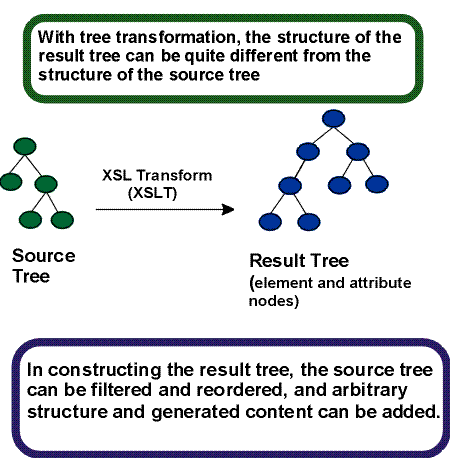
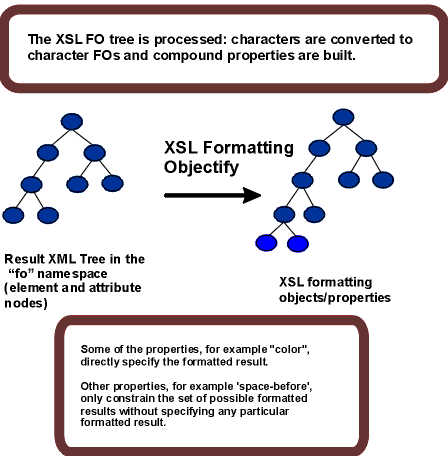
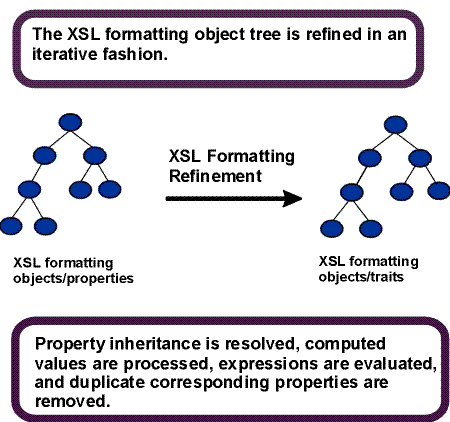
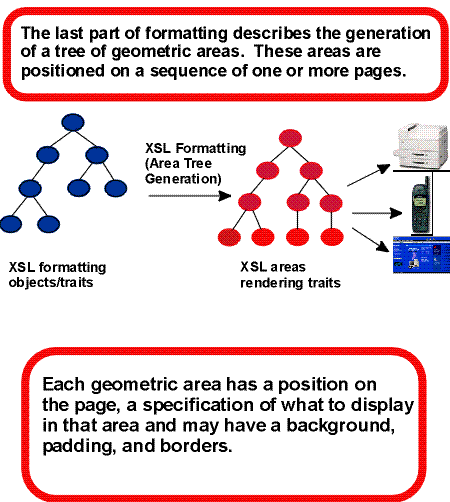
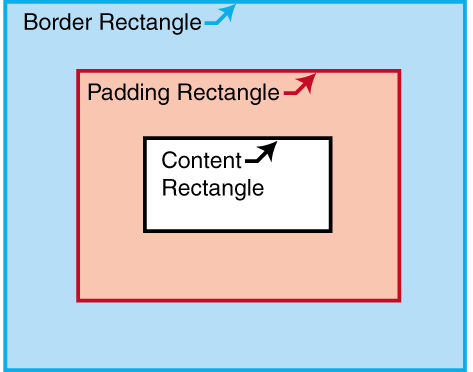
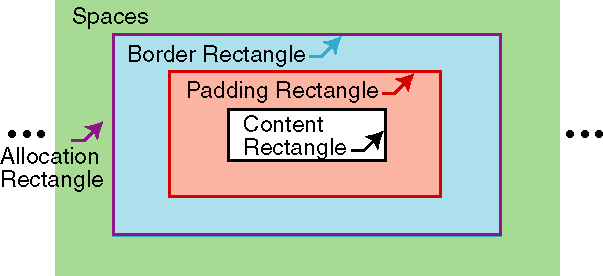
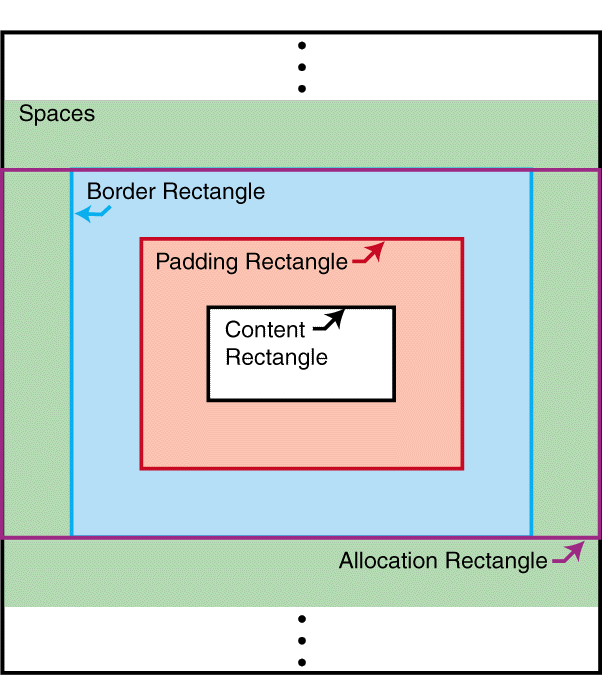
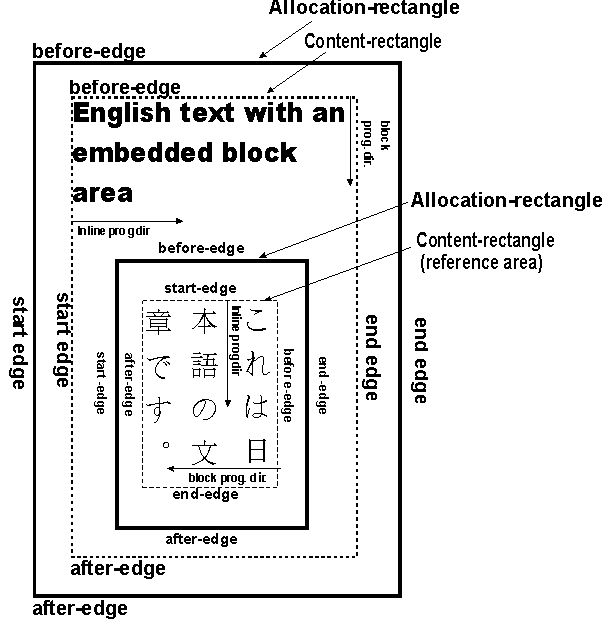
