.
If the attribute value is invalid, an error.semantic event
must be thrown. |
6.2.8.3: <fetch> and
<goto> Example
The following code shows the use of the
<fetch> and <goto> elements
along with the fetchid attribute to handle more
complex fetching situations:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<!-- var to hold the value of the fetch
identifier that we care about -->
<var name="myGoodFetchID"/>
<eventprocessor>
<transition event="ccxml.loaded">
<!-- stick the value of the fetch
identifier in the myGoodFetchID var -->
<fetch fetchid="myGoodFetchID"
next="'http://www.example.com/goodfetch.ccxml'"/>
<!-- do not bother saving the fetch id's for these,
we would just ignore them anyway -->
<fetch next="'http://www.example.com/fakefetch1.ccxml'"/>
<fetch next="'http://www.example.com/fakefetch2.ccxml'"/>
</transition>
<transition event="fetch.done">
<if cond="myGoodFetchID == event$.fetchid">
<!-- only matched if we have fetched
http://www.example.com/goodfetch.ccxml -->
<goto fetchid="event$.fetchid"/>
</if>
</transition>
<transition event="error.fetch">
<!-- Ignore bad fetches in this example -->
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
6.2.9: <createccxml>
6.2.9.1: Overview
<createccxml> is used to create another CCXML
session, which begins execution with the document identified by
this element. The new CCXML session has no relation to its creator
once spawned, and has a wholly separate lifetime and address
space.
Execution returns from the <createccxml>
element immediately, and the CCXML interpreter can continue on
while the new CCXML session is established and loads its initial
document. If the new session is successfully established or a
failure occurs an event is generated and is delivered to the
session that executed the <createccxml>
element.
6.2.9.2 <createccxml>
Attribute Details
| next |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
a valid URI |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns the URI of the resource to be fetched. |
| namelist |
false |
|
Var List |
none |
List of ECMAScript Variable
names |
A list of zero or more whitespace
separated CCXML variable names. These variables must be submitted
to the web server, with the same qualification as used in the
namelist. When an ECMAScript variable is submitted to the web
server, its value must be first converted into a string before
being submitted.
If the variable is an ECMAScript Object, the mechanism by which it
must be submitted is not currently defined. Instead of submitting
ECMAScript Objects directly, the application developer may
explicitly submit the properties of an Object. e.g. "date.month
date.year". |
| fetchparam |
false |
|
ECMAScript expression |
'none' |
'none', 'session-id',
'session' |
Specifies parameters, in addition
to those specified via 'namelist' (if present), that will be passed
to the web server when fetching the CCXML document for the new
session. Three values are legal for this attribute:
none - No additional parameters should be passed
with the fetch;session-id - The 'session.id' property of the
newly created session will be included when fetching the initial
document;session - The 'session.id' property and all
properties of 'session.values' will be included when fetching the
initial document. The evaluation of 'session.values' will occur
after it has been populated as per the 'parameter' attribute above,
providing developers with a simple means of passing data both to
the new CCXML session and to the web server.
|
| parameters |
false |
|
Var List |
none |
List of ECMAScript Variable
names |
A list of zero or more whitespace
separated CCXML variable names. Each named variable will be created
as a property of 'session.values' in the newly created session. For
instance, passing a variable named 'foo' with value '123' will
result in the 'session.values.foo' property evaluating to '123';
similarly, passing a variable named 'foo.bar' would result in a
'session.values.foo.bar' property. Variable values are passed in
string form; the passing of ECMAScript objects is not currently
defined. |
| method |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
get |
get
post |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that indicates the HTTP method to use.
Values defined by the specification are:
- get
- This indicates that the "GET" method must be used to fetch the
URI
- post
- This indicates that the "POST" method must be used while
submitting the URI to the web server.
|
| sessionid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Left Hand Side
Expression |
none |
ECMAScript Variable |
An ECMAScript left hand side
expression evaluating to a previously defined variable. The value
of the attribute must receive an internally generated unique string
identifier which identifies the newly created session. |
| timeout |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string in CSS2 [CSS2]
format |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. This time interval must be
interpreted by the new CCXML session as the maximum time it may
wait for the completion of the fetch for the initial document
specified by the next attribute. If the new CCXML session is
unable to fetch the initial document within the timeout
interval, an error.createccxml event must be
thrown. |
| maxage |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a valid time value for the HTTP 1.1 request [RFC2616] |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. This indicates that the
document is willing to use content whose age must be no greater
than the specified time in seconds (cf. 'max-age' in HTTP 1.1
[RFC2616] ). The document is not willing
to use stale content, unless maxstale is also provided. |
| maxstale |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a valid time value for the HTTP 1.1 request [RFC2616] |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. This indicates that the
document is willing to use content that has exceeded its expiration
time (cf. 'max-age' in HTTP 1.1 [RFC2616] ). If maxstale is assigned a value,
then the document is willing to accept content that has exceeded
its expiration time by no more than the specified number of
seconds. |
| enctype |
false |
Valid only when the
value of the method is "post" , otherwise ignored. |
ECMAScript Expression |
application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
valid media encoding type |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that indicates the media encoding type
of the submitted document (when the value of the method is "post").
Values defined by the specification are:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- This indicates that the ccxml variables specified in the
namelist must be url encoded.
|
6.2.10: <exit>
6.2.10.1: Overview
<exit> ends execution of the CCXML session.
All pending events are discarded, and there is no way to restart
CCXML execution.
6.2.10.2 <exit> Attribute
Details
| expr |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
undefined |
|
A return ECMAScript expression
(e.g. 0 or 'oops!'). If this attribute is omitted, the return value
must be ECMAScript undefined. This value must be stored as a
property of the exit event. |
| namelist |
false |
|
Var List |
none |
List of ECMAScript Variable
names |
A list of zero or more whitespace
separated CCXML unqualified variable names to be returned. These
variable names and their associated values must be set as
properties of the exit event. |
A CCXML document executing the <exit> will
generate a ccxml.exit event to the parent session. The
exiting document will be identified on the exit event by its
session ID.
6.2.11: <log>
6.2.11.1: Overview
<log> allows an application to generate a
logging or debug message which a developer can use to help in
application development or post-execution analysis of application
performance. The manner in which the message is displayed or logged
is platform-dependent. The usage of label is platform-dependent.
The use of <log> SHOULD
have no other side-effects on interpretation.
<log> is an empty element.
6.2.11.2 <log> Attribute
Details
| label |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
|
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string which must be used, for example,
to indicate the purpose of the log. |
| expr |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
|
An ECMAScript expression
evaluating to a string to be logged. |
6.3: Events
6.3.1: Overview
CCXML allows operations such as document fetching, startup and
shutdown to execute independently. CCXML events that describe these
operations are defined below:
6.3.2: fetch.done - Fetch
Completion Event
This event is generated when a fetch request completes
successfully. It is delivered to the document which issued the
request.
The fields of this event are:
| fetchid |
true |
string |
The internally generated unique fetch
identifier |
| uri |
true |
string |
The URI of the resource that was
fetched. If the fetch resulted in one or more HTTP redirects (e.g.
302), the value of this property is set to the final target
URI. |
| statuscode |
true |
int |
The numeric HTTP status code (eg 200,
202 etc) of the HTTP request. |
| content |
true |
string |
An ECMAScript representation of the
fetched content. If the CCXML browser can not represent the content
in ECMAScript (for example some content that was fetched in
processed mode) this may be ECMAScript undefined. In raw mode it is
expected that this attribute will contain a string representation
of the fetched content. |
| contenttype |
true |
string |
The returned content type from the web
server. |
6.3.3: error.fetch -
Fetch Error Event
This event is generated when a fetch request does not
successfully complete. It is delivered to the document which issued
the request.
The fields of this event are:
| fetchid |
true |
string |
The internally generated unique fetch
identifier |
| reason |
true |
string |
A string description of the fetch
error. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
| statuscode |
true |
int |
The numeric HTTP status code (eg
404,500 etc) of the failed HTTP request. |
| uri |
true |
string |
The URI of the resource that was
fetched. If the fetch resulted in one or more HTTP redirects (e.g.
302), the value of this property is set to the final target
URI. |
| content |
true |
string |
An ECMAScript representation of the
fetched content. If the CCXML browser can not represent the content
in ECMAScript (for example some content that was fetched in
processed mode) this may be ECMAScript undefined. In raw mode it is
expected that this attribute will contain a string representation
of the fetched content. |
| contenttype |
true |
string |
The returned content type from the web
server. |
6.3.4: ccxml.exit - CCXML
Document Exit Event
This event is generated when a CCXML session is terminated for
any reason, if the terminated session has a parent session. This
event is sent to the parent session and not the session that was
terminated.
The fields of this event are:
| sessionid |
true |
string |
The identifier of the exiting session.
This must be the same value that was returned to the
sessionid attribute of the createccxml which created
this session. |
| expr |
true |
string |
The value of the exit
expr attribute. If this attribute is omitted in the
exit , the value must be ECMAScript undefined. |
| values.* |
false |
ECMAScript Object |
Return values from the ccxml session.
This would be the values of each of the objects listed in the CCXML
exit element's namelist. |
| reason |
true |
string |
Reason that the session ended. Possible
values are:
"exit" - Session ended due to a <exit> element
"error" - Session ended due to an unhandled error event
"kill" - Session ended due to ccxml.kill* event |
6.3.5: ccxml.loaded -
CCXML Document Loaded Event
This event is thrown once the document is parsed and ready for
execution (document initialization occurs between the fetched and
loaded events). The CCXML platform MUST
generate this event when the CCXML document is first loaded, both
at session startup and after transferring control to a new document
with the <goto> . This event would be processed
after the platform had executed the document initialization
including executing any elements under the
<ccxml> and before events such as
connection.alerting which may have triggered creation of the
session.
The fields of this event are:
| sessionid |
true |
string |
The identifier of the session on which
this document is executing. |
| parent |
true |
string |
The identifier of the session which
issued the createccxml to start this document. If this
document was started directly by the CCXML platform the value is
ECMAScript undefined. |
6.3.6: ccxml.kill - CCXML
kill Event
The kill event can be used by the platform to
terminate a session without an explicit <exit> .
There are two versions of this event: catchable, and
non-catchable.
The ccxml.kill event can be caught, typically to
perform a clean-up operation at the end of a session. If the event
is caught the session will not be terminated unless an
<exit> element is processed. If the event is not
caught the session will be terminated and all active connections,
conferences and dialogs that are owned by that session will be
automatically terminated by the platform.
Unlike other events, the ccxml.kill.unconditional
event is the only event that cannot be caught by an application; it
will unconditionally terminate the session and all active
connections, conferences and dialogs that are owned by that session
will be automatically terminated by the platform.
Note that while the normal cause of a ccxml.kill or
ccxml.kill.unconditional event being queued to a
session is that the platform wishes to terminate the session, it is
legal for any event I/O processor to generate a
ccxml.kill or ccxml.kill.unconditional
event. For instance, it is legal for one CCXML session to
unconditionally kill another session by sending a
ccxml.kill.unconditional event using
<send> . Note, however, that platforms may
impose rules that prevent one session from arbitrarily killing
another (to prevent malicious applications, for instance).
The fields of this event are:
| sessionid |
true
false |
string |
The identifier of the session. session
who has sent the event
. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A string describing the reason the
platform sent the kill event. Content of this field is
platform-specific, and is only for informative purposes. |
6.3.7: ccxml.created -
CCXML Session Create Completion Event
This event is generated when a <createccxml>
request completes successfully. It is delivered to the document
which issued the request and indicates that the new session has
retrieved the specified initial CCXML document, parsed and has
begun execution of it by sending the ccxml.loaded
event to the new session.
The fields of this event are:
| sessionid |
true |
string |
The identifier of the newly created
CCXML session. This must be the same identifier as was returned on
the sessionid attribute of the createccxml request
that created the session. |
6.3.8:
error.createccxml - CCXML Session Create Failed
Event
This event is generated when a <createccxml>
request fails to complete. It is delivered to the document which
issued the request and indicates that the new session has not been
created.
The fields of this event are:
| sessionid |
true |
string |
The identifier of the failing CCXML
session. This is the same identifier as was returned on the
sessionid attribute of the createccxml request that
created the session. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A string description of the error
encountered. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
6.3.9: error.unsupported -
CCXML Unsupported Operation
This event is generated when an operation that is not supported
by the platform is executed.
The fields of this event are:
| reason |
true |
string |
A string description of the error
encountered. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
7: Dialogs
7.1: Overview
CCXML does not provide any mechanism for interacting with
callers but relies on separate dialog environments such as VoiceXML
[ VOICEXML ].
Whenever interaction with a caller is required, a CCXML session can
create a separate dialog to perform that interaction. After the
dialog interaction is complete, an asynchronous event is sent to
the CCXML session which can use any results returned by the dialog
environment to decide what should happen next.
Dialogs initiated by CCXML sessions are not tied to any single
dialog language or technology. Any dialog system which fulfils
CCXML's requirements MAY be used for
interaction with the caller. Examples of dialog systems include
VoiceXML, SALT, traditional IVR , 3GPP MRF as well as simple media
handling systems for fax, media playback and recording, DTMF
detection, answer-machine detectors, etc. A CCXML platform
MAY support interaction with several
dialog systems with the selection of the particular technology
being based on the MIME type specified when the dialog is
initiated.
All CCXML elements that manipulate dialogs are asynchronous with
control returning immediately to the CCXML session after the
operation is initiated. The CCXML session is notified when the
dialog operation successfully completes, or fails, by an
asynchronous event. Execution of a
<dialogprepare> or
<dialogstart> without preparation creates a
Dialog Object immediately, allowing the Dialog Object to be
accessed following the
<dialogprepare>/<dialogstart> , within the
same transition. However, existence of the Dialog Object does not
guarantee anything about the success of the
<dialogprepare>/<dialogstart> request.
A CCXML program initiates a dialog using the
<dialogstart> element. Execution of this element
connects a dialog environment to a connection and instructs it to
start interacting with the caller. For some dialog environments it
may take some time to initialize the dialog environment and thus
the use of the <dialogstart> element alone may
cause the caller to hear silence, or "dead air". To avoid this
situation CCXML provides an ability to ready a dialog environment
prior to connecting and starting it, this is done using the
<dialogprepare> element. Any dialog that has
been either started with <dialogstart> , or
prepared with <dialogprepare> can be terminated
using the <dialogterminate> element. CCXML
implementations MUST support the
<dialogprepare> ,
<dialogstart> , and
<dialogterminate> elements though the exact
behavior may vary depending on the dialog environments
supported.
The following examples illustrate the valid use patterns for
these three elements. Firstly the normal case of preparing a
dialog, starting it, then optionally terminating it before normal
completion. This example illustrates the use of
<dialogprepare> to ready a dialog while the call
is left in alerting state. When the alerting notification arrives
the script executes a <dialogprepare> to prepare
a dialog and associate it with the connection. When the dialog is
prepared the script executes an <accept> to
connect the call and then when the connection transitions to
connected state, a <dialogstart> element is used
to execute the previously prepared dialog.
<transition event="connection.alerting">
<dialogprepare src="..." connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
</transition>
<transition event="dialog.prepared">
<accept connectionid="session.dialogs[event$.dialogid].connectionid"/>
</transition>
<transition event="connection.connected" >
<dialogstart prepareddialogid="event$.connection.dialogid"
connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
</transition>
<transition event="???">
<dialogterminate dialogid="..." />
</transition>
<transition event="connection.alerting">
<dialogprepare dialogid="preparedId" src="..." connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
</transition>
<transition event="dialog.prepared">
<accept connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
</transition>
<transition event="connection.connected" >
<dialogstart prepareddialogid="preparedId"
connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
</transition>
(optionally)
<transition event="???">
<dialogterminate dialogid="..." />
</transition>
The next example shows a single step dialog invocation without
dialog preparation. In this case a connection in alerting state is
accepted and, when the transition to connected state occurs, a
<dialogstart> element is used to start the
dialog.
<transition event="connection.alerting">
<accept connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
</transition>
<transition event="connection.connected">
<dialogstart src="..." connectionid="connectionid"/>
<dialogstart src="..." connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
</transition>
(optionally)
<transition event="???">
<dialogterminate dialogid="..." />
</transition>
This next example shows the preparation of a dialog for an
outbound call:
<transition event="...">
<dialogprepare src="..."> <!-- no connectionid -->
</transition>
<transition event="dialog.prepared" >
<createcall dest="..." joinid="event$.dialogid"> <!-- use joinid -->
</transition>
<transition event="connection.connected">
<dialogstart prepareddialogid="event$.connection.dialogid"
connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
<transition event="...">
<dialogprepare src="..." dialogid="preparedId"> <!-- no connectionid --> </transition> <transition event="dialog.prepared" >
<createcall dest="..." joinid="event$.dialogid"> <!-- use joinid --> </transition> <transition event="connection.connected">
<dialogstart prepareddialogid="preparedId"
connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
</transition>
The final example shows the case where a dialog which has been
previously prepared is cancelled before a
<dialogstart> has been issued. A dialog may be
terminated when it is in the prepared state or while it is being
prepared such as might be the case if the caller hangs up at some
arbitrary point. In this case the
<dialogterminate> may be executed before or
after the dialog.prepared event is processed.
<transition event="connection.connected">>
<dialogprepare src="..." connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
<transition event="connection.connected">
<dialogprepare dialogid="preparedId" src="..." connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
</transition>
<transition event="connection.disconnected" >
<dialogterminate dialogid="event$.connection.dialogid" />
<transition event="connection.disconnected" >
<dialogterminate dialogid="preparedId" />
</transition>
It is possible for Dialogs to exist that are not joined to a
Connection or a Conference. For example, this could be due to a
Connection disconnecting, or due to the application performing an
<unjoin/> operation.
7.2: Elements
7.2.1:
<dialogprepare>
7.2.1.1: Overview
<dialogprepare> is used to get an appropriate
dialog handler ready to process, it is used as the precursor to a
<dialogstart> request. The element includes a
URI reference to the initial document for the dialog. The new
dialog is prepared on a separate logical execution thread (this may
be a thread, process, or system depending upon platform
implementation) and does not block the processing of further events
by the CCXML session. The use of the
<dialogprepare> element is entirely optional,
applications may choose to simply use
<dialogstart> without prior preparation.
Optionally the new dialog may be associated with a connection by
specifying the connectionid attribute, or with a
conference by specifying the conferenceid
attribute.
When preparation of the dialog completes successfully a
dialog.prepared event MUST be
posted to the event queue of the CCXML session. If however the
dialog cannot be prepared for any reason, an
error.dialog.notprepared event MUST be posted. However should the dialog be
terminated using <dialogterminate> while it is
being prepared the platform MUST only post
a dialog.exit event.
CCXML implementations MUST support
dialog preparation though the processing carried out as part of a
<dialogprepare> request is dialog manager
specific. In the case of a dialog manager that does not support
preparation, the CCXML implementation MUST
as a minimum, note the values provided in the
<dialogprepare> attributes, create a Dialog
object, and return a new unique value to the location defined by
the dialogid attribute and throw a
dialog.prepared event.
If the connectionid or conferenceid
attributes are specified on <dialogprepare> the Dialog
Object's connectionid/conferenceid properties MUST be set to the
appropriate values. Additionally the dialogid attribute of the
Connection Object MUST be set to the dialogid of the new
Dialog. The CCXML session selects what it believes to be the
appropriate dialog manager based on the MIME type specified by the
type attribute without retrieving the resource
specified by the src URI. If, when the dialog manager
retrieves the content, it finds the MIME type, as specified by the
HTTP
headers, differs from that specifed by the type
attribute, it MUST raise an
error.dialog.notprepared event with a
reason indicating the type mismatch. The dialog
manager MUST NOT ignore the type mismatch
or render the resource as a different type based on the
HTTP
headers or on inspection of the document data. Refer to the W3C
guidelines for client handling of MIME types [ MIME-TAG ] for further
information.
7.2.1.2: <dialogprepare>
Attribute Details
| src |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
a Dialog URI |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string identifying the URI of the dialog
document that the dialog interpreter must prepare. |
| type |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
application/voicexml+xml |
a Valid MIME Type |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that specifies the MIME type of the
document, and as a result determines which dialog manager
environment must actually be used. Values defined by the
specification are:
- application/voicexml+xml
- This MIME type would request a VoiceXML interpreter
instance.
- audio/x-wav
- This MIME type would request a dialog manager that merely plays
wave files.
|
| namelist |
false |
|
Var List |
none |
List of ECMAScript Variable
names |
A list of zero or more whitespace
separated CCXML variable names. These variables must be submitted
to the web server, with the same qualification as used in the
namelist. When an ECMAScript variable is submitted to the web
server, its value must be first converted into a string before
being submitted.
If the variable is an ECMAScript Object, the mechanism by which it
is submitted is not currently defined. Instead of submitting
ECMAScript Objects directly, the application developer may
explicitly submit the properties of an Object. e.g. "date.month
date.year". |
| parameters |
false |
|
Var List |
none |
List of ECMAScript Variable
names |
A list of one or more whitespace
separated CCXML variable names. These variables are sent to the
dialog environment as a list of name/value pairs. Names are sent
exactly as they are specified; values are formed by converting the
referenced ECMAScript variable to string form (which is undefined
for objects). The dialog environment determines how passed
parameters will be handled |
| dialogid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Left Hand Side
Expression |
none |
ECMAScript Variable |
An ECMAScript left hand side
expression evaluating to a previously defined variable. The value
of the attribute must receive a dialog identifier value for the
launched dialog interpreter instance. If the attribute value is
invalid, an error.semantic event MUST be thrown |
| connectionid |
false |
Must not be used with
conferenceid |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
Connection IDs |
An Optional ECMAScript expression
which returns the identifier of a connection. If specified, the
dialog being prepared MUST be joined to
the referenced connection as specified by the
mediadirection attribute. Note that if the referenced
connection is already bridged to another media endpoint, those
existing bridges may be affected according to the rules specified
in section 10.4 even prior to <dialogstart>
being performed If the attribute value is invalid an
error.semantic event must be
thrown. |
| conferenceid |
false |
Must not be used with
connectionid |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
Conference IDs |
An Optional ECMAScript expression
which returns the identifier of a conference bridge. If specified,
the dialog being prepared MUST be joined
to the referenced conference as specified by the
mediadirection attribute. If the attribute value is
invalid an error.semantic event must be thrown. |
| mediadirection |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
both |
both dialogtransmit
dialogreceive |
An ECMAScript expression that
defines the direction of the media flow between the Dialog and the
Connection or Conference. The following values must be used:
- both
- Specifies a full duplex connection where the media flows in
both directions.
- dialogtransmit
- The dialog transmits media to the Connection or Conference but
does not receive any media streams.
- dialogreceive
- The dialog receives media from the Connection or Conference but
does not transmit any media streams.
The bridge does not take place until a subsequent
<dialogstart> is executed, but this attribute
may be provided as guidance to the dialog environment for
preparation. If no value is specified, the dialog environment must
make no assumptions as to the bridging type. For more information
about connections and bridges, refer to Section 10 . |
| maxage |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A valid time value for the HTTP
1.1 request [RFC2616] |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. This indicates that the
document is willing to use content whose age is no greater than the
specified time in seconds (cf. 'max-age' in HTTP 1.1 [RFC2616] ). The document is not willing to use
stale content, unless maxstale is also provided. |
| maxstale |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A valid time value for the HTTP
1.1 request [RFC2616] |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. This indicates that the
document is willing to use content that has exceeded its expiration
time (cf. 'max-stale' in HTTP 1.1 [RFC2616] ). If maxstale is assigned a value,
then the document is willing to accept content that has exceeded
its expiration time by no more than the specified number of
seconds. |
| enctype |
false |
Valid only when the
value of the method is "post" , otherwise ignored. |
ECMAScript Expression |
application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
valid media encoding type |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that indicates the media encoding type
of the submitted document (when the value of the method is "post").
Values defined by the specification are:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- This indicates that the ccxml variables specified in the
namelist must be url encoded.
|
| method |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
get |
get post |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that indicates the HTTP method to use.
Values defined by the specification are:
- get
- This indicates that the "GET" method must be used by the dialog
manager.
- post
- This indicates that the "POST" method must be used by the
dialog manager.
|
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform for implementing the dialog operation. Note: The meaning
of these hints is specific to the implementing platform and
protocol. Platforms that do not support hints MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
7.2.2: <dialogstart>
7.2.2.1: Overview
<dialogstart> is used to start a dialog and
associate the dialog with a connection or conference. (See Section 10 for a discussion of
connections and bridges). The element MUST
include either a URI reference to the initial document for the
dialog or the identity of a previously prepared dialog. The dialog
executes on a separate logical execution thread (this may be a
thread, process, or system depending upon platform implementation)
and does not block the processing of further events by the CCXML
session.
If the dialog cannot be started for any reason, an
error.dialog.notstarted event MUST be posted to the event queue of the CCXML
session that processed the <dialogstart>
request, otherwise a dialog.started event MUST be posted to indicate that the dialog has
started successfully. When the dialog completes, a
dialog.exit event MUST be
posted.
If the connectionid attribute of
<dialogstart> is specified, and if the dialog
language allows access to telephony variables such as ANI, DNIS and
UUI, values of these variables MUST be
propagated from the specified connection to the dialog
application.
If the prepareddialogid attribute is specified and
any attribute values conflict with the values specified in the
<dialogprepare> element this MUST result in the throwing of an
error.dialog.notstarted event.
Dialogs MAY only be started on
connections while they are in the ALERTING or CONNECTED states. For
connections in the ALERTING state media MAY not be sent or received by the connection making
the bridge effectively full-duplex, half-duplex or silent depending
on the underlying telephony environment and the restrictions
imposed by it.
It is not possible to start a dialog that is not joined to a
connection or a conference. For dialogs prepared using
<dialogprepare> with neither
connectionid nor conferenceid specified
and dialogs being started directly without preparation, if neither
connectionid nor conferenceid are
specified then execution of the dialogstart MUST fail, with an
error.dialog.notstarted event generated.
The CCXML session selects the appropriate dialog manager based
on the MIME type specified by the type attribute
without retrieving the resource specified by the src
URI. If, when the dialog manager retrieves the content, it finds
the MIME type, as specified by the HTTP headers, differs from
that specifed by the type attribute, it MUST raise an error.dialog.notstarted
event with a reason indicating the type mismatch. The
dialog manager MUST NOT ignore the type
mismatch or render the resource as a different type based on the
HTTP
headers or on inspection of the document data. Refer to the W3C
guidelines for client handling of MIME types [ MIME-TAG ] for further
information.
7.2.2.2: <dialogstart>
Attribute Details
| src |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the prepareddialogid
attribute. |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
a valid Dialog URI |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string identifying the URI of the dialog
document that the dialog interpreter must load and begin execution
upon startup. |
| prepareddialogid |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the src ,
type , parameters, maxage, maxstale, enctype,
method or namelist attributes. |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
a valid dialogid |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a dialog identifier of a dialog previously prepared by the
execution of a <dialogprepare> element. |
| type |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the prepareddialogid
attribute. |
ECMAScript Expression |
application/voicexml+xml |
a Valid MIME Type |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that specifies the MIME type of the
document, and as a result determines which dialog manager
environment must actually be used. Values defined by the
specification are:
- application/voicexml+xml
- This MIME type would request a VoiceXML interpreter
instance.
- audio/x-wav
- This MIME type would request a dialog manager that merely plays
wave files.
|
| namelist |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the prepareddialogid
attribute. |
Var List |
none |
List of ECMAScript Variable
names |
A list of zero or more whitespace
separated CCXML variable names. These variables must be submitted
to the web server, with the same qualification as used in the
namelist . When an ECMAScript variable is submitted to
the web server, its value must be first converted into a string
before being submitted.
If the variable is an ECMAScript Object, the mechanism by which it
is submitted is not currently defined. Instead of submitting
ECMAScript Objects directly, the application developer may
explicitly submit the properties of an Object. e.g. "
date.month date.year ". |
| parameters |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the prepareddialogid
attribute. |
Var List |
none |
List of ECMAScript Variable
names |
A list of one or more whitespace
separated CCXML variable names. These variables are sent to the
dialog environment as a list of name/value pairs. Names are sent
exactly as they are specified; values are formed by converting the
referenced ECMAScript variable to string form (which is undefined
for objects). The dialog environment determines how passed
parameters will be handled |
| dialogid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Left Hand Side
Expression |
none |
ECMAScript Variable |
An ECMAScript left hand side
expression evaluating to a previously defined variable. The value
of the attribute must receive a dialog identifier value for the
launched dialog interpreter instance. This identifier may be used
on future invocations of <dialogterminate> . If
the attribute value is invalid, an error.semantic
event MUST be thrown |
| connectionid |
false |
Must not be used with
conferenceid . |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
Connection IDs |
An Optional ECMAScript expression
which returns the identifier of a connection. If specified, the
dialog being started MUST be joined to the referenced connection as
specified by the mediadirection attribute.
If the dialog was previously prepared using a
<dialogprepare> element with a
connectionid or conferenceid specified,
and this attribute is also specified, execution of the
<dialogstart> MUST fail
with an error.dialog.notstarted event. Note that if
the referenced connection is already bridged to another media
endpoint, those existing bridges may be affected according to the
rules specified in section 10.4 even prior to
<dialogstart> being performed If the attribute
value is invalid an error.semantic event must be thrown. |
| conferenceid |
false |
Must not be used with
connectionid. |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
Conference IDs |
An Optional ECMAScript expression
which returns the identifier of a conference bridge. If specified,
the dialog being started MUST be joined to the referenced
conference as specified by the mediadirection
attribute.
If the dialog was previously prepared using a
<dialogprepare> element with a
connectionid or conferenceid specified,
and this attribute is also specified, execution of the
<dialogstart> MUST fail
with an error.dialog.notstarted event. If the
attribute value is invalid an error.semantic event
must be thrown. |
| mediadirection |
false |
If used in conjunction
with prepareddialogid , the bridge type must match
that used on the previous <dialogprepare>
element. |
ECMAScript Expression |
both |
both dialogtransmit
dialogreceive |
An ECMAScript expression that
defines the direction of the media flow between the Dialog and the
Connection or Conference. The following values must be used:
- both
- Specifies a full duplex connection where the media flows in
both directions.
- dialogtransmit
- The dialog transmits media to the Connection or Conference but
does not receive any media streams.
- dialogreceive
- The dialog receives media from the Connection or Conference but
does not transmit any media streams.
If both the mediadirection and the
prepareddialogid are specified and the bridge type
specified by the mediadirection attribute does not match
that used on the previous <dialogprepare>
element, an error.dialog.notstarted event must be raised. If
no value for the mediadirection attribute was specified on
the previous <dialogprepare> element, any
mediadirection type option may be specified. |
| maxage |
false |
Must not be used with
prepareddialogid. |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A valid time value for the HTTP
1.1 request [RFC2616] |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. This indicates that the
document is willing to use content whose age is no greater than the
specified time in seconds (cf. 'max-age' in HTTP 1.1 [RFC2616] ). The document is not willing to use
stale content, unless maxstale is also provided. |
| maxstale |
false |
Must not be used with
prepareddialogid. |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A valid time value for the HTTP
1.1 request [RFC2616] |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. This indicates that the
document is willing to use content that has exceeded its expiration
time (cf. 'max-stale' in HTTP 1.1 [RFC2616] ). If maxstale is assigned a value,
then the document is willing to accept content that has exceeded
its expiration time by no more than the specified number of
seconds. |
| enctype |
false |
Valid only when the
value of the method is "post".
"post" ,otherwise ignored . Must not be used with
prepareddialogid. |
ECMAScript Expression |
application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
valid media encoding type |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that indicates the media encoding type
of the submitted document (when the value of the method is "post").
Values defined by the specification are:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- This indicates that the ccxml variables specified in the
namelist must be url encoded.
|
| method |
false |
Must not be used with
prepareddialogid . |
ECMAScript Expression |
get |
get post |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that indicates the HTTP method to use.
Values defined by the specification are:
- get
- This indicates that the "GET" method must be used by the dialog
manager.
