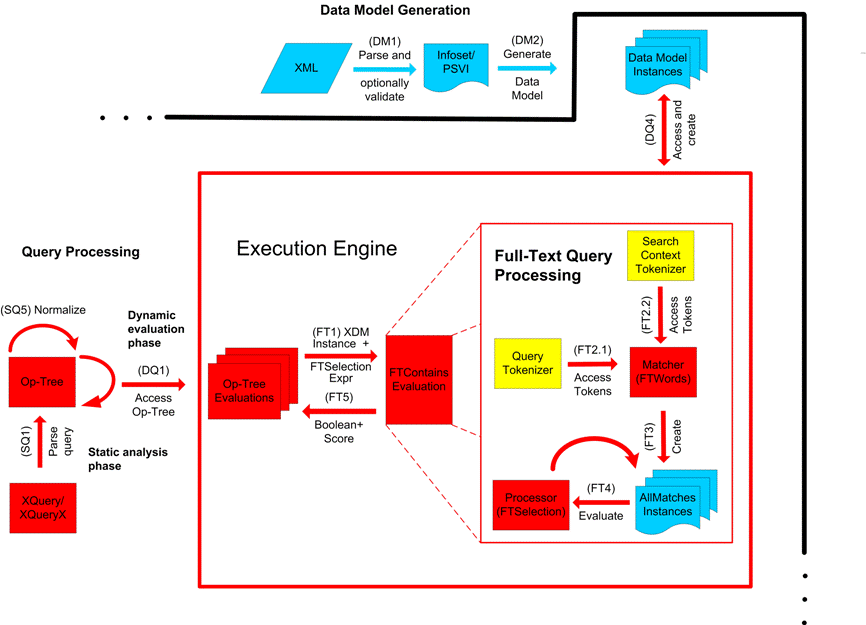
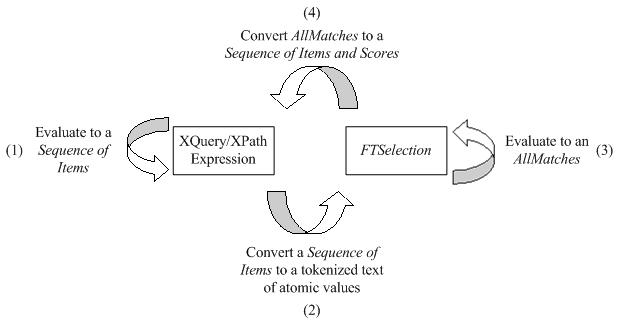
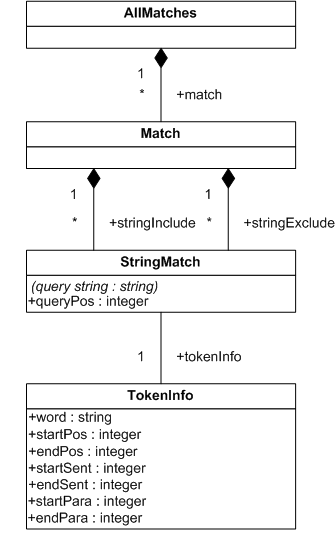
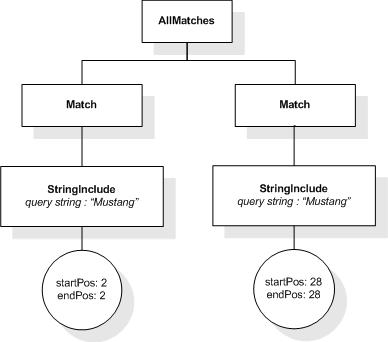
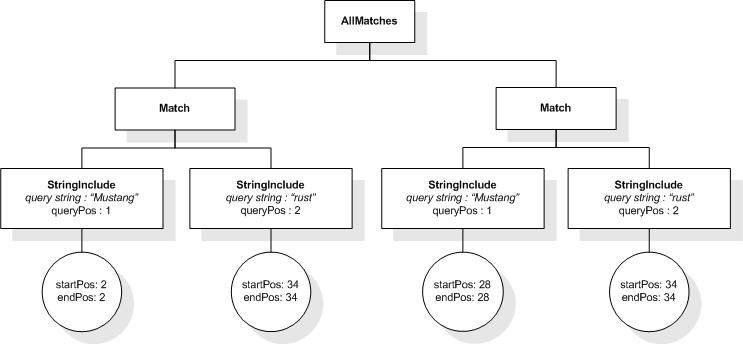
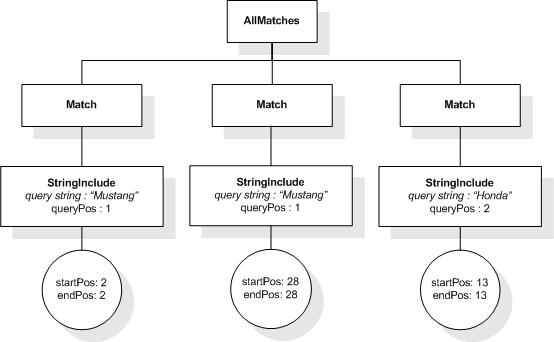
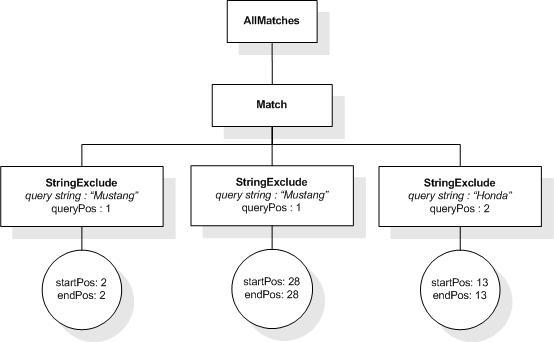
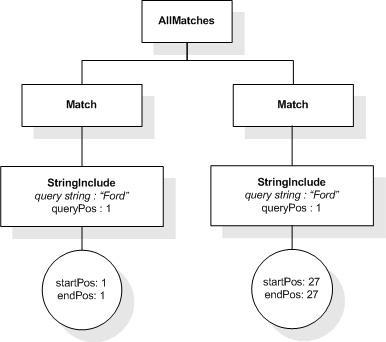
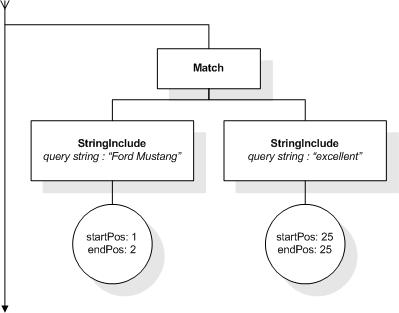
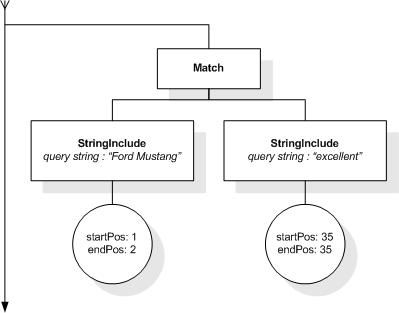
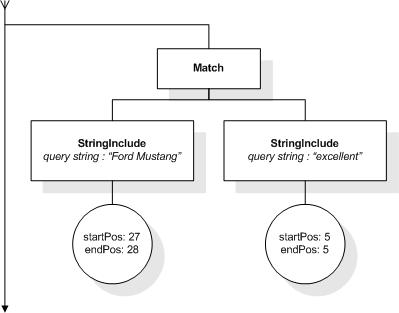
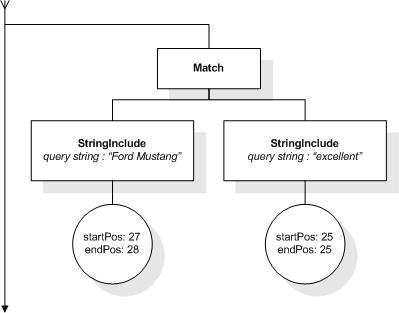
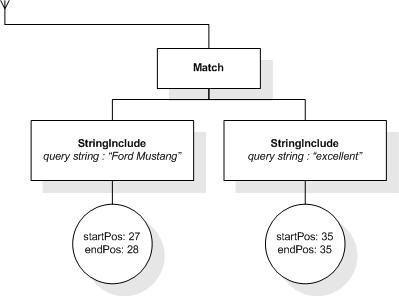
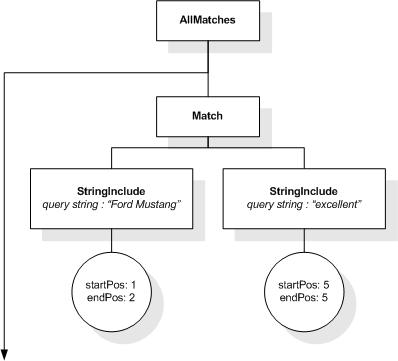
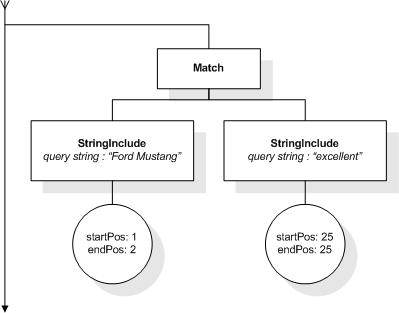
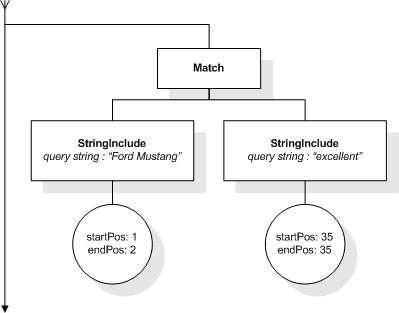
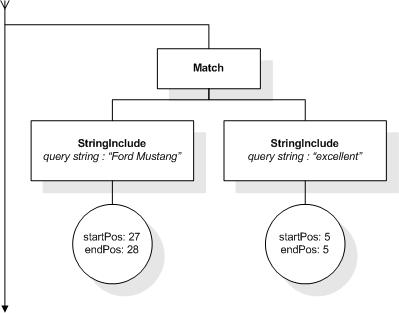
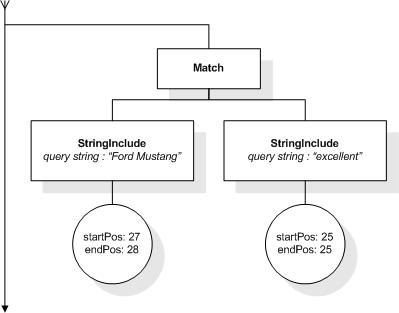