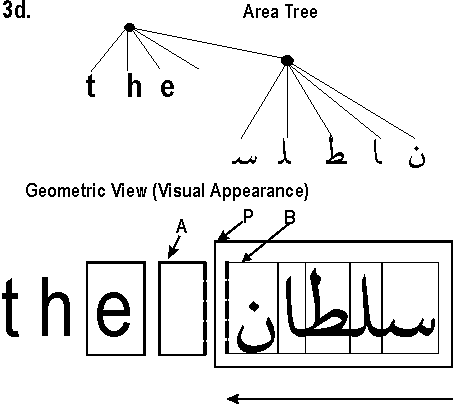
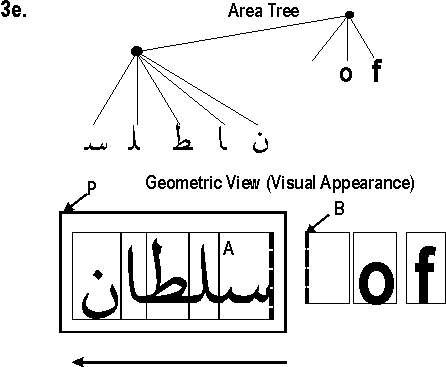
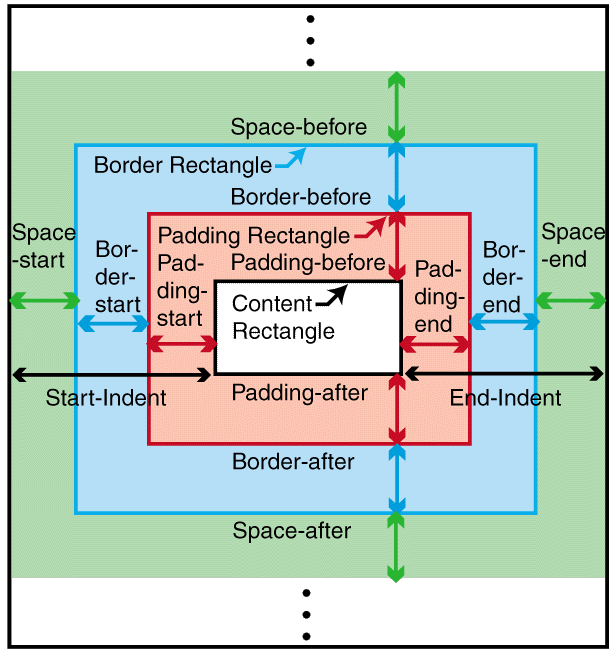
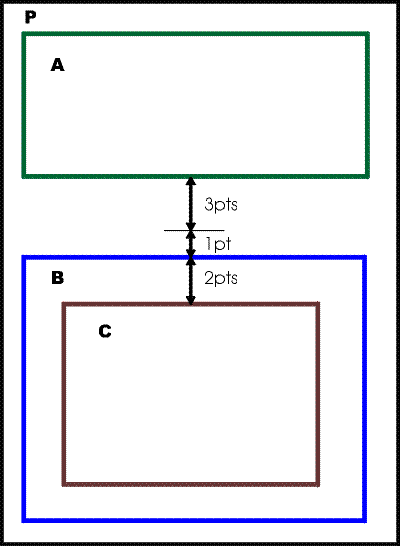
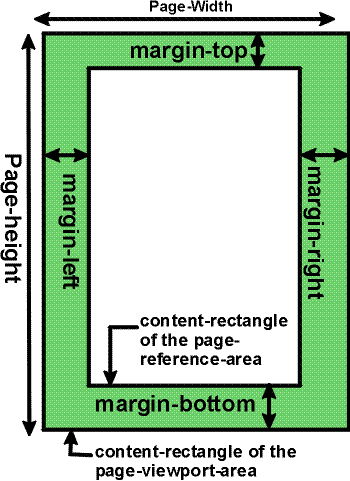
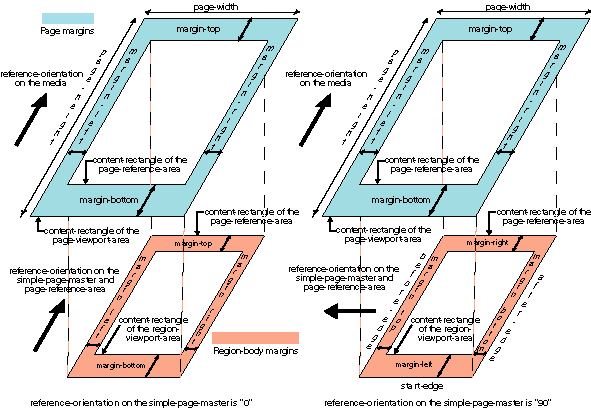
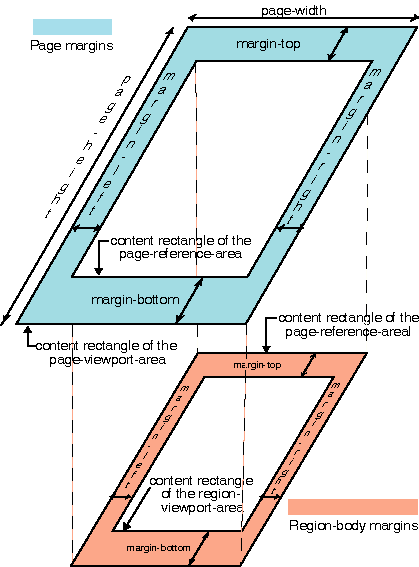
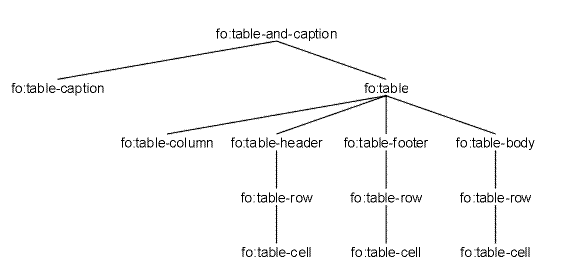
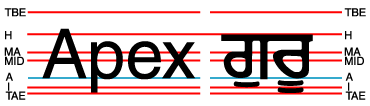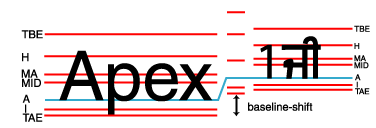C.4 Properties and the FOs they apply to
For each property the formatting objects it applies to is
listed. It should be noted, however, that for some formatting objects
there are qualifications on applicability or values permitted.
