4.10. Forms
4.10.1. Introduction
This section is non-normative.
A form is a component of a Web page that has form controls, such as text fields, buttons, checkboxes, range controls, or color pickers. A user can interact with such a form, providing data that can then be sent to the server for further processing (e.g., returning the results of a search or calculation). No client-side scripting is needed in many cases, though an API is available so that scripts can augment the user experience or use forms for purposes other than submitting data to a server.
Writing a form consists of several steps, which can be performed in any order: writing the user interface, implementing the server-side processing, and configuring the user interface to communicate with the server.
4.10.1.1. Writing a form’s user interface
This section is non-normative.
For the purposes of this brief introduction, we will create a pizza ordering form.
Any form starts with a form element, inside which are placed the controls. Most
controls are represented by the input element, which by default provides a one-line
text field. To label a control, the label element is used; the label text and the
control itself go inside the label element. Each area within a form is typically represented
using a div element. Putting this together, here is how one might ask for the customer’s name:
<form> <div><label>Customer name: <input></label></div> </form>
To let the user select the size of the pizza, we can use a set of radio buttons. Radio buttons
also use the input element, this time with a type attribute with the value radio. To make the radio buttons work as a group, they are
given a common name using the name attribute. To group a batch
of controls together, such as, in this case, the radio buttons, one can use the fieldset element. The title of such a group of controls is given by the first element
in the fieldset, which has to be a legend element.
<form> <div><label>Customer name: <input></label></div> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Small </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Medium </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Large </label></div> </fieldset> </form>
Changes from the previous step are highlighted.
To pick toppings, we can use checkboxes. These use the input element with a type attribute with the value checkbox:
<form> <div><label>Customer name: <input></label></div> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Small </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Medium </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Large </label></div> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Toppings </legend> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Bacon </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Extra Cheese </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Onion </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Mushroom </label></div> </fieldset> </form>
The pizzeria for which this form is being written is always making mistakes, so it needs a way
to contact the customer. For this purpose, we can use form controls specifically for telephone
numbers (input elements with their type attribute set to tel) and e-mail addresses
(input elements with their type attribute set to email):
<form> <div><label>Customer name: <input></label></div> <div><label>Telephone: <input type=tel></label></div> <div><label>E-mail address: <input type=email></label></div> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Small </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Medium </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Large </label></div> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Toppings </legend> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Bacon </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Extra Cheese </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Onion </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Mushroom </label></div> </fieldset> </form>
We can use an input element with its type attribute set to time to ask for a delivery time. Many
of these form controls have attributes to control exactly what values can be specified; in this
case, three attributes of particular interest are min, max, and step. These set the
minimum time, the maximum time, and the interval between allowed values (in seconds). This
pizzeria only delivers between 11am and 9pm, and doesn’t promise anything better than 15 minute
increments, which we can mark up as follows:
<form> <div><label>Customer name: <input></label></div> <div><label>Telephone: <input type=tel></label></div> <div><label>E-mail address: <input type=email></label></div> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Small </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Medium </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Large </label></div> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Toppings </legend> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Bacon </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Extra Cheese </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Onion </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Mushroom </label></div> </fieldset> <div><label>Preferred delivery time: <input type=time min="11:00" max="21:00" step="900"></label></div> </form>
The textarea element can be used to provide a free-form text field. In this
instance, we are going to use it to provide a space for the customer to give delivery
instructions:
<form> <div><label>Customer name: <input></label></div> <div><label>Telephone: <input type=tel></label></div> <div><label>E-mail address: <input type=email></label></div> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Small </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Medium </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Large </label></div> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Toppings </legend> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Bacon </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Extra Cheese </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Onion </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Mushroom </label></div> </fieldset> <div><label>Preferred delivery time: <input type=time min="11:00" max="21:00" step="900"></label></div> <div><label>Delivery instructions: <textarea></textarea></label></div> </form>
Finally, to make the form submittable we use the button element:
<form> <div><label>Customer name: <input></label></div> <div><label>Telephone: <input type=tel></label></div> <div><label>E-mail address: <input type=email></label></div> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Small </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Medium </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size> Large </label></div> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Toppings </legend> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Bacon </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Extra Cheese </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Onion </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox> Mushroom </label></div> </fieldset> <div><label>Preferred delivery time: <input type=time min="11:00" max="21:00" step="900"></label></div> <div><label>Delivery instructions: <textarea></textarea></label></div> <div><button>Submit order</button></div> </form>
4.10.1.2. Implementing the server-side processing for a form
This section is non-normative.