- post
- This indicates that the "POST" method must be used by the
dialog manager.
|
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform for implementing the dialog operation. Note: The meaning
of these hints is specific to the implementing platform and
protocol. Platforms that do not support hints MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
7.2.3:
<dialogterminate>
7.2.3.1: Overview
A CCXML document may decide that it wants to terminate a
currently executing dialog, to throw away a previously prepared
dialog, or to terminate the preparation of a dialog. This is
accomplished using the <dialogterminate>
element. When the CCXML interpreter encounters a
<dialogterminate> element, it MUST send a terminate request to the specified
dialog.
A dialog terminated due to the processing of a
<dialogterminate> element MAY still return data to the CCXML application using
a dialog.exit event if the value of the
immediate attribute is false or
unspecified. The details of the data returned are dialog
environment specific.
If the immediate attribute is set to
true the dialog MUST NOT
return data to the CCXML application and the CCXML interpreter
MUST post a dialog.exit event
immediately.
The platform MUST tear down any
existing bridges to the dialog and send a
conference.unjoined to the CCXML document once the
media paths have been freed.
7.2.3.2: <dialogterminate>
Attribute Details
| dialogid |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
valid dialog ID |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string identifying the dialog. This dialogid
was returned in the variable identified by the dialogid
attribute of previous <dialogstart> or
<dialogprepare> request or the value in a
dialog.started or dialog.prepared event. If the
attribute value is invalid, an error.semantic event
MUST be thrown |
| immediate |
false |
|
ECMAScript Boolean Expression |
false |
true false |
An ECMAScript Boolean expression which returns a
character string, that identifies the termination style of the
dialog. Valid values are:
- true
- This indicates that the dialog must be terminated
immediately.
- false
- This indicates that the dialog must be terminated in a normal
fashion.
|
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform for implementing the dialog operation. Note: The meaning
of these hints is specific to the implementing platform and
protocol. Platforms that do not support hints MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
7.3: Events
7.3.1: Overview
The majority of communication between CCXML interpreter sessions
and dialogs is by way of events. Dialog environments post events to
the CCXML interpreter event queue and a CCXML application MAY send
an event to a dialog. How this is handled on the dialog side is
dialog manager and CCXML interpreter dependent. On the CCXML side
it is done by using <send> and passing in the
dialogid that was received as a result of processing a
<dialogstart> or a
<dialogprepare> .
The following are the CCXML events related to dialogs:
7.3.2:
dialog.started
The dialog.started event MUST be thrown when a dialog is successfully
started. The fields available in the event are:
| dialogid |
true |
string |
The ID of the dialog. |
| dialog |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
dialog object identified by the dialogid property of this
event. |
| connectionid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the connection to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
connectionid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a conference the value must be
undefined. |
| conferenceid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the conference to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
conferenceid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a connection the value must be
undefined. |
7.3.3:
dialog.exit
The dialog.exit event MUST
be thrown when a dialog terminates either normally or following a
<dialogterminate> request. Termination of a
dialog always results in a single dialog.exit event;
if normal dialog termination and a
<dialogterminate> occur simultaneously, the
dialog.exit event will reflect the condition that the
platform processes first. For example, if a
dialog.exit event is thrown based on normal
termination, and the platform subsequently processes a
<dialogterminate> request made by the
application, it will discard the
<dialogterminate> and will not generate a second
dialog.exit event. The fields available in the event
are:
| dialogid |
true |
string |
The ID of the dialog. |
| dialog |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
dialog object identified by the dialogid property of this
event. |
| connectionid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the connection to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
connectionid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a conference the value must be
undefined. |
| conferenceid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the conference to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
conferenceid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a connection the value must be
undefined. |
| values.* |
false |
ECMAScript Object |
Return values from the dialog. In
VoiceXML this would be the values of each of the objects listed in
the exit element's namelist. |
7.3.4:
dialog.disconnect
The dialog.disconnect event represents a request by
a dialog to disconnect the Connection or Conference with which it
is presently associated. The actual handling of this event is
determined entirely by the running CCXML application, which may
disconnect the associated Connection, detach the dialog from the
Connection/Conference, or elect to ignore the
dialog.disconnect event altogether. The fields
available in the event are:
| dialogid |
true |
string |
The ID of the dialog. |
| dialog |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
dialog object identified by the dialogid property of this
event. |
| connectionid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the connection to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
connectionid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a conference the value must be
undefined. |
| conferenceid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the conference to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
conferenceid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a connection the value must be
undefined. |
| values.* |
false |
ECMAScript Object |
Return values from the dialog. In
VoiceXML this would be the values of each of the objects listed in
the dialog element's namelist. |
7.3.5:
dialog.transfer
The dialog.transfer event represents a request by a
dialog to transfer the Connection or Conference with which it is
presently associated to a new destination. The actual handling of
this event is determined entirely by the running CCXML application,
which may perform a <redirect> on the associated
Connection, use <createcall> and
<join> to establish a bridged transfer, handle
the transfer request in some other way, or elect to ignore the
dialog.transfer event altogether. The properties of
the dialog.transfer event reflect the information
dialog environments are most likely to supply when requesting a
transfer, but are up to the running CCXML application to interpret.
The fields available in the event are:
| dialogid |
true |
string |
The ID of the dialog. |
| dialog |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
dialog object identified by the dialogid property of this
event. |
| connectionid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the connection to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
connectionid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a conference the value must be
undefined. |
| conferenceid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the conference to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
conferenceid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a connection the value must be
undefined. |
| type |
true |
string |
A string value specifying the transfer
type. |
| uri |
true |
a valid URI |
A URI describing the destination to
which this call must be transferred. The format of this information
is protocol and platform specific but might consist of a telephone
URI RFC2806 RFC3966 or a SIP URI
RFC3261 . |
| values.* |
false |
ECMAScript Object |
Properties returned from the dialog
processor relating to the dialogs transfer request. |
| maxtime |
true |
string |
A string in CSS2 format that specifies
the maximum amount of time the transfer may stay connected. If the
amount of time is unlimited the value must be 0s. |
| connecttimeout |
true |
string |
A string in CSS2 format that specifies
the maximum amount of time to spend while attempting to connect the
call. |
| aai |
false |
string |
A string of application-to-application
information to be passed to the destination party when establishing
the transfer. |
7.3.6:
dialog.terminatetransfer
The dialog.terminatetransfer event represents a
request by a dialog to terminate an ongoing transfer for example
due to a "hotword" recognition. The actual handling of this event
is determined entirely by the running CCXML application, which may
terminate the outgoing call leg and return the media stream of the
original call to the dialog using the <join>
element, handle the terminate transfer request in some other way,
or elect to ignore the dialog.terminatetransfer event
altogether. The properties of the
dialog.terminatetransfer event reflect the information
dialog environments are most likely to supply when terminating a
transfer, but are up to the running CCXML application to interpret.
The fields available in the event are:
| dialogid |
true |
string |
The ID of the dialog. |
| dialog |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
dialog object identified by the dialogid property of this
event. |
| connectionid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the connection to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
connectionid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a conference the value must be
undefined. |
| conferenceid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the conference to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
conferenceid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a connection the value must be
undefined. |
| reason |
true
false |
string |
A description of the reason the dialog
wants the transfer to be terminated. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
7.3.7:
error.dialog
The error.dialog event MUST be thrown when there was an unspecified error
with the dialog (for example the dialog server crashed).
The platform MUST implicitly tear down
any existing bridges to the dialog and send a
conference.unjoined to the CCXML document once the
media paths have been freed. The fields available in the event
are:
| dialogid |
true |
string |
The ID of the dialog. |
| dialog |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
dialog object identified by the dialogid property of this
event. |
| connectionid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the connection to
which the dialog was connected to (usually the connectionid
that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog was being connected to a conference the value must be
undefined. |
| conferenceid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the conference to
which the dialog was connected to (usually the conferenceid
that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog was being connected to a connection the value must be
undefined. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the dialog
had an error. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
7.3.8:
error.dialog.notstarted
The error.dialog.notstarted event MUST be thrown when the processing of a
<dialogstart> element fails because the dialog
cannot be started for some reason. The fields available in the
event are:
| dialogid |
true |
string |
The ID of the dialog. |
| dialog |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
dialog object identified by the dialogid property of this
event. |
| connectionid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the connection to
which the dialog connection could not be started (usually the
connectionid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog was being connected to a conference the value must be
undefined. |
| conferenceid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the conference to
which the dialog connection could not be started (usually the
conferenceid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog was being connected to a connection the value must be
undefined. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the dialog
could not be started. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
7.3.9: blank
This section is intentionally left blank.
7.3.10:
dialog.user.*
The dialog.user.* (where * is the name of the user
defined event) MUST be thrown when a
dialog sends a user/application-defined event. The fields available
in the event are:
| dialogid |
true |
string |
The ID of the dialog. |
| dialog |
true
false |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
dialog object identified by the dialogid property of this
event. NOTE that dialog property in this
event is optional because there is not a standard way to raise this
event from a dialog system such as [ VOICEXML ] while
a basichttp implementation is allowed. |
| connectionid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the connection to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
connectionid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a conference the value must be
undefined. |
| conferenceid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the conference to
which the dialog connection is bridged (usually the
conferenceid that was specified in the dialogstart or
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog is bridged to a connection the value must be
undefined. |
| values.* |
false |
ECMAScript Object |
Return values from the dialog for the
user event. |
7.3.11:
dialog.prepared
The dialog.prepared event MUST be thrown when a dialog has been successfully
prepared following the execution of a
<dialogprepare> element. The fields available in
the event are:
| dialogid |
true |
string |
The ID of the dialog. |
| dialog |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
dialog object identified by the dialogid property of this
event. |
| connectionid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the connection to
which the dialog connection is prepared (usually the
connectionid that was specified in the dialogprepare
).
If the dialog was prepared without a connection, the value must be
undefined. |
| conferenceid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the conference to
which the dialog connection is prepared (usually the
conferenceid that was specified in the dialogprepare
).
If the dialog was prepared without a conference , the value must be
undefined. |
7.3.12:
error.dialog.notprepared
The error.dialog.notprepared event MUST be thrown when the processing of a
<dialogprepare> element fails. The fields
available in the event are:
| dialogid |
true |
string |
The ID of the dialog. |
| dialog |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
dialog object identified by the dialogid property of this
event. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the dialog
could not be prepared. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
| connectionid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the connection to
which the dialog connection was attempting to be prepared (usually
the connectionid that was specified in the
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog was prepared without a connection, the value must be
undefined. |
| conferenceid |
false |
string |
The identifier of the conference to
which the dialog connection was attempting to be prepared (usually
the conferenceid that was specified in the
dialogprepare ).
If the dialog was prepared without a conference, the value must be
undefined. |
7.4: Dialog Object Properties
An instance of the Dialog object is associated with each dialog
created by <dialogstart> or
<dialogprepare> and referenced in the
session.dialogs associative array.
The Dialog Object is an extension of the Media Endpoint Object as defined
in section 10.4.3.
| dialogid |
true |
This property is the ECMAScript string
value of the Dialog Identifier, which uniquely identifies each
instance of the Dialog class. |
| type |
true |
An ECMAScript string value that
specifies the MIME type of the document that loaded the dialog |
| src |
true |
An ECMAScript string value identifying
the initial URI of the dialog document. |
| input |
true |
As defined by the Media Endpoint
Object in 10.4.3. |
| outputs |
true |
As defined by the Media Endpoint
Object in 10.4.3. |
| objecttype |
true |
This property states the type of this
object which must be 'dialog'. |
7.5: Dialog class
All dialog objects MUST be initiated via the Dialog class. The
Dialog class currently has no defined properties.
8: Variables and Expressions
8.1: Overview
CCXML expressions are valid ECMAScript [ ECMASCRIPT ] expressions,
assignable to variables with valid ECMAScript names. For further
details please see section 3.4 .
Many CCXML elements have multiple attributes that are ECMAScript
expressions. The CCXML language does not guarantee a specific order
of evaluation of these expressions. Also, some elements such as
<transition> may or may not evaluate all
attributes. Hence, attributes containing expressions with
side-effects can lead to implementation specific behavior. It is
RECOMMENDED that applications do not use
ECMAScript expressions with side-effects in attributes.
If the implementation is unable to evaluate an ECMAScript
expression it MUST throw an
error.semantic event.
8.2: Elements
8.2.1: <assign> and <var>
8.2.1.1: Overview
Variables are declared using the <var>
element and are initialized with the results of evaluating the
OPTIONAL expr attribute as an
ECMAScript expression. If the expr attribute is not
present in the <var> declaration, the variable
is initialized to ECMAScript undefined . The values of
variables MAY be subsequently changed with
<assign> .
Variables are declared explicitly by <var>
:
<var name="sessionid" />
<var name="currentstate" expr="'initial'" />
Variables declared without an explicit initial value MUST be initialized to the ECMAScript value
undefined by the implementation.
It is illegal to make an assignment to a variable that has not
been explicitly declared using <var> or a
var statement within a <script> .
Attempting to assign to an undeclared variable causes an
error.semantic event to be thrown. Please see Section 9.5 for a detailed description of
error events.
Note that when an ECMAScript object, e.g. " obj ",
has been properly initialized then its properties, for instance "
obj.prop1 ", can be assigned without explicit
declaration. An attempt to declare ECMAScript object properties
such as " obj.prop1 " results in an
error.semantic event being thrown.
CCXML uses an ECMAScript scope chain (please see section 3.4 ) to
allow variables to be declared at different levels of hierarchy in
an application. For instance, a variable declared at ccxml
(document) scope can be referenced anywhere within that document,
whereas a local variable declared in a
<transition> is only available within that
element.
The implementation MUST define four
scopes - session , application ,
ccxml and transition . The relationship
between these scopes is shown below.
Variable Scoping
A description of the scopes is provided in the table below.
| Scope
Name |
Details |
session |
This scope is
opened by CCXML implementation before interpretation of a new
session starts and exists until the session exits. Variables within
this scope are provided by CCXML implementation and are read-only.
Any attempt to modify the session object or it's properties by the
application MUST result in an error.semantic event to be thrown by
the platform. |
application |
This scope is
opened by CCXML implementation before interpretation of a new
session starts and exists until the session exits. Variables within
this scope cannot be explicitly declared using <var> element
or var statement within a <script>. They can be created only
by assigning a value to a property of the application object
(application.varname = value;). Unlike in the session scope,
variables in this scope can be modified by CCXML programs. They are
visible to documents within the CCXML application. |
ccxml |
This scope is
opened by CCXML implementation for each CCXML document when it is
loaded and exists while the document is loaded. Variables within
this scope are declared with <var> and <script>
elements that are children of <ccxml>. They are initialized
in document order when the document is loaded. They exist while the
document is loaded. They are visible only within that document.
Variables in this scope can be also created without an explicit
declaration by assigning a value to a property of the ccxml object
(ccxml.varname = value;). |
transition |
Each
<transition> element has a scope that exists while the
implementation is processing the executable content within that
<transition>, and which is visible to the elements of that
<transition>. Variables with transition scope are declared by
<var> and <script> child elements of
<transition>. The child <var> and <script>
elements of <transition> are initialized in document order
when the executable content is executed. Variables in this scope
can be also created without an explicit declaration by assigning a
value to a property of the transition object (transition.varname =
value;). |
The implementation MUST instantiate a
variable within the scope of the closest containing scope element.
The fully-qualified name of a variable is the name of the
variable's scope object prepended with a dot to the name of the
variable. The implementation MUST allow
reference to variables by their fully qualified names. The
implementation MUST allow reference to
variables without requiring use of their fully qualified names. In
the case of like-named variables declared in different scopes, the
implementation MUST reference the variable
in the closest containing scope, unless the fully-qualified
variable name is used.
The implementation MUST resolve
variables by searching the enclosing transition scope
first (if applicable) followed by the ccxml scope, the
application scope and then the session
scope, unless the variable reference is qualified with a scope
prefix.
If the variable includes a scope prefix, the implementation
MUST resolve the variable by searching the
named scope.
If a variable is declared more than once, the implementation
MUST evaluate the expr
attribute of each subsequent declaration, and assign the result to
the variable declared by the first <var> .
Variables can be assigned new values using
<assign> :
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'cleanup'" />
The implementation MUST evaluate the
ECMAScript expression contained in the expr attribute
of <assign> , and assign the results to the
variable referenced in the name attribute.
The variable naming convention is as in ECMAScript, but names
beginning with the underscore character ("_") and names ending with
a dollar sign ("$") are reserved for internal use. CCXML variables
MUST NOT contain ECMAScript reserved
words. They MUST also follow ECMAScript
rules for referential correctness. For example, variable names must
be unique and their declaration MUST NOT
include a dot - " var x.y " is an illegal declaration
in ECMAScript. Variable names which violate naming conventions or
ECMAScript rules MUST cause an '
error.semantic ' event to be thrown.
8.2.1.2: <var> Attribute
Details
| name |
true |
|
String |
none |
Valid ECMAScript Variable
name |
Indicates the name of the
variable. It must be a valid ECMAScript variable name.
However, it must not contain a scope prefix. The scope in
which the variable is defined must be determined from the position
in the document at which the variable is defined. |
| expr |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
undefined |
Valid ECMAScript Expression |
Indicates the new value of the
variable. This will be the initial value. It must be a valid
ECMAScript expression. |
8.2.1.3: <assign> Attribute
Details
| name |
true |
|
ECMAScript Left Hand Side
Expression |
none |
ECMAScript Variable |
An ECMAScript left hand side
expression evaluating to a previously defined variable. The value
of the attribute must receive the result of the expr
attribute. |
| expr |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
Valid ECMAScript Expression |
Indicates the new value of the
variable. It must be a valid ECMAScript expression. |
8.2.2: <script>
8.2.2.1: Overview
<script> encloses computations written in the
ECMAScript Compact Profile [ ECMA327 ] scripting language. The ECMAScript
Compact Profile is a strict subset of the third edition of ECMA-262
[ ECMASCRIPT ]. It has been designed to meet the
needs of resource-constrained environments. Special attention has
been paid to constraining ECMAScript features that require
proportionately large amounts of system memory, and continuous or
proportionately large amounts of processing power. In particular,
it is designed to facilitate prior compilation for execution in a
lightweight environment. For specific details on what ECMAScript
functions are not supported please take a look at ECMA-327
specification [ ECMA327 ].
An implementation MUST support the
ECMAScript Compact Profile and MAY support
the full ECMA-262 ECMAScript specification.
The example <script> below defines a function
that computes the greatest common factor of two integers:
<script>
<![CDATA[
function gcd(a, b)
{
var t;
if (a < 1 || b < 1)
return -1;
do
{
t = a % b;
a = b;
b = t;
}
while (b > 1);
return (b == 0) ? a : b;
}
]]>
</script>
An implementation MUST support
<script> within the <ccxml>
element and in executable content. <transition>
and <if> contain executable content. The
implementation MUST evaluate
<script> in a <ccxml>
immediately after the document is loaded, along with any
<var> and <assign> elements,
in document order. When used as a child of the
<ccxml> element, <script>
cannot be used to execute dynamically fetched content obtained
using <fetch> . The implementation MUST evaluate <script> in
executable content as it is processed.
The ECMAScript contained within the <script>
can declare variables with the ECMAScript var
statement. Variables declared in this manner are declared in the
scope of the closest containing scope CCXML element. They are known
from the point of declaration to the end of the containing scope.
The implementation MUST allow reference to
these variables from CCXML and from ECMAScript, using either the
fully-qualified variable name, or the declared name.
If the implementation is unable to run the script referenced it
MUST throw an error.semantic
event.
INFORMATIVE NOTE: The <script> element's
resource loading model is a bit different than the rest of CCXML
for a number of reasons. Because CCXML and ECMAScript applications
can be CPU intensive to compile we define
<script> 's src attribute (defining the URI of
the document to load) to be a static string instead of a
dynamically valued ECMAScript result. This allows implementations
to load ECMAScript content at CCXML document load time and perform
compiling and/or caching of the resulting ECMAScript code. We do
however recognize that there are cases where a CCXML application
needs to load a dynamic ECMAScript resource, for this reason
applications can use the the <fetch> element to
asynchronously load a resource and then execute it by referencing
it's fetchid in the the <script>
element.
8.2.2.2: <script> Attribute
Details
| src |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the fetchid attribute. |
Valid URI |
none |
a valid URI |
A URI which references a resource
which is the script content, and which must be resolved when the
CCXML document is compiled.
Note that the value of the src attribute must not be an
ECMAScript expression in order to allow it to be resolved at
compile-time. If the ECMAScript script referenced can not be loaded
at the CCXML document loading and parsing phase it should be
considered a Fetching & compilation error as defined in section
9.5.1. |
| fetchid |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the src attribute. attribute
,otherwise ignored . |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
valid fetch ID |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns the fetch identifier of a completed fetch request, acquired
either in a fetch with the fetchid attribute, or from the fetchid
attribute of a fetch.done event. If the fetch identifier is
invalid, has not completed, or the fetched content is not valid
ECMAScript, an error.semantic event must be thrown. |
| timeout |
false |
This attribute is only
valid in conjunction with the src attribute. attribute
,otherwise ignored . |
Character string |
none |
Character string in CSS2 [CSS2] format |
The character string must be
interpreted as a time interval. This interval must begin when the
script is requested; If the script has not been fetched at the end
of this interval, an error.fetch or error.createccxml event must be
thrown. |
| maxage |
false |
This attribute is only
valid in conjunction with the src attribute. attribute
,otherwise ignored . |
Character string |
none |
A valid time value for the HTTP
1.1 request [RFC2616] |
The character string must be
interpreted as a time interval. This indicates that the document is
willing to use content whose age must be no greater than the
specified time in seconds (cf. 'max-age' in HTTP 1.1 [RFC2616] ). The document is not willing to use
stale content, unless maxstale is also provided. |
| maxstale |
false |
This attribute is only
valid in conjunction with the src attribute. attribute
,otherwise ignored . |
Character string |
none |
A valid time value for the HTTP
1.1 request [RFC2616] |
The character string must be
interpreted as a time interval. This indicates that the document is
willing to use content that has exceeded its expiration time (cf.
'max-stale' in HTTP 1.1 [RFC2616] ). If
maxstale is assigned a value, then the document is willing to
accept content that has exceeded its expiration time by no more
than the specified number of seconds. |
| charset |
false |
|
Character string |
UTF-8 |
valid character encoding
type |
A character string that indicates
the character encoding type of the script. UTF-8 and
UTF-16 encodings of ISO/IEC 10646 must be supported
(as in [XML] ) and other encodings, as
defined in the [IANA] , may be
supported. |
8.3: Session Variables
Every CCXML session has a set of standard ECMAScript variables
that are available to the program during execution called session
variables. The session variables are defined by the CCXML
implementation when the CCXML session is created and are read-only
to the running script and cannot be modified by the CCXML program.
New session variables cannot be declared by CCXML programs.
Session variable values visible to a CCXML application reflect
the state of the executing CCXML session, current as of the
occurrence of the event being processed. For example, when an
application processes a Connection event such as
connection.alerting , the value of the state property
of the corresponding Connection object will be updated by the CCXML
implementation so that if the CCXML program's event handler
evaluates the state variable, it will evaluate to
ALERTING , since connection.alerting
always results in a transition to the ALERTING state.
This is true even if the underlying connection is actually
DISCONNECTED , in which case a
connection.disconnected event would be queued. It is
the responsibility of the CCXML implementation to control and
update the session changes as they occur in the CCXML session. It
is assumed that session changes are visible to the CCXML program as
they occur. However, it is permissible for a CCXML implementation
to optimize session changes by "lazy-binding" values as they
are accessed or evaluated by a CCXML program, so as to minimize
processing time. For example, an implementation might only update
the current Connection states when a CCXML program evaluates the
variable during execution time versus continually updating the
Connection states inside ECMAScript scope as state changes.
Regardless of when session variables are updated to reflect
changes, the CCXML implementation is REQUIRED to provide the correct values when accessed
by a CCXML program.
Variables defined in the session scope are subject to the parent
scope chain delegation model but do not have a parent scope
defined.
The following are the list of standard session variables:
session.startupmode- String that indicates the startup mode that the script was
started as:
Value
|
Details
|
newcall |
Session was started due to
a new incoming call. |
external |
Session was started due to
a external session launch request. |
createccxml |
Session was started due to
a <createccxml> request. |
session.id- A globally unique string that indicates the session identifier
of the executing CCXML session.
session.uri- URI that was used when creating the current CCXML session. If
the interpreter fetched multiple documents as a result of one or
more HTTP redirects (e.g. 302), the value of this session variable
is set to the URI of the final target.
session.uri
includes the query string used when fetching the document, if one
is present.
session.parentid- String that indicates the session identifier of the parent of
the CCXML session that created this session. In the case the
current session has no parent, the value of the variable will be
ECMAScript undefined. Once a new CCXML session is created, the new
session and its parent are completely independent.
session.connections- Associative Array which contains a list of the Connection
objects that the session is currently using. The array is
associative and each key in the array is the connection identifier
for the Connection. For example,
session.connections["1234"] would return the
Connection object for connection ID 1234. The following example
demonstrates the use of the session.connections
variable:
<transition state="in_vxml_session" event="connection.disconnected">
<if cond="session.connections['1234'].connectionid==event$.connid">
<-- if the disconnect is on the first connection, do something -->
<else/>
<exit/>
</if>
</transition>
session.conferences- An Associative array which contains a list of the Conference
objects for which the session is attached using
<createconference> For example,
session.conferences["1234"] would return the
Conference object for conference id 1234.
session.dialogs- Associative Array which contains a list of the Dialog objects
that the session is currently using. The array is associative and
each key in the array is the dialog identifier for the Dialog. For
example,
session.dialogs["1234"] would return the
Dialog object for dialog id 1234.
session.ioprocessors- Associative Array which contains a list of external event I/O
access URIs which are available to the current session. The array
is associative and each key in the array is the type of the event
I/O processor. For example,
session.ioprocessors["basichttp"] would return the
access URI (e.g.
http://www.example.com/ccxml/basichttp ) for the
"basichttp" type event I/O processor.
session.values- Associative array which contains a list of session parameters
passed on session creation. For sessions created using
<createccxml> , session.values
contains variables passed using the ' parameters '
attribute of <createccxml> . Other session
creation mechanisms, such as the HTTP-based session creation I/O
processor defined in Appendix L, define other mechanisms for
populating this variable.
8.4: Application Variables
CCXML provides application variables which, like session
variables, persists across the CCXML application . Application variables differ
from session variables in that they can be modified by CCXML
programs.
The application object is initialized by the CCXML
implementation. Application variables that are properties of the
application object are not explicitly declared. Application variables that are not properties, e.g.
objects, must be declared. By default, application variables
have the value ECMAScript undefined. Variables in the application
scope are subject to the parent scope chain delegation model and
have session as their parent scope. For example:
<assign name="application.userid" expr="'user001'"/>
<assign name="application.obj" expr="new Object()"/>
<assign name="application.obj.prop1" expr="'value of prop1'"/>
<assign name="application.obj.prop2" expr="'value of prop2'"/>
Application variables are visible within documents which form
the CCXML
application . For example, a document in a CCXML application
could assign an application variable a value using <assign
name="application.userid" expr="'user001'"/> , and a
later document in the CCXML application could reference
application.userid to retrieve the value
'user001'.
Application developers should be careful in their use of
application variables since they are visible to all CCXML
documents within a CCXML application.
9: Event Handling
This section contains information on
<eventprocessor> , <send> ,
<cancel> , <transition> and
<move> .
9.1: Overview
Event Handling is one of the most powerful features of CCXML.
CCXML events can be delivered at any time and from a variety of
sources. This flexible event-handling mechanism is essential for
many telephony applications.
Every CCXML session can send and receive events. These might be
in response to a previous action by the CCXML session (e.g., an
outbound-call request, which generates an event to indicate when
the call goes off-hook), or on the initiative of some external
source (e.g., an incoming call to be answered). Events can be
generated by the telephony system (as in the two previous
examples), other CCXML sessions (which emit events via
<send> ), Dialogs, or external sources. CCXML
sessions can also send events to themselves.
There is a core set of telephony-related events (derived from
the JCC event model for connection objects; see the JAIN Call
Control API (JCC) [JSR021]
for more information) that a browser MUST
support. Implementers MAY define and
support any platform-specific events they like. In addition,
users/programmers may use <send> to send
arbitrary events to internal or external destinations, or may send
arbitrary events to CCXML documents from internal or external
sources and may specify transition handlers to handle these
events.
The transmission and reception of events both external and
internal is controlled by a logical component in the platform
called the "Event I/O Processor". A platform MAY support more than one type of Event I/O
Processor and each of them may support a different format of
external events (For example: SOAP, JMS, SIP, Simple HTTP or any
other event transmission approaches). For incoming events the Event
I/O Processor is responsible for accepting the incoming event and
transforming it into an ECMAScript event object that can be
accessed by CCXML. For outgoing events the Event I/O Processor is
responsible for deciding the serialization and transport formats.
The operation and behavior of Event I/O Processors is platform
dependent; however, this specification defines a Basic HTTP Event
I/O Processor (Appendix K) that defines event transmission over
HTTP. External Event I/O processors and new events created using
<send> will typically generate
application-specific events with different names than those of the
standard events in this specification; however, it is legal for
external sources and for events created using
<send> to generate standard events. For
instance, it is useful to be able to generate a
ccxml.kill event to attempt graceful termination of a
session from an external context, or from another CCXML session.
Platforms SHOULD reject any standard
events that do not contain all of the mandatory properties defined
in this specification, and SHOULD notify
the sender of the rejection (for instance with an
error.send event).
Each running CCXML interpreter has a queue, into which it places
incoming events. Events are generally queued on a first-in,
first-out (FIFO) basis; however, certain classes of events are
queued differently, as described in the paragraphs below. A CCXML
programmer can only gain access to these queued events by using the
<eventprocessor> element with associated
<transition> elements.
An event can be delivered to a CCXML session using a
<send> element in which case an optional delay
may be specified. If a delay is specified, the event is not
delivered to the target CCXML session until the delay time has
elapsed. When the delay has elapsed, the event is queued as if it
had just occurred, using standard queueing rules.
There are three types of events that, when delivered to a CCXML
session, are handled differently. All ccxml.kill and
ccxml.kill.* events are placed at the head of the
event queue rather than the tail so that they are processed in
preference to all other events. All error.* events are
placed at the head of the queue but behind any error.*
, ccxml.kill , or ccxml.kill.* events
that are already on the queue. ccxml.loaded events are
always placed at the head of the queue.
An <eventprocessor> is interpreted by an
implicit Event Handler Interpretation Algorithm (EHIA). The EHIA's
main loop removes the first event from the CCXML session's event
queue, and then selects from the set of
<transition> s contained in the
<eventprocessor> . A
<transition> always indicates a set of patterns
to match event names, MAY indicate a
required current value of the ECMAScript state variable specified
in the <eventprocessor> , and MAY indicate a further ECMAScript conditional
expression to be evaluated. The <transition>
that accepts the type for the just-removed event, is in the
specified state, has a satisfied conditional expression, and
appears first in the <eventprocessor> in
document order, is the selected <transition>
.
Once selected, an object representing the event being processed
is created at transition scope, and the elements inside the
<transition> are executed in document order. If
an ECMAScript evaluation error occurs during the execution of an
element within a <transition> ,
error.semantic MUST be raised
for that element, and successive elements within that
<transition> MUST NOT
be executed; Note that while an element that references an invalid
connection, dialog, or conference identifier also causes the
platform to raise error.semantic , these scenarios
MUST NOT terminate execution of the
<transition> in which that element is
contained.
At most one <transition> will be chosen. If
no <transition> meets all the criteria, none are
selected and the event is simply dropped; the EHIA loop then starts
over again, removing the event at the head of the queue. The only
exception to this rule is when ccxml.kill ,
ccxml.kill.* and error.* events are
received; in this case, the CCXML interpreter will end the session
if there are no <transition> s that match the
ccxml.kill , ccxml.kill.* and
error.* events explicitly.