Property absolute-position applies to:
fo:block-container.
Property active-state applies to:
fo:multi-property-set.
Property alignment-adjust applies to:
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property alignment-baseline applies to:
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property allowed-height-scale applies to:
fo:external-graphic, and
fo:instream-foreign-object.
Property allowed-width-scale applies to:
fo:external-graphic, and
fo:instream-foreign-object.
Property auto-restore applies to:
fo:multi-switch.
Property azimuth applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property background-attachment applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property background-color applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property background-image applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property background-position-horizontal applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property background-position-vertical applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property background-repeat applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
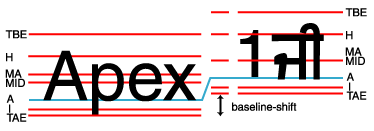
Property baseline-shift applies to:
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property blank-or-not-blank applies to:
fo:conditional-page-master-reference.
Property block-progression-dimension applies to:
fo:block-container,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-row, and
fo:table-cell.
Property border-after-color applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-after-precedence applies to:
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row, and
fo:table-cell.
Property border-after-style applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-after-width applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-before-color applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-before-precedence applies to:
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row, and
fo:table-cell.
Property border-before-style applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-before-width applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-bottom-color applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-bottom-style applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-bottom-width applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-collapse applies to:
fo:table.
Property border-end-color applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-end-precedence applies to:
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row, and
fo:table-cell.
Property border-end-style applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-end-width applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-left-color applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-left-style applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-left-width applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-right-color applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-right-style applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-right-width applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-separation applies to:
fo:table.
Property border-start-color applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-start-precedence applies to:
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row, and
fo:table-cell.
Property border-start-style applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-start-width applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-top-color applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-top-style applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property border-top-width applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property bottom applies to:
fo:block-container.
Property bottom applies to:
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property break-after applies to:
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-row,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property break-before applies to:
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-row,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property caption-side applies to:
fo:table-and-caption.
Property case-name applies to:
fo:multi-case.
Property case-title applies to:
fo:multi-case.
Property change-bar-class applies to:
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property change-bar-color applies to:
fo:change-bar-begin.
Property change-bar-offset applies to:
fo:change-bar-begin.
Property change-bar-placement applies to:
fo:change-bar-begin.
Property change-bar-style applies to:
fo:change-bar-begin.
Property change-bar-width applies to:
fo:change-bar-begin.
Property character applies to:
fo:character.
Property clear applies to:
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:list-block, and
fo:float.
Property clip applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:block-container,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object, and
fo:inline-container.
Property color applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:inline, and
fo:leader.
Property color-profile-name applies to:
fo:color-profile.
Property column-count applies to:
fo:region-body.
Property column-gap applies to:
fo:region-body.
Property column-number applies to:
fo:table-column, and
fo:table-cell.
Property column-width applies to:
fo:table-column.
Property content-height applies to:
fo:external-graphic, and
fo:instream-foreign-object.
Property content-type applies to:
fo:external-graphic, and
fo:instream-foreign-object.
Property content-width applies to:
fo:external-graphic, and
fo:instream-foreign-object.
Property country applies to:
fo:block, and
fo:character.
Property cue-after applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property cue-before applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property destination-placement-offset applies to:
fo:basic-link.
Property direction applies to:
fo:bidi-override.