The exact details for writing a server-side processor are out of scope for this specification.
For the purposes of this introduction, we will assume that the script at https://pizza.example.com/order.cgi is configured to accept submissions using the application/x-www-form-urlencoded format,
expecting the following parameters sent in an HTTP POST body:
custname-
Customer’s name
custtel-
Customer’s telephone number
custemail-
Customer’s e-mail address
size-
The pizza size, either
small,medium, orlarge topping-
A topping, specified once for each selected topping, with the allowed values being
bacon,cheese,onion, andmushroom delivery-
The requested delivery time
comments-
The delivery instructions
4.10.1.3. Configuring a form to communicate with a server
This section is non-normative.
Form submissions are exposed to servers in a variety of ways, most commonly as HTTP GET or
POST requests. To specify the exact method used, the method attribute is specified on the form element. This doesn’t specify how the form data is
encoded, though; to specify that, you use the enctype attribute. You also have to specify the URL of the service that will handle the
submitted data, using the action attribute.
For each form control you want submitted, you then have to give a name that will be used to
refer to the data in the submission. We already specified the name for the group of radio buttons;
the same attribute (name) also specifies the submission name.
Radio buttons can be distinguished from each other in the submission by giving them different
values, using the value attribute.
Multiple controls can have the same name; for example, here we give all the checkboxes the same
name, and the server distinguishes which checkbox was checked by seeing which values are submitted
with that name — like the radio buttons, they are also given unique values with the value attribute.
Given the settings in the previous section, this all becomes:
<form method="post" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded" action="https://pizza.example.com/order.cgi"> <p><label>Customer name: <input name="custname"></label></p> <p><label>Telephone: <input type=tel name="custtel"></label></p> <p><label>E-mail address: <input type=email name="custemail"></label></p> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size value="small"> Small </label></p> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size value="medium"> Medium </label></p> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size value="large"> Large </label></p> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Toppings </legend> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="bacon"> Bacon </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="cheese"> Extra Cheese </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="onion"> Onion </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="mushroom"> Mushroom </label></p> </fieldset> <p><label>Preferred delivery time: <input type=time min="11:00" max="21:00" step="900" name="delivery"></label></p> <p><label>Delivery instructions: <textarea name="comments"></textarea></label></p> <p><button>Submit order</button></p> </form>
There is no particular significance to the way some of the attributes have their values quoted and others don’t. The HTML syntax allows a variety of equally valid ways to specify attributes, as discussed in §8 The HTML syntax.
For example, if the customer entered "Denise Lawrence" as their name, "555-321-8642" as their telephone number, did not specify an e-mail address, asked for a medium-sized pizza, selected the Extra Cheese and Mushroom toppings, entered a delivery time of 7pm, and left the delivery instructions text field blank, the user agent would submit the following to the online Web service:
custname=Denise+Lawrence&custtel=555-321-8642&custemail=&size=medium&topping=cheese&topping=mushroom&delivery=19%3A00&comments=
4.10.1.4. Client-side form validation
This section is non-normative.
Forms can be annotated in such a way that the user agent will check the user’s input before the form is submitted. The server still has to verify the input is valid (since hostile users can easily bypass the form validation), but it allows the user to avoid the wait incurred by having the server be the sole checker of the user’s input.