Any events that arrive while an event is already being processed
are just placed on the queue for later. If the event queue is
empty, and the EHIA wants to process an event, execution pauses
until an event arrives.
During the processing of an event by the EHIA, the state of any
ECMAScript objects exposed by a platform, such as the Connection
object, must reflect the state of the
CCXML session immediately following the occurrence of the event.
For instance, if a ' connection.alerting ' event is
being processed against a connection with ID 1234, then
session.connections['1234'].state would have a value
of Connection.ALERTING . This is true even if the
actual connection has already been terminated, with a '
connection.disconnected ' event queued (but not yet
processed) against the session. It is required that the ECMAScript context for the session
is updated prior to the selection of a matching
<transition> , since the
<transition> might contain an ECMAScript
conditional expression, the value of which depends on the state
changes caused by the event.
Elements inside an <transition> SHOULD run "quickly", without blocking execution.
This will allow events to be rapidly processed. CCXML applications
should be aware of this and should keep calculations such as large
ECMAScript functions within a transition to a minimum.
The only way for CCXML execution to leave an
<eventprocessor> is via an explicit
<goto> or <exit> inside a
<transition> or an unhandled error or
ccxml.kill event .
An <eventprocessor> MAY also declare a state variable attribute. An
<eventprocessor> 's state variable must be
declared in the ccxml scope using a <var> or a
<script> . The
<eventprocessor> can be considered, and
programmed as, a finite-state-automaton, with the state variable
indicating the automaton's current state or node, and the
<transition> s, driven by incoming events,
moving the machine to a new state and creating side effects along
the way. If a state variable is not defined in the
<eventprocessor> 's statevariable
attribute a default variable named " state$ " defined
at the ccxml scope will be used instead. The initial value will be
ECMAScript ' undefined '.
9.2: Elements
9.2.1:
<eventprocessor>
9.2.1.1: Overview
The <eventprocessor> acts as a container for
<transition> s. A valid CCXML document
MUST only have a single
<eventprocessor> .
9.2.1.2: <eventprocessor>
Attribute Details
| statevariable |
false |
|
string |
state$ |
ECMAScript Variable name |
This is a CCXML variable name,
which is the name of the eventprocessor 's state variable.
This variable must be defined using the var or the
script element in the ccxml scope. |
<eventprocessor> MUST contain only <transition>
elements.
9.2.2: <transition>
9.2.2.1: Overview
The content of a <transition> specifies the
actions to be taken when it is selected. The
<transition> are examined by the EHIA in
document order.
In order to be selected, a <transition>
MUST satisfy three criteria:
- If a state attribute is specified on the
<transition> the current value of the associated
state variable (as specified in the parent
<eventprocessor> ) MUST
be equal to one of the values specified in the state attribute of
the <transition> . If no state
attribute is specified on the <transition> ,
this criteria is met regardless of the value of the
statevariable .
- the expression specified by the
<transition>
's cond attribute MUST
evaluate to true , if that attribute is present
- the current event's
name property MUST match the pattern specified by the
<transition> 's event attribute, if
that attribute is present
A <transition> with none of the attributes,
state , cond , or event ,
will always be selected when encountered by the EHIA.
The contents of the received event object MUST be available via the transition scoped
read-only event$ ECMAScript variable. This variable is
accessible from the <transition>
cond attribute to allow CCXML Applications to
conditionally select <transition> 's based on
the contents of the event.
9.2.2.2: <transition>
Attribute Details
| state |
false |
|
string |
none |
|
This indicates the current
possible value of the variable associated with the statevariable
attribute of the parent <eventprocessor> . More
than one value may be specified, separated by whitespace. |
| event |
false |
|
string |
none |
|
This is a pattern used to match
event names as specified in Section 9.2.2.3. |
| cond |
false |
|
ECMAScript Boolean Expression |
true |
|
An ECMAScript Boolean expression.
If this attribute is present, it must evaluate to true for the
transition to be selected. |
9.2.2.3: <transition> Event
Matching
The event attribute of a <transition>
specifies a pattern used to match event names. Each character in
the pattern specified by event must match the
corresponding character in the event name, except for the asterisk
('*') character, which acts as a wildcard that matches any
substring of zero or more characters in the event name. Patterns
are dot-separated strings of arbitrary length. Event names are
case-insensitive.
Pattern match examples
Pattern
|
Matches |
*
|
any event
name
|
error.*
|
error.fetch, error.dialog.notstarted
|
error.*.*
|
error.dialog.notstarted |
err*
|
any event name
starting with "err" |
9.2.3: <send>
9.2.3.1: Overview
<send> is used to send messages containing
events or other information directly to another CCXML Interpreter
or other external systems using an Event I/O Processor.
The event target of <send> is specified using
the target and targettype attributes.
These attributes control how the platform should dispatch the event
to its final destination.
The target attribute specifies the unique
identifier of the event target that the Event I/O Processor should
send the event to. This can be the value of a CCXML Session ID or a
Dialog ID if you wish to send an event to one of these respective
targets. In the case where you are using some other Event I/O
Processor this attribute should be able to describe how to connect
to the event destination (for example a SIP URI for SIP-INFO
messages or a HTTP URI for Web Services). If the value of the
target attribute is not supported, invalid or
unreachable by the Event I/O Processor the Platform MUST throw a
error.send.targetunavailable event.
The targettype attribute controls what Event I/O
Processor the event should be sent to. The default value of this
attribute is ' ccxml '. If the event
targettype specified is not supported the platform
MUST throw a
error.send.targettypeinvalid event.
A platform MUST support the following
values for the targettype attribute:
Value
|
Details
|
ccxml |
CCXML Session Event
Processor. |
dialog |
Dialog Event
Processor. |
basichttp |
Basic HTTP Event I/O
engine (See Appendix K). |
Platforms MAY support other types of
Event I/O Processors, for example: Web-services, SIP or basic HTTP
GET. However, platforms SHOULD name the
Event I/O Processor beginning with " x- " to signify
that they are platform dependent.
<send> also specifies the content of the
message to be sent. <send> MUST specify message content in one of two ways (the
following mechanisms are mutually exclusive):
name attribute with an OPTIONAL namelist
- The
name attribute specifies an ECMAScript
expression that returns the name of the event.
- The
namelist attribute specifies a space separated
list of CCXML ECMAScript variables to be included with the
message.
<var name="target" expr="'tel:+18005551212'"/>
<var name="content" expr="'http://www.example.com/mycontent.txt'"/>
<send target="target"
targettype="'x-messaging'"
name="'fax.SEND'"
namelist="content"/>
- Inline XML content that specifies the contents of the message
being sent.
<send target="'csta://csta-server.example.com/'" targettype="'x-csta'"
xmlns:csta="http://www.ecma-international.org/standards/ecma-323/csta/ed3">
<csta:MakeCall>
<csta:callingDevice>22343</csta:callingDevice>
<csta:calledDirectoryNumber>18005551212</csta:calledDirectoryNumber>
</csta:MakeCall>
</send>
When inline XML is specified, the content of the
<send> is parsed but MUST be ignored by the sending CCXML Interpreter
until the <send> is executed. XML namespace
binding within the <send> element MUST be preserved in the message sent to the
<send> target. This may result in XML namespace
declarations being added to the message contents in order to
resolve XML namespace prefixes whose associated namespace
declarations were not contained in the message contents in the
original CCXML document. It is the responsibility of the Event I/O
Processor responsible for forwarding events to the
<send> target to parse the incoming message and
remove the namespace bindings, if required by the
<send> target.
The sending CCXML Interpreter MUST NOT
alter the content of the <send> other than by
adding namespace declarations for unresolved namespace bindings.
The data contained within a <send> MUST be sent to the destination specified in the
target attribute of <send> using
the Event I/O Processor specified by the targettype
attribute.
The mechanism by which the content of the message is made
available to the target depends on both the targettype
and the way in which the content is specified:
- When
<send> is used with the
name and namelist attributes, and the
targettype is " ccxml ", the mapping from
namelist variables to event object properties is well
defined. Each variable listed in the namelist
attribute is added as a property of the event object. Qualified
variables retain their qualification and are mapped into nested
properties of the event object. If a variable is an ECMAScript
Object, then all properties of the variable are mapped into nested
properties of the event object.
- When
<send> is used with inline XML content,
and the targettype is " ccxml ", the
mapping of that XML content to event object properties is
implementation-specific, and outside the scope of this
specification.
- When
<send> is used with the
name and namelist attributes, and the
targettype is " basichttp ", each
variable in the namelist is sent to the web server as
defined in Appendix K
- When
<send> is used with either
name and namelist attributes or inline
XML content, and the targettype is "
dialog " or a platform extension, the mechanism by
which namelist variables or XML content are made
available to the event target is implementation-specific, and
outside the scope of this specification.
Although the full set of requirements for the Event I/O
Processor is not within the scope of this specification, an event
processor sending an event to a CCXML Interpreter is required to
generate an event which can be processed in a CCXML Session. See
Section 9.1 for details regarding the processing of incoming events
by an CCXML Interpreter.
When a message is successfully sent to the target, a
send.successful event MUST be
thrown. Note that this does not mean that the target processed the
message successfully. It is up to the target to generate events
specific to the message. These events are application specific.
If the send request fails, an event signifying the error
MUST be returned to the CCXML Session. The
failure events are documented at the end of this section.
Events generated by <send> will have their
eventid , eventsource and
eventsourcetype attributes derived from the execution
of the <send> element. eventid will
match the value returned via sendid .
eventsource will be the ccxml session id.
eventsourcetype will be set to the string '
ccxml '.
9.2.3.2: <send> Attribute
Details
| target |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A valid target URI |
An ECMAScript expression
returning the target location of the event. The target
attribute specifies the unique identifier of the event target that
the Event I/O Processor must send the event to. |
| targettype |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
ccxml |
ccxml
dialog
basichttp |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that specifies the type of the Event I/O
Processor that the event must be dispatched to. |
| sendid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Left Hand Side
Expression |
none |
ECMAScript Variable |
An ECMAScript left hand side
expression evaluating to a previously defined variable. The value
of the attribute must receive an internally generated unique string
identifier to be associated with the event being sent. |
| delay |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
'0s' |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string in CSS2 [CSS2]
format |
The character string returned
must be interpreted as a time interval. The send element
must return immediately, but the event must not be dispatched until
the delay interval elapses. Timers are useful for a wide variety of
programming tasks, and can be implemented using this
attribute.
Note: The delayed event queue for sending events must be
maintained locally. Any events waiting to be sent must be purged
when the session that issued this request terminates. |
| name |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with inline content |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
|
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string that indicates the event name being
generated. The event name may include alphanumeric
characters characters, "_"
(underscore) and the "." (dot) character. The first
character MUST NOT be a dot or a
digit.
event names are case-insensitive. |
| namelist |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with inline content |
Var List |
none |
List of ECMAScript Variable
names |
A list of zero or more whitespace
separated CCXML variable names to be included with the event.
Values for these variables are evaluated when the
<send> element is processed See section 9.2.3.1
for details on how these variables are made available to the
target. |
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform to configure the Event I/O Processor. The meaning of these
hints is specific to the implementing platform and the Event I/O
Processor. Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the
implementing platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support
hints MAY ignore this attribute. See
Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements
when hints are supported by the implementing platform. |
9.2.3.3: <send> Examples
In this example we send the current CCXML session a
hello.jack event that contains a single field. We
catch the event, log the field and exit:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<eventprocessor>
<transition event="ccxml.loaded">
<var name="jacksvar"
expr="'I am Jack\'s complete lack of surprise.'"/>
<send target="session.id" targettype="'ccxml'"
name="'hello.jack'" namelist="jacksvar"/>
</transition>
<transition event="hello.jack">
<log expr="event$.jacksvar"/>
<exit/>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
In this example we send a event to our parent and then exit:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<eventprocessor>
<transition event="ccxml.loaded">
<var name="jacksvar"
expr="'I am Jack\'s inflamed sense of rejection.'"/>
<send target="session.parentid" name="'hello.jack'"
targettype="'ccxml'" namelist="jacksvar"/>
<exit/>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
In this example we catch a dialog.transfer request
and just return a error event back to the dialog:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<eventprocessor>
<transition event="dialog.transfer">
<var name="reason" expr="'I am a jack's unsupported transfer.'"/>
<send target="event$.dialogid" name="error.unsupported.transfer"
targettype="'dialog'" namelist="reason"/>
<exit/>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
In this example we send the current CCXML session an event that
contains an ECMAScript Object and a qualified variable. We catch
the event, log some properties resulting in the string " 1,
2, 3, 4 ", and exit:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<eventprocessor>
<transition event="ccxml.loaded">
<var name="obj1"/>
<assign name="obj1.prop1" expr="'1'"/>
<assign name="obj1.prop2.a" expr="'2'"/>
<assign name="obj1.prop2.b" expr="'3'"/>
<var name="obj2"/>
<assign name="obj2.prop1" expr="'4'"/>
<send target="session.id" targettype="'ccxml'"
name="'my.complex.event'" namelist="obj1 obj2.prop1"/>
</transition>
<transition event="my.complex.event">
<log expr="event$.obj1.prop1 + ', ' + event$.obj1.prop2.a + ', ' +
event$.obj1.prop2.b + ', ' + event$.obj2.prop1"/>
<exit/>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
9.2.4: <move>
9.2.4.1: Overview
<move> is used to move an event source (such
as a Connection object) to an executing CCXML session. When an
event source is moved to a session, events originating from that
source MUST be delivered to that session's
currently executing CCXML document. The event OR the
source attribute MUST be
specified. If neither attribute is specified or both attributes are
specified, an error.fetch event MUST be thrown.
Support for the <move> element is optional in
CCXML platforms. Even if <move> is supported
platforms MAY only support it between a
restricted set of CCXML sessions. If <move> is
unsupported the CCXML platform MUST raise
an error.move event.
A <move> attempt MUST fail under any of the following conditions:
- The referenced event source does not exist, or does not belong
to the session executing the
<move> ;
- The referenced event source is immovable - the CCXML session
itself and various external event I/O processors are examples of
this;
- The referenced event source is currently bridged to another
object through an implicit or explicit join;
- The session to which the event source is being moved does not
exist, or cannot accept the event source that is being moved;
- The
event attribute is used to identify the event
source, but refers to multiple event sources (such as
connection.merge.failed );
A <move> attempt MAY
fail for causes other than the above, which may or may not be
platform specific
In the event of a <move> failure, an
error.move event MUST be
generated to indicate that the <move> attempt
was unsuccessful. Otherwise, a move.successful event
MUST be generated against the session that
performed the <move> to indicate that the
request has completed successfully.
Since each CCXML session has an event queue, it is possible that
a session executing a <move> will already have
events in its queue from the event source that is being moved. As
an example, this situation could easily occur with
connection.alerting and
connection.disconnected if the incoming connection is
abandoned before a CCXML platform initiates processing. Any such
events MUST be removed from the queue of
the session performing the <move> , and placed
into the queue of the session that the event source is being moved
to. Each event moved in this manner MUST
be inserted into the queue of the target session as if it was a new
event occurring in the context of that session. The order in which
events are queued is the order in which they appear in the event
queue of the session performing the <move> . If
the event attribute is specified, then the referenced
event MUST be placed into the queue of the
target session before other queued events from the event source are
inserted. Note that queueing rules governing the order in which the
inserted events will be processed continue to apply.
Like all CCXML elements, <move> executes
asynchronously. As such, there is a period of time during which
events generated by the event source being moved cannot be
processed either by the session performing the
<move> , or by the target session. If the
<move> fails, then these events remain in the
queue of the session that attempted the <move> ,
and MUST be processed normally. However,
while the <move> is being performed, events from
event sources other than the one being moved MUST continue to be processed according to the EHIA.
As such, a failed <move> request may result in
events being processed in a different order than if no
<move> operation was performed. Note that the
relative ordering of events from the event source being moved is
not changed even as a result of such a failure.
9.2.4.2: <move> Attribute
Details
| source |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the event attribute. |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
(valid connection or dialog
ID) |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a connection ID or dialog ID. The event source associated
with this identifier must be moved to the target session. |
| event |
false |
This attribute must not
be specified in conjunction with the source attribute. |
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns an event object. |
The event source from which the
event object originated, if any, must be moved to the target
session. The event must also be sent to the target session to
provide a notification. |
| sessionid |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A valid CCXML session id |
An ECMAScript expression that
identifies the session to which the event source must be
moved. |
9.2.5: <cancel>
9.2.5.1: Overview
When a CCXML program uses <send> to send an
event and includes a delay attribute, the
<cancel> command will cancel the pending event,
if possible.
The cancel operation cancels a pending event by removing it from
the delayed event queue of the CCXML session that initiated the
<send> , preventing it from ever being
delivered. If the delay has expired and the event has already been
removed from the delayed event queue, the
<cancel> request MUST
fail and an error.notallowed event MUST be delivered to the event queue of the CCXML
session that executed the <cancel> . with
the id property populated with the sendid of the event
that the <cancel> was
requested for. Otherwise, a
cancel.successful event MUST
be delivered to indicate that the <cancel> was
successful, and that the cancelled event was not delivered.
Sessions are only permitted to cancel their own delayed events;
they may not cancel the delayed events of other sessions.
9.2.5.2: <cancel> Attribute
Details
| sendid |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A valid event identifier |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns the value of the event identifier that was received when
the send command was issued. |
9.3: Events
9.3.1: error.notallowed
This error event MUST be thrown when
the execution of an element causes an invalid operation to be
performed on a session and/or connection. The fields available in
this event are:
| sessionid |
true |
string |
The ID of the affected session. |
| id |
false |
string |
The ID, if specified in the element
being executed, of the affected connection, dialog, session,
event, or conference. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation was denied. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
| tagname |
true |
string |
This property must be set to the
ECMAScript string value of the name of the element that produced
the error (ie accept , reject , etc). |
9.3.2: error.semantic
This error event MUST be thrown when
there is a semantic error in a CCXML element ( e.g. passing an
incorrect value for an attribute, etc.).
The fields of this event are:
| reason |
true |
string |
This property must be set to the
ECMAScript string value of the printable error message associated
with this error. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
| tagname |
true |
string |
This property must be set to the
ECMAScript string value of the name of the element that produced
the error (ie accept , reject , etc). |
| attributelist.* |
false |
ECMAScript Object |
If available in the interpreter, this
property must be an object whose properties are the names of the
attributes of the element in error. The value of each attribute
property must be the corresponding string value of the
attribute. |
| scope |
true |
string |
Identifies the scope and impact of the
semantic error; this attribute MUST be set
to one of the following string values:
transition - ECMAScript evaluation error, terminating the execution
of the transition in which the error occurred.
element - Error at element scope, resulting in the affected element
not being executed correctly but not terminating the execution of
other elements within the transition. |
9.3.3:
error.send.targetunavailable
This error event MUST be thrown when
CCXML could not send the event to the target listed in
<send> due to it currently being unavailable.
The fields available in this event are:
| sendid |
true |
string |
The ID of the affected event. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation was denied. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
9.3.4:
error.send.targettypeinvalid
This error event MUST be thrown when
the targettype attribute specified in a
<send> is not valid.
The fields available in this event are:
| sendid |
true |
string |
The ID of the affected event. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation was denied. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
9.3.5: error.send.failed
This error event MUST be thrown when a
<send> could not be completed for a reason not
covered by another error.send.* event. event
(for example, due to an invalid event
name specified on <send>) .
The fields available in this event are:
| sendid |
true |
string |
The ID of the affected event. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation was denied. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
9.3.6: send.successful
This event MUST be thrown when an event
is successfully delivered to the specified receiver. Receipt of the
event does not imply the event has been processed by the receiver
but simply that it has been sent without error. The fields
available in this event are:
| sendid |
true |
string |
The ID of the send request as returned
in the sendid attribute of the send element. |
9.3.7: move.successful
This event MUST be thrown when an event
source is successfully moved to a CCXML session. The fields
available in this event are:
| sourceid |
true |
string |
The ID of the event source that has
been moved as specified either directly via the source
attribute or indirectly via the event attribute of the
move element. |
9.3.8: cancel.successful
This event MUST be thrown when the
sending of an event has been successfully cancelled. The fields
available in this event are:
| sendid |
true |
string |
The ID of the send event that has been
cancelled as specified in the sendid attribute of the
cancel element. |
9.3.9: error.move
This event MUST be thrown when a move
request performed by a session fails to complete successfully. The
fields available in this event are:
| sourceid |
true |
string |
The ID of the event source referenced
either directly via the source attribute or indirectly via
the event attribute of the move element. |
| sessionid |
true |
string |
The ID of the target session to which
it was attempted to move the event source. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason for which
the move request failed. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
9.4: Standard Events
9.4.1: Overview
CCXML can generate arbitrarily-named events. While any event
name is possible, there is a small set of well-known events that
are generated as a matter of course, and which any telephone
application should handle. There are three kinds of these events:
connection events, language events and error events.
The first, and larger set, is present so a CCXML session can
keep abreast of events happening with the telephone network. CCXML
is designed to be neutral with respect to the telephony layer, so
the event set must be very generic and capable of describing the
behavior of a wide variety of systems (e.g., [Q931] , [SS7]
, VoIP, etc).
9.4.2: Standard Event Attributes
9.4.2.1: Overview
All events received in a CCXML session must have a number of
standard fields. It is the responsibility of the Event I/O
Processor that delivered the event to make sure that they are
present.
9.4.2.2: Standard Event Attribute Table
| name |
true |
string |
This property MUST be set to the ECMAScript string value of the
event name. |
| eventid |
true |
string |
The unique identifier for the event.
This MUST match the sendid
attribute of send , if the event was generated by a CCXML
document. |
| eventsource |
true |
string |
The unique identifier of the event
source. If the event source can receive events, you can use this
identifier in the target of send . |
| eventsourcetype |
true |
string |
The name of the Event I/O Processor
that sent this event. If the event source can receive events, you
can use this in the targettype attribute of send
. |
9.4.3: Connection Events
9.4.3.1: Overview
CCXML applications are notified of Connection activities by
events, which often reflect Connection state changes. Applications
may also take actions which change the state of a Connection and
which cause other events to be generated.
Connection events and their properties are specified in sections
10.6: Events , and 10.2.3: Connection Events
9.4.4: Language Events
Language Events are a general class of responses that occur as a
result of the execution of elements within a CCXML document. These
events may be further categorized as follows:
9.4.5: Error Events
9.4.5.1: Overview
CCXML uses its event handling mechanism to notify a CCXML
document of errors that occur during execution. An error
notification takes the form of an error event that is added to the
event queue of the CCXML document where the error occurred. All
error events are named with the prefix "error." so
that a properly defined <transition> can filter
out error events.
Here is an example of a <transition> that can
be used to filter out and report error events:
<transition event="error.*">
<log expr="'an error has occurred (' + event$.reason+ ')'" />
<exit/>
</transition>
All error events have a set of properties in common, shown in
the following table:
| reason |
true |
string |
This property is set to the ECMAScript
string value of the printable error message associated with this
error |
9.5: Error Handling
Due to the nature of CCXML's event handling mechanism, some
error scenarios are treated differently. These scenarios are
described below.
9.5.1: Fetching & compilation errors
Errors that occur in trying to load and compile a CCXML
document, such as the inability to fetch the CCXML page or
statically referenced ECMAScript content, XML parsing or validation
errors (Including checks for mutually exclusive attributes or any
other constraints as defined in the this specification, it's
attribute tables, schema or DTD), compilation errors or other
errors that occur as a result of trying to fetch and run a CCXML
page prior to document initialization. The handling of fetching
errors is dependent on the context of the fetch; if the fetch was
triggered by a running CCXML document using
<createccxml> or <fetch> ,
then an error.createccxml or error.fetch
(respectively) MUST be thrown to the
initiating session. If an error occurs fetching the initial CCXML
document for a session created to handle an incoming call, the
CCXML session created for the incoming call MUST be terminated; the incoming call SHOULD be rejected. If the session is created
through other means (such as the Session Creation Event I/O
Processor), the session MUST be
terminated; the creator of the session SHOULD be notified.
9.5.2: Document Initialization Errors
Errors that occur during documentation initialization (elements
that occur in the CCXML document before
<eventprocessor> ) occur outside of CCXML's
event handling mechanism. These errors MUST cause the CCXML thread of execution to
terminate and notify the platform of the document error.
9.5.3: Error In <eventprocessor>
attributes
An <eventprocessor> contains
<transition>s that comprise CCXML's event
handling mechanism. Since errors in
<eventprocessor> attribute evaluation could keep
the EHIA from correctly processing an event, these errors
MUST cause the CCXML thread of execution
to terminate and notify the platform of the document error.
9.5.4: Error in <transition>
attributes
<transition> attributes specify when the
elements contained by the <transition> should be
executed. Since errors in <transition> attribute
evaluation could keep the <transition> from
correctly handling the error event, these errors MUST cause the CCXML thread of execution to
terminate and notify the platform of the document error.
9.5.5: Errors While Handling Error Events
If an error occurs during the handling of an error event another
error event will be raised and posted to the front of the event
queue. In many cases this may be perfectly acceptable and the CCXML
application may be able to successfully recover from the error. In
some situations however this can lead to an infinite loop in the
CCXML session. Implementations MAY choose
to include some form of loop detection and to terminate the CCXML
session when a loop is detected.
9.5.6: Errors in hints attributes
Several elements within this specification define a
hints attribute. Platforms that do not support
hints on an element MAY
ignore this attribute. If a platform supports the
hints attribute on an element, the attribute is
specified, and ECMAScript evaluation of the value of the hint fails
or the ECMAScript expression does not resolve to an ECMAScript
object, error.semantic MUST
be raised for that element and successive elements within the
<transition> containing that element MUST NOT be executed. Additional processing of hints
by the implementing platform is platform-specific.
10: Telephony Operations and Resources
This section contains information on <accept>
, <createcall> ,
<createconference> ,
<destroyconference> ,
<disconnect> , <join> ,
<merge> , <redirect> ,
<reject> , and <unjoin> .
10.1: Overview
The primary goal of CCXML is to provide call control throughout
the duration of a call. Call control includes handling incoming
calls, placing outgoing calls, bridging (or conferencing) multiple
call legs, and ultimately disconnecting calls.
In CCXML call control occurs through three major concepts:
Connections, Conferences and Bridges.
A Connection is an object modeling a resource by which two
independent unidirectional media streams, and optionally any
associated network signaling traffic, can be controlled by a CCXML
session. This corresponds roughly to a "call leg" as the term is
used informally. The picture below illustrates the media streams
associated with the Connection c1 .

A Bridge occurs when the input and/or output media streams of
Connections or Conferences are linked or "joined" together. The
picture below depicts the result of a full duplex
<join> between the connections c1 and
c2 .
A Conference is an object that controls the mixing of media
streams for two or more Connections through Bridges.In the picture
below, the connections c1 and c2 are joined in a full
duplex mode to the conference C1 .

These concepts are discussed in greater detail in the sections
below.
10.1.1 Concepts Background (INFORMATIVE)
The goals of the CCXML call model are to focus on relatively
simple types of call control and to be sufficiently abstract so
that the call model can be implemented using all major telephony
definitions such as JAIN Call Control(JCC) [JSR021] , [CSTA] , and [S.100] . The JCC call model meets these requirements by
providing an event model for connections which abstracts away many
of the differences between telephone networks (e.g., [Q931] , [SS7] , VoIP, etc). Additionally, this call model is
small and easily-understood so that concrete example programs can
be written.
JCC was designed to be a cross-platform high-level event set to
describe as generic a phone model as possible. The JCC call model
consists of Addresses, Calls, Connections, and Providers. In the
context of CCXML, it was felt that the Address, Call, and Provider
objects would add more complexity than value, so these were omitted
as explicitly visible objects. Instead the behavior of Connections
became the focus.
The CCXML call model therefore is based on the behavior of
Connections. A call is received or initiated under control of a
CCXML session through the properties of a Connection.
Note that the JCC model is designed for endpoint devices
only.
10.2 Connections
The CCXML call model is based on the behavior of
Connections.
Each Connection has one input by which it receives a media
stream from another Connection or Conference.
Each Connection has one output media stream that can be directed
to the inputs of multiple Connections and/or Conferences.
If a network call is active on a Connection (in the
CONNECTED , PROGRESSING or
ALERTING state), the media stream received from the
network is the Connection output, and the Connection input media
stream is transmitted to the network.
Dialogs are also modeled internally as a Connection for the
purposes of media interaction. The Dialog object behaves as if it
was a Connection object and can be joined to other resources in the
same way as any other Connection. A Dialog will not however be
listed in the session.connections session variable.
<dialogstart connectionid="c1" src="'example.vxml'" duplex="'full'">

For a Connection created by <dialogstart> ,
the Connection input and output media streams are available to the
Dialog resource.
10.2.1: Connection State
The state of a Connection Object reflects events that are
generated, either a result of actions that occur within the
telephony network, or as a result of actions performed by the CCXML
application. The following state diagram shows the major aspects of
Connection behavior, but omits some detail in favor of clarity
(e.g. the ERROR state).
The list of valid states that a connection can be in is:
ALERTINGPROGRESSINGCONNECTEDFAILEDDISCONNECTEDERRORCREATED
Connection Objects are created when a incoming call arrives to
the platform via a connection.alerting event or via
the execution of <createcall> .
Connection Objects are automatically destroyed by the platform
after they have reached the DISCONNECTED ,
FAILED or ERROR states. Platforms are
responsible for deciding when to remove unused Connection Objects,
however platforms MUST maintain a Connection Object at least
through the <transition> for the corresponding
connection.disconnected ,
connection.failed , connection.redirected
, connection.merged or error.connection
event
The PROGRESSING and ALERTING states
have reflexive transitions. This is intended to model protocols
which have additional states at these points, and which may
exchange messages such as PROCEEDING ,
ALERTING , FACILITY , or
NOTIFY . Platforms MAY choose
to implement additional states which may be reflected in the
substate property of the Connection object.
10.2.2: Connection Object
An instance of the Connection Object is associated with each
telephony event source. Each instance is uniquely identified by its
connection identifier. All Connection instances have a set of
properties in common, shown in the following table. Properties that
are not indicated as required only appear on an instance of the
Connection object if they have a value. Other properties will
always be present.
The Connection Object is an extension of the Media Endpoint Object as defined
in section 10.4.3.
| connectionid |
true |
This property is the ECMAScript string
value of the Connection Identifier, which uniquely identifies each
instance of the Connection object. |
| state |
true |
This property identifies the current
state of the Connection instance; the value of this property is one
of the constants defined in section 10.2.5
. |
| substate |
false |
This property is a protocol-dependent
property which allows further refinement of the state of a
Connection, if desired. |
| local |
false |
This property is a URI which addresses
the interpreter platform; for an incoming call, this is the called
URI; for a redirected incoming call, this is also the most recent
redirection, and the prior values are contained in the "redirect"
property; for an outgoing call, this is the calling URI. |
| remote |
false |
This property is a URI which addresses
the remote device; for an incoming call, this is the calling URI;
for a redirected incoming call, this is the requester of the most
recent redirection, and prior values are contained in the
"redirect" property; for an outgoing call, this is the called
URI. |
| protocol |
false |
This property is a reference to an
object defining protocol information for the protocol used on this
connection; the referenced object defines information which applies
to all connections using this protocol, and it has at least two
properties:
- name - the name of the connection protocol; the name
MAY also be a property on the connection
instance referencing protocol specific information; if no further
protocol specific information is available, then
Connection.protocol[Connection.protocol.name] is
undefined; (see Appendix E for a suggested set of protocol
names)
- version - the version of the connection protocol
For example, the assignment of
protocol-dependent user-to-user information to a variable
tmp from a Connection instance referenced by the
variable cx would be:
<assign name="tmp"
expr="cx.protocol[cx.protocol.name].uui"/>
|
| redirect |
false |
This property is an array representing
the connection redirection paths; the first element,
Connection.redirect[0] , is the original number, with
each subsequent element representing the target as of subsequent
redirections. Each element of the array MAY define any of the following four properties:
- uri - this element's path
- pi - presentation information
- si - screening information
- reason - this is the reason for the redirect for
example, "unknown", "user busy", "no reply", "deflection during
alerting", "deflection immediate response", "mobile subscriber not
reachable"
|
| aai |
false |
This property is the
application-to-application information passed during connection
setup. |
| originator |
false |
This property is set to either "local"
or "remote" and indicates the originator of the connection; for an
incoming call, this property is set to "remote"; for an outgoing
call, it is set to "local";
For example, the assignment of the originating URI to a variable
uri from a Connection instance referenced by the
variable cx would be:
<assign name="uri"
expr="cx[cx.originator]"/>
|
| input |
true |
As defined by the Media Endpoint
Object in 10.4.3. |
| outputs |
true |
As defined by the Media Endpoint
Object in 10.4.3. |
| objecttype |
true |
This property states the type of this
object which must be 'connection'. |
Platforms MAY choose to add properties
to Connection instances. By convention, the properties MUST begin with an underscore, "_", to identify them
as platform-dependent.