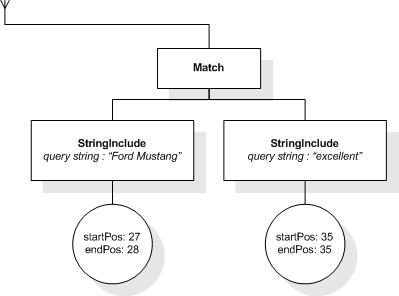
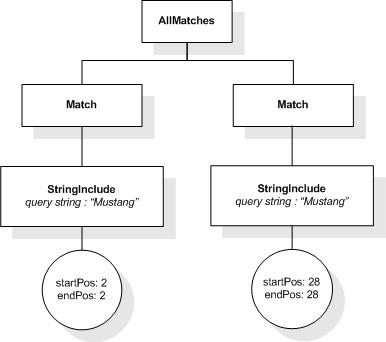
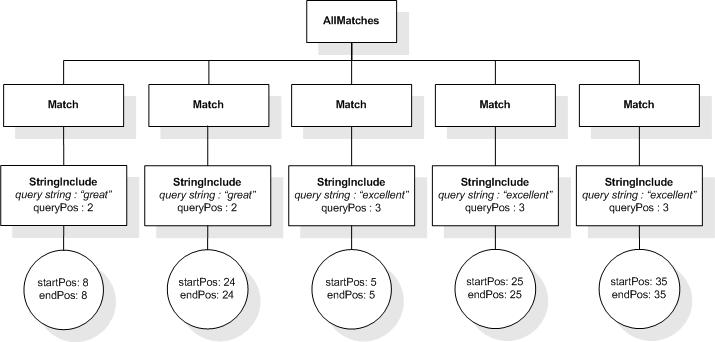
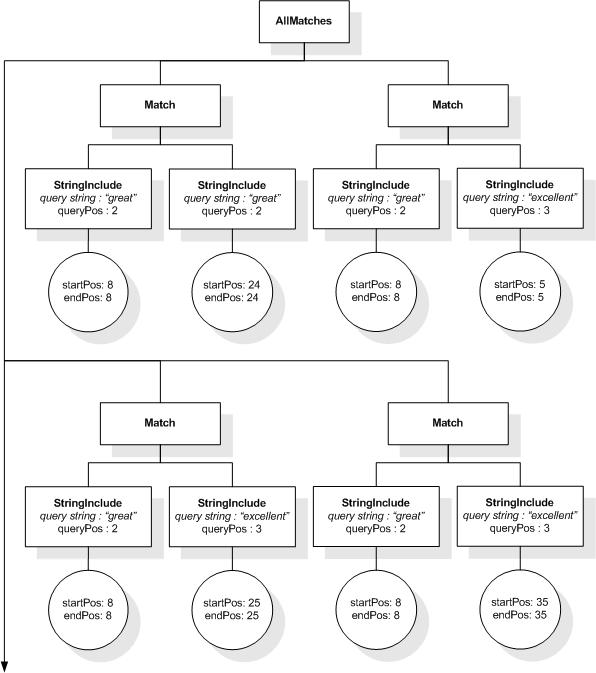
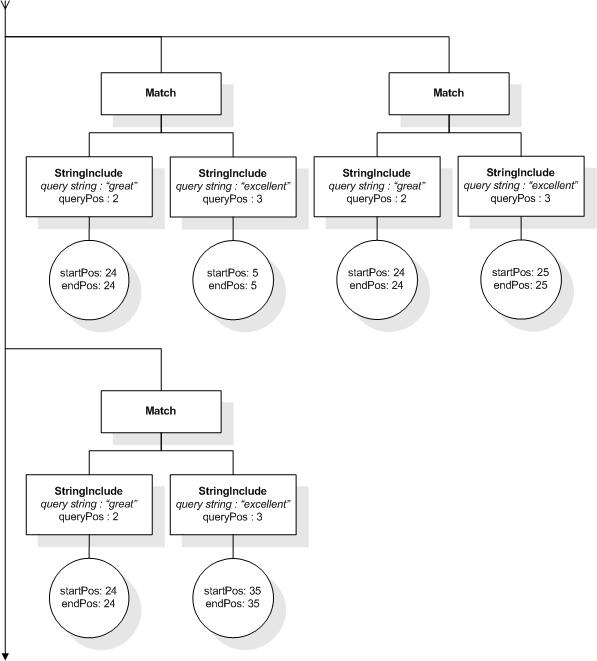
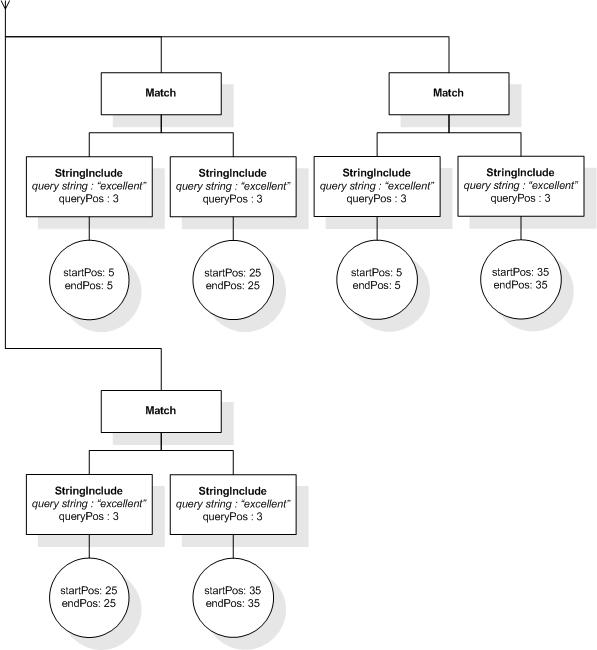
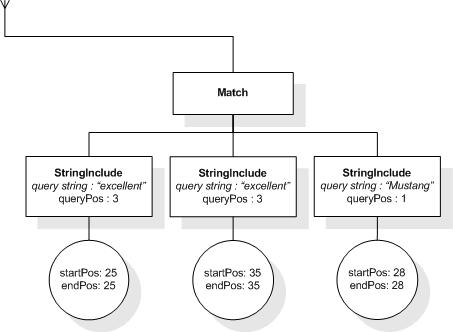
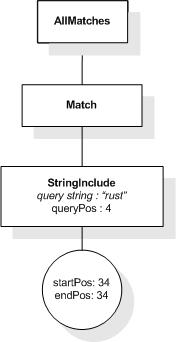
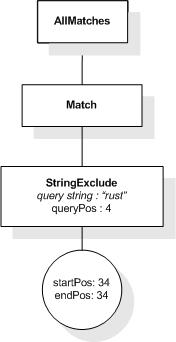
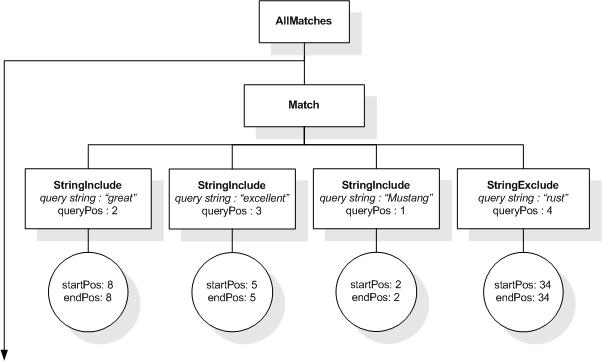
This section describes the full-text selections which contain
the full-text operators in a full-text
contains expression (FTContainsExpr), as well as the
match options which modify the matching semantics of the full-text
selections. In the following the syntax for each type of full-text
selection is given together with an informal statement of its
meaning.