The simplest annotation is the required attribute,
which can be specified on input elements to indicate that the form is not to be
submitted until a value is given. By adding this attribute to the customer name, pizza size, and
delivery time fields, we allow the user agent to notify the user when the user submits the form
without filling in those fields:
<form method="post" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded" action="https://pizza.example.com/order.cgi"> <p><label>Customer name: <input name="custname" required></label></p> <p><label>Telephone: <input type=tel name="custtel"></label></p> <p><label>E-mail address: <input type=email name="custemail"></label></p> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="small"> Small </label></p> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="medium"> Medium </label></p> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="large"> Large </label></p> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Toppings </legend> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="bacon"> Bacon </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="cheese"> Extra Cheese </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="onion"> Onion </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="mushroom"> Mushroom </label></p> </fieldset> <p><label>Preferred delivery time: <input type=time min="11:00" max="21:00" step="900" name="delivery" required></label></p> <p><label>Delivery instructions: <textarea name="comments"></textarea></label></p> <p><button>Submit order</button></p> </form>
It is also possible to limit the length of the input, using the maxlength attribute. By adding this to the textarea element, we can limit users to 1000 characters, preventing them from writing huge essays to the
busy delivery drivers instead of staying focused and to the point:
<form method="post" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded" action="https://pizza.example.com/order.cgi"> <p><label>Customer name: <input name="custname" required></label></p> <p><label>Telephone: <input type=tel name="custtel"></label></p> <p><label>E-mail address: <input type=email name="custemail"></label></p> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="small"> Small </label></p> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="medium"> Medium </label></p> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="large"> Large </label></p> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Toppings </legend> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="bacon"> Bacon </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="cheese"> Extra Cheese </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="onion"> Onion </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="mushroom"> Mushroom </label></p> </fieldset> <p><label>Preferred delivery time: <input type=time min="11:00" max="21:00" step="900" name="delivery" required></label></p> <p><label>Delivery instructions: <textarea name="comments" maxlength=1000></textarea></label></p> <p><button>Submit order</button></p> </form>
When a form is submitted, invalid events are
fired at each form control that is invalid, and then at the form element itself. This
can be useful for displaying a summary of the problems with the form, since typically the browser
itself will only report one problem at a time.
4.10.1.5. Enabling client-side automatic filling of form controls
This section is non-normative.
Some browsers attempt to aid the user by automatically filling form controls rather than having the user reenter their information each time. For example, a field asking for the user’s telephone number can be automatically filled with the user’s phone number.
To help the user agent with this, the autocomplete attribute can be used to describe the field’s purpose. In the case of this form, we have three
fields that can be usefully annotated in this way: the information about who the pizza is to be
delivered to. Adding this information looks like this:
<form method="post" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded" action="https://pizza.example.com/order.cgi"> <p><label>Customer name: <input name="custname" required autocomplete="shipping name"></label></p> <p><label>Telephone: <input type=tel name="custtel" autocomplete="shipping tel"></label></p> <p><label>E-mail address: <input type=email name="custemail" autocomplete="shipping email"></label></p> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="small"> Small </label></p> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="medium"> Medium </label></p> <p><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="large"> Large </label></p> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Toppings </legend> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="bacon"> Bacon </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="cheese"> Extra Cheese </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="onion"> Onion </label></p> <p><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="mushroom"> Mushroom </label></p> </fieldset> <p><label>Preferred delivery time: <input type=time min="11:00" max="21:00" step="900" name="delivery" required></label></p> <p><label>Delivery instructions: <textarea name="comments" maxlength=1000></textarea></label></p> <p><button>Submit order</button></p> </form>
4.10.1.6. Improving the user experience on mobile devices
This section is non-normative.
Some devices, in particular those with on-screen keyboards and those in locales with languages with many characters (e.g., Japanese), can provide the user with multiple input modalities. For example, when typing in a credit card number the user may wish to only see keys for digits 0-9, while when typing in their name they may wish to see a form field that by default capitalizes each word.
Using the inputmode attribute we can select appropriate
input modalities:
<form method="post" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded" action="https://pizza.example.com/order.cgi"> <div><label>Customer name: <input name="custname" required autocomplete="shipping name" inputmode="latin-name"></label></div> <div><label>Telephone: <input type=tel name="custtel" autocomplete="shipping tel"></label></div> <div><label>E-mail address: <input type=email name="custemail" autocomplete="shipping email"></label></div> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Size </legend> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="small"> Small </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="medium"> Medium </label></div> <div><label> <input type=radio name=size required value="large"> Large </label></div> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend> Pizza Toppings </legend> <div><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="bacon"> Bacon </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="cheese"> Extra Cheese </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="onion"> Onion </label></div> <div><label> <input type=checkbox name="topping" value="mushroom"> Mushroom </label></divp> </fieldset> <div><label>Preferred delivery time: <input type=time min="11:00" max="21:00" step="900" name="delivery" required></label></divp> <div><label>Delivery instructions: <textarea name="comments" maxlength=1000 inputmode="latin-prose"></textarea></label></div> <div><button>Submit order</button></div> </form>
4.10.1.7. The difference between the field type, the autofill field name, and the input modality
This section is non-normative.