10.2.3: Connection Events
CCXML applications are notified of Connection activities by
events, which often reflect Connection state changes. Applications
may also take actions which change the state of a Connection and
which cause other events to be generated.
In addition to the standard event attributes detailed in
Section 9.4.2 , all Connection
events have a set of properties in common, shown in the following
table. Fields that are not indicated as required only appear on the
event object if they have a value. Other fields will always be
present.
| connectionid |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection associated
with this event. |
| protocol |
false |
string |
The platform protocol ID of the
Connection protocol. |
| info |
false |
ECMAScript Object |
An object which provides additional
platform or protocol dependent information |
| connection |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
Connection object identified by the connectionid property of this
event. |
Platforms MAY choose to add properties
to events. By convention, the properties MUST begin with an underscore, "_", to identify them
as platform-dependent.
10.2.4: Connection Operations
CCXML defines a number of elements, specified in detail in
section 10.5, that are used to interact with Connection Objects.
Execution of these elements MUST NOT
immediately change the state of the Connection Object; Connection
Objects change their state once the event corresponding to the
event transition is handed. Elements, such as
<accept> or <disconnect> , do
not actually change the state of the connection but instead issue
requests to the platform to process the corresponding command that
will in turn raise the events that chance the connection state. The
sole exception to this is <createcall> , which
creates a Connection Object immediately, with its '
state ' property set to CREATED ,
allowing the Connection Object to be accessed following the
<createcall> , within the same transition.
However, existence of the Connection Object does not guarantee
anything about the success of the <createcall>
request.
When elements are used to request an action against a Connection
Object, a corresponding event is always generated to indicate the
result of executing that request. For instance, when the
<accept> element is used to answer an incoming
call, a ' connection.connected ' event indicates that
the call was accepted successfully, whereas a '
connection.failed ' indicates that the call could not
be accepted. The events that can be generated by elements that act
on connections, and the circumstances under which those events
occur, are summarized in the table below. Note that the
<join> and <unjoin> elements
are not included, since these apply to both Connections and
Conferences, and are discussed in detail in Section 10.4 on
Bridges.
There are two common events that can be generated by any of the
connection-affecting elements:
- If the element cannot be evaluated, for example if the
referenced
connectionid contained an invalid
ECMAScript expression, then an ' error.semantic '
event is thrown - as is the case for all CCXML elements. The
error.semantic event MUST NOT
change the state of the associated Connection Object(s).
- If the element cannot be executed because the current state of
the referenced Connection Object (or Objects, in the case of
<merge> ) is not valid for the requested action,
then an ' error.connection.wrongstate ' event is
thrown. Note that an error.connection.wrongstate event
is thrown based on the state of the Connection Object, which in
turn reflects the events that have been processed by the CCXML
application; it is not based on the actual real-time state of the
underlying connection, which could change at any time.
It is important to note that because CCXML is fully
asynchronous, and because events can occur on the underlying
communications network at any time, that connection-related events
can occur that are not related to application actions. The most
common of these is connection.disconnected , which can
be triggered by a user-initiated hangup, and which can occur in any
state during which the call is active.
Finally, once an event is emitted by a Connection Object that
transitions to a final state (such as DISCONNECTED ),
further events MUST NOT be generated by
that Connection Object. Thus, even if an application has performed
an <accept> and expects to receive one of
connection.connected , '
connection.accept.failed ', or
'connection.failed' , it could receive a
'connection.disconnected' instead. Since this event is
associated with a transition to the DISCONNECTED
state, no further events will be generated; thus the application
will not receive any event as a result of having performed an
<accept> .
The following table shows the events that reflect the outcome of
the connection-oriented elements defined by CCXML, for this reason
the table omits the event generated by the underling network (i.e.
connection.alerting and connection.signal
):
|
Element
|
Event
|
Reason
|
|
(any)
|
error.semantic
|
A semantic error
in the application, such as the use of an invalid ECMAScript
expression, preventing the element from being executed. The
intended target Connection Object state is unchanged by this
event.
|
|
error.connection.wrongstate
|
An element was
used on a Connection Object in a state that is not valid for that
element. For instance, performing an <accept> on
a Connection Object in the CONNECTED state would result in this
event. The state of the Connection Object is unchanged by this
event.
|
|
connection.disconnected
|
The connection has
disconnected; no further events, including events for any pending
requests, will be generated. The Connection Object is now in the
DISCONNECTED state. Properties of this event allow the cause of the
disconnection to be determined.
|
|
error.connection
|
A platform
operational error has occurred on the connection; no further
events, including events for any pending requests, will be
generated. The Connection Object is now in the ERROR
state.
|
|
<accept>
|
connection.connected
|
A connection in
the ALERTING state was successfully accepted by the platform. This
event is associated with a transition to the CONNECTED
state.
|
|
connection.accept.failed
|
The
<accept> request failed to complete – the
event’s reason property may indicate why the request failed. The
state of the Connection Object is unchanged by this event. Example
situations that could result in this event include performing
<accept> twice (by the time the second
<accept> is processed, the underlying connection
would already have been accepted), or performing
<accept> after performing a
<reject>.
|
|
connection.failed
|
The
<accept> request failed to complete – the
event’s reason property may indicate why the request failed. This
differs from connection.accept.failed in that the state of the
Connection Object changes to FAILED. This event would typically
occur if an error occurred during the process of trying to accept
the call.
|
|
<redirect>
|
connection.redirected
|
The
<redirect> request completed successfully; the call was
redirected to the specified destination. This event is associated
with a transition to the DISCONNECTED state.
|
|
connection.redirect.failed
|
The
<redirect> request failed to complete – the event’s reason
property may indicate why the request failed. This can happen for
any number of common reasons – redirect target status (busy, no
answer, etc), invalid destination number, insufficient resources,
and others. This event does not change the state of the call; a
CCXML application might well try to redirect to an alternate
number, or perform some other action.
|
|
connection.failed
|
The
<redirect> request failed to complete, but terminated the
connection in the process of attempting the redirection. The
Connection Object transitions to the FAILED
state.
|
|
<reject>
|
connection.disconnected
|
A connection in
the ALERTING state was either declined successfully (as a result of
the <reject> request), OR was withdrawn before the rejection
was performed. The properties of the connection.disconnected event
must be consulted to determine the actual cause. In either case,
the Connection Object transitions to the DISCONNECTED
state.
|
|
connection.reject.failed
|
The <reject>
request failed to complete – the event’s reason property may
indicate why the request failed. The state of the Connection Object
is unchanged by this request. Similarly to
connection.accept.failed, this event can be caused by performing an
<accept> followed by a
<reject>.
|
|
connection.failed
|
The <reject>
request failed to complete – the event’s reason property may
indicate why the request failed. Unlike connection.reject.failed,
the state of the Connection Object changes to
FAILED.
|
|
<createcall>
|
connection.progressing
|
An outbound
connection is progressing; properties of the event may provide
additional information about the progress of the outbound
connection. This event does not imply final success or failure of
an outbound connection, and does not change connection state – the
Connection Object remains in the PROGRESSING
state.
|
|
connection.connected
|
The
<createcall> request completed successfully,
resulting in the establishment of a connection. The Connection
Object transitions to the CONNECTED state.
|
|
connection.failed
|
The
<createcall> request was unsuccessful in
establishing an outgoing connection. This can happen for any number
of common reasons – target status (busy, no answer, etc), invalid
destination number, insufficient resources, and others. Properties
of the connection.failed event provide more information as to why
the connection attempt failed. The Connection Object transitions to
the FAILED state.
|
|
connection.disconnected
|
The
<createcall> request was abandoned at the
request of the application (using <disconnect>). The
Connection Object transitions to the DISCONNECTED state. This event
is technically the result of the <disconnect> request, but is
listed here because it is a possible outcome of the
<createcall> caused by the application. Note
also that a network-triggered connection.disconnected is not
possible when establishing an outbound call, as this would trigger
a connection.failed event.
|
|
<disconnect>
|
connection.disconnected
|
A connection in
the PROGRESSING or CONNECTED states was disconnected successfully
at the request of the application, or as a result of
network-initiated disconnection occurred. The properties of the
event indicate the actual reason for the disconnection. This event
is associated with a transition to the DISCONNECTED
state.
|
|
connection.failed
|
The
<disconnect> request failed to complete successfully,
resulting in a transition to the FAILED state. This could reflect
an error in the disconnection process (such as the lack of a
disconnect acknowledgement from the network).
|
|
<merge>
|
connection.merged
|
Two connections
were merged successfully as requested by the application. One
connection.merged event is received on each of the two connections
that were merged. Both Connection Objects transition to the
DISCONNECTED state when their respective connection.merged events
are processed.
|
|
connection.merge.failed
|
A <merge>
request failed to complete successfully – the event’s reason
property may indicate why the request failed. The states of the
involved Connection Objects are left unchanged.
|
10.2.5: Connection Class
All connection objects MUST be
initiated via the Connection class. The Connection class MUST be read-only and provide the properties defined
below.
The following table lists the constants that correspond to the
possible values of the state property of the
connection object.
| Constant |
Value |
| Connection.ALERTING |
0 |
| Connection.PROGRESSING |
1 |
| Connection.CONNECTED |
2 |
| Connection.FAILED |
3 |
| Connection.DISCONNECTED |
4 |
| Connection.ERROR |
5 |
| Connection.CREATED |
6 |
The following table lists the values of each index in the array
of Connection states. This array MUST be
read-only. Each connection state constant can be used to index into
this array to return the human-readable string corresponding to
that constant.
| Constant |
Value |
| Connection.states[0] |
ALERTING |
| Connection.states[1] |
PROGRESSING |
| Connection.states[2] |
CONNECTED |
| Connection.states[3] |
FAILED |
| Connection.states[4] |
DISCONNECTED |
| Connection.states[5] |
ERROR |
| Connection.states[6] |
CREATED |
The following example logs the current state of the connection
object:
<transition event="connection.*">
<log expr="Connection.states[event$.connection.state]"/>
</transition>
10.3: Conferences
CCXML applications can use <createconference>
to create a new conference, or to attach to an existing conference.
The CCXML application can connect or disconnect existing
connections/conferences/dialogs to the new conference using
<join> and <unjoin> (as
described in Section 10.4 ).
When a session no longer requires the use of a conference, it uses
<destroyconference> to detach from the
conference. Asynchronous events will be sent to the CCXML document
upon completion of each of these operations.
Each Conference Object has one logical output and multiple
inputs. The actual output streams of a Conference Object are
derived by mixing all its input streams, less any contributed audio
of an individual Connection, Conference Object who receives that
output. The output of a Conference Object can be directed to the
inputs of multiple Connections and/or Conference Object (as a
result of bridging).
Some telephony call control definitions do not define a separate
Conference Object, instead defining a conference simply as a call
with more than two parties. In order to accommodate the widest
range of underlying telephony API's, CCXML requires explicit use of
a Conference Object whenever two or more audio streams are
mixed.
Unlike connections and dialogs, which are local to a single
session (but can be moved between sessions using
<move> ), conferences are global across all
sessions, and can be bridged with the
connections/conferences/dialogs of any session. Conferences can be
named in order to facilitate the use of that conference in other
sessions. Assigning a name using the confname
attribute allows other sessions to access the created conference by
performing a <createconference> with the same
value for confname . Conferences continue to exist so
long as at least one session exists that has attached to the
conference using <createconference> without a
corresponding <destroyconference> . When a
session terminates, it implicitly detaches from any conferences to
which it is still attached. Note that it is not necessary for a
session to share a conference by assigning it a name in order for
other sessions to make use of that conference. Other sessions may
still establish bridges to a conference using
<join> and <unjoin> ,
regardless of whether or not they have accessed the conference
using <createconference> ; only the conference
ID is required for this. Because conferences are global, it is not
legal to perform a <move> against a
conference.
NOTE: A simple two-party call does not require the use of a
conference object. This is discussed in Section 10.4 .
10.3.1: Conference Object Properties
An instance of the Conference class is associated with each
Conference Object created by <createconference>
and referenced in the session.conferences associative
array.
| conferenceid |
true |
This property is the ECMAScript string
value of the Conference Identifier, which uniquely identifies each
instance of the Conference class. |
| bridges |
true |
This property is an ECMAScript
associative array containing the identifiers of all
connections/dialogs within the session that are currently bridged
with the conference. Connections/dialogs owned by other sessions
and joined to the same conference are not visible |
| conferencename |
true |
This property is the ECMAScript string
value of the conference name that was passed in
<createconference>. If no name was provided the value is
ECMAScript undefined . |
| objecttype |
true |
This property states the type of this
object which must be 'conference'. |
10.3.2: Conference class
All conference objects MUST be
initiated via the Conference class. The Conference class currently
has no defined properties.
10.4: Bridges
A "bridge" is a relationship between the input and/or output
streams of Connection, Dialog, and Conference Objects. The bridge
concept and the details of its behavior are fundamental to CCXML
Dialogs and Connections are equivalent with respect to establishing
and terminating bridges; the term "Media Endpoint" is used as a
common term to refer both to Connections and Dialogs from the
perspective of bridging operations.
There are two main ways in which CCXML applications can
manipulate bridges:
- Implicitly, using the
<createcall> (with '
joinid ') and
<dialogprepare>/<dialogstart> (with '
connectionid '/' conferenceid ')
elements;
- Explicitly, via the
<join> and
<unjoin> elements.
Even in the simplest case of a network party interacting with a
dialog, two Media Endpoints are REQUIRED ,
and a bridge is established between them implicitly by the action
of <dialogstart> . More complex situations, such
as two-party calls, two-party calls with "hotword" recognition,
conference control, and "coaching" scenarios, all involve the use
of multiple Media Endpoint and explicit control of one or more
bridges between them by using <join> and
<unjoin> .
The nature of bridges, and the behavior of
<join> and <unjoin> , is
concerned with the mapping between the media stream inputs and
outputs of Media Endpoints and Conferences:
- Each Media Endpoint has one input, and 0 or more outputs. If a
network call is active on a Media Endpoint, the media stream
received from the network is the Media Endpoint input, and the
Media Endpoint output media stream is transmitted to the network.
For a Media Endpoint created by
<dialogstart> ,
the Media Endpoint input media stream is available to a recognizer
under control of the CCXML session, and the Media Endpoint output
media stream can be sourced from a resource (such as a Text To
Speech engine) under control of the CCXML session.
- The output of a Media Endpoint or Conference can be directed to
the inputs of one or more Media Endpoints and/or Conferences. This
is sometimes called "splitting" media streams. Not all
environments/implementations will necessarily support "splitting" a
media stream in this manner. In such environments, a request to
establish a bridge that requires the presence of splitting may
fail.
- A Media Endpoint input can come from the output of only one
Media Endpoint or Conference.
- A Conference input can have multiple inputs from the outputs of
Media Endpoints or Conferences.
- If a new bridge requires a Media Endpoint to "listen", and the
Media Endpoint is already listening to a different source, this
existing stream relationship is torn down automatically.
Bridges can be either one-way, in which the media stream flows
only from party A to party B (such that B can hear A, but A cannot
hear B), or two-way, in which the media stream flows in both
directions between the parties involved. <join>
has a duplex attribute to distinguish between two-way
bridges and one-way bridges. For example, <join>
ing Media Endpoint A to Media Endpoint B with
duplex=full will direct the A output to the B input,
and the B output to the A input, creating a simple two-party call.
If instead the same <join> is done with
duplex=half , it will direct the B output to the A
input, and will not have any effect on the B input. Similarly,
<dialogprepare> /
<dialogstart> have the '
mediadirection ' attribute and
<createcall> has the '
joindirection ' attribute for controlling what kind of
bridge is established.
For "hotword" recognition on a two-party call, a two-way (full
duplex) bridge must be established between two network Connections,
and a one-way (half duplex) bridge must be established from one of
the network Connections to a Dialog used to perform the
recognition. There are several ways this arrangement can be
achieved, depending on the initial states of the Connections and
Dialogs. For example, if the network party on Connection A is
initially interacting with Dialog D (i.e., a full duplex bridge
exists between them), all that is needed then is to do a
<join> of Connection A to Connection B (the
other network party) with duplex=full . This example
highlights an important and subtle aspect of the behavior of
<join> when one, or both, of the Connections
being joined is already in one or more established bridges.
Note that <join> MUST
NOT be used to add a Media Endpoint to an existing two-party
bridge in order to create a 3-way Conference Instead, this
functionality can be achieved by first using
<createconference> to create a Conference object
and then <join> ing all three Media Endpoints to
this Conference. If a two-way bridge exists between A and B, and A
is then <join> ed full duplex to C, the result
will be a two-party bridge between A and C and a one-way bridge
from A to B.
CCXML applications MUST only establish
bridges on Media Endpoints that are owned by the session running
that application. As such, a session cannot bridge a Media Endpoint
that it owns to a Media Endpoint that is owned by another session,
nor can it establish a bridge between two Media Endpoints owned by
another session. Since Conferences are global, however, a session
MAY bridge a Media Endpoint that it owns
to any Conference
Asynchronous events are used to notify the CCXML application
upon the completion of bridging operations performed by that
application. Such events are also used to notify the application of
changes to existing bridges that were not requested by the
application - such as a <destroyconference>
terminating a conference that a local connection has a bridge to.
However, the execution of bridging operations and completion
notification varies depending on how the bridging operation was
performed:
- Implicit bridges created using
<dialogprepare>/<dialogstart> (by
specifing ' connectionid ' or '
conferenceid ') are established when the dialog is
started. No bridging events are generated; the '
dialog.started ' event indicates that the dialog was
started and the bridge is in place. If the specified bridge cannot
be established, then the dialog MUST not
be started, and an error.dialog.notstarted event is
generated. Note that a session could still receive a
conference.joined event when a dialog is implicitly
joined to a conference; this event is generated by the
conference.
- Implicit bridges created using
<createcall>
(with ' joinid ') are physically realized as soon as a
platform is capable of doing so; however, the inability to
establish the bridge immediately upon execution of a
<createcall> does not constitute an error. Prior
to the point in time at which the call enters the
CONNECTED state, it may not be possible to establish
the requested bridge, or it may only be possible to establish the
bridge one direction. As a result, when using
<createcall> with ' joinid ', an
event MUST be generated when the requested
bridge operation is completed. This event is independent of
connection-related events such as '
connection.connected ', and may occur before or after
such events depending on when the bridge is actually realized. If
the bridge is established successfully, the '
conference.joined ' event is generated. If the
requested bridge cannot be established even after the connection
reaches the CONNECTED state, or if some other issue
prevents the bridge from being established, an '
error.conference.join ' event will be generated.
Referencing a dialog that has been prepared but not started in '
joinid ' always result in an error, and thus an '
error.conference.join ' event. Note that the call
itself MUST proceed independently of
whether or not the bridge can be established. For instance, it is
possible to receive both an ' error.conference.join '
event and a ' connection.connected ' event for a
single call initiated using <createcall> .
- Explicit bridges creation requests using
<join> are performed immediately independently,
of the state of the underlying resource. Requests to terminate
existing bridges using <unjoin> are also
performed immediately. CCXML applications can use
<join> and <unjoin> at any
time, except in the case of dialogs, where
<join> and <unjoin> can only
be used on dialogs that have been started. For instance, a CCXML
application can join two connections where one (or even both) of
the connections is in the ALERTING state, providing
early media on the ALERTING connection. If the CCXML
implementation does not support a requested
<join> due to the current state of an underlying
entity, then this will result in an
error.conference.join event with the '
reason ' field set appropriately.
10.4.1: <join> Outcomes
As an aid to understanding, the outcomes of all possible
<join> operations are shown diagrammatically
below for three different initial conditions:
- a single Connection A, that is not currently in a bridge,
represented graphically as: (A)
- two Connections A and B, with a half duplex bridge (A output to
B input), represented graphically as: A -----> B
- two Connections A and B, with a full duplex bridge (A output to
B input & B output to A input), represented graphically as: A
<====> B
For the initial condition in which a single Connection A is not
currently in a bridge, there are four possible
<join> s:
| initially |
(A)(B) |
| join A to B half |
A <-----
B |
| join A to B full |
A <====>
B |
| join B to A half |
A ----->
B |
| join B to A full |
A <====>
B |
For the initial condition in which a half duplex bridge exists from
Connection A to Connection B (A output to B input), there are
twelve possible <join> s:
| initially |
A ----->
B |
| join A to B half |
A <-----
B |
| join A to B full |
A <====>
B |
| join B to A half |
A ----->
B |
| join B to A full |
A <====>
B |
| join A to C half |
A -----> B
& A <----- C |
| join A to C full |
A -----> B
& A <====> C |
| join C to A half |
A -----> B
& A -----> C |
| join C to A full |
A -----> B
& A <====> C |
| join B to C half |
(A) & B
<----- C |
| join B to C full |
(A) & B
<====> C |
| join C to B half |
A -----> B
& B -----> C |
| join C to B full |
(A) & B
<====> C |
For the initial condition in which a full duplex bridge exists
between two Connections A and B (A output to B input & B output
to A input), there are twelve possible <join>
s:
| initially |
A <====>
B |
| join A to B half |
A <-----
B |
| join A to B full |
A <====>
B |
| join B to A half |
A ----->
B |
| join B to A full |
A <====>
B |
| join A to C half |
A -----> B
& A <----- C |
| join A to C full |
A -----> B
& A <====> C |
| join C to A half |
A <====> B
& A -----> C |
| join C to A full |
A -----> B
& A <====> C |
| join B to C half |
A <----- B
& B <----- C |
| join B to C full |
A <----- B
& B <====> C |
| join C to B half |
A <====> B
& B -----> C |
| join C to B full |
A <----- B
& B <====> C |
In summary, <join> behavior always respects
three invariants:
- The media stream relationship specified in the
<join> is established between the two
Connections/Conferences referenced in the <join>
. In particular, any existing stream relationship between these two
Connections/Conferences is torn down automatically if it conflicts
with the specified relationship.
- If the relationship specified in the
<join>
requires a Connection to "listen" and the Connection is already
listening to a different source, this existing stream relationship
is torn down automatically.
- Any existing stream relationship that does not present a
conflict according to invariant #1 or invariant #2 is
preserved.
10.4.2: Invariant Examples
To illustrate some typical invocations of
<join> invariants a few example scenarios are
presented below. In the first scenario, connection c1 is
bridged to a conference C1 , via a <join>
where the duplex mode is full .
After <join id1="'C1'" id2="'c1'" duplex="'full'">
Session object properties
session.connections['c1'].input == 'C1'
session.connections['c1'].outputs.length == 1
session.connections['c1'].outputs[0] == 'C1'
session.conferences['C1'].bridges['c1'] == 'c1'

If c1 then became a participant in a
<dialogstart> where d1 represents a
connection to a dialog and the mediadirection is both,
the original picture would change as follows:
After <dialogstart connectionid="'c1'" src="'example.vxml'" mediadirection="'both'">
session.connections['c1'].input == 'd1'
session.connections['c1'].outputs.length == 2
session.connections['c1'].outputs[0] == 'C1'
session.connections['c1'].outputs[1] == 'd1'
session.connections['c1'].dialogid == 'd1'
session.conferences['C1'].bridges['c1'] == 'c1'
session.dialogs['d1'].input == 'c1'
session.dialogs['d1'].outputs[0] == 'c1'
session.dialogs['d1'].outputs.length == 1

The <dialogstart> required c1 to
"listen" to d1 , however, c1 was already in an
established bridge listening to C1 . Consequently, the full
duplex bridge between c1 and C1 is changed to a half
duplex, where c1 is not allowed to "listen" to C1 and
a full duplex bridge is established between c1 and d1
.
In this second scenario, c1 and c2 have been
joined into a conference, C1 .
After <join id1="'C1'" id2="'c1'" duplex="'full'">
and: <join id1="'C1'" id2="'c2'" duplex="'full'">
session.connections['c1'].input == 'C1'
session.connections['c1'].outputs.length == 1
session.connections['c1'].outputs[0] == 'C1'
session.connections['c2'].input == 'C1'
session.connections['c2'].outputs.length == 1
session.connections['c2'].outputs[0] == 'C1'
session.conferences['C1'].bridges['c1'] == 'c1'
session.conferences['C1'].bridges['c2'] == 'c2'

If a <join> is then executed that specifies
c2 and C1 as participants and the duplex mode is
half, the bridge between c2 and C1 will be
re-established with C1 able to "listen" to c2 , but
c2 no longer able to "listen" to C1 .
After <join id1="C1" id2="c2" duplex="'half'">
session.connections['c1'].input == 'C1'
session.connections['c1'].outputs.length == 1
session.connections['c1'].outputs[0] == 'C1'
session.connections['c2'].input == undefned
session.connections['c2'].input == undefined
session.connections['c2'].outputs.length == 1
session.connections['c2'].outputs[0] == 'C1'
session.conferences['C1'].bridges['c1'] == 'c1'
session.conferences['C1'].bridges['c2'] == 'c2'

In this third scenario, there are three connections c1, c2 and
c3. Connections c1 and c2 are connected with a half duplex bridge,
connection 3 is not bridged at this point.
After <join id1="'c1'" id2="'c2'" duplex="'half'">
Session object properties
session.connections['c1'].input == 'c2'
session.connections['c1'].outputs.length == 0
session.connections['c2'].input == undefined
session.connections['c2'].outputs.length == 1
session.connections['c2'].outputs[0] == 'c1'
session.connections['c3'].input == undefined
session.connections['c3'].outputs.length == 0

A full bridge is established between connections c2 and c3,
connection c1 is still receiving from c2.
After <join id1="'c2'" id2="'c3'" duplex="'full'">
session.connections['c1'].input == 'c2'
session.connections['c1'].outputs.length == 0
session.connections['c2'].input == 'c3'
session.connections['c2'].outputs.length == 2
session.connections['c2'].outputs[0] == 'c1'
session.connections['c2'].outputs[1] == 'c3'
session.connections['c3'].input == 'c2'
session.connections['c3'].outputs.length == 1
session.connections['c3'].outputs[0] == 'c2'

Connection and Dialog objects all have a common set of base
properties relating to media input/output. The standard set of
media endpoint properties are defined below:
| input |
true |
The identifier
(connectiondid/conferenceid/dialogid) of the single media endpoint
(connection, dialog or conference) providing the input stream to
this media endpoint or undefined if there is no input stream. This
property MUST be updated each time a
<join>/<unjoin> or any other media
operation changes the media source to this media endpoint.
If the media endpoint does not have a media source the value
MUST be ECMAScript undefined.
For example the creation of a half duplex bridge
<join id1="con1" id2="con2" duplex="'half'"
/>
Result
session.connections[con1].input = "con2"
session.connections[con2].input = undefined
|
| outputs |
true |
An array containing the identifiers of
all media endpoints to which the output stream of this media
endpoint is sent. If the media endpoint does not have any media
destinations the length of the array MUST
be 0.
For example the creation of a half duplex bridge
<join id1="con1" id2="con2" duplex="'half'"
/>
Result
session.connections[con1].outputs.length = 0
session.connections[con2].outputs.length = 1
|
10.5: Elements
10.5.1: <accept>
10.5.1.1: Overview
The execution of an <accept> MUST cause the underlying platform to signal the
telephony system to connect the specified Connection to the CCXML
platform. The CCXML document MAY then
initiate interactive dialog sessions with the incoming caller, or
perform other telephony operations (e.g., place outgoing calls,
join calls, etc).
10.5.1.2: <accept> Attribute
Details
| connectionid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
event$.connectionid if defined,
ECMAScript undefined otherwise |
Connection IDs |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that must be the identifier of a Connection on
which the incoming call is signaled. If the connectionid
attribute is omitted, the interpreter must accept using the id
indicated in the current event being processed.
If the attribute value is invalid or there is no valid default
value, an error.semantic event must be thrown. |
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform or passed to the network accepting the connection. This
information may consist of protocol-specific
parameters.
Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the implementing
platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support hints
MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
10.5.2: <redirect>
10.5.2.1: Overview
When a CCXML document executes a <redirect>
within the <transition> block, this MUST cause the underlying platform to signal the
telephony system to send the call to a specified destination. The
use of <redirect> is only valid when a call is
in the ALERTING and CONNECTED states.
If the call is currently joined, it MUST be unjoined before the redirect is performed
and a conference.unjoined event MUST be generated. Note the platform is not required
to generate the conference.unjoined or
connection.redirected in any particular order.
10.5.2.2: <redirect>
Attribute Details
| connectionid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
event$.connectionid if defined,
ECMAScript undefined otherwise |
Connection IDs |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the identifier of a Connection on which a
call is active or on which an incoming call is being signaled. This
call must be redirected. If the connectionid attribute is
omitted, the interpreter must redirect using the id indicated in
the current event being processed.
If the attribute value is invalid or there is no valid default
value, an error.semantic event must be thrown. |
| dest |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A Valid URI |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the address where the call should be
redirected to. A platform MUST support a
telephone URI, as described in [RFC2806] [RFC3966] and MAY
support other URI schemes such as "sip:" or "h323:". |
| reason |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
|
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the reason the call is being
redirected. |
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform or passed to the network redirecting the connection. This
information may consist of protocol-specific
parameters.
Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the implementing
platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support hints
MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
If the platform is unable to redirect the call this MUST result in the generation of an
connection.redirect.failed event.
10.5.3: <reject>
10.5.3.1: Overview
The execution of an <reject> MUST cause the underlying platform to signal the
telephony system to reject the incoming Connection from the
platform.
10.5.3.2: <reject> Attribute
Details
| connectionid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
event$.connectionid if defined,
ECMAScript undefined otherwise |
Connection IDs |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the identifier of a Connection on which an
incoming call is being signaled. This call must be rejected. If the
connectionid attribute is omitted, the interpreter must
reject using the id indicated in the current event being
processed.
If the attribute value is invalid or there is no valid default
value, an error.semantic event must be thrown. |
| reason |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
|
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the reason the call is being
rejected. |
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform or passed to the network rejecting the connection. This
information may consist of protocol-specific
parameters.
Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the implementing
platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support hints
MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
10.5.4: <createcall>
10.5.4.1: Overview
A CCXML document is able to instruct the platform to attempt to
place an outgoing call with <createcall> . This
element MUST instruct the platform to
allocate a Connection and attempt to place an outgoing call to a
specified address. The CCXML interpreter MUST receive an asynchronous event when the call
attempt is completed. An <eventprocessor>
<transition> block can handle this event and perform
further call control, such as conferencing. If the call was
successfully placed, the transition block can also initiate a
dialog interaction with the called party.
The execution of <createcall> MUST result in the generation of one or more
connection.progressing events (depending on platform
support for call progress) followed by a
connection.connected event on success, or zero or more
connection.progressing events followed by a
connection.failed event on failure.
10.5.4.2: <createcall>
Attribute Details
| dest |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
A Valid URI |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the target of the outbound telephone call.
A platform MUST support a telephone URI,
as described in [RFC2806] [RFC3966] and
MAY support other URI schemes such as
"sip:" or "h323:" or a SIP URI as described in [RFC3261] . |
| connectionid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Left Hand Side
Expression |
none |
ECMAScript Variable |
An ECMAScript left hand side
expression evaluating to a previously defined variable. The value
of the attribute must receive the identifier of the Connection on
which the outgoing call is attempted. |
| aai |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
|
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string of application-to-application information to be
passed to the destination endpoint when establishing the
connection.