Property display-align applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:block-container,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline-container, and
fo:table-cell.
Property dominant-baseline applies to:
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property elevation applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property empty-cells applies to:
fo:table-cell.
Property end-indent applies to:
fo:simple-page-master,
fo:region-body,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property ends-row applies to:
fo:table-cell.
Property extent applies to:
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start, and
fo:region-end.
Property external-destination applies to:
fo:basic-link, and
fo:bookmark.
Property float applies to:
fo:float.
Property flow-map-name applies to:
fo:flow-map.
Property flow-map-reference applies to:
fo:page-sequence.
Property flow-name applies to:
fo:flow, and
fo:static-content.
Property flow-name-reference applies to:
fo:flow-name-specifier.
Property font-family applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property font-selection-strategy applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property font-size applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property font-size-adjust applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property font-stretch applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property font-style applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property font-variant applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property font-weight applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property force-page-count applies to:
fo:page-sequence.
Property format applies to:
fo:page-sequence, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property glyph-orientation-horizontal applies to:
fo:character.
Property glyph-orientation-vertical applies to:
fo:character.
Property grouping-separator applies to:
fo:page-sequence, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property grouping-size applies to:
fo:page-sequence, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property height applies to:
fo:block-container,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-row, and
fo:table-cell.
Property hyphenate applies to:
fo:block, and
fo:character.
Property hyphenation-character applies to:
fo:block, and
fo:character.
Property hyphenation-keep applies to:
fo:block.
Property hyphenation-ladder-count applies to:
fo:block.
Property hyphenation-push-character-count applies to:
fo:block, and
fo:character.
Property hyphenation-remain-character-count applies to:
fo:block, and
fo:character.
Property id applies to:
fo:root,
fo:page-sequence,
fo:page-sequence-wrapper,
fo:flow,
fo:static-content,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:list-item-body,
fo:list-item-label,
fo:basic-link,
fo:multi-switch,
fo:multi-case,
fo:multi-toggle,
fo:multi-property-set,
fo:index-range-begin,
fo:float,
fo:footnote,
fo:footnote-body, and
fo:wrapper.
Property index-class applies to:
fo:root,
fo:page-sequence,
fo:page-sequence-wrapper,
fo:flow,
fo:static-content,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:list-item-body,
fo:list-item-label,
fo:basic-link,
fo:multi-switch,
fo:multi-case,
fo:multi-toggle,
fo:multi-property-set,
fo:index-range-begin,
fo:float,
fo:footnote,
fo:footnote-body, and
fo:wrapper.
Property index-key applies to:
fo:root,
fo:page-sequence,
fo:page-sequence-wrapper,
fo:flow,
fo:static-content,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:list-item-body,
fo:list-item-label,
fo:basic-link,
fo:multi-switch,
fo:multi-case,
fo:multi-toggle,
fo:multi-property-set,
fo:index-range-begin,
fo:float,
fo:footnote,
fo:footnote-body, and
fo:wrapper.
Property indicate-destination applies to:
fo:basic-link.
Property initial-page-number applies to:
fo:page-sequence.
Property inline-progression-dimension applies to:
fo:block-container,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption, and
fo:table-cell.
Property internal-destination applies to:
fo:basic-link, and
fo:bookmark.
Property intrinsic-scale-value applies to:
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property intrusion-displace applies to:
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property keep-together applies to:
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-row,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:list-item-body,
fo:list-item-label, and
fo:basic-link.
Property keep-with-next applies to:
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-row,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property keep-with-previous applies to:
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-row,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property language applies to:
fo:block, and
fo:character.
Property last-line-end-indent applies to:
fo:block.
Property leader-alignment applies to:
fo:leader.
Property leader-length applies to:
fo:leader.
Property leader-pattern applies to:
fo:leader.
Property leader-pattern-width applies to:
fo:leader.
Property left applies to:
fo:block-container.
Property left applies to:
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property letter-spacing applies to:
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property letter-value applies to:
fo:page-sequence, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property linefeed-treatment applies to:
fo:block.
Property line-height applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property line-height-shift-adjustment applies to:
fo:block.
Property line-stacking-strategy applies to:
fo:block.
