Depending on the level of DOM support, or the devices used to
display (e.g. screen) or interact with (e.g. mouse, keyboard, touch
screen, voice, ...), these event types could be generated by the
implementation. When used with an [XML 1.0] or [HTML 4.01]
application, the specifications of those languages may restrict the
semantics and scope (in particular the possible target nodes)
associated with an event type. For example,
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "click"} can be
targeted to all [XHTML 1.0] elements but applet, base,
basefont, bdo, br, font, frame, frameset, head, html, iframe,
isindex, meta, param, script, style, and title. Refer to the
specification defining the language used in order to find those
restrictions or to find event types that are not defined in this
document.
The following table defines all event types provided in this
specification (with the exception of two event types preserved for
backward compatibility with [HTML 4.01]). All events will
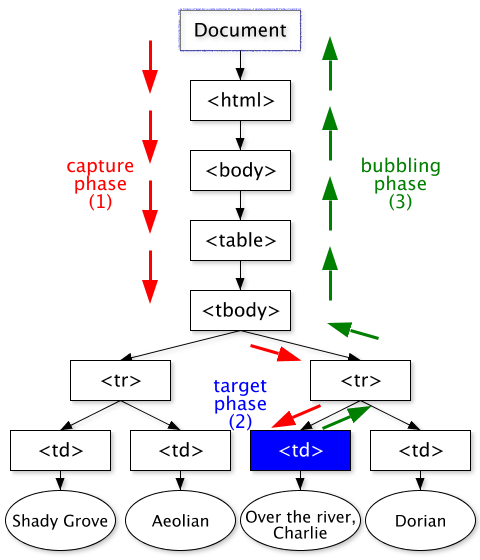
accomplish the capture phase and target phases, but not all of them
will accomplish the bubbling phase (see also DOM event flow). Some events are not
cancelable
(see Default actions
and cancelable events). Contextual information related to the
event type are accessible using DOM interfaces.
| Event type |
Description |
Bubbling phase |
Cancelable |
Target node |
DOM interface |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMActivate" |
An element is activated,
for instance, using a mouse device, a keyboard device, or a voice
command.
Note: The activation of an element is device dependent
but is also application dependent, e.g. a link in a document can be
activated using a mouse click or a mouse double click.
|
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
UIEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMFocusIn" |
An event target receives
focus, for instance via a pointing device being moved onto an
element or using keyboard navigation. The focus is given to the
element before the dispatch of this event type. |
Yes |
No |
Element |
UIEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMFocusOut" |
A event target loses
focus, for instance via a pointing device being moved out of an
element or by tabbing navigation out of the element. The focus is
taken from the element before the dispatch of this event type. |
Yes |
No |
Element |
UIEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "textInput" |
One or more characters
have been entered. The characters can originate from a variety of
sources. For example, it could be a character resulting from a key
being pressed or released on a keyboard device, a character
resulting from the processing of an input method editor, or resulting
from a voice command. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
TextEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "click" |
A pointing device button
is clicked over an element. The definition of a click depends on
the environment configuration; i.e. may depend on the screen
location or the delay between the press and release of the pointing
device button. In any case, the target node must be the same
between the mousedown, mouseup, and click. The sequence of these
events is: {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"mousedown"}, {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"mouseup"}, and {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"click"}. Note that, given the definition of a click, If one
or more of the event types
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mouseover"},
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mousemove"},
and {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mouseout"}
occur between the press and release of the pointing device button,
the event type {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"click"} cannot occur. In the case of nested elements, this
event type is always targeted at the most deeply nested
element. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mousedown" |
A pointing device button
is pressed over an element. In the case of nested elements, this
event type is always targeted at the most deeply nested
element. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mouseup" |
A pointing device button
is released over an element. In the case of nested elements, this
event type is always targeted at the most deeply nested
element. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mouseover" |
A pointing device is moved
onto an element. In the case of nested elements, this event type is
always targeted at the most deeply nested element. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mousemove" |
A pointing device is moved
while it is over an element. In the case of nested elements, this
event type is always targeted at the most deeply nested
element. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mouseout" |
A pointing device is moved
away from an element. In the case of nested elements, this event
type is always targeted at the most deeply nested element. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "keydown" |
A key is pressed down.
This event type is device dependent and relies on the capabilities
of the input devices and how they are mapped in the operating
system. This event type is generated after the keyboard mapping but
before the processing of the input
method editor. This event should logically happen before
the event {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"keyup"} is produced. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
KeyboardEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "keyup" |
A key is released. This
event type is device dependent and relies on the capabilities of
the input devices and how they are mapped in the operating system.
This event type is generated after the keyboard mapping but before
the processing of the input method
editor. This event should logically happen after the event
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "keydown"} is
produced. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
KeyboardEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMSubtreeModified" |
This is a general event
for notification of all changes to the document. It can be used
instead of the more specific events listed below. It may be
dispatched after a single modification to the document or, at the
implementation's discretion, after multiple changes have occurred.