Note: Even if an implementation platform accepts the
aai data, certain protocols and network elements may
prevent the transmission to the target endpoint. If the platform
does not support the transmission of aai data it must
raise a connection.progressing event and indicate that the
use of aai is not supported. |
| callerid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
|
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string defining the caller identity to be used when
making the outbound connection. The format of this information is
protocol and platform specific but might consist of a telephone
URI, as described in [RFC2806] [RFC3966] or a SIP
URI as described in [RFC3261] .
Note: An implementation platform is not required to
use the specified data and certain protocols and network elements
may prevent its use. If the platform does not support the
specification of callerid it must raise a
connection.progressing event and indicate that the use of
callerid is not supported. |
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform when establishing the outbound connection. This
information may consist of protocol-specific parameters,
protocol selection guidelines, or routing hints.
Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the implementing
platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support hints
MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
| timeout |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a character string in CSS2 [CSS2]
format |
The character string returned is
interpreted as a time interval. This interval begins when
createcall is executed. The createcall must fail if
not completed by the end of this interval. A completion is defined
as the call getting to a CONNECTED state as signaled by a
connection.connected event. A failed createcall must
return the connection.failed event. |
| joinid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
(valid connection, conference, or
dialog ID) |
An ECMAScript expression that
identifies a connection, conference, or dialog ID that the new call
must be joined to. This is equivalent, from the perspective of the
CCXML application, to performing a <join> immediately
following the <createcall>. However, platforms may use
knowledge about the connection/conference/dialog to which the new
call will be connected to optimize the call creation process. If
the attribute value is invalid an error.semantic event
must be thrown. |
| joindirection |
false |
If
this This attribute is
specified only
valid in conjunction with the joinid attribute MUST be present. attribute, otherwise ignored. |
ECMAScript Expression |
both |
both
calltransmit
callreceive |
An ECMAScript expression that
defines the direction of the media flow between the newly created
connection, and the existing connection/conference/dialog
referenced by joinid:
- both
- Specifes a full duplex connection where the media flows in both
directions.
- calltransmit
- The new connection transmits media to the referenced
connection/conference/dialog but does not receive any media
streams.
- callreceive
- The new connection receives media from the referenced
connection/conference/dialog but does not transmit any media
streams.
|
10.5.4.3: <createcall>
examples
The following example illustrates the simplest use of
<createcall> .
<createcall dest="'tel:1235551234'"/>
This example illustrates the use of several attributes of
<createcall> . A SIP URI is provided as the
originators caller id, a selection of protocol specific parameters
are provided ( callingDevice and
callCharacteristics ) and a string of application
specific data is provided to be presented to the remote endpoint.
The connection ID for the new connection is returned in the
variable " myConidVar ".
<var name="myConidVar"/>
<createcall
dest="'sip:+1-212-555-1212:1234@gateway.com;'"
callerid="'sip:j.doe@big.com'"
connectionid="myConidVar"
aai="'This is application specific data'"
hints="var tmp = {callingDevice: 'notSpecified', callCharacteristics: 'voiceUnitCall'}; tmp"/>
10.5.5:
<createconference>
10.5.5.1: Overview
A CCXML document can attempt to create or attach to a Conference
Object using <createconference> . This element
instructs the implementation to allocate a Conference Object using
the specified options. The successful execution of
<createconference> MUST
result in the generation of a conference.created
event. If for any reason the implementation is unable to create the
Conference Object using the specified options it MUST fail with a
error.conference.create event.
Since conferences are global in scope, it is possible that other
sessions will establish or terminate bridges to a Conference
created by an application. Sessions that have created or attached
to a Conference using <createconference> receive
notifications of any bridges that are created or destroyed, through
the ' conference.joined ' and '
conference.unjoined ' events. However, if a session
establishes or terminates a bridge between a Connection that it
owns and a Conference that it has created/attached to, it will only
receive one such event - not one event each for the Connection and
for the Conference.
It is legal for a session to perform a
<createconference> multiple times with the same
value for the ' confname ' parameter. The same
conference ID will be returned in each case, allowing this to be
used as a mechanism for looking up conference IDs.
10.5.5.2: <createconference>
Attribute Details
| conferenceid |
true |
|
ECMAScript Left Hand Side
Expression |
none |
ECMAScript Variable |
An ECMAScript left hand side
expression evaluating to a previously defined variable. The value
of the attribute must receive the conference identifier. A
conference identifier must be globally unique, so
that conferences can be uniquely addressed and possibly connected
to. |
| confname |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
valid conference URI |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the name of the conference. The conference
name corresponds to the conference identifier that will be returned
in the variable specified in the conferenceid
attribute.
If the named conference does not exist, the platform must
create a conference object as requested and return the value of the
conference identifier to the variable specified in the
conferenceid attribute. If a conference already exists the
platform must return the conference identifier of the
previously created conference. |
| reservedtalkers |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
|
An ECMAScript expression which
returns the number of guaranteed speaker slots the conference mixer
must reserve. If the conference already exists, then this attribute
must be ignored.
If the conference mixer is unable to reserve this many speaker
slots, the createconference must fail with a
error.conference.create event. |
| reservedlisteners |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
|
An ECMAScript expression which
returns the number of guaranteed listener slots the conference
mixer must reserve. If the conference already exists, then this
attribute must be ignored.
If the conference mixer is unable to reserve this many listener
slots, the createconference must fail with a
error.conference.create event. |
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform when creating the conference.
Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the implementing
platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support hints
MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
10.5.6:
<destroyconference>
10.5.6.1: Overview
A CCXML document is able to instruct the platform to attempt to
detach from an existing Conference Object using
<destroyconference> . This destroys the
conference if no other sessions are attached to it. The target
Conference Object is identified using the conferenceid
attribute. The successful execution of
<destroyconference> MUST result in the generation of a
conference.destroyed event. If for any reason the
implementation is unable to deallocate the Conference Object it
MUST fail with a
error.conference.destroy event.
Since other sessions may have created bridges to a conference
using the conference's ID, but without performing a
<createconference> , destroying a conference
MAY affect the bridges established by
other sessions. If any bridges are terminated in this fashion, a '
conference.unjoined ' event MUST be posted to indicate to the session that its
Connection is no longer bridged to the Conference.
The platform MUST implicitly tear down
any existing bridges to the dialog and send a
conference.unjoined to the CCXML document once the
media paths have been freed.
10.5.6.2: <destroyconference>
Attribute Details
| conferenceid |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
Conference IDs |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the identifier of the conference that
must be destroyed.
If the attribute value is invalid an error.semantic event
must be thrown. |
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform when destroying the conference.
Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the implementing
platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support hints
MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
10.5.7: <join>
10.5.7.1: Overview
A CCXML document can attempt to create a bridge between two
connections, conferences, or dialogs using
<join> . This element instructs the
implementation to bridge the connections, conferences, or dialogs
specified using the id1 and id2
attributes in accordance with media options specified by the other
attributes of <join> . The successful execution
of <join> MUST result
in the generation of a conference.joined event. If for
any reason the implementation is unable to create the bridge using
the specified options it MUST fail with a
error.conference.join event.
Any Connections or Dialogs referenced by the ' id1
' and ' id2 ' attributes of <join>
MUST be owned by the session performing
the <join> . If id1 or
id2 refer to Conferences, then it is not necessary
that the session has performed a
<createconference> to create/attach to that
conference; it is sufficient that it has a valid conference ID.
When joining a Connection or Dialog to a Conference, or when
joining two Conferences, the ' conference.joined '
event MUST be posted to all sessions that
are attached to the affected Conference(s). This MUST NOT result in multiple '
conference.joined ' events if the session performing
the <join> is attached to the conference, nor if
any session owns both conferences when two conferences are joined
together. If the implementation is unable to join the objects an
error.conference.join MUST
only be sent to the session that issued the
<join> .
Implementations MAY disallow two
dialogs from being joined together. If both id1 and
id2 specify dialogs and the platform does not support
joining together two dialogs, then an
error.conference.join event is thrown.
10.5.7.2: <join> Attribute
Details
| id1 |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
(valid connection, conference, or
dialog ID) |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the identifier of a Connection, Dialog or
Conference.
If the attribute value is invalid an error.semantic event
must be thrown. |
| id2 |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
(valid connection, conference, or
dialog ID) |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the identifier of a Connection, Dialog or
Conference.
If the attribute value is invalid an error.semantic event
must be thrown. |
| duplex |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
full |
full
half |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns a character string equal to "half" or "full", which defines
the direction of the media flow between id1 resource and id2
resource. Refer to the discussion of bridging in Section 10.4 . The duplex attribute
determines whether the join must establish a half-duplex
(unidirectional) or full-duplex (bi-directional) bridge. The
following values can be used:
- full
- Specifies a full duplex bridge where the media flows in both
directions.
- half
- Species a half duplex bridge where the media flows towards id1
resource, but no media flows from id1 resource to id2
resource.
|
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform or passed to the network when the two specified
Connections, Dialogs or Conferences (id1 and id2) are joined. This
information may consist of protocol-specific
parameters.
Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the implementing
platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support hints
MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
| entertone |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
'true' |
'true'
'false'
URI |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns a character string that must be used to play a tone or a
custom wav file to the conference participants when this Connection
joins. The following values can be used:
- 'true'
- Setting this to 'true' must play the default system beep.
- 'false'
- Setting this to 'false' must result in no alerting sound being
played at all.
- URI
- The developer may also specify a URI value which points to a
user-defined wav file to be played instead of the default system
beep.
|
| exittone |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
'true' |
'true'
'false'
URI |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns a character string that must be used to play a tone or a
custom wav file to the conference participants when this Connection
exits. exits (Note: The exact
order of operations in this scenario is to play exittone, then
unjoin and finally send conference.unjoined).
The following values can be used:
- 'true'
- Setting this to 'true' will play the default system beep.
- 'false'
- Setting this to 'false' will result in no alerting sound being
played at all.
- A Valid
- The developer may also specify a URI value which points to a
user-defined wav file to be played instead of the default system
beep.
|
| autoinputgain |
false |
|
ECMAScript Boolean Expression |
true |
true
false |
An ECMAScript Boolean expression
that tells the conference mixer if it must use AGC to determine the
input gain for this leg. If a platform does not support AGC, it
must ignore this attribute. The following values can be used:
- true
- AGC must be used to determine input gain for a leg.
- false
- AGC must not be used.
|
| autooutputgain |
false |
|
ECMAScript Boolean Expression |
true |
true
false |
An ECMAScript boolean expression
that tells the conference mixer if it must use AGC to determine the
output gain for this leg. If a platform does not support AGC, it
must ignore this attribute. The following values can be used:
- true
- AGC must be used to determine output gain for a leg.
- false
- AGC must not be used.
|
| dtmfclamp |
false |
|
ECMAScript Boolean Expression |
true |
true
false |
An ECMAScript Boolean expression
that tells the conference mixer if it must attempt to remove
detected DTMF tones If a platform does not support removal of DTMF
tones, it must ignore this attribute. The following values can be
used:
- true
- Conference mixer must attempt to remove detected DTMF
tones.
- false
- Conference mixer must not attempt to remove any detected DTMF
tones.
|
| toneclamp |
false |
|
ECMAScript Boolean Expression |
true |
true
false |
An ECMAScript Boolean expression
that tells the conference mixer if it must attempt to remove loud
single-frequency tones from the audio stream for this leg. If a
platform does not support removal of tones, it must ignore this
attribute. The following values can be used:
- true
- Conference mixer must attempt to remove loud single-frequency
tones.
- false
- Conference mixer must not attempt to remove any loud
single-frequency tones.
|
10.5.8: <unjoin>
10.5.8.1: Overview
A CCXML document is able to instruct the platform to attempt to
tear down a bridge between two existing connections, conferences,
or dialogs using <unjoin> . This element
instructs the implementation to tear down the bridge between two
connections/conferences/dialogs specified using the
id1 and id2 attributes. The successful
execution of <unjoin> MUST result in the generation of a
conference.unjoined event. If for any reason the
implementation is unable to terminate the bridge between the
specified connections/conferences/dialogs, or if no such bridge
exists, it MUST fail with a
error.conference.unjoin event.
Any Connections or Dialogs referenced by the ' id1
' and ' id2 ' attributes of
<unjoin> MUST be owned
by the session performing the <unjoin> .
When ' id1 ', ' id2 ', or both
reference to a Conference, the ' conference.unjoined '
event MUST be posted to all session that
are attached to the affected Conference(s). This MUST NOT result in multiple '
conference.unjoined ' events if the session performing
the <unjoin> is attached to the conference, or
if any session owns both conferences when two conferences are being
unjoined. If the implementation is unable to unjoin the objects an
error.conference.unjoin MUST
only be sent to the session that issued the
<unjoin> .
10.5.8.2: <unjoin> Attribute
Details
| id1 |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
(valid connection, conference, or
dialog ID) |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the identifier of a Connection, Dialog or
Conference.
If the attribute value is invalid an error.semantic event
must be thrown. |
| id2 |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
(valid connection, conference, or
dialog ID) |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the identifier of a Connection, Dialog or
Conference. All media streams between the two specified
Connections, Dialogs or Conferences (id1 and id2 ) must be torn
down.
If the attribute value is invalid an error.semantic event
must be thrown. |
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform or passed to the network when the two specified
Connections, Dialogs or Conferences (id1 and id2) are unjoined.
This information may consist of protocol-specific
parameters.
Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the implementing
platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support hints
MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
10.5.9: <disconnect>
10.5.9.1: Overview
A CCXML document is able to instruct the platform to disconnect
a Connection by using <disconnect> . The
underlying platform MUST send the
appropriate protocol messages to perform the disconnect, and send
an asynchronous event to the CCXML document when the disconnect
operation completes. A CCXML document may use
<disconnect> to abandon an outbound connection
created using <createcall> which has not yet
entered the CONNECTED state. If
<disconnect> is used to abandon an outbound
call, it results in the generation of a '
connection.disconnected ' event.
If the connection had been bridged when the
<disconnect> request was made, the platform
MUST tear down all bridges to the
connection and send a conference.unjoined to the CCXML
document once the media paths have been freed.
Note the platform is not required to generate the
connection.disconnected /
connection.failed or conference.unjoined
in any particular order, unless an outbound call was abandoned in
which case a connection.disconnected event MUST be generated.
10.5.9.2: <disconnect>
Attribute Details
| connectionid |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
event$.connectionid if defined,
ECMAScript undefined otherwise |
Connection IDs |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the id of a call leg that must be
disconnected. If the connectionid attribute is omitted, the
interpreter must disconnect using the id indicated in the current
event being processed.
If the attribute value is invalid or there is no valid default
value, an error.semantic event must be thrown. |
| reason |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
|
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the reason the call is being
disconnected. |
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform or passed to the network disconnecting the connection.
This information may consist of protocol-specific
parameters.
Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the implementing
platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support hints
MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
10.5.10: <merge>
10.5.10.1: Background
Many of the network environments in which a CCXML implementation
may be expected to operate provide facilities by which two existing
calls can be merged into a single call at the network level. The
following diagram illustrates this for the case where user A has
two independent calls with users B and C, and utilizes this
functionality to merge the calls together:
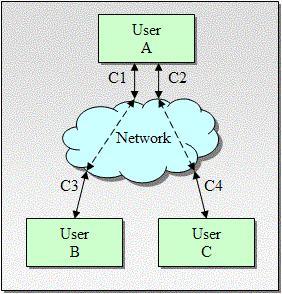 Figure 1: Initial Call State Figure 1: Initial Call State |
 Figure 2: State Following Merge Figure 2: State Following Merge |
The diagram illustrates the call control connections, or
sessions, that exist between users A, B, C and the network that
connects them; the media streams between users is not shown on the
above diagram and may differ from the path for call control that is
shown. The media path between users may or may not be affected as a
result of the merge, depending on the properties of the underlying
network; typically any media streams to user A would be terminated
since call control sessions between user A and the network are
terminated.
There are many different implementations of the merging
capabilities described above, across both PSTN and Voice-over-IP
networks. Known implementations include the following:
- Release Link Trunk (RLT) (ISDN [ Q.931/DSS1 ], SS7 ISUP [ SS7 ])
- Two B-Channel Transfer (TBCT) (ISDN [ Q.931/DSS1 ], SS7 ISUP [ SS7 ])
- Explicit Call Transfer (ECT) (ISDN [ Q.931/DSS1 ], SS7 ISUP [ SS7 ]ISUP)
- AT&T Transfer Connect (some variants) (ISDN [
Q.931/DSS1
])
- Q.SIG Path Replacement (ISDN [ Q.931/DSS1 ])
- SIP REFER with Replaces (SIP [ RFC3261 ])
- H.450.2 Consultative Transfer (H.323 [ H.323 ])
- CSTA and other interfaces to PSTN switches
- Hook-flash Transfers (Analog, T-1 RBS, E-1 CAS)
Different implementations may also have different restrictions
on when and how merge functionality can be used. Some
implementations might allow calls that are alerting to be merged,
whereas others might only operate on calls that are already in the
connected state. In addition, some implementations might only be
able to merge calls in which one of the calls is an outbound call
that specifically identifies the associated inbound call when that
outbound call is placed (via hints on
<createcall> ).
10.5.10.2: Overview
The <merge> element allows two calls being
handled by a particular CCXML session to be merged together at the
network level, if supported by the underlying network and CCXML
platform.
If successful, the two referenced calls MUST be merged at the network level, and the
connections to the CCXML platform associated with those calls
MUST be terminated. A
connection.merged event MUST
be generated on each of the two calls affected by a merge. If the
merge fails, then a single connection.merge.failed
event MUST be thrown which identifies both
of the connections against which the merge was performed.
The platform MUST implicitly tear down
any existing bridges to the connections and send a
conference.unjoined to the CCXML document once the
media paths have been freed, except for the media path between the
two connections being merged.
10.5.10.3: <merge> Attribute Details
| connectionid1 |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
Connection IDs |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the identifier of the first connection
that is to be merged. The order (connectionid1 vs. connectionid2)
of the Connections does not matter.
If the attribute value is invalid an error.semantic event
must be thrown. |
| connectionid2 |
true |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
Connection IDs |
An ECMAScript expression which
returns a string that is the identifier of the second connection
that is to be merged.
If the attribute value is invalid an error.semantic event
must be thrown. |
| hints |
false |
|
ECMAScript Expression |
none |
An ECMAScript expression that
returns an ECMAScript object |
The ECMAScript object returned
contains information which may be used by the implementing
platform or passed to the network when merging the two connections.
This information MAY consist of protocol-specific
parameters.
Note: The meaning of these hints is specific to the implementing
platform and protocol. Platforms that do not support hints
MAY ignore this attribute. See Section 9.5.6 for additional requirements when hints
are supported by the implementing platform. |
10.6: Events
10.6.1: Overview
This section defines the events related to telephony operations
including events related to the call state, success and failure
events for the various telephony operations.
Several of the events defined in this section are associated
with the change in state of a Connection Object. For instance, the
' connection.connected ' event causes a transition to
the CONNECTED state. Platforms MUST perform updates to Connection Object state when
events are dequeued by the EHIA before the
<transition> selection process (and thus before
execution of <transition> content). This is
necessary such that conditional expressions on transitions, as well
as executable content, can reference Connection Object state that
is consistent with the event being processed
10.6.2: connection.alerting
This event MUST be emitted when the
underlying telephony connection transitions to an
ALERTING state or sends notification of call progress
while the Connection Object is in the ALERTING state.
This event is a transition to state ALERTING .
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
Information provided by the protocol prior to connection is
accumulated and stored with the identified Connection object. This
information MAY be available when the
connection.alerting event is delivered to the
application. Any further information provided by the protocol prior
to connection MAY be provided in
subsequent connection.alerting events, and made
available in the updated Connection object.
10.6.3: connection.progressing
This event MUST be emitted when the
underlying telephony connection sends a notification of call
progress while the Connection Object is in the
PROGRESSING state. This event is a transition to state
PROGRESSING .
Subsequent connection.progressing events MAY be generated to support protocols which exchange
multiple messages during the PROGRESSING state.
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
10.6.4: connection.connected
This event must be emitted when an
incoming connection is accepted successfully, or as when an
outgoing connection is answered. This event is a transition to
state CONNECTED .
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
10.6.5: connection.disconnected
This event must be emitted when a
connection is disconnected due to an action by the underlying
network (e.g. the user hanging up), the CCXML platform, or the
CCXML application. This event is a transition to state
DISCONNECTED .
If this is an off-platform event, the platform MUST implicitly tear down any existing bridges to
the connection and send a conference.unjoined to the
CCXML document once the media paths have been freed.
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
| reason |
false |
string |
A disconnection reason code. Content of
this field is platform-specific. |
| trigger |
true |
string |
Indicates which entity cause the
disconnection to occur. Valid values are 'network' for
network-initiated disconnections, 'platform' for disconnections
triggered by platform-based rules (such as a maximum connection
duration), or 'application' for disconnections performed as a
result of application actions (such as execution of a
<disconnect>). |
10.6.6: connection.redirected
This event MUST be emitted to indicate
a successful redirection of a connection. This event is a
transition to state DISCONNECTED .
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
| reason |
false |
string |
A redirect result code. Content of this
field is platform-specific. |
10.6.7: connection.merged
This event MUST be emitted to indicate
that a connection has been successfully merged with another
connection at the network level, and is therefore disconnected from
the CCXML application. This event is a transition to state
DISCONNECTED .
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
| mergeid |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection with which the
Connected referenced by this event was merged. |
Note that connectionid1 and
connectionid2 of the <merge>
element are present in this event as connectionid
property (see section 10.2.3) and mergeid property,
respectively
10.6.8: connection.failed
This event MUST be emitted when an
incoming or outgoing call fails to complete its connection. This
event is a transition to state FAILED .
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
| reason |
false |
string |
A failure reason code. Content of this
field is platform-specific. |
10.6.9: error.connection
This event MUST be emitted if a
platform operational error occurs on a connection which renders
that connection unusable. This event is a transition to state
ERROR .
If this is an off-platform event, the platform MUST implicitly tear down any existing bridges to
the connection and send a conference.unjoined to the
CCXML document once the media paths have been freed.
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation failed. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
10.6.10: connection.signal
This event MAY be emitted by the
platform to notify the application of non state changing Connection
related events. This event MUST NOT
directly change the state of the connection. Examples where
connection.signal could be generated include:
- DTMF received on the media stream after connection, perhaps
identifying call setup information such as DNIS;
- Messaging received by the protocol after connection, such as
that delivered by SIP INFO or ISDN FACILITY messages;
- Call analysis results indicating the results of answering
machine, FAX, TDD or modem detection attempts.
The Connection Object MAY be updated
with new or changed information as the result of a
connection.signal event.
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
10.6.11: conference.created
This event MUST be emitted when a
conference has been successfully established using
<createconference> . The fields of this event
are:
| conferenceid |
true |
string |
The ID of the Conference associated
with this event. |
| conference |
true |
ECMAScript Object |
An ECMAScript object reference to the
Conference object identified by the conferenceid property of
this event. |
| info |
false |
ECMAScript Object |
An object which provides additional
platform or protocol dependent information |
10.6.12: conference.destroyed
This event MUST be emitted when a
session detaches from a conference using
<destroyconference> . Note that this does not
imply that the underlying conference has necessarily been
destroyed, since there may be other sessions attached to that
conference. The fields of this event are:
| conferenceid |
true |
string |
The ID of the Conference associated
with this event. |
| info |
false |
ECMAScript Object |
An object which provides additional
platform or protocol dependent information |
10.6.13: conference.joined
This event MUST be emitted when two
resources (which are connections or conferences) have been bridged
using <join> or <createcall>
. The fields of this event are shown below.
If a session receives a ' conference.joined ' event
because it is attached to a Conference, either ' id1 '
or ' id2 ' may refer to a Connection/Dialog owned by
another session. Such identifiers are not locally meaningful to the
session receiving the event (although they can still be used for
logging or other purposes).
Join-related events (including conference.joined ,
conference.unjoined ,
error.conference.join , and
error.conference.unjoin ) use the id1 and
id2 attributes to identify the connections,
conferences, or dialogs against which the event occurs. The value
of id1 and id2 will depend on why the
event was generated, and will be set according to the following
rules:
- For events resulting from a
<join> or
<unjoin> operation, id1 and
id2 will have the same values supplied via the
id1 and id2 attributes in the original
element;
- For events resulting from a
<createcall>
with a joinid attribute, id1 will reflect
Connection ID of the created call, and id2 will have
the same value as the joinid attribute;
- For events resulting from a Connection, Conference, or Dialog
becoming unavailable,
id1 will reflect the ID of the
object that became unavailable, and id2 will reflect
the ID of the object it was previously joined to. Such events may
occur for many reasons - asynchronous disconnection,
<disconnect> , <merge> , or
<redirect> (on a Connection),
<destroyconference> , and
dialog.exit or <dialogterminate>
(on a Dialog). Failures may also cause the termination of bridges.
However, due to the asynchronous nature of CCXML, applications
should not generally rely on this ordering, since (for example) a
Connection might disconnect at the same time that an application
performs a <dialogterminate> .
The fields of this event are:
| id1 |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection, Conference or
Dialog representing a resource associated with this event. |
| id2 |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection, Conference or
Dialog representing a resource associated with this event. |
| object1 |
true |
string
ECMAScript Object |
A Connection, Conference or Dialog
object associated with this event. |
| object2 |
true |
string
ECMAScript Object |
A Connection, Conference or Dialog
object associated with this event. |
10.6.14: conference.unjoined
This event MUST be emitted when a
bridge is torn down between two resources using
<unjoin> .
A conference.unjoined MUST
also be emitted when a bridge needs to be torn down before an
element can be executed or when an event indicates the loss of a
one end of a bridge, such as when processing
<disconnect>, <redirect>,
<dialogterminate>, <destroyconference> or
<merge> elements or when receiving asynchronous events
such as connection.disconnected, error.connection or
error.dialog .
If a session receives a ' conference.unjoined '
event because it is attached to a Conference, either '
id1 ' or ' id2 ' may refer to a
Connection/Dialog owned by another session. Such identifiers are
not locally meaningful to the session receiving the event (although
they can still be used for logging or other purposes).
The ordering of the id1 and id2
attributes is as specified in 10.6.13:
conference.joined .
The fields of this event are:
| id1 |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection, Conference or
Dialog representing a resource associated with this event. |
| id2 |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection, Conference or
Dialog representing a resource associated with this event. |
| object1 |
true |
string
ECMAScript Object |
A Connection, Conference or Dialog
object associated with this event. |
| object2 |
true |
string
ECMAScript Object |
A Connection, Conference or Dialog
object associated with this event. |
10.6.15:
error.conference.create
The processing associated with the
<createconference> failed. The fields in this
event are:
| conferenceid |
true |
string |
The ID of the affected conference. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation failed. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
10.6.16:
error.conference.destroy
The processing associated with the
<destroyconference> failed. The fields in this
event are:
| conferenceid |
true |
string |
The ID of the affected conference. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation failed. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
10.6.17: error.conference.join
The processing associated with the <join>
failed.
The ordering of the id1 and id2
attributes is as specified in 10.6.13:
conference.joined .
The fields in this event are:
| id1 |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection, Conference or
Dialog representing a resource associated with this event. |
| id2 |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection, Conference or
Dialog representing a resource associated with this event. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation failed. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
10.6.18:
error.conference.unjoin
The processing associated with the <unjoin>
failed.
The ordering of the id1 and id2
attributes is as specified in 10.6.13:
conference.joined .
The fields in this event are:
| id1 |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection, Conference or
Dialog representing a resource associated with this event. |
| id2 |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection, Conference or
Dialog representing a resource associated with this event. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation failed. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
10.6.19:
connection.merge.failed
This event MUST be emitted when a
<merge> attempt fails. This event MUST NOT change the state of either of the
Connection Objects involved in the merge operation.
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
| mergeid |
true |
string |
The ID of the Connection with which the
Connected referenced by this event was merged. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
merge failed. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
Note that connectionid1 and
connectionid2 of the <merge>
element are present in this event as connectionid
property (see section 10.2.3) and mergeid property,
respectively
10.6.20:
error.connection.wrongstate
This event MUST be emitted when an
application attempts a telephony operation that is not legal for
the current state of the Connection Object. Note that the
Connection Object state is current as of the event currently being
processed, but may not reflect events that are currently queued, or
other events that occur before the request generated by an element
is processed; therefore, not all failures caused by the state of
the actual connection will result in
error.connection.wrongstate . This event indicates
that an application performed an action that it should know to be
illegal, and generally reflects an incorrectly written
application.
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation failed. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
| tagname |
true |
string |
This property must be set to the
ECMAScript string value of the name of the element that produced
the error (ie accept , reject , etc). |
10.6.21: error.conference
This event MUST be emitted when an
error occurs on a conference that a session has created or attached
to, and signals the termination of the referenced conference. It is
not necessary for applications to call
<destroyconference> after receiving an
error.conference event (in much the same way that it
is not necessary to call <disconnect> upon
receiving an error.connection event).
The fields of this event are:
| conferenceid |
true |
string |
The ID of the affected conference. |
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
operation failed. Content of this field is platform-specific. |
10.6.22:
connection.redirect.failed
This event MUST be emitted when an
error occurs when there is an error redirecting a connection using
the <redirect> element.
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
redirect failed. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
10.6.23:
connection.accept.failed
This event MUST be generated when a
request to accept an incoming connection cannot be completed. This
event MUST NOT change the state of the
Connection Object.
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
accept failed. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
10.6.24:
connection.reject.failed
This event MUST be generated when a
request to reject an incoming connection cannot be completed. This
event MUST NOT change the state of the
Connection Object.
This event includes the standard event and connection event
properties along with the following additional event specific
properties:
| reason |
true |
string |
A description of the reason the
reject failed. Content of this field is
platform-specific. |
11: Complex Examples
11.1: Calling Card Application
Caller calls an 800 number and after some interaction with an
IVR system
places an outbound call to a friend.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml" version="1.0">
<!-- Create our ccxml level vars -->
<var name="in_connectionid" expr="''" />
<var name="out_connectionid" expr="''" />
<!-- Set our initial state -->
<var name="currentstate" expr="'initial'" />
<eventprocessor statevariable="currentstate">
<!-- Deal with the incoming call -->
<transition state="initial" event="connection.alerting" >
<assign name="in_connectionid" expr="event$.connectionid" />
<accept connectionid="in_connectionid" />
</transition>
<transition state="initial" event="connection.connected">
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'in_vxml_session'" />
<!-- VoiceXML dialog is started on a separate thread - see pin.vxml -->
<dialogstart namelist="session.id" connectionid="in_connectionid" src="'pin.vxml'" />
</transition>
<!-- happens when pin.vxml VoiceXML dialog thread exits -->
<transition state="in_vxml_session" event="dialog.exit">
<createcall dest="'tel:+' + event$.values.telnum" connectionid="out_connectionid" />
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'calling'" />
</transition>
<transition state="calling" event="connection.failed">
<!-- tell the caller there was a error -->
<dialogstart namelist="session.id" connectionid="in_connectionid" src="'error.vxml'" />
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'outb_failed'" />
</transition>
<!-- happens when called party picks up the phone -->
<transition state="calling" event="connection.connected">
<assign name="out_connectionid" expr="event$.connectionid" />
<!-- tell the callee he is receiving a call -->
<dialogstart namelist="session.id" connectionid="out_connectionid" src="'callee.vxml'" />
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'outb_ready_to_join'" />
</transition>
<transition state="outb_failed" event="dialog.exit">
<exit />
</transition>
<!-- happens when callee's vxml dialog (callee.vxml exits) -->
<transition state="outb_ready_to_join" event="dialog.exit">
<join id1="in_connectionid" id2="out_connectionid" />
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'wtg_for_joined'" />
</transition>
<transition state="wtg_for_joined" event="ccxml.joined">
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'active'" />
</transition>
<!-- Lets clean up the call -->
<transition state="active" event="connection.disconnected" >
<if cond="event$.connectionid == in_connectionid">
<disconnect connectionid="out_connectionid"/>
<exit />
</if>
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'in_vxml_session'" />
<!-- start VoiceXML dialog again to see
if caller wants to make another call -->
<dialogstart namelist="session.id" connectionid="in_connectionid" src="'pin.vxml'" />
</transition>
<!-- Catch disconnects in unexpected states -->
<transition event="connection.disconnected">
<exit />
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml
http://www.w3.org/TR/voicexml20/vxml.xsd"
version="2.0">
<form id="pin">
<block> Welcome to Acme's Calling Card </block>
<field name="pin" type="digits">
<prompt> Please say your PIN number </prompt>
<filled>
<if cond="pin.length != 8">
<clear namelist="pin"/>
<else/>
<submit next="checktime.asp" namelist="pin"/>
</if>
</filled>
</field>
</form>
</vxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form>
<block>
Sorry. The Party you are trying to call
is unavailble.