Property margin-bottom applies to:
fo:simple-page-master,
fo:region-body,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property margin-bottom applies to:
fo:title,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property margin-left applies to:
fo:simple-page-master,
fo:region-body,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property margin-left applies to:
fo:title,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property margin-right applies to:
fo:simple-page-master,
fo:region-body,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property margin-right applies to:
fo:title,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property margin-top applies to:
fo:simple-page-master,
fo:region-body,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property margin-top applies to:
fo:title,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property marker-class-name applies to:
fo:marker.
Property master-name applies to:
fo:page-sequence-master, and
fo:simple-page-master.
Property master-reference applies to:
fo:page-sequence,
fo:single-page-master-reference,
fo:repeatable-page-master-reference, and
fo:conditional-page-master-reference.
Property maximum-repeats applies to:
fo:repeatable-page-master-reference, and
fo:repeatable-page-master-alternatives.
Property media-usage applies to:
fo:root.
Property merge-pages-across-index-key-references applies to:
fo:index-page-citation-list.
Property merge-ranges-across-index-key-references applies to:
fo:index-page-citation-list.
Property merge-sequential-page-numbers applies to:
fo:index-page-citation-list.
Property number-columns-repeated applies to:
fo:table-column.
Property number-columns-spanned applies to:
fo:table-column, and
fo:table-cell.
Property number-rows-spanned applies to:
fo:table-cell.
Property odd-or-even applies to:
fo:conditional-page-master-reference.
Property orphans applies to:
fo:block.
Property overflow applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:block-container,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object, and
fo:inline-container.
Property padding-after applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property padding-before applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property padding-bottom applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property padding-end applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property padding-left applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property padding-right applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property padding-start applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property padding-top applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property page-citation-strategy applies to:
fo:page-number-citation-last.
Property page-height applies to:
fo:simple-page-master.
Property page-number-treatment applies to:
fo:index-key-reference.
Property page-position applies to:
fo:conditional-page-master-reference.
Property page-width applies to:
fo:simple-page-master.
Property pause-after applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property pause-before applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property pitch applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property pitch-range applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property play-during applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property precedence applies to:
fo:region-before, and
fo:region-after.
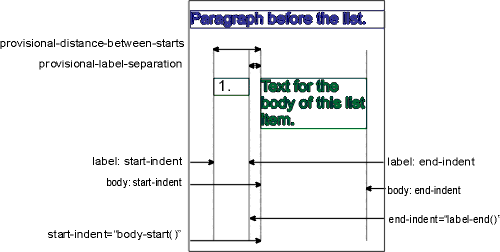
Property provisional-distance-between-starts applies to:
fo:list-block.
Property provisional-label-separation applies to:
fo:list-block.
Property reference-orientation applies to:
fo:page-sequence,
fo:simple-page-master,
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:block-container, and
fo:inline-container.
Property ref-id applies to:
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:index-range-end.
Property ref-index-key applies to:
fo:index-key-reference.
Property region-name applies to:
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start, and
fo:region-end.
Property region-name-reference applies to:
fo:region-name-specifier.
Property relative-align applies to:
fo:table-cell, and
fo:list-item.
Property relative-position applies to:
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property rendering-intent applies to:
fo:color-profile.
Property retrieve-boundary applies to:
fo:retrieve-marker.
Property retrieve-boundary-within-table applies to:
fo:retrieve-table-marker.
Property retrieve-class-name applies to:
fo:retrieve-marker, and
fo:retrieve-table-marker.
Property retrieve-position applies to:
fo:retrieve-marker.
Property retrieve-position-within-table applies to:
fo:retrieve-table-marker.
Property richness applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property right applies to:
fo:block-container.
Property right applies to:
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property role applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:list-item-body,
fo:list-item-label,
fo:basic-link,
fo:multi-switch,
fo:multi-case,
fo:multi-toggle,
fo:multi-properties,
fo:bookmark,
fo:bookmark-title,
fo:footnote,
fo:footnote-body,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property rule-style applies to:
fo:leader.
Property rule-thickness applies to:
fo:leader.
Property scale-option applies to:
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property scaling applies to:
fo:external-graphic, and
fo:instream-foreign-object.