As shown in the grammar, a full-text selection consists of
search conditions possibly involving logical operators (FTOr) followed by an arbitrary number of
positional filters (FTPosFilter) optionally followed by a
"weight" value which is specified using a range expression. The
RangeExpr is evaluated, as if it were an argument to a function
with an expected type "xs:double"; it must be between 0.0 and
1000.0 inclusive.
The syntax and semantics of the individual full-text selection
operators follow.
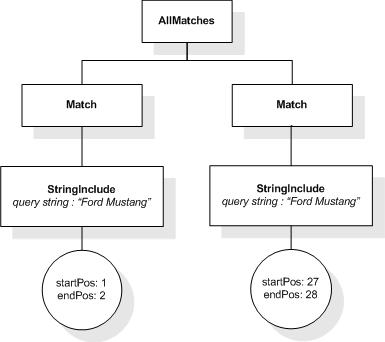
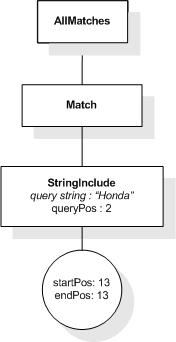
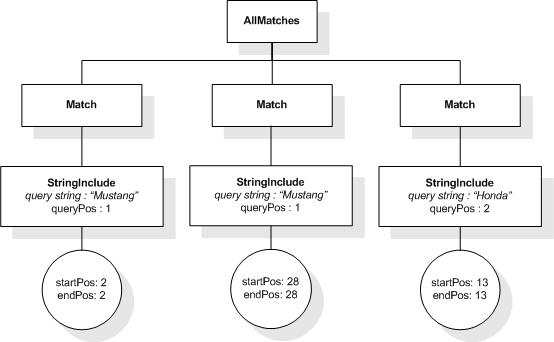
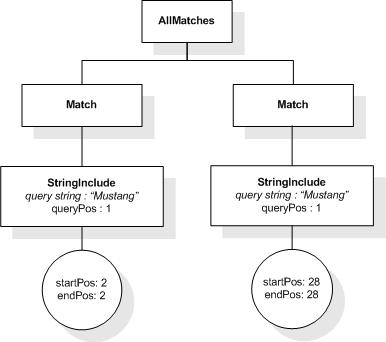
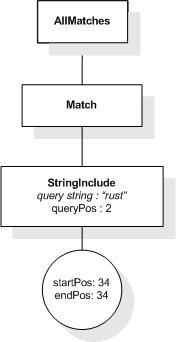
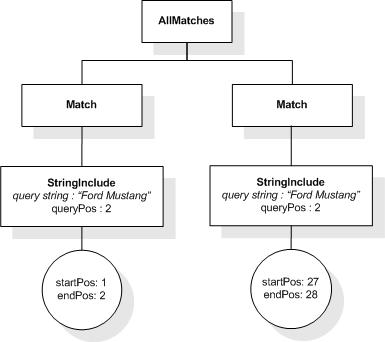
This XML document fragment is the source document for examples
in this section.
The first five tokens in this example using the sample
tokenization would be "Improving", "the", "usability", "of", and
"a".
Unless stated otherwise, the results assume a case-insensitive
match.
3.2 Search Tokens and
Phrases
FTWords finds matches that
contain the specified tokens and phrases.
FTWords consists of two parts: a mandatory FTWordsValue part and an optional
FTAnyallOption part.
FTWordsValue specifies the
tokens and phrases that must be contained in the matches. FTAnyallOption specifies how
containment is checked.
The FTWordsValue is
converted as though it were an argument to a function with the
expected type of "xs:string*".
In general, the tokens and phrases in FTWordsValue are specified using a
nested XQuery expression. To simplify notation, the enclosing
braces may be omitted if FTWordsValue consists of a single
literal.
The following rules specify how the containment of the strings
from the FTWordsValue
sequence is checked. First, every string is tokenized into a
sequence of tokens as described in Section 4.1 Tokenization. Then, FTAnyallOption is checked.
If FTAnyallOption is
"any", the sequence of tokens for every string is considered as a
phrase, i.e. the tokens must occur consecutively in the text in the
specified order. If the sequence contains more than one string, the
different strings are considered to be alternatives, i.e. the
resulting matches must contain at least one of the generated
phrases.
If FTAnyallOption is
"all", the sequence of tokens for every string is considered as a
phrase. The resulting matches must contain all of the generated
phrases.
If FTAnyallOption is
"phrase", the tokens from all the strings are concatenated in a
single sequence, which is considered as a phrase. The resulting
matches must contain the generated phrase.
If FTAnyallOption is
"any word", the tokens from all the strings are combined into a
single set. The resulting matches must contain at least one of the
tokens in the set.
If FTAnyallOption is
"all words", the tokens from all the strings are combined into a
single set. The resulting matches must contain all of the tokens in
the set.
If the FTWordsValue
evaluates to a single string, the use of "any", "all", and "phrase"
in FTAnyallOption produces
the same results.
If FTAnyallOptions is
omitted, "any" is the default.
The following expression returns the book element
whose number is 1, because its title
element contains the token "Expert":
/book[@number="1" and ./title ftcontains "Expert"]
The following expression returns the book element
whose number is 1, because its title
element contains the phrase "Expert Reviews":
/book[@number="1" and ./title ftcontains "Expert Reviews"]
The following expression returns the book element
whose number is 1, because its title
element contains two tokens "Expert" and "Reviews":
/book[@number="1" and ./title ftcontains {"Expert",
"Reviews"} all]
The following expression returns false, because the
p element doesn't contain the phrase "Web Site
Usability" although it contains all of the tokens in the
phrase:
/book[@number="1"]//p ftcontains "Web Site Usability"
The following expression returns book numbers of
book elements by "Marigold" with a title about "Web
Site Usability", sorting them in descending score order:
for $book in /book[.//author ftcontains "Marigold"]
let score $score := $book/title ftcontains "Web Site Usability"
where $score > 0.8
order by $score descending
return $book/@number
3.3 Match
Options
Full-text match options modify the matching behaviour of the
primary
full-text selection to which they are applied.
[Definition: Match options modify the
set of tokens in the query, or how they are matched against tokens
in the text.]
[Definition: Each of the seven
alternatives of production FTMatchOption corresponds to one
match option group. ] The match options from any given group
are mutually exclusive, i.e., only one of these settings can be in
effect, whereas match options of different groups can be combined
freely.
Note that, along with the syntax rules above, there is an
extra-grammatical constraint, multiple-match-options ,
which needs to be considered, if multiple match options are
specified. It states that within a single FTMatchOptions at most one match
option of any given match option group may be specified.
For example, if the FTCaseOption "lowercase" is
specified, then "uppercase" cannot also be specified as part of the
same FTMatchOptions.
Although match options only take effect in the application of
FTWords, the syntax also allows
to specify match options that modify the non-primitive full-text
selection "(" FTSelection ")". Such a higher-level
match option provides a default for the respective match option
group for any embedded FTPrimary, just as the static context
components corresponding to the match option groups provide default
match options for the whole query. Details about these context
components, including their default values, are given in Appendix
C Static Context
Components.