The type, autocomplete, and inputmode attributes can seem confusingly similar. For instance,
in all three cases, the string "email" is a valid value. This section
attempts to illustrate the difference between the three attributes and provides advice suggesting
how to use them.
The type attribute on input elements decides
what kind of control the user agent will use to expose the field. Choosing between different
values of this attribute is the same choice as choosing whether to use an input element, a textarea element, a select element, etc.
The autocomplete attribute, in contrast, describes
what the value that the user will enter actually represents. Choosing between different values of
this attribute is the same choice as choosing what the label for the element will be.
First, consider telephone numbers. If a page is asking for a telephone number from the user,
the right form control to use is <input type=tel>.
However, which autocomplete value to use depends on
which phone number the page is asking for, whether they expect a telephone number in the
international format or just the local format, and so forth.
For example, a page that forms part of a checkout process on an e-commerce site for a customer buying a gift to be shipped to a friend might need both the buyer’s telephone number (in case of payment issues) and the friend’s telephone number (in case of delivery issues). If the site expects international phone numbers (with the country code prefix), this could thus look like this:
<div><label>Your phone number: <input type=tel name=custtel autocomplete="billing tel"></label> <div><label>Recipient’s phone number: <input type=tel name=shiptel autocomplete="shipping tel"></label> <p>Please enter complete phone numbers including the country code prefix, as in "+1 555 123 4567".
But if the site only supports British customers and recipients, it might instead look like this
(notice the use of tel-national rather than tel):
<div><label>Your phone number: <input type=tel name=custtel autocomplete="billing tel-national"></label> <div><label>Recipient’s phone number: <input type=tel name=shiptel autocomplete="shipping tel-national"></label> <p>Please enter complete UK phone numbers, as in "(01632) 960 123".
Now, consider a person’s preferred languages. The right autocomplete value is language. However, there could be a number of
different form controls used for the purpose: a free text field (<input type=text>), a drop-down list (<select>), radio buttons (<input
type=radio>), etc. It only depends on what kind of interface is desired.
The inputmode decides what kind of input modality (e.g.,
keyboard) to use, when the control is a free-form text field.
Consider names. If a page just wants one name from the user, then the relevant control is <input type=text>. If the page is asking for the user’s
full name, then the relevant autocomplete value is name. But if the user is Japanese, and the page is asking
for the user’s Japanese name and the user’s romanized name, then it would be helpful to the user
if the first field defaulted to a Japanese input modality, while the second defaulted to a Latin
input modality (ideally with automatic capitalization of each word). This is where the inputmode attribute can help:
<p><label>Japanese name: <input name="j" type="text" autocomplete="section-jp name" inputmode="kana"></label> <label>Romanized name: <input name="e" type="text" autocomplete="section-en name" inputmode="latin-name"></label>
In this example, the "section-*" keywords in
the autocomplete attributes' values tell the user agent
that the two fields expect different names. Without them, the user agent could
automatically fill the second field with the value given in the first field when the user gave a
value to the first field.
The "-jp" and "-en" parts of the
keywords are opaque to the user agent; the user agent cannot guess, from those, that the two names
are expected to be in Japanese and English respectively.
4.10.1.8. Date, time, and number formats
This section is non-normative.
In this pizza delivery example, the times are specified in the format "HH:MM": two digits for the hour, in 24-hour format, and two digits for the time. (Seconds could also be specified, though they are not necessary in this example.)
In some locales, however, times are often expressed differently when presented to users. For example, in the United States, it is still common to use the 12-hour clock with an am/pm indicator, as in "2pm". In France, it is common to use the 24-hour clock, and separate the hours from the minutes using an "h" character, as in "14h00".
Similar issues exist with dates, with the added complication that even the order of the components is not always consistent — for example, in Cyprus the first of February 2003 would typically be written "1/2/03", while that same date in Japan would typically be written as "2003年02月01日" — and even with numbers, where locales differ, for example, in what punctuation is used as the decimal separator and the thousands separator.