The latter use should generally be used to accommodate multiple
changes which occur either simultaneously or in rapid succession.
The target of this event is the lowest common parent of the changes
which have taken place. This event is dispatched after any other
events caused by the mutation(s) have occurred. |
Yes |
No |
Document,
DocumentFragment, Element,
Attr |
MutationEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMNodeInserted" |
A node has been added as a
child of another
node. This event is dispatched after the insertion has taken place.
The target node
of this event is the node being inserted. |
Yes |
No |
Element,
Attr, Text, Comment,
CDATASection, DocumentType,
EntityReference,
ProcessingInstruction |
MutationEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMNodeRemoved" |
A node is being removed
from its parent node. This event is dispatched before the node is
removed from the tree. The target node of this
event is the node being removed. |
Yes |
No |
Element,
Attr, Text, Comment,
CDATASection, DocumentType,
EntityReference,
ProcessingInstruction |
MutationEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMNodeRemovedFromDocument" |
A node is being removed
from a document, either through direct removal of the node or
removal of a subtree in which it is contained. This event is
dispatched before the removal takes place. The target node of this
event type is the node being removed. If the node is being directly
removed, the event type {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMNodeRemoved"} will fire before this event type. |
No |
No |
Element,
Attr, Text, Comment,
CDATASection, DocumentType,
EntityReference,
ProcessingInstruction |
MutationEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMNodeInsertedIntoDocument" |
A node is being inserted
into a document, either through direct insertion of the node or
insertion of a subtree in which it is contained. This event is
dispatched after the insertion has taken place. The target node of this
event is the node being inserted. If the node is being directly
inserted, the event type
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMNodeInserted"} will fire before this event type. |
No |
No |
Element,
Attr, Text, Comment,
CDATASection, DocumentType,
EntityReference,
ProcessingInstruction |
MutationEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMAttrModified" |
Occurs after an
Attr has been modified on a node. The target node of this
event is the parent Element node whose
Attr changed. It is expected that string based
replacement of an Attr value will be viewed as a
modification of the Attr since its identity does not
change. Subsequently replacement of the Attr node with
a different Attr node is viewed as the removal of the
first Attr node and the addition of the second. |
Yes |
No |
Element |
MutationEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMCharacterDataModified" |
Occurs after
CharacterData.data or
ProcessingInstruction.data have been modified but the
node itself has not been inserted or deleted. The target node of this
event is the CharacterData node or the
ProcessingInstruction node. |
Yes |
No |
Text,
Comment, CDATASection,
ProcessingInstruction |
MutationEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMElementNameChanged" |
Occurs after the
namespaceURI and/or the nodeName of an
Element node have been modified (e.g., the element was
renamed using Document.renameNode). The target of this
event is the renamed Element node. |
Yes |
No |
Element |
MutationNameEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMAttributeNameChanged" |
Occurs after the
namespaceURI and/or the nodeName of a
Attr node have been modified (e.g., the attribute was
renamed using Document.renameNode). The target of this
event is the parent Element node whose
Attr has been renamed. |
Yes |
No |
Element |
MutationNameEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "load" |
The DOM Implementation
finishes loading the resource (such as the document) and any
dependent resources (such as images, style sheets, or scripts).
Dependent resources that fail to load will not prevent this event
from firing if the resource that loaded them is still accessible
via the DOM. |
No |
No |
Element |
Event |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "unload" |
The DOM implementation
removes from the environment the resource (such as the document) or
any dependent resources (such as images, style sheets, scripts).
The document is unloaded after the dispatch of this event
type. |
No |
No |
Element |
Event |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "abort" |
The loading of the
document, or a resource linked from it, is stopped before being
entirely loaded. |
Yes |
No |
Element |
Event |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "error" |
The document, or a
resource linked from it, has been loaded but cannot be interpreted
according to its semantic, such as an invalid image or a script
execution error. |
Yes |
No |
Element |
Event |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "select" |
A user selects some text.
DOM Level 3 Events does not provide contextual information to
access the selected text. The selection occured before the dispatch
of this event type. |
Yes |
No |
Element |
Event |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "change" |
A control loses the input
focus and its values has been modified since gaining focus. |
Yes |
No |
Element |
Event |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "submit" |
A form, such as [HTML 4.01],
[XHTML
1.0], or [XForms 1.0] forms, is
submitted. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
Event |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "reset" |
A form, such as [HTML 4.01],
[XHTML
1.0], or [XForms 1.0] forms, is reset. |
Yes |
Yes |
Element |
Event |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "resize" |
A document view has been
resized. The resize occured before the dispatch of this event
type. |
Yes |
No |
Document
|
UIEvent |
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "scroll" |
A document view has been
scrolled. The scroll occured before the dispatch of this event
type. |
Yes |
No |
Document
|
UIEvent |
The event objects associated with the event types described
above may contain context information. Refer to the description of
the DOM interfaces for further information.