In other words, there is a tuple of seven effective match
options, one from each group, which are propagated from top to
bottom in the query syntax tree. For the top-level query the seven
values are given by the static context and at each FTPrimary the locally (like postfix
operators) specified match options may override these propagated
values. Thus, any occurrence of an FTWords in a query is associated with
seven effective match options, one from each group, that influence
its matching.
The order in which effective match options for an FTWords are applied is subject to some
constraints:
-
The Language Option must be applied first
-
The Stemming Option must be applied before the Case Option and
the Diacritics Option
Aside from these constraints, the full order of the application
of match options is implementation-defined. [Definition: This order is called the
match option application order.]
More information on their semantics is given in 4.2.6 Match Options Semantics.
If no match options declarations are present in the prolog and
the implementation does not define any overwriting of the static
context components for the match options, the query:
/book/title ftcontains "usability"
is, assuming "de" is the implementation-defined default
language, equivalent to the query:
/book/title ftcontains "usability" case insensitive
diacritics insensitive
without stemming without thesaurus
without stop words language "de" without wildcards
We describe each match option group in more detail in the
following sections.
3.3.1 Case
Option
| [167] |
FTCaseOption |
::= |
("case" "insensitive")
| ("case" "sensitive")
| "lowercase"
| "uppercase" |
[Definition: A case option modifies the
matching of tokens and phrases by specifying how uppercase and
lowercase characters are considered.]
There are four possible character case options:
-
Using the option "case insensitive" tokens and phrases are
matched, regardless of the case of characters of the query tokens
and phrases.
-
Using the option "case sensitive" tokens and phrases are
matched, if and only if the case of their characters is the same as
written in the query.
-
Using the option "lowercase" tokens and phrases are matched, if
and only if they match the query without regard to character case,
but contain only lowercase characters.
-
Using the option "uppercase" tokens and phrases are matched, if
and only if they match the query without regard to character case,
but contain only uppercase characters.
The default is "case insensitive".
The following table summarizes the interactions between the case
match options and the use of the default collation.
Case Matrix
| Default collation options/Case options |
UCC (Unicode Codepoint Collation) |
CCS (some generic case-sensitive collation) |
CCI (some generic case-insensitive collation) |
| insensitive |
compare as if both lower |
case-insensitive variant of CCS if it exists, else error |
CCI |
| sensitive |
UCC |
CCS |
case-sensitive variant of CCI if it exists, else error |
| lowercase |
lowercase(Expr) + UCC |
lowercase(Expr) + CCS |
CCI |
| uppercase |
uppercase(Expr) + UCC |
uppercase(Expr) + CCS |
CCI |
Note:
In this table, "else error" means "Otherwise, an error is
raised: [err:FOCH0002]FO".
The phrase "if it exists" is used, because the case-sensitive
collation CCS does not always have a case-insensitive variant (and,
even if one exists, it may not be possible to determine it
algorithmically), and because the case-insensitive collation CCI
does not always have a case-sensitive variant (and, even if one
exists, it may not be possible to determine it
algorithmically).
Note:
Using the "lowercase" (respectively "uppercase") option is
equivalent to using the option "case sensitive", while converting
the query strings to their lowercase (respectively uppercase) form
before matching.
The following expression returns false, because the
title element doesn't contain "usability" in
lower-case characters:
/book[@number="1"]/title ftcontains "Usability" lowercase
The following expression returns true, because the character
case is not considered:
/book[@number="1"]/title ftcontains "usability"
case insensitive
3.3.2
Diacritics Option
[Definition: A diacritics option
modifies token and phrase matching by specifying how diacritics are
considered. ]
There are two possible diacritics options:
-
The option "diacritics" "insensitive" matches tokens and phrases
with and without diacritics. Whether diacritics are written in the
query or not is not considered.
-
The option "diacritics" "sensitive" matches tokens and phrases
only if they contain the diacritics as they are written in the
query.
The default is "diacritics insensitive".
The following table summarizes the interactions between the
diacritics match options and the use of the default collations.
Diacritics Matrix
| Default collation options/Diacritics options |
UCC (Unicode Codepoint Collation) |
CDS (some generic diacritics-sensitive collation) |
CDI (some generic diacritics-insensitive collation) |
| insensitive |
UCC comparison, but without considering diacritics |
diacritics-insensitive variant of CDS if it exists, else
error |
CDI |
| sensitive |
UCC |
CDS |
diacritics-sensitive variant of CDI if it exists, else
error |
Note:
In this table, "else error" means "Otherwise, an error is
raised: [err:FOCH0002]FO".
The phrase "if it exists" is used, because the diacritics-sensitive
collation CDS does not always have a diacritics-insensitive variant
(and, even if one exists, it may not be possible to determine it
algorithmically), and because the diacritics-insensitive collation
CDI does not always have a diacritics-sensitive variant (and, even
if one exists, it may not be possible to determine it
algorithmically).
The following expression returns true, because the token "Véra"
in the editor element is matched, as the acute accent
is not considered in the comparison:
/book[@number="1"]//editor ftcontains "Vera" diacritics insensitive
This returns false, because the editor element does
not contain the token "Vera" in this exact form, i.e. without any
diacritics:
/book[@number="1"]/editors ftcontains "Vera" diacritics sensitive
3.3.3 Stemming
Option
| [169] |
FTStemOption |
::= |
("with" "stemming") | ("without" "stemming") |
[Definition: A stemming option modifies
token and phrase matching by specifying whether stemming is applied
or not. ]
The "with stemming" option specifies that matches may contain
tokens that have the same stem as the tokens and phrases written in
the query. It is implementation-defined what a stem
of a token is.
The "without stemming" option specifies that the tokens and
phrases are not stemmed.
It is implementation-defined whether the
stemming is based on an algorithm, dictionary, or mixed
approach.
The default is "without stemming".
The following expression returns true, because the
title of the specified book contains
"improving" which has the same stem as "improve":
/book[@number="1"]/title ftcontains "improve" with stemming
3.3.4
Thesaurus Option
[Definition: A thesaurus option
modifies token and phrase matching by specifying whether a
thesaurus is used or not.] If thesauri are used, the thesaurus
option specifies information to locate the thesauri either by
default or through a URI reference. It also states the relationship
to be applied and how many levels within the thesaurus to be
traversed.
The value of the FTThesaurusID must be a URILiteral.
Thesauri add related tokens and phrases to the search. Thus, the
user may narrow, broaden, or otherwise modify the search using
synonyms, hypernyms (more generic terms), etc. The search is
performed as though the user has specified all related search
tokens and phrases in a disjunction (FTOr).
Note:
A thesaurus may be standards-based or locally-defined. It may be
a traditional thesaurus, or a taxonomy, soundex, ontology, or topic
map. How the thesaurus is represented is implementation-dependent.
FTThesaurusID specifies the relationship sought between tokens
and phrases written in the query and terms in the thesaurus and the
number of levels to be queried in hierarchical relationships by
including an FTRange "levels". If no levels are specified, the
default is to query all levels in hierarchical relationships.
Relationships include, but are not limited to, the relationships
and their abbreviations presented in [ISO
2788] and their equivalents in other languages. The set of
relationships supported by an implementation is implementation-defined, but
implementations SHOULD support
the relationships defined in [ISO 2788].
The following list of terms have the meanings defined in [ISO 2788]. If a query specifies thesaurus
relationships or levels not supported by the thesaurus, the
behavior is implementation-defined.
-
equivalence relationships (synoymns): PREFERRED TERM
(USE), NONPREFERRED USED FOR TERM (UF);
-
hierarchical relationships: BROADER TERM (BT), NARROWER
TERM (NT), BROADER TERM GENERIC (BTG), NARROWER TERM GENERIC (NTG),
BROADER TERM PARTITIVE (BTP), NARROWER TERM PARTITIVE (NTP), TOP
Terms (TT); and
-
associative relationships: RELATED TERM (RT).
The "with thesaurus" option specifies that string matches
include tokens that can be found in one of the specified
thesauri.
The "without thesaurus" option specifies that no thesaurus will
be used.
The "with default thesaurus" option specifies that a
system-defined default thesaurus with a system-defined relationship
is used. The default thesaurus may be used in combination with
other explicitly specified thesauri.
The default is "without thesaurus".