<exit/>
</block>
</form>
</vxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form>
<block>You have a call. Connecting</block>
</form>
</vxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form id="form2">
<!--.asp consults back-end database before filling this value-->
<assign name="timeleft" expr="600"/>
<block> Time remaining is <value expr="timeleft"/> seconds </block>
<field name="telnum" type="digits" >
<prompt> Please speak the telephone number you want to call including the country code.
for example you would say <say-as interpret-as="characters">14075551234</say-as>
</prompt>
<filled>
<exit namelist="telnum"/>
</filled>
</field>
</form>
</vxml>
11.2: Conferencing application
Different callers call into a conference through an agreed upon
telephone number. When each one of them joins the conference he is
told how many people are there in the conference and those already
in the conference are informed about a new entrant to the
conference. Similarly when someone hangs up, the fact that a
conference participant has exited is announced. A conference object
is created at the beginning of the conference and is destroyed when
all the participants have hung up.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml" version="1.0">
<var name="in_connectionid" expr="''" />
<var name="currentstate" expr="'initial'" />
<eventprocessor statevariable="currentstate">
<transition state="initial" event="connection.alerting">
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'alerting'" />
<assign name="in_connectionid" expr="event$.connectionid" />
<accept connectionid="in_connectionid" />
</transition>
<transition state="alerting" event="connection.connected">
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'fetching'" />
<fetch next="'http://example.com/conference.asp'" namelist="in_connectionid" />
</transition>
<transition state="fetching" event="fetch.done" >
<goto fetchid="event$.fetchid" />
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml" version="1.0">
<var name="conf_id" expr="''" />
<var name="currentstate" expr="'starting'" />
<var name="in_connectionid" expr="'0f0c0d@host1.com'" />
<!-- above value is the value submitted to conference.asp-->
<eventprocessor statevariable="currentstate">
<transition state="starting" event="ccxml.loaded">
<createconference conferenceid="conf_id" />
</transition>
<transition state="starting" event="conference.created" >
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'fetching'" />
<fetch next="'http://example.com/conference.asp'" namelist="in_connectionid conf_id" />
</transition>
<transition state="fetching" event="fetch.done" >
<goto fetchid="event$.fetchid" />
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml" version="1.0">
<var name="currentstate" expr="'ready_to_conf'" />
<var name="in_connectionid" expr="'ff0d01@host2.com'" />
<var name="conf_id" expr="'0a4602@host1.com'" />
<!-- above values are the values submitted to conference.asp-->
<eventprocessor statevariable="currentstate">
<transition event="ccxml.loaded">
<dialogstart connectionid="in_connectionid" src="'vconference.asp'" />
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'announcing'" />
</transition>
<transition state="announcing" event="dialog.exit">
<join entertone="false" exittone="false" id1="conf_id" id2="in_connectionid" />
<join entertone="'false'" exittone="'false'" id1="conf_id" id2="in_connectionid" />
</transition>
<transition state="announcing" event="conference.joined">
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'active'" />
<dialogstart conferenceid="conf_id" src="'newcaller.vxml'" />
</transition>
<transition state="active" event="connection.disconnected">
<dialogstart conferenceid="conf_id" src="'leave.vxml'" />
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'fetching'" />
<fetch next="'http://example.com/teardown.asp'" namelist="in_connectionid conf_id" />
</transition>
<transition state="fetching" event="fetch.done">
<goto fetchid="event$.fetchid" />
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form>
<block>
Welcome to the W3C conference. There are already
<value expr="'3'" />
participants in the conference.
<!--above value is based on count kept by vconference.asp-->
</block>
</form>
</vxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form>
<block>
A new participant has entered the conference.
</block>
</form>
</vxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form>
<block>
Someone just left the conference.
</block>
</form>
</vxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml" version="1.0">
<var name="currentstate" expr="'destroying'" />
<var name="conf_id" expr="'0a4602@host1.com'" />
<var name="in_connectionid" expr="'ff0d01@host2.com'" />
<!-- above values are the values submitted to teardown.asp-->
<eventprocessor statevariable="currentstate">
<transition event="ccxml.loaded">
<exit />
<!-- just exit and destroy the session -->
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml" version="1.0">
<assign name="currentstate" expr="'destroying'" />
<assign name="conf_id" expr="'0a4602@host1.com'" />
<assign name="in_connectionid" expr="'ff0d01@host2.com'" />
<!-- above values are the values submitted to teardown.asp -->
<eventprocessor statevariable="currentstate">
<transition event="ccxml.loaded">
<destroyconference conferenceid="conf_id" />
<exit />
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
11.3: Personal Assistant
This program is a Personal Assistant that operates as an
automated answering service.
A subscriber to this service would receive a phone number to the
automated service. When a caller wants to talk to the subscriber,
he calls the given number. This automated system asks who the
caller is, and records the audio. Then the system calls the current
number of the target person, and asks if the call should be
connected.
If so, the calls are bridged. If not, then the original caller
is warned and disconnected.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml" version="1.0">
<var expr="'initial'" name="currentstate" />
<var name="in_connectionid" />
<var name="dlg_onhold" />
<var name="out_connectionid" />
<var name="accepted" />
<eventprocessor statevariable="currentstate">
<transition event="connection.alerting" state="initial">
<assign expr="event$.connectionid" name="in_connectionid" />
<accept />
</transition>
<transition event="connection.connected" state="initial">
<assign expr="'welcoming_caller'" name="currentstate" />
<dialogstart src="'welcome_message.vxml'" />
</transition>
<transition event="dialog.exit" state="welcoming_caller">
<!-- place the caller on hold -->
<dialogstart dialogid="dlg_onhold" connectionid="in_connectionid" src="'holdmusic.vxml'" />
<!-- Contact the target. The number here is server-generated -->
<assign expr="'contacting_target'" name="currentstate" />
<createcall dest="'tel:+1-555-555-6666'" connectionid="out_connectionid" />
</transition>
<transition event="connection.connected" state="contacting_target">
<!-- Ask the target if (s)he would like to accept the call -->
<assign expr="'waiting_for_target_answer'" name="currentstate" />
<dialogstart src="'outbound_greetings.vxml'" />
</transition>
<transition event="dialog.exit" state="waiting_for_target_answer">
<assign expr="event$.values.willaccept" name="accepted" />
<if cond="accepted == 'false'">
<!-- disconnect the called party (but still notify the other one) -->
<disconnect connectionid="out_connectionid" />
</if>
<assign expr="'stop_hold'" name="currentstate" />
<dialogterminate dialogid="dlg_onhold" />
</transition>
<transition event="dialog.exit" state="stop_hold">
<if cond="accepted == 'false'">
<assign expr="'voice_mail'" name="currentstate" />
<dialogstart connectionid="in_connectionid" src="'vm.vxml'" />
<else />
<assign expr="'playing_connecting'" name="currentstate" />
<dialogstart connectionid="in_connectionid" src="'connecting.vxml'" />
</if>
</transition>
<transition event="dialog.exit" state="playing_connecting">
<join id1="in_connectionid" id2="out_connectionid" />
<assign expr="'talking'" name="currentstate" />
</transition>
<transition event="connection.disconnected" >
<if cond="event$.connectionid == in_connectionid">
<exit />
</if>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form>
<record name="recording">
<prompt>
You have reached the personal assistant for Bill Lumbergh of InnoTech.
If is about the new TPS format please call Dom Portwood to get the new cover sheet.
If this is for any other reason go on and state your name
and I will decide if I want to take your call.
Oh ya, if this is Milt, we're gonna need to go ahead and
move you downstairs into storage B. We have some new people
coming in, and we need all the space we can get. So if you
could go ahead and pack up your stuff and move it down there,
that would be terrific, OK
</prompt>
<filled>
OK, thanks.
<submit next="postRecordingAndExit.vxml" namelist="recording" />
</filled>
</record>
</form>
</vxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<var name="willaccept"/>
<form>
<field id="answer">
<grammar src="yesnogrammar.grxml" />
<prompt>
Hi bill, you have a message from
<audio src="dynamicallyRecordedName.wav" />
Would you like to take it? Say Yes, or No.
</prompt>
<filled>
<if cond="answer=='yes'">
Just a moment, please hold.
<assign name="willaccept" value="true" />
<exit namelist="willaccept" />
<elseif cond="answer==no" />
OK, goodbye.
<assign name="willaccept" value="false" />
<exit namelist="willaccept" />
</if>
</filled>
</field>
</form>
</vxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form>
<prompt>
Transferring you to voice mail hell.
</prompt>
<block>
<goto next="voicemail.vxml" />
</block>
</form>
</vxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form>
<prompt>
Just a moment, please hold...
</prompt>
<block>
<exit />
</block>
</form>
</vxml>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml" version="2.0">
<form id="Form">
<block>
<prompt bargein="false">
When a man loves a woman
Can't keep his mind on nothin' else
He'd trade the world
For a good thing he's found
If she is bad, he can't see it
She can do no wrong
Turn his back on his best friend
If he puts her down.
</prompt>
<goto next="holdmusic.vxml" />
</block>
</form>
</vxml>
CPL
The Call Processing Language [ CPL ] is an XML based language that can be used
to describe and control Internet telephony services. Its focus is
user scripting of call handling behavior for incoming calls. It is
designed to be suitable for running on a server where users may not
be allowed to execute arbitrary programs, and so is not
Turing-complete.
CallXML
CallXML [ CALLXML ] is a markup language created by Voxeo
Corporation that includes both voice and call-control
functionality. CallXML is an XML based markup language used to
describe the user interface of a telephone, voice over IP, or
multi-media call application to a CallXML browser.
CallXML was designed to make it easy for Web developers to
create applications that can interact with and control any number
or type of calls, including:
- Telephone or Voice over IP call applications which can control
the initiation and routing of a phone call itself, supporting such
features as outbound dialing, conferencing, and multi-call
interactions (e.g., conference bridges, Internet call waiting,
follow-me/find-me, etc)
- Telephone or Voice over IP call applications which can easily
interact and respond to touch-tone based entry and selection (e.g.,
voicemail, interactive voice response)
- Call Applications which include support for additional media,
such as faxes and video (e.g., unified messaging, video
conferencing, etc.)
ECMA-CSTA
The description of CSTA [ CSTA ] from http://www.ecma-international.org/ is
as follows:
"CSTA specifies an Applications Interface and Protocols for
monitoring and controlling calls and devices in a communications
network.
These calls and devices may support various media and can reside
in various network environments such as IP, Switched Circuit
Networks and mobile networks. CSTA however, abstracts various
details of underlying signalling protocols (e.g. SIP/H.323) and
networks for the applications."
The architecture of CCXML would allow a platform to be based on
CSTA for the underlying telephony protocol while still providing
the CCXML execution environment for ease of integration with voice
browsers.
TXML
TXML (Telera's Extensible Markup Language) [ TXML ] is an XML based language
designed by Genesys (formerly Telera) for remotely controlling the
behavior of Point of Presence (POP) servers.
TXML provides the syntax for the XML Pages, which are generated
at the customer's application at the premises and used by a POP
server to execute actions on behalf of the customer's application.
The XML Pages are simple ASCII text files that are either stored in
a Web server's directory at the premises or generated by scripts at
the premises server. The XMLPages are requested from the premises
server via HTTP requests made by a
client on the POP gateway.
The language includes elements for
- Media Control
- Call Control and Telephony
- Call Router Integration
SIP
SIP, the Session Initiation Protocol, [ RFC3261 ] is a signaling
protocol for Internet conferencing, telephony, presence, events
notification and instant messaging. As a signaling protocol, SIP
sits "below" the application description level of VoiceXML and
CCXML. We expect many CCXML and VoiceXML browsers to support SIP
signaling.
Appendix B - CCXML DTD
This section is Normative.
The CCXML DTD is located at http://www.w3.org/TR/2010/CR-ccxml-20100401/ccxml.dtd
.
Appendix C - CCXML XML Schema
This section is Normative.
The CCXML schema is located at http://www.w3.org/TR/2010/CR-ccxml-20100401/ccxml.xsd
.
Appendix D - VoiceXML 2.0 Integration
Details
This section is Normative.
D.1 Overview
This section describes the details of how CCXML and VoiceXML 2.0
work together to provide dialog functionality in CCXML.
The CCXML application behaviors described below are guidelines
and applications are not required to support the full set of
VoiceXML interactions. Platforms however should support the events
and methods specified below to allow CCXML applications to
implement the behaviors documented in this Appendix.
Since HTTP is a stateless protocol, application servers
typically use cookie-based and/or URI rewriting techniques to
enable stateful interactions with the server. Authors should be
aware that application servers employing cookie-based management
techniques will view concurrently executing CCXML and VoiceXML
applications as independent (the CCXML and VoiceXML cookie stores
are independent). Authors wishing to correlate CCXML and VoiceXML
data at the server can use URI rewriting or alternatively employ
the CCXML sessionid variable together with the connectionid or
conferenceid as a common, unique key across the CCXML and VoiceXML
applications.
D.2 Events
CCXML and VoiceXML 2.0 need to be able to exchange events
between the browsers. The method of the message passing is up to
the platform but it is assumed that there is some basic capacity in
place.
Each running CCXML session has an event queue used to process
CCXML events, independently of VoiceXML event processing by the
dialogs created by that CCXML session. The execution of certain
CCXML elements, such as <dialogterminate> and
<send> , may cause events to be sent to the
VoiceXML browser; similar, certain VoiceXML elements such as
<transfer> will result in the generation of
dialog events delivered to the CCXML session that owns the dialog
in question. The sections below define the event relationship
between the CCXML and VoiceXML environments.
VoiceXML 2.0 provides limited capabilities for handling
asynchronous or unexpected events. Since CCXML is designed around a
robust event processing mechanism, and since the CCXML session
manages connections to the underlying network, processing of
asynchronous events - which may be delivered through externally
accessible event I/O processors - typically occurs primarily within
the CCXML application, which can then control the VoiceXML session
as appropriate. The VoiceXML dialog can therefore focus exclusively
on interaction with the user.
D.3 VoiceXML Session
Variables
When a VoiceXML dialog is bridged to a connection with an
associated call leg, the standard VoiceXML session variables obtain
their values from the call leg. Otherwise, these variables are
undefined. After the dialog is bridged to a connection, VoiceXML
session variables are not updated again. CCXML defines an
additional read-only VoiceXML session variable, also populated when
the dialog is bridged to a connection, called
session.connection.ccxml with the following
sub-properties:
- session.connection.ccxml.sessionid
- This variable evaluates to the CCXML Session ID to which the
VoiceXML dialog is currently associated.
- session.connection.ccxml.dialogid
- This variable evaluates to the CCXML Dialog ID for the current
dialog.
- session.connection.ccxml.connectionid
- This variable evaluates to the CCXML Connection ID to which the
VoiceXML dialog is currently bridged. This variable is undefined if
the dialog is not bridged to a connection.
- session.connection.ccxml.conferenceid
- This variable evaluates to the CCXML Conference ID to which the
VoiceXML dialog is currently bridged. This variable is undefined if
the dialog is not bridged to a conference.
- session.connection.ccxml.values
- This associative array contains the names and values of the
parameters attribute supplied in a CCXML
<dialogprepare> or
<dialogstart> invocation.
D.4 CCXML
<dialogprepare>
When a CCXML application processes a
<dialogprepare> element it prepares a VoiceXML
application with the URI that is passed in on the
<dialogprepare> element.
Normally it is expected that a VoiceXML dialog environment will
use the <dialogprepare> request as an
opportunity to fetch the initial document indicated by the
src and namelist attributes along with
any referenced resources such as <audio> ,
<script> , and <grammar>
elements marked as prefetchable.
Even if a VoiceXML dialog environment is unable to perform any
useful preparation the CCXML implementation MUST support the <dialogprepare>
element and deliver a dialog.prepared event in
response. The implementation MUST as a
minimum, note the values provided via the src ,
namelist , and connectionid attributes,
create a Dialog object, and return a new unique value to the
location defined by the dialogid attribute.
D.5 CCXML
<dialogstart>
When a CCXML application processes a
<dialogstart> element it starts up a VoiceXML
application on the connection with the URI that is passed in on the
<dialogstart> element or to the dialog that was
prepared using <dialogprepare> and specified
using the prepareddialogid attribute.
D.6 CCXML
<dialogterminate>
When a CCXML application processes a
<dialogterminate> it causes a
"connection.disconnect.hangup" event to be thrown to
the VoiceXML application. As far as the VoiceXML application knows
the call was just disconnected. The VoiceXML application still has
a chance to return data to the CCXML application by using
<exit> in its <catch>
statement.
D.7 VoiceXML
<exit>
When a VoiceXML application processes a VoiceXML
<exit> it will cause the VoiceXML application to
exit and return the contents of the namelist attribute
to the CCXML application in the "dialog.exit" event in
the following form:
<exit namelist="foo bar jar"/>
maps into an event that looks like the following:
dialog.exit
values.foo
values.bar
values.jar
and could be accessed in a CCXML Application like this:
<!-- Process the incoming call -->
<transition state="dialogActive" event="dialog.exit">
<log expr="'Houston, the dialog foo: [' + event$.values.foo + ']'" />
<log expr="'Houston, the dialog bar: [' + event$.values['bar'] + ']'" />
<var name="xxx" expr="'jar'/>
<log expr="'Houston, the dialog jar: [' + event$.values[xxx] + ']'" />
<exit />
</transition>
If the VoiceXML application is returning data using the
expr attribute the data will be stored in
"values" .
<!-- Process the incoming call -->
<transition state="dialogActive" event="dialog.exit">
<log expr="'Houston, the dialog using expr [' + event$.values + ']'" />
<exit />
</transition>
D.8 VoiceXML
<disconnect>
When the VoiceXML application processes a
<disconnect> element it causes a
"dialog.disconnect" event to be thrown in the CCXML
application. It is then up to the CCXML application to disconnect
the call and sends back a
"connection.disconnect.hangup" event by using the
<dialogterminate> element. The following is an
example of what would happen:
- The VoiceXML application executes a
<disconnect> .
- As a result, the VoiceXML interpreter sends a disconnect event
to CCXML.
- CCXML receives a
"dialog.disconnect" event from
the VoiceXML application. It interprets this as a request from the
VoiceXML application to "please disconnect me".
- An eventprocessor in the CCXML document SHOULD have a
<transition>
element intended to handle the "dialog.disconnect"
event.
- The CCXML application would have a
<disconnect> element as the child of the
transition event. This would disconnect the call.
- An eventprocessor in the CCXML document should have a
<transition> element intended to handle the
"connection.disconnected" event.
- The
<transition> element has a child element
which performs a <dialogterminate> on the
dialog.
Here is the example CCXML code that completes the disconnect and
returns the "connection.disconnect.hangup" event back
to VoiceXML using <dialogterminate> :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<var name="dialogid"/>
<eventprocessor statevariable="mystate">
<transition event="dialog.disconnect">
<assign name="dialogid" expr="event$.dialogid"/>
<disconnect connectionid="event$.connectionid" />
</transition>
<transition event="connection.disconnected" >
<dialogterminate dialogid="dialogid"/>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
D.9 VoiceXML
<transfer>
When a VoiceXML application processes a
<transfer> element it is handled within CCXML
via series of events between the VoiceXML platform and the CCXML
application. The type of transfer is controlled in VoiceXML 2.0 by
the bridge attribute. If the value of
bridge is " true " this will come in with
a transfer type of " bridge " and if the value is "
false " it will have a type of " blind ".
Here is an example of the logic to support the VoiceXML 2.0
transfer types:
- The VoiceXML application executes a
<transfer> causing a
dialog.transfer event to be sent to the CCXML
Session.
- The CCXML document should have a
<transition> to handle the
dialog.transfer event. This transition should
implement the logic in the following steps.
- If the
type attribute of the
dialog.transfer event is " blind "
perform the following:
- Execute a
<redirect> to move the call to URI
specified in the dialog.transfer event
- The CCXML Application sends a
connection.disconnect.transfer event to inform the
VoiceXML session that the <transfer> is
complete.
- If the
type attribute of the
dialog.transfer event is " bridge "
perform the following:
- Invoke a
<createcall> to create an outgoing
call leg.
- If the
<createcall> completes with a
connection.connected event then do the following:
- Join the two call leg together as full duplex and if needed
start a
maxtime timer.
- If a
connection.disconnected event comes in for
the original party:
- Disconnect the new party
- Return a
connection.disconnect.hangup using
<dialogterminate> to the VoiceXML session.
- If a
connection.disconnected event comes in for
the new party:
<join> the original connection back to the
dialog full dupex- return a
dialog.transfer.complete event to the
dialog with a reason of far_end_disconnect .
- If a
maxtime event comes in:
- Disconnect the new party
<join> the original connection back to the
dialog full dupex- send a
dialog.transfer.complete event to the
dialog with a reason of maxtime_disconnect
- If a
dialog.terminatetransfer event comes in:
- Disconnect the new party
<join> the original connection back to the
dialog full dupex- send a
dialog.transfer.complete event to the
dialog with a reason of near_end_disconnect
- If the
<createcall> fails with a
connection.failed event then do the following:
- Send a
dialog.transfer.complete event to the
VoiceXML dialog with the failure reason.
- If the
type attribute of the
dialog.transfer event is bridge , and if
early media is desired/permissible, then the above steps should be
performed with the following exceptions:
- When invoking
<createcall> to create the
outgoing call leg, the joinid attribute should be
specified and should refer to the connection ID of the inbound leg
associated with the dialog performing the
<transfer> ;
- If the
<createcall> completes with a
connection.connected event, start a maxtime timer (if
needed), but do not perform a <join> (since the
calls are already joined).
dialog.transfer.complete
This event MUST be sent from the CCXML
application to the Dialog which uses this to fill transfer results
(i.e. for VoiceXML platforms to fill field item results). The
<send> attributes used to send this event
are:
| target |
true |
ECMAScript Expression |
dialogid of the dialog whose
transfer is complete |
| targettype |
true |
ECMAScript Expression |
dialog |
| sendid |
false |
ECMAScript Left Hand Side Expression |
Optional sendid |
| delay |
false |
ECMAScript Expression |
Optional delay |
| name |
true |
ECMAScript Expression |
dialog.transfer.complete |
| namelist |
true |
Var List |
results object with the value of the transfer field to be
filled in |
An example of this send element is below:
<var name="results" expr="'near_end_disconnect'">
<send name="'dialog.transfer.complete'"
target="dialogid"
targettype="'dialog'"
namelist="results" />
dialog.terminatetransfer
The VoiceXML interpreter is responsible for throwing this event
when a "hotword" grammar is matched while performing a bridged
transfer.
D.10 User Disconnect
When a caller hangs up on one of the connections the VoiceXML
dialog is not automatically disconnected. The CCXML application
then needs to send a "connection.disconnect.hangup"
event to the VoiceXML application by using the
<dialogterminate> element so it can complete any
cleanup that is required. The VoiceXML application can then still
return data to the CCXML application by using the VoiceXML
<exit> element.
D.11 VoiceXML 2.0
Example
The following example code shows how you would duplicate the
standard VoiceXML 2.0 Interpreter Context in a CCXML Application.
This example is not meant to be a complete application and does not
handle all error events but is rather meant to give an overview of
what such an application may look like.
You may also download
the source of this application.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml">
<!-- Declare the vars we are going to use -->
<var name="in_connectionid" />
<var name="out_connectionid" />
<var name="dialogid" />
<var name="vxml_maxtime"/>
<var name="URI"/>
<var name="maxtime_sendid"/>
<var name="results"/>
<!-- Set an initial state -->
<var name="mystate" expr="'init'"/>
<eventprocessor statevariable="mystate">
<!--
- Deal with an incoming call
-->
<transition state="init" event="connection.alerting">
<!-- Save off the connection ID -->
<assign name="in_connectionid" expr="event$.connectionid" />
<accept connectionid="event$.connectionid"/>
</transition>
<!--
- Call is connected so lets start the dialog
-->
<transition state="init" event="connection.connected">
<dialogstart connectionid="event$.connectionid"
src="http://www.example.com/dialog.vxml"
dialogid="dialogid"/>
<assign name="mystate" expr="'connected'" />
</transition>
<!--
- Dialog is active
-->
<transition state="connected" event="dialog.started">
<assign name="mystate" expr="'dialogActive'" />
</transition>
<!--
- Dialog requests that we disconnect the call
-->
<transition state="dialogActive" event="dialog.disconnect">
<disconnect connectionid="event$.connectionid" />
<assign name="mystate" expr="'disconnecting'" />
</transition>
<!--
- We have disconnected the call. Do a dialog terminate to the dialog.
-->
<transition state="disconnecting" event="connection.disconnected">
<dialogterminate dialogid="dialogid"/>
</transition>
<!--
- Dialog has exited after we disconnected the call.
- We just are going to exit from this CCXML session...
-->
<transition state="disconnecting" event="dialog.exit">
<exit/>
</transition>
<!--
- The caller disconnected. We need to send the event up to
- the Dialog and change our state.
-->
<transition state="dialogActive"
event="connection.disconnected">
<dialogterminate dialogid="dialogid"/>
<assign name="mystate" expr="'userDisconnect'" />
</transition>
<!--
- Dialog has exited after the caller hungup.
- We just are going to exit from this CCXML session...
-->
<transition state="userDisconnect" event="dialog.exit">
<exit/>
</transition>
<!--
-
- Handle a transfer request from a VXML script.
-
-->
<transition state="dialogActive" event="dialog.transfer">
<!-- Branch on transfer type -->
<if cond="event$.type == 'blind'">
<!-- Bridge == false. We are going to just redirect the call -->
<!-- Update our state var -->
<assign name="mystate" expr="'redirecting'" />
<!-- And redirect to the uri specified in the event -->
<redirect connectionid="in_connectionid" dest="event$.URI" />
<redirect connectionid="in_connectionid" dest="event$.uri" />
<!-- Just send the success event to the dialog -->
<send name="'connection.disconnect.transfer'"
target="dialogid"
targettype="'dialog'"/>
<else/>
<!-- Bridge == true. In this case we need to
place a call and bridge the calls -->
<!-- save off maxtime -->
<assign name="vxml_maxtime" expr="event$.maxtime" />
<!-- Update our state var -->
<assign name="mystate" expr="'calling'" />
<!-- Place the call using the values from the transfer request -->
<assign name="URI" expr="event$.URI" />
<createcall dest="event$.URI"
<assign name="URI" expr="event$.uri" />
<createcall dest="event$.uri"
connectionid="out_connectionid"
aai="event$.aai"
timeout="event$.connecttimeout"/>
</if>
</transition>
<!--
- We will get the following events but we do not do anything
- because in VoiceXML 2.0 you just ignore redirect errors.
- We do however process the dialog.exit and shutdown
- the CCXML Session.
-->
<transition state="redirecting"
event="connection.redirected">
</transition>
<transition state="redirecting" event="connection.redirect.failed">
</transition>
<transition state="redirecting" event="dialog.exit">
<exit/>
</transition>
<!--
-
- Handle bridge=true Events
-
- This first event is for if the outbound call failed.
-
-->
<transition state="calling" event="connection.failed">
<!-- Just send the error event to the dialog -->
<assign name="results" expr="event$.reason"/>
<send name="'dialog.transfer.complete'"
target="dialogid"
targettype="'dialog'"
namelist="results" />
<!-- Update our state var back to the original state -->
<assign name="mystate" expr="'dialogActive'" />
</transition>
<!--
- The outbound call has been answered.
-->
<transition state="calling" event="connection.connected">
<!-- Update our state var back to show that we are connected -->
<assign name="mystate" expr="'outgoing_call_active'" />
<!-- Unjoin the calls before it can be connected to other call -->
<join id1=" dialogid" id2=" in_connectionid" duplex="'half'" dtmfclamp="false"/>
</transition>
<!--
- Now connecte the outbound.
-->
<transition state="outgoing_call_active" event="conference.joined">
<!-- Join the two calls together -->
<join id1="in_connectionid" id2="out_connectionid" duplex="'full'" />
</transition>
<!--
- We will get here once the join completes.
-->
<transition state="outgoing_call_active"
event="conference.joined">
<!-- If maxtime has been set then we setup a timer -->
<if cond="vxml_maxtime != null">
<send name="'vxml_maxtime'"
target="session.id"
delay="vxml_maxtime"
sendid="maxtime_sendid"/>
</if>
</transition>
<!--
- Deal with someone disconnecting.
-->
<transition state="outgoing_call_active"
event="connection.disconnected">
<!-- Cancel any maxtime events that are waiting to be fired -->
<if cond="maxtime_sendid != null">
<cancel sendid="maxtime_sendid"/>
<assign name="maxtime_sendid" expr="null"/>
</if>
<!-- Branch off based on what call leg this is for and send
the proper event to the dialog -->
<if cond="event$.connectionid == out_connectionid">
<assign name="results" expr="'far_end_disconnect'" />
<send name="'dialog.transfer.complete'"
target="dialogid"
targettype="'dialog'"
namelist="results" />
<!-- Update our state var back to the original state -->
<assign name="mystate" expr="'dialogActive'" />
<else />
<!-- Set our state to show that the
original caller is disconnected. -->
<assign name="mystate" expr="'userDisconnect'" />
<dialogterminate dialogid="dialogid"/>
</if>
</transition>
<!--
- Deal with a "hotword" type event where the dialog
- requests that we stop the transfer.
-->
<transition state="outgoing_call_active"
event="dialog.terminatetransfer">
<!-- Change our state to show we are dealing with hotword stuff -->
<assign name="mystate" expr="'hotword'" />
<!-- Cancel any maxtime events that are waiting to be fired -->
<if cond="maxtime_sendid != null">
<cancel sendid="maxtime_sendid"/>
<assign name="maxtime_sendid" expr="null"/>
</if>
<!-- unjoin our connections -->
<unjoin id1="in_connectionid" id2="out_connectionid"/>
</transition>
<!--
- Calls have been unjoined.
-->
<transition state="hotword" event="conference.unjoined">
<!-- Rejoin the first connection to the dialog -->
<join id1="in_connectionid" id2="dialogid"/>
<!-- Disconnect the outbound call -->
<disconnect connectionid="out_connectionid"/>
</transition>
<!--
- Send an event to the dialog once we are all back together again.
-->
<transition state="hotword" event="conference.joined">
<!-- Build up our event -->
<assign name="results" expr="'near_end_disconnect'" />
<send name="'dialog.transfer.complete'"
target="dialogid"
targettype="'dialog'"
namelist="results" />
<!-- Update our state var back to the dialogActive state -->
<assign name="mystate" expr="'dialogActive'" />
</transition>
<!--
- Deal with connection.disconnected events in the hotword state.
- We are only going to deal with stuff if the event is
- for the incoming call.
-->
<transition state="hotword" event="connection.disconnected">
<if cond="event$.connectionid == in_connectionid">
<dialogterminate dialogid="dialogid"/>
<!-- Update our state var to the userDisconnect state -->
<assign name="mystate" expr="'userDisconnect'" />
</if>
</transition>
<!--
- Deal with the maxtime event during a call transfer.