Property scaling-method applies to:
fo:external-graphic, and
fo:instream-foreign-object.
Property score-spaces applies to:
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property script applies to:
fo:block, and
fo:character.
Property show-destination applies to:
fo:basic-link.
Property source-document applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:list-item-body,
fo:list-item-label,
fo:basic-link,
fo:multi-switch,
fo:multi-case,
fo:multi-toggle,
fo:multi-properties,
fo:bookmark,
fo:bookmark-title,
fo:footnote,
fo:footnote-body,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property space-after applies to:
fo:simple-page-master,
fo:region-body,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property space-before applies to:
fo:simple-page-master,
fo:region-body,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property space-end applies to:
fo:title,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property space-start applies to:
fo:title,
fo:character,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation, and
fo:basic-link.
Property span applies to:
fo:block, and
fo:block-container.
Property speak applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property speak-header applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property speak-numeral applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property speak-punctuation applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property speech-rate applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property src applies to:
fo:color-profile, and
fo:external-graphic.
Property start-indent applies to:
fo:simple-page-master,
fo:region-body,
fo:block,
fo:block-container,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:list-block, and
fo:list-item.
Property starting-state applies to:
fo:multi-case, and
fo:bookmark.
Property starts-row applies to:
fo:table-cell.
Property stress applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property suppress-at-line-break applies to:
fo:character.
Property switch-to applies to:
fo:multi-toggle.
Property table-layout applies to:
fo:table.
Property table-omit-footer-at-break applies to:
fo:table.
Property table-omit-header-at-break applies to:
fo:table.
Property target-presentation-context applies to:
fo:basic-link.
Property target-processing-context applies to:
fo:basic-link.
Property target-stylesheet applies to:
fo:basic-link.
Property text-align applies to:
fo:block,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object, and
fo:table-and-caption.
Property text-align-last applies to:
fo:block.
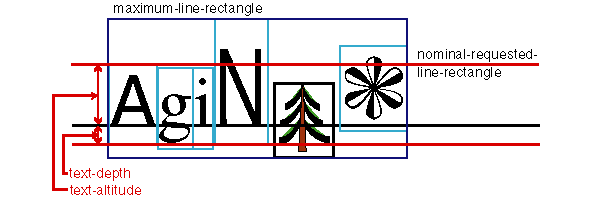
Property text-altitude applies to:
fo:block,
fo:character,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property text-decoration applies to:
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:inline,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property text-depth applies to:
fo:block,
fo:character,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property text-indent applies to:
fo:block.
Property text-shadow applies to:
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property text-transform applies to:
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property top applies to:
fo:block-container.
Property top applies to:
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item, and
fo:basic-link.
Property treat-as-word-space applies to:
fo:character.
Property unicode-bidi applies to:
fo:bidi-override.
Property visibility applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:character,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-column,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body, and
fo:table-row.
Property voice-family applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property volume applies to:
fo:title,
fo:block,
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last,
fo:scaling-value-citation,
fo:table-and-caption,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption,
fo:table-header,
fo:table-footer,
fo:table-body,
fo:table-row,
fo:table-cell,
fo:list-block,
fo:list-item,
fo:basic-link,
fo:change-bar-begin, and
fo:change-bar-end.
Property white-space-collapse applies to:
fo:block.
Property white-space-treatment applies to:
fo:block.
Property widows applies to:
fo:block.
Property width applies to:
fo:block-container,
fo:external-graphic,
fo:instream-foreign-object,
fo:inline,
fo:inline-container,
fo:table,
fo:table-caption, and
fo:table-cell.
Property word-spacing applies to:
fo:bidi-override,
fo:character,
fo:initial-property-set,
fo:leader,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property wrap-option applies to:
fo:block,
fo:inline,
fo:page-number,
fo:page-number-citation,
fo:page-number-citation-last, and
fo:scaling-value-citation.
Property writing-mode applies to:
fo:page-sequence,
fo:simple-page-master,
fo:region-body,
fo:region-before,
fo:region-after,
fo:region-start,
fo:region-end,
fo:block-container,
fo:inline-container, and
fo:table.
Property z-index applies to:
fo:block-container, and
fo:change-bar-begin.