The following expression returns true, because it finds a
content element containing "tasks" which the thesaurus
identified as a synonym for "duties":
count(.//book/content ftcontains "duties" with
thesaurus at "http://bstore1.example.com/UsabilityThesaurus.xml"
relationship "UF")>0
The following expression returns book elements,
because it finds a content element containing "web
site components", and narrower terms "navigation" and "layout":
doc("http://bstore1.example.com/full-text.xml")
/books/book[count(./content ftcontains "web site components" with
thesaurus at "http://bstore1.example.com/UsabilityThesaurus.xml"
relationship "NT" at most 2 levels)>0]
Assuming that there is a locally defined thesaurus that contains
soundex capabilities, the following query returns a
book element containing "Marigold" which sounds which
sound like "Merrygould":
doc("http://bstore1.example.com/full-text.xml")
/books/book[count(. ftcontains "Merrygould" with thesaurus at
"http://bstore1.example.com/UsabilitySoundex.xml" relationship
"sounds like")>0]
3.3.5 Stop
Word Option
[Definition: A stop word option
controls word matching by specifying whether stop words are used or
not. Stop words are tokens in the query that match any token in the
text. ] Normally a stop word matches exactly one token, but there
may be implementation-defined conditions,
under which a stop word may match a different number of tokens.
FTRefOrList specifies the
list of stop words either explicitly as a comma-separated list of
string literals, or by the keyword at followed by a
literal URI. If the URI specifies a list of stop words that is not
found in the statically known stop word lists, an error is raised
[err:FTST0008].
Whether the stop word list is resolved from the statically known
stop word lists or given explicitly, no tokenization is performed
on the stop words: they are used as they occur in the sequence.
The "with stop words" option specifies that if a token is within
the specified collection of stop words, it is removed from the
search and any token may be substituted for it. Stop words retain
their position numbers and are counted in FTDistance and FTWindow searches.
Multiple stop word lists may be combined using "union" or
"except". The keywords "union" and "except" are applied from left
to right. If "union" is specified, every string occurring in the
lists specified by the left-hand side or the right-hand side is a
stop word. If "except" is specified, only strings occurring in the
list specified by the left-hand side but not in the list specified
by the right-hand side are stop words.
The "with default stop words" option specifies that an implementation-defined collection
of stop words is used.
The "without stop words" option specifies that no stop words are
used. This is equivalent to specifying an empty list of stop
words.
The default is "without stop words".
Note:
Stop word lists may be applied during indexing. If applied
during indexing asking for stop words to not be used during a
query, will have no effect.
The following expression returns true, because the document
contains the phrase "propagating few errors":
/book[@number="1"]//p ftcontains "propagation of errors"
with stemming with stop words ("a", "the", "of")
Note the asymmetry in the stop word semantics: the property of
being a stop word is only relevant to query terms, not to document
terms. Hence, it is irrelevant for the above-mentioned match
whether "few" is a stop word or not, and on the other hand we do
not want the query above to match "propagation" followed by 2 stop
words, or even a sequence of 3 stop words in the document.
The following expression returns false, because "of" is not in
the p element between "propagating" and "errors":
/book[@number="1"]//p ftcontains "propagation of errors"
with stemming without stop words
The following expression uses the stop words list specified at
the URL. Assuming that the specified stop word list contains the
"then", this query is reduced to a query on the phrase "planning X
conducting", allowing any token as a substitute for X. It returns a
book element, because its content element
contains "planning then conducting". It would also return the
book if the phrases "planning and conducting" and
"planning before conducting" had been in its
content:
doc("http://bstore1.example.com/full-text.xml")
/books/book[count(.//content ftcontains "planning then
conducting" with stop words at
"http://bstore1.example.com/StopWordList.xml")>0]
The following expression returns books containing
"planning then conducting", but not does not return
books containing "planning and conducting", since it
is exempting "then" from being a stop word:
doc("http://bstore1.example.com/full-text.xml")
/books/book[count(.//content ftcontains "planning then conducting"
with stop words at "http://bstore1.example.com/StopWordList.xml"
except ("the then"))>0]
3.3.6
Language Option
[Definition: A language option
modifies token matching by specifying the language of search tokens
and phrases.]
The StringLiteral following the keyword language
designates one language. It must be castable to "xs:language";
otherwise, an error is raised: [err:XPTY0004]XP.
The "language" option influences tokenization, stemming, and
stop words in an implementation-defined way. The
"language" option MAY influence the
behavior of other match options in an implementation-defined way.
The set of standardized language identifiers are defined in
[BCP 47]. The set of valid language
identifiers among the standardized set is implementation-defined. An
implementation MAY choose to use
private extensions introduced by a singleton 'x' for additional
language identifiers, or other singletons for registered extensions
as described in sec. 2.2.6 of [BCP 47]. It is
implementation-defined what
additional language identifiers, if any, are valid. If an invalid
language identifier is specified, then the behavior is implementation-defined. If the
implementation chooses to raise an error in that case, it must
raise [err:FTST0009].
The default language is specified in the static context.
When an XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Full-Text processor evaluates
text in a document that is governed by an xml:lang attribute and
the portion of the full-text query doing that evaluation contains
an FTLanguageOption that specifies a different language that the
language specified by the governing xml:lang attribute, the
language-related behavior of that full-text query is implementation-defined.
This is an example where the language option is used to select
the appropriate stop word list:
/book[@number="1"]//editor ftcontains "salon de the"
with default stop words language "fr"
3.3.7
Wildcard Option
[Definition: A wildcard option
modifies token and phrase matching by specifying whether wildcards
are used or not.]
When the "with wildcards" option is used, wildcard indicators
(represented by periods (.)) and qualifiers may be appended to or
inserted into the query tokens. If the period is at the beginning
of a query token, the wildcard is a prefix wildcard. If the period
is at the end of a query token, it is a suffix wildcard. If the
period is inserted into a query token, it is an infix wildcard.
Each indicator and qualifier in a query token will match zero or
more characters within a token in the text, as described below. The
number of characters matched depends on the qualifier. Qualifiers
available are none, question mark, asterisk, plus sign, and two
numbers separated by a comma, both enclosed by curly braces.
-
If a period is present, but there are no qualifiers, one
character in the text will match.
-
If a period is followed by a question mark (.?), zero or one
characters in the text will match.
-
If a period is followed by an asterisk (.*), zero or more
characters will match.
-
If a period is followed by a plus sign (.+), one or more
characters will match.
-
If a period is followed by two numbers separated by a comma,
both enclosed by curly braces (.{n,m}), a specified range of
characters (at least n characters and no more than m characters)
will match.
When "with wildcards" is present and an indicator or qualifier
character is intended to be taken literally (as itself), that
character must be preceded by ("escaped by") a backslash (\). For
example, a period (.) that is intended to be a sentence terminator
or a decimal point must be preceded by a backslash so that it is
not interpreted to be an indicator. Similarly a question mark (?),
asterisk (*), or plus sign (+) that is intended to be interpreted
as an ordinary text character must be preceded by a backslash so
that it is not interpreted to be an indicator.
The "without wildcards" option finds tokens without recognizing
wildcard indicators and qualifiers. Periods, question marks,
asterisks, plus signs, and two numbers separated by a comma, both
enclosed by curly braces, are always recognized as ordinary text
characters.
The default is "without wildcards".
Note: Wildcard indicators and qualifiers may be token
boundaries. How text with wildcard indicators and qualifiers is
tokenized is implementation-defined.
The expression returns true, because the title
element contains "improving":
/book[@number="1"]/title ftcontains "improv.*" with
wildcards
The following expression returns true, because the
title element contains "site":
/book[@number="1"]/title ftcontains ".?site" with
wildcards
The following expression returns true, because the
p element contains "well":
/book[@number="1"]/p ftcontains "w.ll" with
wildcards
The following expression returns false, because the
p element does not contain "w.ll":
/book[@number="1"]/p ftcontains "w.ll" without wildcards
3.3.8
Extension Option
[Definition: An extension option
is a match option that acts in an implementation-defined way.
]
An extension option consists of an identifying QName and a
StringLiteral. Typically, a particular option will be recognized by
some implementations and not by others. The syntax is designed so
that option declarations can be successfully parsed by all
implementations.
The QName of an option must resolve to a namespace URI and local
name, using the statically known namespaces.
Note:
There is no default namespace for options.
Each implementation recognizes an implementation-defined set of
namespace URIs used to denote extension options.
If the namespace part of the QName is not a namespace recognized
by the implementation as one used to denote extension option, then
the extension option is ignored.