- Should this happen we just disconnect the outbound call leg
- and get back to the dialogActive state.
-
- Step one is to disconnect the call...
-->
<transition state="outgoing_call_active"
event="vxml_maxtime">
<assign name="maxtime_sendid" expr="null"/>
<assign name="mystate" expr="'maxtime'" />
<disconnect connectionid="out_connectionid"/>
</transition>
<!--
- Once we have the disconnect event we verify that we
- got it for the outbound call and rejoin the dialog to the
- inbound call. If the inbound call disconnected
- we are going to go on and forward the event along
- and wait for the dialog to exit.
-
-->
<transition state="maxtime" event="connection.disconnected">
<if cond="event$.connectionid == out_connectionid">
<join id1="dialogid" id2="in_connectionid"/>
<else />
<dialogterminate dialogid="dialogid"/>
</if>
</transition>
<!--
-
- We are rejoined. Update our state and send the transfer
- event back to the dialog.
-
-->
<transition state="maxtime" event="conference.joined">
<!-- Update our state var back to the dialogActive state -->
<assign name="mystate" expr="'dialogActive'" />
<assign name="results" expr="'maxtime_disconnect'" />
<send name="'dialog.transfer.complete'"
target="dialogid"
targettype="'dialog'"
namelist="results" />
</transition>
<!--
- Dialog has exited while we were in a hotword state.
- We just are going to exit from this CCXML session...
-->
<transition state="maxtime" event="dialog.exit">
<exit/>
</transition>
<!--
-
- Deal with any extra random events that may come in.
-
-->
<!--
- Make sure that we deal with any extra dialog events
- by ending the session. A real ccxml app would do something
- better here.
-->
<transition event="dialog.*">
<exit/>
</transition>
<!--
- And do the same for any exit events.
-->
<transition event="error.*">
<exit/>
</transition>
<!--
- And last but not least catch any connection.disconnect
- events that made it past us.
-->
<transition event="connection.disconnected">
<exit/>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
Appendix E - Telephony
Protocol Names
Overview
This section defines a list of recommended telephony protocol names to be used in
CCXML platforms within the connection event objects (See 10.2.3: Connection Events ). Platforms
MUST use the following list when
available. If the protocol is not defined in this list the platform
MUST prefix the name with an underscore,
"_", to identify them as platform-dependent.
Protocol names
| Protocol
Name |
Details |
| sip |
Session
initiation protocol [ RFC3261 ]. |
| h323 |
ITU H.323
Voice over IP protocol [ H.323 ]. |
| q931 |
ISDN q.931
call control [ Q.931/DSS1 ]. |
| ss7 |
Signaling
System 7 [ SS7
]. |
| csta |
ECMA
Computer Supported Telecommunications Applications [ CSTA ]. |
| pots |
Plain Old
Telephone Service. |
| cas |
Channel
Associated Signaling. |
Appendix F - Changes
The following is the list of changes made
to this document at each stage of the Recommendation Track
process.
Changes in Working Draft 2
- Added the redirect element.
- Added the reason attribute to the disconnect and reject
elements.
- Removed the submit element.
- Updated the fetch element.
- Updated the goto element.
- Updated the exit element.
- Updated the createccxml element.
- Added the move element.
- Updated the DTD.
- Added a Schema.
- Updated the examples to match the new spec changes.
- Major Editorial Work.
- Updated transition element with default cond of "true".
- Updated the join element.
- Updated the unjoin element.
- Updated the createconference element.
- Updated the destroyconference element.
- Added ECMAScript.
- Added the script element.
- Updated the dialog interaction.
- Updated the dialogstart element
- Updated the dialogterminate element
- Added VoiceXML interaction section
- Added new dialog events
- Added new ccxml core events
- Updated attribute names to be more consistent
Changes in Working Draft 3
- Major editorial changes to reflect current status of the
document (Entire Document)
- Minor corrections to all examples to reflect changes to the
spec (Entire Document)
- Rewrote introduction (Section 1)
- Rewrote background (Section 2)
- Updated overview of call management (Section 3.3)
- Added CSS 2 times reference to the definitions section (Section
3.4.2)
- Rewrote section 4 introduction to cover updated object models
(Section 4)
- Updated description of <if>, <elseif> and
<else> (Section 6.2.2-6.2.6)
- Updated namelist attribute of <fetch> (Section
6.2.7.2)
- Updated method attribute of <fetch> (Section
6.2.7.2)
- Added timeout attribute of <fetch> (Section 6.2.7.2)
- Updated namelist attribute of <exit> (Section
6.2.10.2)
- Added <log> tag (Section 6.2.11)
- Updated threading description of section 6.3.1 (Section
6.3.1)
- Added clarification to "ccxml.loaded" event (Section
6.3.5)
- Updated overview of <dialogstart> to reflect object model
changes (Section 7.2.1.1)
- Updated overview of <dialogstart> having to do with
passing of call data (Section 7.2.1.1)
- Renamed the callid attribute to conid on <dialogstart>
(Section 7.2.1.2)
- Updated type attribute of <dialogstart> to make it a
ECMAScript expression (Section 7.2.1.2)
- Updated namelist attribute of <dialogstart> (Section
7.2.1.2)
- Added duplex attribute of <dialogstart> (Section
7.2.1.2)
- Renamed callid attribute of the "dialog.started" event to conid
(Section 7.3.2)
- Renamed callid attribute of the "dialog.exit" event to conid
(Section 7.3.3)
- Renamed callid attribute of the "dialog.disconnect" event to
conid (Section 7.3.4)
- Renamed callid attribute of the "dialog.transfer" event to
conid (Section 7.3.5)
- Renamed callid attribute of the "error.dialog.notstarted" event
to conid (Section 7.3.6)
- Renamed callid attribute of the "error.dialog.wrongstate" event
to conid (Section 7.3.7)
- Renamed callid attribute of the "dialog.user.*" event to conid
(Section 7.3.8)
- Added scope diagram to section 8.2.1.1 (Section 8.2.1.1)
- Updated event concepts in section 9.1 to reflect updated call
control model (Section 9.1)
- Updated event delivery details in section 9.1 to deal with user
specified event delay (Section 9.1)
- Added description to <eventhandler> details (Section
9.2.1)
- Removed id attribute from <eventhandler> (Section
9.2.1.1)
- Added description to <transition> details to explain
event selection (Section 9.2.2)
- Updated state attribute of the <transition> element to
allow for more then one state (Section 9.2.2.1)
- Updated event attribute of the <transition> element to
add regex support (Section 9.2.2.1)
- Added event matching text to define regex behavior (Section
9.2.2.2)
- Added clarification to <send> element processing (Section
9.2.3.1)
- Updated namelist attribute of the <send> tag (Section
9.2.3.2)
- Added clarification to <move> element processing (Section
9.2.4.1)
- Renamed endpoint attribute of <move> element to source
and minor updates (Section 9.2.4.2)
- Updated event attribute of <move> element (Section
9.2.4.2)
- Complete rewrite of most of section 9.4 to reflect new event
model (Section 9.4)
- Added error events section (Section 9.5)
- Major rewrite of section 10 introduction to reflect new call
control model (Section 10)
- Renamed callid attribute of
<accept> element
to conid (Section 10.1.2.2)
- Renamed callid attribute of <redirect> element to conid
(Section 10.1.3.2)
- Updated dest attribute of <redirect> element (Section
10.1.3.2)
- Renamed callid attribute of <reject> element to conid
(Section 10.1.4.2)
- Added <hold> tag (Section 10.1.5)
- Updated overview of
<createcall> element
(Section 10.2.1.1)
- Updated dest attribute of
<createcall>
(Section 10.2.1.2)
- Renamed name attribute of
<createcall> to
conid (Section 10.2.1.2)
- Added aai attribute to
<createcall> (Section
10.2.1.2)
- Added callerid attribute to
<createcall>
(Section 10.2.1.2)
- Added hints attribute to
<createcall>
(Section 10.2.1.2)
- Added use attribute to
<createcall> (Section
10.2.1.2)
- Added timeout attribute to
<createcall>
(Section 10.2.1.2)
- Added examples section to
<createcall>
(Section 10.2.1.3)
- Major rewrite of Section 10.3 and 10.4 to reflect new call
control models (Section 10.3 and 10.4)
- Updated disconnect section to update call control model
(Section 10.5)
- Renamed callid attribute of <disconnect> to conid
(Section 10.5.1.2)
- Added dialog attribute to <disconnect> (Section
10.5.1.2)
- Updated reason attribute of <disconnect> (Section
10.5.1.2)
- Updated details of the <authenticate> tag having to do
with the "ccxml.exit" event (Section 11.2.2)
- Updated all examples to work with changes (Section 12)
- Moved all issues to Appendix A (Appendix A)
- Added ECMA-CSTA to Appendix B (Appendix B)
- Updated DTD (Appendix C)
- Updated Schema (Appendix D)
- Updated VoiceXML Integration Details (Appendix E)
- Added Recommended Telephony Protocol names (Appendix F)
- Renamed Changes and Acknowledgments Appendixes (Appendixes G
and H)
Changes in Last Call Working Draft
- Rewrite of dialog section to prepare for LCWD. This includes
language cleanup and references to external specifications.
(Section 7)
- Rewrite of variables and expressions section to prepare for
LCWD. This includes language cleanup and references to external
specifications. (Section 8)
- Better details on variable scope issues. (Section 8)
- charset Attribute added to script tag. (Section 8)
- New section listing session variables. (Section 8.3)
- Rewrite of Event Handling section to prepare for LCWD. This
includes language cleanup and references to external
specifications. Some content has been moved to section 10. (Section
9)
- Rewrite of Telephony Operations and Resources section to
prepare for LCWD. This includes language cleanup and references to
external specifications. (Section 10)
- Removed incomplete security section. (Section 11)
- Removed inline DTD. (Appendix C)
- Removed inline Schema. (Appendix D)
- Updated Schema text. (Appendix D)
- Updated telephony protocol names to change "SHOULD" to be
"MUST". (Appendix F)
- Added CAS to list of telephony protocol names. (Appendix
F)
- Added references section. (Appendix I)
- Update of if, elseif, else tags. (Section 6)
- New table formats
- New example formats
- Updated text for section 9. (Section 9)
- Updated text for section 10. (Section 10)
- Updated text for section 6. (Section 6)
- Cleanup of text in full spec. (All)
- New session text. (Sections 1, 2, 3 and 6)
- CR 122 Text for XMLNS and XML-BASE. (Section 6)
- CR 133 Text for meta and metadata. (Section 6)
- Cleanup of Schema text. (Appendix D)
- Removal of "Section" in section titles. (All)
- Update references of <eventhandler> to
<eventprocessor>. (All)
- Update of Acknowledgments. (Appendix H)
- Change elements --> Elements in titles. (All)
- Correction of the use of the term "element". (All)
- Added ACRONYM tag for IVR. (All)
- Added telephony standard references in section 2. (Section
2)
- Added URI to defined terms. (Section 3.4.2)
- Cleanup of RFC2119 terms. (All)
- Added references to Appendix G. (Appendix G)
- Reworking of Appendix B (Appendix B)
- Update of Acknowledgments. (Appendix H)
- Split conid into conferenceid and connectionid for dialog
stuff. (Section 7)
- CR-136, createccxml/fetch updates. (Section 6)
- CR-140, hints attributes on telephony elements. (Section
10.5)
- CR-141, move, send, and cancel have no positive confirmation
event. (Section 9.3)
- Updated Schema (CR-130). (Appendix D)
- Updated DTD (CR-130). (Appendix C)
- Conference events. (Section 10)
- CR-131 src vs srcexpr on script. (Section 8)
- Added MIME Type registration info. (Appendix J)
- Some of the changes suggested by Paolo. (All)
- CR-139 text (Issues with send and cancel) (9.2.5)
- CR-52 (Conferencing) text. (10.5.5 and 10.5.7)
- CR-144 timeout attribute for createccxml. (6.2.9.2)
- Reworked Sections 1 and 2 from F2F meeting (Sections 1-2)
- CR-124 Session lifecycle (Section 3)
- CR-126 Simple Examples (Section 4)
- CR-128 Join Diagrams (Section 10)
- CR-138 Script src/expr changes (Section 8)
- CR-142 Dialog Dialogprepare (Section 7, Appendix E)
- Synced error attributes in all events to "reason" (All)
- changed session.mode to session.startupmode (Section 3 and
8)
- Added values for session.startupmode (Section 8)
- Reworked connection state text and changed from text list to
HTML tables. (Section 10.2.1)
- Update of status (Status)
- Removed old issue text (Appendix A)
- Updated DTD. (Appendix C)
- Added missing conferenceid attribute to dialogprepare. (Section
7)
- Removed old cancel attribute.
- Changes as requested by Jeff Haynie. (All)
- Updated Examples 1, 2 and 4. (Section 12)
- New Event I/O text. (Section 9)
- New TOC. (TOC)
- Lowercase Event Names. (All)
- Lots of minor text cleanup/link updates. (All)
- Updates for W3C Publication Rules. (All)
- Added definition for "CCXML Application/Program". (Section
3.5)
- New VoiceXML Appendix. (Appendix D)
- Removed Issues Appendix. (Was Appendix A)
- Re-lettered Appendixes. (All)
- Lots of minor text cleanup/link updates. (All)
- Updates for W3C Publication Rules. (All)
- Removed change marks to prepare for publishing (All)
- Removed Complex Example 3 (Section 11)
Changes in Last Call Working Draft 2
- CR149: Lost changes from April 19th have been added back in
(Several Sections)
- CR149: IBM Editorial Changes (Several Sections)
- CR159: HTTP Caching changes (Several Sections)
- CR160: disconnect clarification (Section 10.5.9)
- CR161: Extend dialog.prepared (and error.dialog.notprepared)
(Section 7.3.10 and 7.3.11)
- CR162: Change disconnect examples to use dialog-terminate
instead of send (Appendix D)
- CR163: VoxPilot Comments - Editorial (All)
- CR164: error.fetch vs. error.semantic - Emily Updates (Several
Sections)
- CR165: DTD defines "eventprocesser" rather than
"eventprocessor" (DTD)
- CR166: Error in error handling (Section 9.4.5.4)
- CR167: Remove FIA text from dialogprepare (Appendix D)
- CR169: Change dialogprepare connection rules (Section 7)
- CR170: merge tag (Section 10)
- CR172: dialogstart Attribute Detail (Section 7.2.2.2)
- CR173: error.dialog.notstarted attributes (Section 7.3.7)
- CR174: New connection state diagram (Section 10.2.1)
- CR176: HTTP Encoding changes (Several Sections)
- CR179: Clarification of createcall timeout (Section
10.5.4.2)
- CR182: Fetch Lifecycle (Several Sections)
- CR182: Removal of sync fetches (Several Sections)
- CR182: Change of script sync options (Several Sections)
- CR171: Master Session Lifecycle Diagram (Section 3.6.3.8)
- CR174: Added connection.signal to PROGRESSING state in
connection state diagram (Section 10.2.1)
- CR184: ECMAScript Left Hand Side Expression (Section 3.5)
- CR184: Fetch/Goto example using and ECMAScript Left Hand Side
Expression (Section 6.2.8.3)
- CR185: HP Comment - Typo (Section 6.1)
- CR187: HP Comment - Example Error (Section 11.2)
- CR190: HP Comment - Typo (Section 9.2.3.3)
- CR147: DTD Updates from Alex Davis (Appendix B)
- CR151: 3.x Section renumber from Greg Massard (Section
3.x)
- CR152: 6.x Section renumber from Greg Massard (Section
6.x)
- CR154: Missing elements in section 5 from Greg Massard (Section
5)
- CR155: DTD/Schema error for var from Greg Massard (Appendix
B/C)
- CR156: DTD/Schema error for accept from Greg Massard (Appendix
B/C)
- CR157: DTD/Schema error for else/elseif from Greg Massard
(Appendix B/C)
- CR159: enctype attribute. First time some changes got lost
(Several sections)
- CR178: Updated Scope Diagram (Section 8.1)
- CR183: Updates to ccxml.kill wording and event queue processing
(Sections 3.6, 6 and 9.1)
- CR202: move effect on queued events from moved source (Section
9.2.4)
- CR203: Conferencing object mixer text changes (Section
10.3)
- CR210: Add DialogID to join/unjoin (Section 10)
- CR211: Remove start attribute from createccxml (Section 6)
- CR207: State Variable Updating (Section 9)
- CR212: DTD/Schema Updates (Appendix B/C)
- CR209: Move Updates (Section 9)
- CR181: Standard format for attribute tables (All)
- CR191: mediadirection attribute for
dialogstart/dialogprepare(All)
- CR208: Scope of sendid, fetchid, dialogid and sessionid
attribute values (All)
- CR177: Complex ECMA Objects and namelist (All)
- CR217: Early Media Support (All)
- CR213: Remove regex on transition (All)
- CR201: Intersession join and Connection/Conferencing IDs
(All)
- CR214: send Delay Semantics on termination (All)
- CR216: Additional text for CCXML Join and disconnect (All)
- CR196: Application level variables (All)
- CR218: Send clarification (All)
- CR206: VoiceXML Session Vars (Appendix D)
- CR210: Dialogs as Connections (Section 10.5.7 and 10.5.8)
- CR219: Clean-up of dialog.vxml.transfer.complete (Section 7,
Appendix D)
- CR180: Application Session/Cookies (Appendix D)
- Updated Acknowledgments Section (Appendix G)
- Clean up of images (All)
- CR193: Default attribute value text (All)
- CR175: Conformance Section (Appendix J)
- CR215: "endpoint" and "duplexmode" Connection/Dialog Object
properties (Section 7/10)
- Minor example 1 fix (Added a tel: prefix)
- Fixed display issues for IE based browsers
- Renamed connection.error to error.connection
- Updated System Architecture Diagram
- Wording changes from Mark Scott (Reviewed on 11/11/2004
- 10.2.2 Protocol example change from Paolo Baggia
- Default dialog MIME type fixes
- Minor changes from VoiceGenie:
- Updated <assign> to make expr required
- On <dialogstart>, updated 'maxage', 'maxstale',
'enctype', and 'method' to be exclusive with
'prepareddialogid'
- Updated <exit> expr default to be undefined
- Updated DTD/Schema
- Changed <dialogterminate> immediate to a ECMAScript
Boolean Expression.
Changes in Last Call Working Draft 3
- Optimsys Comments 1-3, 5-9.
- Updated attribute tables for section 7 based on IR effort.
- Converted to external event tables.
- Editorial cleanup of inline code examples.
- Optimsys Comments 11-25.
- Misc editorial changes
- Added definitions for "CCXML Session", "CCXML Parent Session"
and "Event" to section 3.4.
- Section 6.2.4.1: Changed SHOULD to MUST on else/if logic
- Section 6.2.7.1: Added text listing required URI schemes
- Section 7.1: Added text to address dialogs without
connections
- Section 7.3.7: Added error.dialog event
- Section 8.2.1.1: Updated scope table
- Section 8.3: Added session.ioprocessors session var
- Section 9.2.3: Added basichttp to targettype list
- Section 9.2.3: Updated send text for inline content and xml:ns
comments
- Section 9.5: Removed reference to error.ccxml event
- Section 10.2: Expanded Dialog description.
- Section 10.5.9.2: Removed requirement for connectionid
attribute
- Section 10.6.20: Added error.connection.wrongstate event
- Appendix K/L: Added sections on basichttp I/O and session
launch.
- Misc editorial changes
- Corrected CSTA XML namespace in examples
- Added text to address canceling an outbound call
- Moved Connection/Conference Object tables to XML includes
- Updated section 10.4
- Misc changes to section 10 from VoiceGenie
- Event/Element table cleanup for IR effort (Corrected MUST/MAY
etc)
Changes in Working Draft 7
- Removed Appendix I - CCXML MIME Type.
- Updated description of dialog event fields (E-Mail from Paolo
2005-09-02).
- Other minor section 7 fixes (E-Mail from Paolo
2005-09-02).
- Updated dialog.terminatetransfer text.
- Applied changes from VoiceGenie comments.
- Fixed if/elseif/else definition in DTD.
- Tellme comments 41/42/45.
- Changed support for move to optional.
- Editorial cleanup.
- Updated RFC2119 keyword info for section 10.
- Genesys comments:
- Declared vars in section 3.4 examples.
- Changed "id" to "dialogid" on dialog objects.
- Fixed errors in examples (8.3).
- Joining 2 dialogs made optional.
- Added specific error event to invalid conid/confid on
createcall/dialogprepare/dialogstart
- Added dialog objects to dialog events.
- Removed error.dialog.wrongstate.
- Moved dialog.transfer.complete to Appendix D.
- VoxPilot comments:
- clarifications to the dialog object src property.
- Appendix K cleanup.
- Changed VXML/CCXML example code to use dialog.transfer.complete
instead of dialog.vxml.transfer.complete along with other minor
edits.
- Internationalization working group comments other than
IRIs
- Added a "statuscode" attribute to the error.fetch event.
- Minor changes per Genesys comments on the 9/20 internal
draft.
- Minor updates to send attributes for send delay.
- Details on when send attribute vars are evaluated
- Clarifications to application scoped vars
- Associative Array changes
- added hints to dialog elements
- Clarified error events on join/unjoin
- Removed namelist from events
- Clarified error event on invalid connection or dialog id's
- Added reference to dialog object on dialog events
- Updated call state diagram
- Updated media properties on connections and dialogs
- Added media endpoint object
- Changed the format of RFC keywords
- Minor Editorial Changes
- Conference Object Proposal
- Tellme Comments: 2,3,5,6,8,9,11,13,15,18
- Tellme Comments: 19, 20, 22, 25, 26, 28, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34 and
35
- Tellme Comments: 36, 37, 38, 39, 48, 53
- 8.2.1.1 - Reserved ECMAScript variable names
- Transition name="" to event$ changes
- Section 7 IR review changes
- error.unsupported to be thrown on any unsupported action
- Added tagname to error.connection.wrongstate
- Added tagname to error.notallowed
- (8.1) Reporting ECMAScript errors
- (10.6) Connection state changes from Rachel
- (7) Minor changes editorial changes from Paolo
- (createccxml) Server type clarification
- (dialogprepare) Server type clarification
- (dialogstart) Server type clarification
- (fetch) Server type clarification
- (send) changed tag to element
- (ccxml.exit) values.* clarification
- (dialog.exit) values.* clarification
- (dialog.user.*) values.* clarification
- Removed cookies from I/O processor sections
- Fixed outdated text in I/O processor sections
- Clarification on transition selection criteria
- evt.uri of fetch.done and error.fetch after 302
- connection.state constants
- <send> data --> name
- Connection model changes from Mark Scott (133003)
- Minor connection event table text changes from Paolo
(133003)
- section k multiple value parameters (123991)
- should fail to compile when transition has state but
eventprocessor has no statevariable (123997)
- CCXML spec comments/questions for section 10 (132989)
- ccxml.loaded put at front of event queue (132985)
- Comments on CCXML WD dated 23 March 2006 (132988)
- inconsistency in 10.4 (185805)
- ccxml errata (185808)
- Minutes for 2006-01-19 CCXML call (133002)
- Comments on CCXML WD dated 9 March 2006 (132991)
- Section 10.4 Bridges (132995)
- Section 10.2 Assertion Review (132996)
- Section 10.5 Assertion Review (132998)
- LCWD publication comments from Paolo (187115)
- Namelist changes on session creation, dialogstart and
createccxml (133005)
- CCXML spec change --- Connection states class (185572)
- Publication Prep
Changes in Last Call Working Draft 4
There are no changes in this version.
Changes in Candidate Recommendation
- ISSUE-182 - Section 7.2 - MISSING CHANGES in LCWD
2007_01_19
- ISSUE-183 - Section 7.3 - MISSING CHANGES in LCWD
2007_01_19
- ISSUE-184 - [ccxml] Questions about Appendix D
- ISSUE-182 - removed extra "include" in 7.2.2.1.
- ISSUE-182 - added error.semantic text to dialogid attributes of
dialogprepare and dialogterminate
- ISSUE-193 - removed reference to old "name" attribute on
transition element.
- ISSUE-194 - cleaned up basichttp text in send element and moved
some definitions to appendix K
- ISSUE-196 - added text for <send> around eventid,
eventsource and eventsourcetype
- ISSUE-197 - renamed connectionid to id and added dialogs to the
list for the error.notallowed event properties.
- ISSUE-114 - white space fixes from editorial change list
- ISSUE-117 - fixed references and updated acknowledgments
section
- ISSUE-198/ISSUE-199 - Removed standard attributes.
- ISSUE-241 - Section 9.1 review.
- ISSUE-242 - Section 9.2 review.
- ISSUE-243 - Section 9.3 review.
- ISSUE-242 - Section 9.2 review. - Item 10. Removed error text
from the 9.2.4.2 event table as it's covered in the element
description.
- ISSUE-230 - PUBLIC - LCWD - Nezic-1 - Comments on CCXML Working
Draft 19 January 2007 - Reworked fetch error handing event.
- ISSUE-231 - PUBLIC - LCWD - Nezic-2 - Comments on CCXML Working
Draft 19 January 2007 - Removed unneeded error.fetch references
from the specification. The behavior of parse time / schema
validation errors are defined in section 9.5.1.
- ISSUE-222 - PUBLIC - LCWD - Fixed createccxml element
table.
- ISSUE-224 - PUBLIC - LCWD - Fixed createcall-joindirection
attribute constraints.
- ISSUE-112 - Updating VoiceXML session variables.
- ISSUE-116 - error.semantic/hints.
- ISSUE-234 - PUBLIC - LCWD - murulidhara-2 - query.
- ISSUE-115, ISSUE-122 - XML 1.1 and IRI support.
- ISSUE-228 - Removed connection.rejected from connection state
diagram.
- ISSUE-251 - clarified move behavior.
- ISSUE-231 - Cleaned up 9.5.1 to be more specific.
- ISSUE-231 - Fixed script error handing text.
- ISSUE-231 - Added informative note explaining reasons for
script src being a static string.
- ISSUE-290 - Section 10.5.1.1 - extra MUST
- ISSUE-292 - Review of Section 9.2.1 assertions - closed, but
something strange in spec
- ISSUE-293 - Review on Section 9.2.2 assertions
- ISSUE-294 - Comments on Section 9.2.3 assertions
- ISSUE-295 - Comments on Section 9.2.4 assertions
- ISSUE-297 - Review on Section 9.3 assertions
- ISSUE-298 - Section 9.4 & 9.5 assertions
- ISSUE-291 - Section 9.1 - Assertion review
- ISSUE-244 - Section 10.2 Assertions
- ISSUE-244 - Section 10.2.1 - Removed connection.disconnected
transition from PROGRESSING state
- ISSUE-244 - Section 10.2 - Added PROGRESSING to the list of
active states
- ISSUE-244 - Section 10.6.5 - Reworded text to bring in line
with "This event MUST be emitted..." text used elsewhere in the
document
- ISSUE-252 - Status Section - Created features at risk section
and listed move+dialogs
- ISSUE-293 - Section 9.2.2.1 - Removed reference to
error.fetch
- ISSUE-297 - Section 9.3.4 - Reworded text about when this error
was raised per assertion review
- ISSUE-303 - Appendix K - IR review/rewording
- ISSUE-296 - Section 9.2.5 - IR review/rewording - "will" to
"MUST"
- ISSUE-305 - Appendix L IR Review - updated ignored payload
parameters
- ISSUE-303 - Appendix K IR Review - fixed reference to session
--> sessionid
- ISSUE-313 - Appendix K.4 - 2XX response codes are considered
success.
- ISSUE-314 - Section 10.2 - IR comments and changes.
- ISSUE-314 - Fixed leftover event details in 10.6.2:
connection.alerting
- ISSUE-304 - <join> and <unjoin> error.semantic
text.
- ISSUE-316 - 10.5.5.2 - Removed requirement that conference IDs
MUST be in URI format.
- ISSUE-308 - Connection.signal rewording
- ISSUE-319 - error.semantic and control flow
- ISSUE-320 - connectionid and conferenceid attributes for
<dialogprepare>/<dialogstart>
- ISSUE-238 - PUBLIC - LCWD - Sajeesh-2 [CCXML]Regarding namelist
attribute
- ISSUE-120 - Fixed sub issue 51. Corrected 10.4 text around
multiple inputs to conferences.
- ISSUE-121 - Ordering of id1 and id2 attributes to be
clear.
- ISSUE-233 - Added section 9.5.6 to define error handling for
invalid default attribute values.
- ISSUE-236 - PUBLIC - LCWD - Kuba-1 - CCXML: Dialog and
Connection objects.
- ISSUE-237 - PUBLIC - LCWD - Kuba-2 - CCXML: Dialog and
Connection objects.
- ISSUE-321 - <createccxml> and creation time of associated
Connection Object.
- ISSUE-324 - maxage & maxstale attributes of
<dialogprepare>, <dialogstart> should NOT be CSS2
times.
- ISSUE-336 - replace "audio/wav" with "audio/x-wav"
- ISSUE-482 - connection.disconnect used in appendix D
- ISSUE-483 - Appendix D should use dialog terminate instead of
send with connection.disconnect.hangup
- ISSUE-325 - PUBLIC - CCXML state variable
- ISSUE-488 - Small typo in Appendix D.9
- ISSUE-499 - Editorial review of Section 10.6 - s10.6.13,
s10.6.21
- ISSUE-500 - Changes in current draft and wrong reference -
s9.4.3
- ISSUE-501 - TYPO on CCXML Spec - 10.2.5
- ISSUE-498 - Issues with fetch and non CCXML/ECMAScript
data
- ISSUE-499 - Editorial review of Section 10.6 - s10.6.3,
s10.6.9, 10.6.10, s10.6.20
- ISSUE-502 - event$ is no longer writable
- ISSUE-114 - Minor edits (code markup)
- ISSUE-519 - 10.4 Connection/Dialog -> Media endpoint
- ISSUE-527 - type of statuscode on fetch.done
- ISSUE-524 - <disconnect/> on outbound call
- ISSUE-117 - Twicks before publishing
- ISSUE-115 - LCWD - Comments from i18n core WG on CCXML -
Removed seeAlso from meta tag
- ISSUE-553 - Incorrect example in the CCXML spec
- ISSUE-554 - ISSUE about connection.merge.failed event
properties
- ISSUE-555 - ISSUE about VoiceXMLIntegration example
- ISSUE-225 - PUBLIC - LCWD - Nagesh S-4 - Query in CCXML 1.0
Specification
- ISSUE-227 - PUBLIC - LCWD - Nagesh S-6 - Query in CCXML 1.0
Specification
- ISSUE-556 - Major and minor spec changes
- ISSUE-225, ISSUE-227 - required DTD, Schema and example
updates:
- ISSUE-225, ISSUE-227 - Further updates to schema
- ISSUE-555 - Fixed duplex of join
- ISSUE-556 - Major and minor spec changes
- ISSUE-566 - <dialogstart>/<dialogprepare> attribute
constraints can not be enforced using DTD/Schema. The fix to this
was to relax the schema and DTD and the text in the attribute
tables remain the normative text and expected behavior.
- ISSUE-567 - Make Error Handling within a <transition>
Consistent
- ISSUE-569 - PUBLIC - posting ccxml.exit to parent upon child
getting a ccxml.kill event
- ISSUE-572 - Attribute table missing for <redirect>
- ISSUE-567 - Make Error Handling within a <transition>
Consistent
- ISSUE-580 - TYPO about 'half' and 'full' , values for duplex
attribute
- ISSUE-581 - ISSUE about BRIDGE call transfer management on
Appendix D, paragraph D.11
- ISSUE-603 -
<move event=event$> in
transition for " connection.merge.failed "
- ISSUE-570 - Limiting amount of connection inputs and other
comments
- ISSUE-612 - dialog.transfer
event$.URI event$.uri
- ISSUE-613 - default value for dtmfclamp attribute
- ISSUE-616 - connection.redirect failed instead of
connection.failed event on Appendix D
- ISSUE-622 - Add session to the list of allowed values to
session.notallowed (9.3.1)
- ISSUE-633 - PUBLIC - using Object in the application scope -
example error (8.4)
- ISSUE-637 - PUBLIC - Comments on CCXML specification -
Attribute 'info' in the conference.created and conference.destroyed
events (10.6.11, 10.6.12)
Changes in Proposed
Recommendation
- ISSUE-668 - PUBLIC - CR - April 2010
CCXML's DTD is broken ( Appendix B )
- ISSUE-669 - PUBLIC - CR - attribute type
error in 1 April 2010 CCXML (Sections 10.6.13 and 10.6.14 ) .