Otherwise, the effect of the extension option, including its
error behavior, is implementation-defined. For
example, if the local part of the QName is not recognized, or if
the StringLiteral does not conform to the rules defined by the
implementation for the particular extension option, the
implementation may choose whether to report an error, ignore the
extension option, or take some other action.
Implementations may impose rules on where particular extension
options may appear relative to other match options, and the
interpretation of an option declaration may depend on its
position.
An extension option must not be used to change the syntax
accepted by the processor, or to suppress the detection of static
errors. However, it may be used without restriction to modify the
set of tokens in the query or how they are matched against tokens
in the text. An extension option has the same scope as other match
options.
The following examples illustrate several possible uses for
extension options:
This extension option is set as part of the static context of
all full-text expressions in the module and might be used to ensure
that queries are insensitive to Arabic short-vowels.
declare namespace exq = "http://example.org/XQueryImplementation";
declare ft-option option exq:diacritics "short-vowel insensitive"
This extension option applies only to the matching in the
full-text selection in which it is found and might be used to
specify how compound words should be matched.
declare namespace exq = "http://example.org/XQueryImplementation";
//para[. ftcontains "Kinder" ftand "Platz"
distance 1 words with stemming option exq:compounds "distance=1"
3.4
Logical Full-Text Operators
Full-text selections can be combined with the logical
connectives ftor (full-text or), ftand
(full-text and), not in (mild not), and
ftnot (unary full-text not).
3.4.1 Or-Selection
[Definition: An or-selection combines
two full-text selections using the ftor operator.]
An or-selection finds all matches that satisfy at least one of
the operand full-text selections.
The following expression returns the book element
written by "Millicent":
/book[.//author ftcontains "Millicent" ftor
"Voltaire"]
3.4.2 And-Selection
[Definition: An and-selection combines
two full-text selections using the ftand
operator.]
An and-selection finds matches that satisfy all of the operand
full-text selections simultaneously. A match of an and-selection is
formed by combining matches for each of the operand full-text
selections as described in 4.2.7.2
FTAnd.
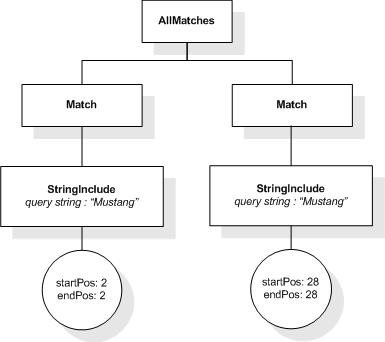
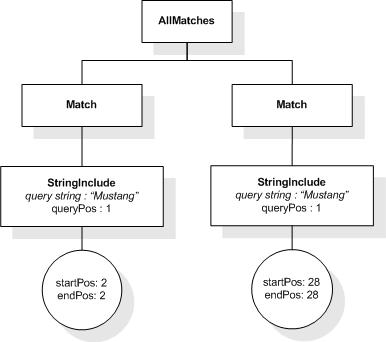
For example, "usability" ftand "testing" will find
two matches in /book[@number="1"]/title: each of the
two matches for the FTWords selection "usability" (the
two occurrences of the token "usability" in the string value of the
title element) is combined with the single match for the FTWords
"testing" (only one occurrence of the token "testing"
in the title). Since the above and-selection has at least one
match, the following expression will return "true".
/book[@number="1"]/title ftcontains ("usability" ftand "testing")
The following expression returns false, because "Millicent" and
"Montana" are not contained by the same author element
in any book element:
/book/author ftcontains "Millicent" ftand "Montana"
No author element in any book element
contains both "Millicent" and "Montana". Therefore, for any such
author element, there are either one match for the
FTWords "Millicent" and zero matches for the FTWords
"Montana", or vice versa, or no matches for both of
them. In any of these cases, the and-selection will have zero
matches.
3.4.3 Mild-Not
Selection
[Definition: A mild-not selection
combines two full-text selections using the not in
operator.]
The not in operator is a milder form of the
operator combination ftand ftnot. The selection
A not in B matches a token sequence that matches
A, but not when it is a part of a match of
B. In contrast, A ftand ftnot B only
finds matches, when the token sequence contains A and
does not contain B.
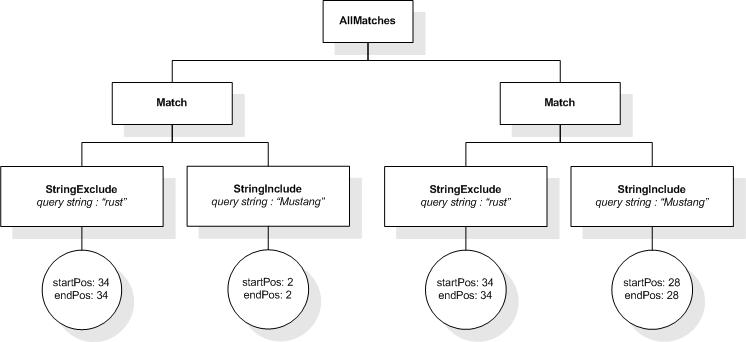
As an example, consider a search for "Mexico" not in "New
Mexico". This may return, among others, a document which is
all about "Mexico" but mentions at the end that "New Mexico was
named after Mexico". The occurrence of "Mexico" in "New Mexico" is
not considered, but other occurrences of "Mexico" are matched. Note
that this document would not be matched by the full-text selection
"Mexico" ftand ftnot "New Mexico".
A match to a mild-not selection must contain at least one token
occurrence that satisfies the first condition and does not satisfy
the second condition. If it contains a token occurrence that
satisfies both the first and the second condition, the occurrence
is not considered as a match.
The following expression returns true, because "usability"
appears in the title and the p elements
and the occurrence within the phrase "Usability Testing" in the
title element is not considered:
/book ftcontains "usability" not in "usability
testing"
Operands of a mild-not selection may not contain a full-text
selection that evaluates to an AllMatches that contains a
StringExclude. Such full-text selections are not-selection
and FTWords with a cardinality
constraint using at most, from ... to,
and exactly occurrences ranges.
3.4.4 Not-Selection
[Definition: A not-selection is
a full-text selection starting with the prefix operator
ftnot.]
A not-selection selects matches that do not satisfy the operand
full-text selection. Details about how such matches are constructed
are given in 4.2.7.3
FTUnaryNot.
The following expression returns the empty sequence, because all
book elements contain "usability":
/book[. ftcontains ftnot "usability"]
The following expression returns true, because book
elements contain "information" and "retrieval" but not "information
retrieval":
/book ftcontains "information" ftand
"retrieval" ftand ftnot "information retrieval"
The following expression returns book elements
containing "web site usability" but not "usability testing":
/book[. ftcontains "web site usability" ftand
ftnot "usability testing"]
3.5 Positional
Filters
[Definition: Positional filters are
postfix operators that serve to filter matches based on various
constraints on their positional information.]
Recall that the grammar rule for FTSelection allows an arbitrary
number of positional filters to follow an FTOr. Multiple adjacent positional filters
are applied from left to right, i.e., the first filter is applied
to the result of the FTOr, the
second is applied to the result of that first application, and so
on.
3.5.1 Ordered Selection
[Definition: An ordered selection
consist of a full-text selection followed by the postfix operator
"ordered".] An ordered selection controls the order of tokens and
phrases to be the same as the order in which they are written in
the operand selection.
The default is unordered. Unordered is in effect when ordered is
not specified in the query. Unordered cannot be written explicitly
in the query.
An ordered selection selects matches which satisfy the operand
full-text selection and for which the order the matching tokens
have in the text is the same order that the corresponding query
tokens have in the operand selection.
The following expression returns true, because titles of
book elements contain "web site" and "usability" in
the order in which they are written in the query, i.e., "web site"
must precede "usability":
/book/title ftcontains ("web site" ftand "usability")
ordered
The following expression returns false, because although
"Montana" and "Millicent" both appear in the book
element, they do not appear in the order they are written in the
query:
/book[@number="1"] ftcontains ("Montana" ftand
"Millicent") ordered
3.5.2 Window
Selection
[Definition: A window selection
consist of a full-text selection followed by one of the (complex)
postfix operators derived from FTWindow.] A window selection selects
matches which satisfy the operand full-text selection and for which
the matched tokens and phrases, more precisely the individual
StringIncludes of that match, are found within a number of FTUnits (words, sentences, and
paragraphs). The number of FTUnits
is specified by an AdditiveExpr that is converted as though it were
an argument to a function with the expected type of
"xs:integer".
A window selection may cross element boundaries. The size of the
window is not affected by the presence or absence of element
boundaries. Stop words are included in the computation of the
window size whether they are ignored by the query or not.
A match of an FTSelection
is considered a match within a window, if there exists a window of
at most the given number of consecutive units (tokens, sentences,
or paragraphs) in the document within which all StringIncludes of
the match lie.
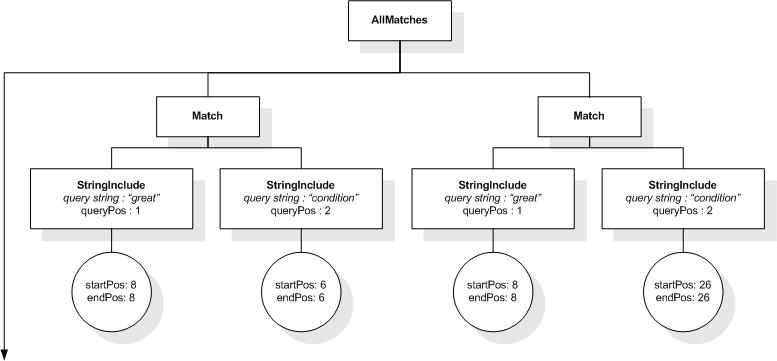
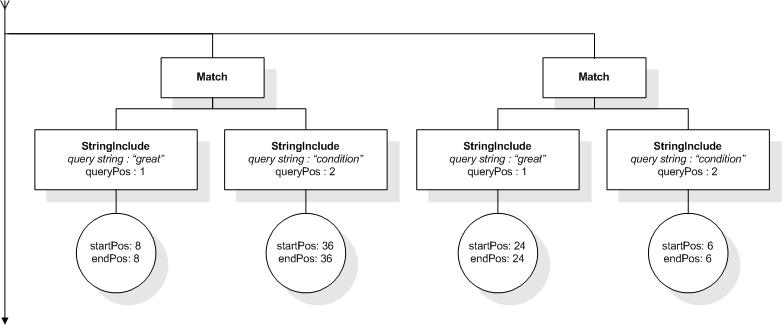
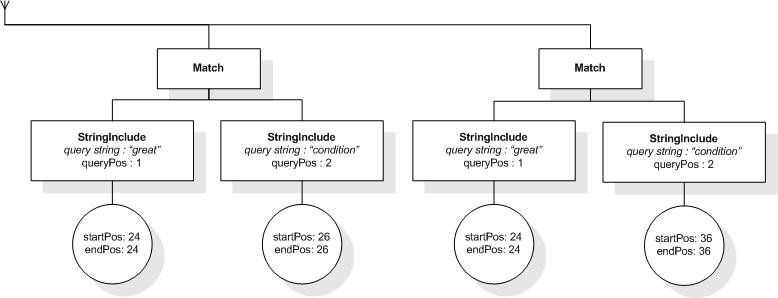
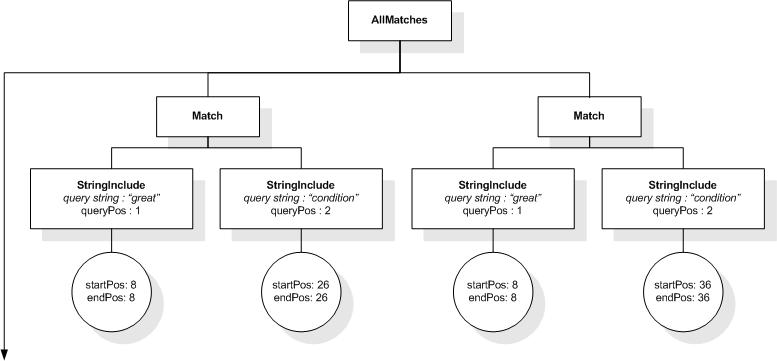
The following expression returns true, because "web", "site",
and "usability" are within a window of 5 tokens in the
title element:
/book/title ftcontains "web" ftand "site"
ftand "usability" window 5 words
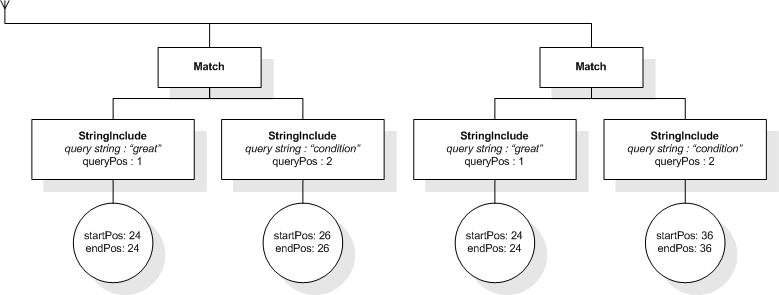
The following expression returns true, because "web" and "site"
in the order they are written in the query and either "usability"
or "testing" are within a window of at most 10 tokens:
/book ftcontains ("web" ftand "site" ordered)
ftand ("usability" ftor "testing") window 10 words
The following expression returns true, because the
title element contains "Web Site Usability". A similar
query on the p element would not return true, because
its occurrences of "web site" and "usability" are not within a
window of 3:
/book//title ftcontains "web site" ftand
"usability" window 3 words
The following expression returns the empty sequence, because in
the selected book element, there is no occurrence of
"efficient" within a window of 3 tokens which would not also
contain an occurrence of "and":
/book[@number="1" and . ftcontains "efficient"
ftand ftnot "and" window 3 words]
In order to allow meaningful results for nested positional
filters, e.g., a window selection embedded inside a distance
selection, the resulting matches for window selections are formed
from the input matches that satisfy the window constraint as
follows. All StringIncludes of such a match are coerced into a
single StringInclude that spans all token positions from the
smallest to the largest position of any input StringIncludes. This
is explained in more detail in Section 3.5.3 Distance Selection.
3.5.3 Distance
Selection
[Definition: A distance selection
consist of a full-text selection followed by one of the (complex)
postfix operators derived from FTDistance.]
A distance selection selects matches which satisfy the operand
full-text selection and for which the matched tokens and phrases
satisfy the specified distance conditions. Distance is specified in
units of FTUnits (words,
sentences, and paragraphs). The number of intervening FTUnits is specified in the integer value
of FTRange.
FTRange specifies a range of
integer values, providing a minimum and maximum value. Each one of
the AdditiveExpr specified in an FTRange is converted as though it were an
argument to a function with the expected parameter type of
"xs:integer".
Let the value of the first (or only) operand be M. If "from" is
specified, let the value of the second operand be N. A distance
selection may cross element boundaries when computing distance.
The following rule applies to the computation of distance:
If "exactly" is specified, then the range is the closed interval
[M, M]. If "at least" is specified, then the range is the
half-closed interval [M, unbounded). If "at most" is specified,
then the range is the closed interval [0, M]. If "from-to" is
specified, then the range is the closed interval [M, N]. Note: If M
is greater then N, the range is empty.
Here are some examples of FTRanges:
-
'exactly 0' specifies the range [0, 0].
-
'at least 1' specifies the range [1,unbounded].
-
'at most 1' specifies the range [0, 1].
-
'from 5 to 10' specifies the range [5, 10].
The distances computed by a distance selection are not affected by
the presence or absence of element boundaries in the text. Stop
words are counted in those computations whether they are ignored or
not.