- ISSUE-670 - PUBLIC - CR - CCXML
Implementation Report: asserts 714 and 715 (Section 6.3.6
).
Added clarification around what session the
attribute referred to and addressed cases for external events where
session id does not exist.
- ISSUE-671 - PUBLIC - CR - Recommended
addition to the April 2010 CCXML DTD ( Appendix B )
- ISSUE-674 - PUBLIC - CR - CCXML
specification: Application variables ( Section
8.4 ).
Clarified and removed legacy text from prior
drafts of the spec.
- ISSUE-675 - PUBLIC - CR - CCXML
specification: typo ( Appendix
K.3 )
- ISSUE-677 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML:
test case conflicts with ECMA rules ( Section 3.3.1
).
Added an implementation note around Line by
line vs Batch ECMAScript execution based on IR testing.
Based on years of implementation experience
the CCXML working group believes that CCXML application code that
would be affected by these scenarios is very rare. Any such code
likely relies on unusual ordering of variable declarations and
assignment statements or the use of confusing variable names and
scopes; such code is discouraged due to its potential for producing
unintended results.
- ISSUE-681 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML:
"Class" definition ( Section
3.4 ).
Removed extra definition text that was
unneeded as what we really were trying to do is just follow
ECMAScript.
- ISSUE-682 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML:
Dialog properties inconsistency ( Section 7.2.1.1
).
Removed old text left over from prior
language.
- ISSUE-697 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML: 3
bugs in 7_1.txml - Item 2 ( Section 7.2.3.2 ).
Clarified that the attribute was a
boolean.
- ISSUE-699 - Another typo on CCXML Spec
( Section
7.1 )
- ISSUE-700 - Typo in CCXML Spec (
Section
10.4.2 )
- ISSUE-702 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML: 3
problems with manual tests 10_5_7_A_*.txml ( Section 10.5.7.2
).
Clarified the order of operations when using
the exittone attribute based on IR testing.
- ISSUE-707 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML:
attribute 'id' of the error.notallowed event (Sections
9.2.5.1
and 9.3.1 ).
Clarified the contents of the id attribute
incase of error.
- ISSUE-710 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML,
7_1: attribute enctype used with the value of the method "post" in
<dialogprepare> (Sections 6.2.7.2 ,6.2.9.2 ,7.2.1.2 and 7.2.2.2 )
- ISSUE-714 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML:
format of the name attribute in <send> ( Section 9.2.3.2
).
Clarified that _ is allowed in event names
based on IR testing and original intent.
- ISSUE-717 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML
7_3: required property reason in dialog.terminatetransfer (
Section 7.3.6 ).
Clarified requirement level of reason
attribute based on results of IR testing.
- ISSUE-719 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML
9_2_3_B: handling of invalid event name in <send> (
Section 9.3.5
)
- ISSUE-720 - Fix 11.2 entertone/exittone
boolean vs string examples ( Section 11.2 )
- ISSUE-724 - PUBLIC - CR - April CCXML,
7_2: combination of attributes in <dialogstart>
(Sections 8.2.2.2 and
10.5.4.2
).
Clarified error handling on attribute
combinations based on IR testing.
- ISSUE-732 - PUBLIC - CR - July CCXML
Implementation Report: 8_2_3: how to handle error in loading static
<script> ( Section 8.2.2.2 ).
Clarified correct event to throw in some
cases based on IR testing.
- ISSUE-734 - PUBLIC - CR - July CCXML
Implementation Report: 9_2_3_B: improper error event used in
<send> ( Section 9.3.5 )
- ISSUE-743 - PUBLIC - CR - CCXML: VoiceXML
dialog.transfer.complete's result type incorrect ( Appendix
D.9 )
- ISSUE-744 - PUBLIC - CR - CCXML:
dialog.transfer example incorrect ( Appendix D.11 )
- ISSUE-754 - PUBLIC - CR - Fix test of
dialog.user.* ( Section
7.3.10 ).
Relaxed requirement level of dialog object
based on IR test results and need to inject event via HTTP IO
Processor.
Appendix G - Acknowledgments
This version of CCXML was written with the participation of
members of the W3C Voice Browser Working Group, and a special
thanks is in order for the following contributors:
- Kazuyuki Ashimura, W3C
- David Attwater, BTexact Technologies
- RJ Auburn, Voxeo Corporation
- Paolo Baggia, Loquendo
- Patrizio Bergallo, Loquendo
- Eric Burger, Snowshore
- David Burke, VoxPilot
- Emily Candell, Comverse
- Ken Davies, Hey Anita
- Rajiv Dharmadhikari, Genesys
- Dave Donnelly, BTexact Technologies
- Daniel Evans
- Mike Galpin, Syntellect
- Rob Green, Voxeo Corporation
- Markus Hahn
- Jeff Haynie, Vocalocity
- David W Heileman, Unisys
- Gadi Inon
- Jim Larson
- Rob Marchand, Genesys
- Scott McGlashan, Hewlett-Packard
- Rachel Muller, Aspect
- Brad Porter, Tellme Networks
- Kenneth Rehor, Cisco
- Dave Renshaw, IBM
- Laura Ricotti, Loquendo
- Mark Scott, Genesys
- Saravanan Shanmugham, Cisco
- Scott Slote, Nortel Networks
- Govardhan Srikant, Nortel Networks
- Jim Trethewey, Intel
- Wai-Yip Tung, Cisco
- Matt Womer, W3C
This W3C specification is based upon a former CCXML
specification, contributed to the Voice Browser Working Group in
April 2001. The CCXML authors were:
- RJ Auburn, Voxeo Corporation
- Michael Cafarella, Tellme
- Don Jackson, Tellme
- Jeff Peck, Intel
- Pramod Sharma, Telera
- Saravanan Shanmugham, Cisco Systems
- Corey Stohs, Cisco Systems
- Yi Zhang, Telera
Appendix H - References
H.1
Normative References
[CPL] CPL 1.0, IETF RFC 3880, October
2004. See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3880.txt . [CSTA] " Services
for Computer Supported Telecommunications Applications (CSTA) Phase
III ", Standard Ecma-269, 2002. See
http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/standards/Ecma-269.htm
[IANA]- " IANA
Character Sets ", IANA.
See http://www.iana.org/assignments/character-sets
[JSR021] " JAIN Call Control ", JSR
000021, 2001. See
http://www.jcp.org/aboutJava/communityprocess/final/jsr021/
[MIME-TAG]- Client handling of MIME headers , Ian Jacobs
(Editor) W3C TAG Finding 09 July 2003. Available at
http://www.w3.org/2001/tag/doc/mime-respect.html
- [RFC2119]
- Key words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement
Levels , S. Bradner Network Working Group RFC2119 March
1997. Available at http://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc2119.txt.
- [RFC3261]
- " SIP: Session Initiation Protocol ", IETF RFC
3261, 2002.
See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3261.txt
[RFC2806] [RFC3966]- " URLs for Telephone Calls ", IETF RFC
2806, 2000. See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2806.txt
[S.100] " S.100 ", ECTF. 3966,
2004.
See http://www.comptia.org/sections/ectf/media_services.aspx
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3966.txt
- [VOICEXML]
- Voice Extensible Markup Language (VoiceXML) Version
2.0 2.1 , Scott
McGlashan, Daniel C. Burnett, Jerry Carter, Matt Oshry, RJ Auburn, Paolo Baggia, et al. W3C
Candidate Recommendation 20 February 2003. 19 June
2007. Available at http://www.w3.org/TR/voicexml20/ http://www.w3.org/TR/voicexml21/
- [XML]
- " Extensible
Markup Language (XML) 1.1 ". Bray et al. W3C
Recommendation.
See http://www.w3.org/TR/xml11/
- [XML10]
- " Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 ". Bray et al. W3C
Recommendation.
See http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/REC-xml-20001006
[Q.931/DSS1] " ITU-T Recommendation Q.931
", ISDN user-network interface layer 3 specification (5/98). See
http://www.itu.int/rec/recommendation.asp?type=folders&lang=e&parent=T-REC-Q.931
[SS7] " ITU-T Recommendations Q.700-775 ", Signalling System No. 7
(3/93). See
http://www.itu.int/rec/recommendation.asp?type=items&lang=e&parent=T-REC-Q.700-199303-I
[ECMAScript]- " ECMAScript Language Specification ",
Standard Ecma-262, 1999.
See http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/standards/Ecma-262.htm
- [ECMA327]
- " ECMAScript 3rd Edition Compact Profile ",
Standard Ecma-327, 2001.
See http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/standards/Ecma-327.htm
- [XMLNS]
- " Namespaces in XML ", World Wide Web Consortium,
W3C Recommendation.
See href="http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml-names/ .
- [XML-BASE]
- " XML Base ", J. Marsh, editor, W3C Recommendation,
June 2001. See
http://www.w3.org/TR/2001/REC-xmlbase-20010627/ . [HTML] " HTML
4.01 Specification ", Dave Raggett et al. W3C Recommendation,
December 1999. January
2009.
See http://www.w3.org/TR/1999/REC-html401-19991224/ .
[RDF-SYNTAX] " Resource Description Framework (RDF) Model and
Syntax Specification. ", Ora Lassila and Ralph R. Swick, W3C
Recommendation, February 1999. See
http://www.w3.org/TR/1999/REC-rdf-syntax-19990222/ . [DC] " Dublin
Core Metadata Element Set, Version 1.1: Reference Description ",
See http://dublincore.org/documents/dces/ http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlbase/ .
- [SCHEMA2]
- XML Schema Part 2: Datatypes Second
Edition , P.V. Biron and A. Malhotra, Editors.
World Wide Web Consortium,
2 May 2001.
October 2004. This version of the XML
Schema Part 2 Recommendation is http://www.w3.org/TR/2001/REC-xmlschema-2-20010502/.
http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/REC-xmlschema-2-20041028/.
The latest
version of XML Schema 2 is available at
http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-2/.
- [URI]
- Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI): Generic
Syntax , T. Berners-Lee et al., Editors. IETF,
August 1998. January 2005. This RFC is available at http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2396.txt. http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3986.txt.
- [IRI]
- Internationalized Resource Identifiers (IRI) , M.
Duerst et al., Editors. IETF, January 2005. This RFC is available
at http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3987.txt.
[RFC2732] [CSS2]Format for Literal IPv6 Addresses
in URL's Cascading Style Sheets, level 2: CSS2
Specification , R.
Hinden, B. Bos, et al., Editors.
IETF, December 1999. World Wide Web Consortium, April 2008. This
RFC version of
the CSS2 Recommendation is
http://www.w3.org/TR/2008/REC-CSS2-20080411/. The latest version of CSS2 is available at
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2732.txt.
http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS2/.[RFC3023] [RFC2616]- " Hypertext Transfer Protocol -- HTTP/1.1
", IETF RFC 2616, 1999.
See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt
- [RFC2617]
- HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest
Access Authentication , IETF RFC
2617, June 1999. See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2617.txt .
- [RFC4267]
XML The W3C Speech Interface Framework Media
Types Types:
application/voicexml+xml, application/ssml+xml, application/srgs,
application/srgs+xml, application/ccxml+xml, and
application/pls+xml , M.
Murata, et al., Editors. Max
Froumentin, Editor. IETF, January
2001 November 2005. This RFC is
available at http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3023.txt http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4267.txt .
[CSS2] [CPL]Cascading Style Sheets, level 2:
CSS2 Specification CPL 1.0, IETF RFC 3880, October 2004.
, B. Bos, et al., Editors. World Wide Web
Consortium, 12 May 1998. This version of the CSS2 Recommendation is
http://www.w3.org/TR/1998/REC-CSS2-19980512/. The latest version of
CSS2 is available at http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-CSS2/.
See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3880.txt .[RFC2119] [CSTA]- "
Key words Services for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels
Computer Supported Telecommunications
Applications (CSTA) Phase III ", IETF RFC 2119, 1997. Standard Ecma-269, 2002.
See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2119.txt
http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/standards/Ecma-269.htm
[H.323] [JSR021]- "
ITU-T Recommendation H.323
JAIN Call
Control ", Packet-based
multimedia communications systems (7/03). JSR 000021, 2001.
See http://www.itu.int/rec/recommendation.asp?type=items&lang=e&parent=T-REC-H.323-200307-P
http://www.jcp.org/aboutJava/communityprocess/final/jsr021/
[CALLXML] [S.100]- " S.100
Revision 1.0 Media Services C Language. Application Programming
Interfaces ", Enterprise
Computer Telephony Forum (ECTF), 1996.
- [Q.931/DSS1]
- "
CallXML Development Guide Version 3.0 ITU-T Recommendation
Q.931 ", ISDN user-network
interface layer 3 specification (5/98).
See http://www.itu.int/rec/recommendation.asp?type=folders&lang=e&parent=T-REC-Q.931
, Voxeo Corporation, 2008.
[TXML] [SS7]- "
Telera Extensible Markup Language ITU-T Recommendations
Q.700-775 ", Signalling
System No. 7 (3/93).
See http://www.itu.int/rec/recommendation.asp?type=items&lang=e&parent=T-REC-Q.700-199303-I
, Telera.
[RFC2616] [HTML]- "
Hypertext Transfer Protocol --
HTTP/1.1 HTML 4.01
Specification ", IETF RFC
2616, Dave Raggett et al. W3C
Recommendation, December 1999.
See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt
http://www.w3.org/TR/1999/REC-html401-19991224/
.
- [H.323]
[RFC2617]
- "
HTTP
Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication
ITU-T Recommendation H.323
, IETF RFC 2617, June 1999.
", Packet-based multimedia communications
systems (12/09).
See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2617.txt
. http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-H.323/e
- [CALLXML]
[RFC2109]
HTTP State Management Mechanism
CallXML Development Guide Version
3.0 , IETF RFC 2109, February 1997.
See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2109.txt . ,
Voxeo Corporation, 2008.- [ACCESS-CONTROL]
- Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (Originally Access Control for Cross-site
Requests , Requests), W3C Working Draft 14 February 2008. 27 July
2010. See http://www.w3.org/TR/access-control http://www.w3.org/TR/cors/ .
[RFC4267] [RDF-SYNTAX]- "
The
W3C Speech Interface Resource Description Framework
Media Types: application/voicexml+xml,
application/ssml+xml, application/srgs, application/srgs+xml,
application/ccxml+xml, (RDF)
Model and application/pls+xml
Syntax Specification. , Max Froumentin, Editor. IETF, November 2005. This RFC
is available at http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4267.txt .
", Ora Lassila and Ralph R. Swick, W3C
Recommendation, February 1999.
See http://www.w3.org/TR/1999/REC-rdf-syntax-19990222/
.
- [DC]
- " Dublin Core Metadata Element Set, Version 1.1: Reference
Description ", See
http://dublincore.org/documents/dces/
.
This section is Normative.
J.1 - Conforming CCXML Document
A document is a Conforming CCXML Document if it meets
all of the following conditions:
- it is a well-formed XML 1.0 or 1.1 document [XML] conforming to namespaces in XML [XMLNS]
- it has a
<ccxml> root element which includes
a version attribute of "1.0"
- the
<ccxml> element designates the CCXML
namespace. This can be achieved by declaring an xmlns
attribute or an attribute with an xmlns prefix
[XMLNS] . The namespace for
CCXML is defined to be "http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml"
- it adheres to the specification described in this document
(Voice Browser Call Control: CCXML Version 1.0) including the
constraints expressed in the schema (see Appendix C)
It is recommended that the <ccxml> element
indicate the location of the CCXML schema (see Appendix C) via the
xsi:schemaLocation attribute from [SCHEMA2] :
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml
http://www.w3.org/TR/ccxml/ccxml.xsd"
There may be a DOCTYPE declaration in the document prior to the
root element. If present, the public identifier included in the
DOCTYPE declaration must reference the CCXML DTD (Appendix B) using
its Formal Public Identifier:
<!DOCTYPE ccxml PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD CCXML 1.0//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/ccxml/ccxml.dtd">
The system identifier may be modified appropriately. The DTD
subset must not be used to override any parameter entities in the
DTD.
Here is an example of a Conforming CCXML Document:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ccxml version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2002/09/ccxml http://www.w3.org/TR/ccxml/ccxml.xsd">
<eventprocessor>
<transition event="connection.alerting">
<log expr="'Hello World'"/>
<exit/>
</transition>
</eventprocessor>
</ccxml>
Note that in this example, the recommended
xmlns:xsi and xsi:schemaLocation
attributes are included. Note also, the inclusion of an XML
declaration. An XML declaration like the one above is not required
in all XML documents. CCXML document authors are strongly
encouraged to use XML declarations in all their documents. Such a
declaration is required when the character encoding of the document
is other than the default UTF-8 or UTF-16 and no encoding was
determined by a higher-level protocol.
The CCXML language or these conformance criteria provide no
designated size limits on any aspect of CCXML documents. There are
no maximum values on the number of elements, the amount of
character data, or the number of characters in attribute
values.
J.2 - Using CCXML with other namespaces
The CCXML namespace may be used with other XML namespaces as per
[XMLNS] , although such
documents are not strictly conforming CCXML documents as defined
above. Future work by W3C will address ways to specify conformance
for documents involving multiple namespaces.
J.3 - Conforming CCXML Processors
A CCXML Processor is a program that can parse and process
Conforming CCXML Documents. In a CCXML Processor, the XML parser
must be able to parse and process all XML constructs defined by XML
1.0 [XML10] , XML 1.1
[XML] and Namespaces in XML
[XMLNS] . This XML parser is
not required to perform validation of a CCXML document as per its
schema or DTD; this implies that during processing of a CCXML
document it is optional to apply or expand external entity
references defined in an external DTD.
A Conforming CCXML Processor must correctly understand and apply
the semantics of each markup element as described by this
document.
When a Conforming CCXML Processor encounters elements or
attributes, other than xml:lang and
xml:base , in a non-CCXML namespace it may:
- ignore the non-standard elements and/or attributes, or
- process the non-standard elements and/or attributes, or
- reject the document containing those elements and/or
attributes
There is, however, no conformance requirement with respect to
performance characteristics of the CCXML Processor.
J.4 - IRI vs URI
In all places that URIs [URI] are referenced as being valid in a CCXML document
a CCXML processor MUST accept IRIs
[IRI] .
Appendix K - Basic HTTP Event I/O
Processor
This section is Normative.
K.1 Overview
This appendix describes a " basichttp " event I/O
event processor which uses HTTP ( [RFC2616] ) to transport events between a CCXML
implementation and external components.
A CCXML implementation receives events from an external
component via the " basichttp " processor. If the
event is destined for an active CCXML session, the event and its
parameters are injected into the session. Using the "
basichttp " processor, events can be sent from a CCXML
session with the <send> element to an external
component.
The " basichttp " processor is intended as a
minimal interoperable mechanism for sending and receiving
events between external components and CCXML 1.0 implementations.
Other event I/O processors may be more appropriate for advanced
application scenarios. HTTP Basic Access Authentication ( [RFC2617] ) should be supported at
a minimum. HTTP Digest Access Authentication ( [RFC2617] ), HTTPS, or other
security techniques should be considered.
A CCXML 1.0 implementation must support the "
basichttp " processor. Implementations may support
other event injection processors so long as they do not have the
type " basichttp " which is reserved for the processor
described in this section.
K.2 Access URI
The access URI for the " basichttp " event I/O
processor is the URI to which an external component can send an
event for injection into an active session.
The access URI is available in a CCXML session via
session.ioprocessors using the key "
basichttp ". For example,
session.ioprocessors["basichttp"] returns the access
URI (e.g. http://www.example.com/ccxml/basichttp ) for
the " basichttp 1" processor.
The access URI for the " basichttp " event
processor may be sent to external components by, for example, its
inclusion in the namelist attribute of the
<send> element.
The access URI may also be specified in an
implementation-specific manner (for example, product
documentation).
K.3 Receiving Events
Input from external components MUST be
received by the CCXML implementation at the "
basichttp " access URI as HTTP POST requests. The
request is analyzed by the " basichttp " event
processor, resulting in
- an event being injected into an active CCXML session, or
- no action being taken (an error occurred, operation not
permitted, etc)
The " basichttp " processor MUST indicate the result to the external component
via the response code contained in the HTTP response.
Parameter values MUST be passed into
the " basichttp " processor using an encoded
application/x-www-form-urlencoded body.
To inject an event into an existing CCXML session, the HTTP
request must specify the id of the session and the name of the
event. The session id MUST be specified as
an HTTP parameter named " sessionid "
The name of the event must be specified using the HTTP parameter
" name ".
The following HTTP parameters are reserved:
sessionid- The value specifies the id of session into which the event is
to be injected.
name- The value specifies the name of the event. The value is
composed of alphanumeric and "." (dot) characters only. The first
character must not be a dot or digit. The parameter is
required.
eventsource- The value specifies a URI to which events may be sent (i.e. it
may be used as the value of the
target attribute in a
<send> element). The parameter is optional.
Any non-reserved HTTP request parameters (in other words, all
HTTP request parameters that are not listed in the table above)
define the properties of the injected CCXML event. For instance, if
the HTTP request contained a parameter named " foo "
with value " bar ", then the corresponding CCXML event
object would have a property named " foo " (accessible
as event$.foo ), the value of which would be the
string value " bar ".
Request parameters names may contain one or more periods, in
order to allow the injection of events with properties that are
objects. For example, a parameter named "1" "a.b" with a value
of " 1 " represents an object named " a
", which has a property " b " with a value of "
1 ". A subsequent parameter " a.c " with
a value of " 2 " would add a property named "
c " with a value of " 2 " to that event.
This scheme applies recursively; using " a.d.x " = "
3 " and " a.d.y " = " 4 "
would result in a multi-level object. Request parameter names must
be valid ECMAScript variable names, or must be composed of
period-separated ECMAScript variable names. Request parameter
values, both reserved and non-reserved, are treated as strings. The
omission of a request parameter value will be treated as an empty
string. Parameter names may not be repeated within a request. A
request with repeated parameter names is considered to be invalid,
and should be rejected by the " basichttp " event I/O
processor.
The following subset of HTTP response codes are defined:
Response
Code
|
Description |
| 204 (No Content) |
Injection successful:
session id matches an active CCXML session id, event name and
payload parameters are valid |
| 400 (Bad Request) |
Injection failed: one or
more parameters have an invalid name or value |
| 401 (Unauthorized) |
Used in conjunction with
HTTP Authentication ( [RFC2617] ): The request requires user
authentication |
| 403 (Forbidden) |
Injection failed: other
reason (e.g. session id does not match an existing CCXML session
id) |
| 404 (Not Found) |
Injection failed: access
URI invalid. |
| 500 (Internal Server Error) |
Injection failed: internal
server error. |
Events injected into an active CCXML session by the "
basichttp " processor provide the standard event
attributes as described in Section
9.4.2 . The name has the value of the "
name " parameter. The eventsource has the
value of the " eventsource " parameter if provided;
otherwise eventsource is undefined . The
eventid is a unique string identifier of the event
generated by the " basichttp " processor. The
eventsourcetype has the value " basichttp
".
The payload parameters and their values are exposed as top level
properties of the event object (complex parameter names require
appropriate initialization of sub-objects). To avoid conflict with
standard event attributes, payload parameters with the name "
eventid " or " eventsourcetype " are
ignored.
For example, if the access URI for the " basichttp
" processor is set to "
http://www.example.com/ccxml/basichttp ", an external
component can send an HTTP request as follows:
http://www.example.com/ccxml/basichttp?sessionid=ccxmlsession1&
name=basichttp.myevent&eventsource=http%3a//www.example.org/ccxmlext&
agent=agent12&site.location=orlando&site.code=RE445
If the session id matches an active CCXML session (i.e. its
session.id is " ccxmlsession1 ") and the
parameter names and values are valid, the processor injects the
event into the session and sends an HTTP 204 response code. The
event may then be handled by a transition such as:
<!-- Process incoming basichttp event -->
<transition state="'dialogActive'" event="basichttp.*" >
<log expr="'Received event'" />
<log expr="'name=' + event$.name" />
<log expr="'sourcetype=' + event$.eventsourcetype" />
<log expr="'eventsource=' + event$.eventsource" />
<log expr="'agent=' + event$.agent" />
<log expr="'site.location=' + event$.site.location" />
<log expr="'site.code=' + event$.site.code" />
</transition>
where event$.name would have the value "
basichttp.myevent ",
event$.eventsourcetype the value "
basichttp ", event$.eventsource the value
" http://www.example.org/ccxmlext ",
event$.agent the value " agent12 ",
event$.site.location the value " orlando
" and event$.site.code the value " RE445
".
K.4 Sending Events
Events may be sent from the CCXML
implementation to an external component with the "
basichttp " processor using the
<send> element ( Section 9.2.3 ) with the targettype
attribute set to " basichttp ". The
target attribute MUST be set
to the access URI of the external component.
The HTTP method MUST be "
POST " and parameter values MUST be encoded in an
application/x-www-form-urlencoded body (
POST method).
The id of the CCXML session id MUST be
sent as a HTTP parameter named " sessionid ".
The name attribute MUST be
specified as an HTTP parameter named " name ". If the
namelist attribute is defined, its variable names and
values MUST be mapped to HTTP parameters.
Inline content is not supported. The parameter name is
the variable name, with the same qualification as used in the
namelist . The parameter value is the variable value
after being converted into a string. If a variable in the
namelist is an ECMAScript Object, the mechanism by
which it must be submitted is not currently defined. Instead of
submitting ECMAScript Objects directly, the application developer
may explicitly submit the properties of an Object (e.g. "
date.month date.year ").
The basic HTTP event I/O processor generates events in response
to <send> as described in Section 9.3 . An HTTP success 2XX response code returned
by the external component (or a successful challenge-response
resulting from a 401 Unauthorized response) MUST be mapped to the CCXML event
send.successful ; all other non-successful (non 2xx)
HTTP response codes MUST be mapped to
error.send.failed .
Appendix L - Session Creation Event I/O
Processor
This section is Normative.
L.1 Overview
This appendix describes a " createsession " event
processor which can receive HTTP ( [RFC2616] ) requests from an external component to
create new CCXML sessions.
The " createsession " processor is intended as a
minimal interoperable mechanism to allow external components
to create new sessions in CCXML 1.0 implementations. Other event
I/O processors may be more appropriate for advanced application
scenarios. Security issues may need to be addressed by the
implementation. If security is not addressed as part of the
deployment network configuration, then HTTP Authentication (
[RFC2617] ) , HTTPS, or
other security techniques should be considered. Implementations may
use additional HTTP parameters specifically to address
security.
A CCXML 1.0 implementation may support a "
createsession " event processor. Implementations may
support alternative session creation event processors so long as
they do not have the type " createsession " which is
reserved for the processor described in this section.
L.2 Access URI
The access URI for the " createsession " event I/O
processor is the URI to which an external component can send a
session creation event.
If the implementation supports the " createsession
" event processor, then its access URI is available in a CCXML
session via session.ioprocessors using the key "
createsession ". For example,
session.ioprocessors["createsession"] returns the
access URI (e.g.
http://www.example.com/ccxml/createsession ) for the "
createsession " type event I/O processor.
The access URI may also be specified in an
implementation-specific manner (for example, product
documentation).
L.3 Receiving Session
Creation Events
A new CCXML session can be created by an external component when
the " createsession " processor receives at its access
URI an HTTP POST request with a " uri " parameter
whose value is the CCXML document to load.
The following HTTP parameters are reserved:
uri- The value specifies the URI of the CCXML document for the
session. The parameter is required.
eventsource- The value specifies a URI to which events may be sent from the
created session using, for example, the "
basichttp "
event processor. The parameter is optional.
method- Equivalent to
<createccxml> 's '
method ' attribute; used to set the HTTP method
applied in the fetch of the specified CCXML document. Allowed
values are " get " or " post "
(case-insensitive). If omitted, the default value is "
get ".
timeout- Equivalent to
<createccxml> 's '
timeout ' attribute; used to set the maximum time
allowed when fetching a CCXML document before abandoning the fetch
attempt and returning an error. If omitted, the CCXML platform will
use a default value
maxage- Equivalent to
<createccxml> 's '
maxage ' attribute; used to set the
max-age value of the Cache-Control header
when fetching CCXML documents. If omitted, the CCXML platform will
use a default value.
maxstale- Equivalent to
<createccxml> 's '
maxstale ' attribute; used to set the
max-stale value of the Cache-Control
header when fetching CCXML documents. If omitted, the CCXML
platform will use a default value.
postbody- Used to set the
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
encoded HTTP body for " post " requests. This
parameter is ignored if ' method ' is set to "
get ". The value of this parameter is the prepared
application/x-www-form-urlencoded content that has
been URL-encoded.
fetchparam- Equivalent to
<createccxml> 's '
fetchparam ' attribute; used to pass information about
the newly created session to the application server. If omitted,
the default value is " none ".
Other parameters provided in the HTTP request are treated as the
event payload and made available in the created session. Single
parameter values must be supported; multiple value parameters may
be supported.
Payload parameter names must be valid ECMAScript variable names.
Valid complex variable names are permitted; for example, "
agent.role ". Reserved and payload parameter values
must be valid ECMAScript expressions.
The following HTTP response codes are defined:
| Response
Code |
Description |
| 200 |
CCXML session created
successful |
| 400 |
Session not created: one
or more parameters have an invalid name or value |
| 401 |
Session not created:
request lacks proper authorization |
| 403 |
Session not created: other
reason (e.g. CCXML document not found) |
| 408 |
Session not created:
timeout fetching CCXML document |
If the CCXML session was created successfully, the HTTP 200
response MUST contain an '
application/x-www-form-urlencoded ' body. The '
session.id ' property of the newly created session
MUST be returned in this body; other
information MAY also be returned by the
platform.
In the created session, session.startupmode is set
to " external ", the session.uri is to
set to the value of the uri p parameter and a
session.values object is defined with the property
type set to the value " createsession " and
the property eventsource set to
the value of the " eventsource "
parameter. Other payload parameters are exposed as properties
of session.values
(complex parameter names require appropriate
initialization of sub-objects). To avoid conflict with
type and eventsource defined
above, payload parameters with the name "type" and
eventsource are ignored.
For example, an external component sends
the following HTTP request to the " createsession "
access URI :
http://www.example.com/ccxml/createsession?
uri=http://www.example.org/ccxml/myscript.ccxml&
eventsource=http://www.example.org/ccxmlext&
delay.value=500&delay.format=msecs&
vxmlscript=http://www.example.org/ccxml/myscript.vxml
If the " createsession "
processor is supported by the CCXML implementation, the request
parameter names and values are valid, and the ccxml document is
successfully fetched and processed, then a new CCXML session is
created with the following session variables:
session.id = 'ccxmlsession2'
session.startupmode = 'external'
session.uri = 'http://www.example.org/ccxml/myscript.ccxml'
session.values.type = 'createsession'
session.values.eventsource = 'http://www.example.org/ccxmlext'
session.values.delay.value = 500
session.values.delay.format = msecs
session.values.vxmlscript = 'http://www.example.org/ccxml/myscript.vxml'
The " createsession "
processor then responds to the originating HTTP request by
generating an HTTP 200 response code. The session id of the newly
created CCXML session MUST be returned in the
body of the response.
Appendix M - MIME Type and File
Suffix
This section is
normative.
The media type associated to the Call
Control eXtensible Markup Language Specification documents is
"application/ccxml+xml"
and the filename suffix is
".ccxml" as defined in [ RFC4267 ].






















 Figure 1: Initial Call State
Figure 1: Initial Call State Figure 2: State Following Merge
Figure 2: State Following Merge