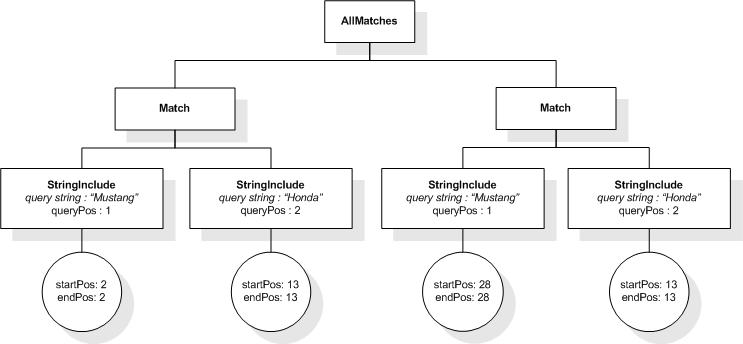
The following expression returns false, because "completion" and
"errors" are less than 11 tokens apart:
/book ftcontains ("completion" ftand "errors"
distance at least 11 words)
The following expression returns true, because the
book element contains tokens "web", "site", and
"usability" that have at most 2 intervening tokens between
them:
/book ftcontains "web" ftand "site" ftand
"usability" distance at most 2 words
The following expression returns the empty sequence, because
between any token "usability" and the token in any occurrence of
the phrase "web site" that is the nearest to the token "usability"
there is always more than one intervening token:
/book[.//p ftcontains "web site"
ftand "usability" distance at most 1 words]
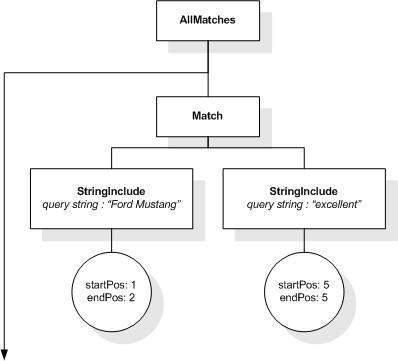
The following expression returns the book title,
because for the occurrences of the tokens "web" and "users" in the
note element only one intervening token appears:
/book[. ftcontains "web"
ftand "users" distance at most 1 words]/title
In order to allow meaningful results for nested positional
filters, e.g., a distance selection embedded inside another
distance selection, the resulting matches for distance selections
are formed from the input matches that satisfy the distance
constraint as follows. All StringIncludes of such a match are
coerced into a single StringInclude that spans all token positions
from the smallest to the largest position of any input
StringIncludes. Thus, a distance selection that embeds a window or
a distance selection takes the result of the embedded selection as
a single unit.
The following gives an example of nested distance
selections:
/books ftcontains ((("richard" ftand "nixon") distance at most 2)
ftand
(("george" ftand "bush") distance at most 2)
distance at least 20)
This expression allows to find book elements that
contain, for instance, "Richard M. Nixon" and "George W. Bush" at
least 20 words apart. The matches for the inner distance selections
are treated as single units (represented by StringIncludes) by the
outer distance selection. Suppose such phrases are present in the
search context, then the outer distance selection enforces a
constraint on the number of intervening tokens ("at least 20")
between the last token of "Richard M. Nixon" and the first token of
"George W. Bush".
3.5.4 Scope Selection
[Definition: A scope selection
consist of a full-text selection followed by one of the (complex)
postfix operators derived from FTScope.]
A scope selection selects matches which satisfy the operand
full-text selection and for which the matched tokens and phrases
are contained in the same scope or in different scopes.
Possible scopes are sentences and paragraphs.
By default, there are no restrictions on the scope of the
matches.
The following expression returns false, because the tokens
"usability" and "Marigold" are not contained within the same
sentence:
/book ftcontains "usability"
ftand "Marigold" same sentence
The following expression returns true, because the tokens
"usability" and "Marigold" are contained within different
sentences:
/book ftcontains "usability"
ftand "Marigold" different sentence
The following expression returns a book element,
because it contains "usability" and "testing" in the same
paragraph:
/book[. ftcontains "usability" ftand "testing"
same paragraph]
The following expression returns a book element,
because "site" and "errors" appear in the same sentence:
/book[. ftcontains "site" ftand "errors"
same sentence]
It is possible that both "same sentence" and "different
sentence" conditions are simultaneously safisfied for several
tokens and/or phrases within the same document fragment. This can
be observed if there are occurrences of the tokens and/or phrases
both within the same sentence and within difference sentences. For
example, consider the following document fragment.
<introduction>
... The usability of a Web site is how well the site supports the user in
achieving specified goals. ... Expert reviews and usability testing are methods of
identifying problems in layout, terminology, and navigation. ...
</introduction>
This sample will satisfy both conditions ("usability"
ftand "reviews") different sentence and ("usability"
ftand "reviews") same sentence. The tokens "usability" and
"reviews" occur both in different sentences (the first and second
shown sentences) and in the same sentence (the second shown
sentences.)
The above observation also holds for the "same paragraph" and
"different paragraph" conditions.
3.5.5 Anchoring
Selection
| [164] |
FTContent |
::= |
("at" "start") | ("at" "end") | ("entire"
"content") |
[Definition: An anchoring
selection consist of a full-text selection followed by one of
the postfix operators "at start", "at end", or "entire
content".]
An anchoring selection selects matches which satisfy the operand
full-text selection and for which the matched tokens and phrases
are the first, last, or all tokens in the tokenized form of the
items being searched.
Using the "at start" operator tokens or phrases are matched
which are the first tokens or phrases in the tokenized string value
of the item being searched.
Using the "at end" operator tokens or phrases are matched which
are the last tokens or phrases in the tokenized string value of the
item being searched.
Using the "entire content" operator tokens or phrases are
matched which are the entire content of the tokenized string value
of the item being searched.
The following expression returns each title element
starting with the phrase "improving the usability of a web
site":
/books//title[. ftcontains "improving the usability
of a web site" at start]
The following expression returns each p element
ending with the phrase "propagating few errors":
/books//p[. ftcontains "propagat.*" with wildcards ftand "few
errors" distance at most 2 words at end]
The following expression returns each note element
whose entire content is "this site has been approved by the web
site users association":
/books//note[. ftcontains "this site has been
approved by the web site users association" entire content]
3.8 Extension Selections
[Definition: An extension
selection is a full-text selection whose semantics are
implementation-defined.]
Typically, a particular extension will be recognized by some
implementations and not by others. The syntax is designed so that
extension selections can be successfully parsed by all
implementations, and so that fallback behavior can be defined for
implementations that do not recognize a particular extension.
An extension selection consists of one or more pragmas followed
by a full-text selection enclosed in curly braces. See Section 3.14
Extension ExpressionsXQ for
information on pragmas in general. A pragma is denoted by the
delimiters (# and #), and consists of an
identifying QName followed by implementation-defined
content. The content of a pragma may consist of any string of
characters that does not contain the ending delimiter
#). The QName of a pragma must resolve to a namespace
URI and local name, using the statically known namespaces.
Note:
Since there is no default namespace for pragmas, a pragma QName
must include a namespace prefix.
Each implementation recognizes an implementation-defined set of
namespace URIs used to denote pragmas.
If the namespace part of a pragma QName is not recognized by the
implementation as a pragma namespace, then the pragma is ignored.
If all the pragmas in an FTExtensionSelection are
ignored, then full-text extension selection is just the full-text
selection enclosed in curly braces; if this full-text selection is
absent, then a static error is raised [err:XQST0079]XQ.
If an implementation recognizes the namespace of one or more
pragmas in an FTExtensionSelection, then
the value of the FTExtensionSelection,
including its error behavior, is implementation-defined. For
example, an implementation that recognizes the namespace of a
pragma QName, but does not recognize the local part of the QName,
might choose either to raise an error or to ignore the pragma.
It is a static error [err:XQST0013]XQ
if an implementation recognizes a pragma but determines that its
content is invalid.
If an implementation recognizes a pragma, it must report any
static errors in the following full-text selection even if it will
not apply that selection.
The following examples illustrate three ways in which extension
selections might be used.
A pragma can be used to furnish a hint for how to evaluate the
following full-text selection, without actually changing the
result. For example:
declare namespace exq = "http://example.org/XQueryImplementation";
/book/author[name ftcontains (# exq:use-index #) {'Berners-Lee'}]
An implementation that recognizes the exq:use-index
pragma might use an index to evaluate the full-text selection that
follows. An implementation that does not recognize this pragma
would evaluate the full-text selection in its normal way.
A pragma might be used to modify the semantics of the following
full-text selection in ways that would not (in the absence of the
pragma) be conformant with this specification. For example, a
pragma might be used to change distance counting so that adjacent
words are at a distance of 1 (otherwise they would be at a distance
of 0):
declare namespace exq = "http://example.org/XQueryImplementation";
/book[.//p ftcontains (# exq:distance #) { "web site"
ftand "usability" distance at most 1 words] }
Such changes to the language semantics must be scoped to the
expression contained within the curly braces following the
pragma.
A pragma might contain syntactic constructs that are evaluated
in place of the following full-text selection. In this case, the
following selection itself (if it is present) provides a fallback
for use by implementations that do not recognize the pragma. For
example:
declare namespace exq = "http://example.org/XQueryImplementation";
//city[. ftcontains (# exq:classifier with class 'Animals' #)
{"animal" with thesaurus at "http://example.org/thesaurus.xml"
relationship "RT"}
Here an implementation that recognizes the pragma will return
the result of evaluating the proprietary syntax with class
'animals', while an implementation that does not recognize
the pragma will instead return the result of the thesaurus option.
If no fallback expression is required, or if none is feasible, then
the expression between the curly braces may be omitted, in which
case implementations that do not recognize the pragma will raise a
static error.