It is therefore important to distinguish the time, date, and number formats used in HTML and in form submissions, which are always the formats defined in this specification (and based on the well-established ISO 8601 standard for computer-readable date and time formats), from the time, date, and number formats presented to the user by the browser and accepted as input from the user by the browser.
The format used "on the wire", i.e. in HTML markup and in form submissions, is intended to be computer-readable and consistent irrespective of the user’s locale. Dates, for instance, are always written in the format "YYYY-MM-DD", as in "2003-02-01". Users are not expected to ever see this format.
The time, date, or number given by the page in the wire format is then translated to the user’s preferred presentation (based on user preferences or on the locale of the page itself), before being displayed to the user. Similarly, after the user inputs a time, date, or number using their preferred format, the user agent converts it back to the wire format before putting it in the DOM or submitting it.
This allows scripts in pages and on servers to process times, dates, and numbers in a consistent manner without needing to support dozens of different formats, while still supporting the users' needs.
See also the implementation notes regarding localization of form controls.
4.10.2. Categories
Mostly for historical reasons, elements in this section fall into several overlapping (but subtly different) categories in addition to the usual ones like flow content, phrasing content, and interactive content.
A number of the elements are form-associated elements, which means they can have a form owner.
The form-associated elements fall into several subcategories:
- Listed elements
-
Denotes elements that are listed in the
form.elementsandfieldset.elementsAPIs. - Submittable elements
-
Denotes elements that can be used for constructing the form data set when a
formelement is submitted.Some submittable elements can be, depending on their attributes, buttons. The prose below defines when an element is a button. Some buttons are specifically submit buttons.
- Resettable elements
-
Denotes elements that can be affected when a
formelement is reset. - Reassociateable elements
-
Denotes elements that have a
formcontent attribute, and a matchingformIDL attribute, that allow authors to specify an explicit form owner.
Some elements, not all of them form-associated,
are categorized as labelable elements. These are elements that
can be associated with a label element.
The following table is non-normative and summarizes the above categories of form elements:
| form-associated | listed | submittable | resettable | reassociateable | labelable | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| can have a form owner | listed in the form.elements and fieldset.elements APIs
| can be used for constructing the form data set when a form element is submitted | can be affected when a form element is reset | have a form attribute (allows authors to specify an explicit form owner)
| can be associated with a label element
| |
input
| yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes (except "hidden") |
button
| yes | yes | yes | no | yes | yes |
select
| yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
textarea
| yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
fieldset
| yes | yes | no | no | yes | no |
output
| yes | yes | no | yes | yes | yes |
object
| yes | yes | yes | no | yes | no |
meter
| no | no | no | no | no | yes |
progress
| no | no | no | no | no | yes |
label
| yes | no | no | no | no | no |
img
| yes | no | no | no | no | no |
4.10.3. The form element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Palpable content.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where flow content is expected.
- Content model:
- Flow content, but with no
formelement descendants. - Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible.
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
accept-charset- Character encodings to use for §4.10.21 Form submissionaction- URL to use for §4.10.21 Form submissionautocomplete- Default setting for autofill feature for controls in the formenctype- Form data set encoding type to use for §4.10.21 Form submissionmethod- HTTP method to use for §4.10.21 Form submissionname- Name of form to use in thedocument.formsAPInovalidate- Bypass form control validation for §4.10.21 Form submissiontarget- browsing context for §4.10.21 Form submission- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
dd>
form(default - do not set),searchorpresentation. - Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles. - DOM interface:
-
[OverrideBuiltins] interface HTMLFormElement : HTMLElement { attribute DOMString acceptCharset; attribute DOMString action; attribute DOMString autocomplete; attribute DOMString enctype; attribute DOMString encoding; attribute DOMString method; attribute DOMString name; attribute boolean noValidate; attribute DOMString target; [SameObject] readonly attribute HTMLFormControlsCollection elements; readonly attribute unsigned long length; getter Element (unsigned long index); getter (RadioNodeList or Element) (DOMString name); void submit(); void reset(); boolean checkValidity(); boolean reportValidity(); };
The form element represents a collection of form-associated elements, some of which can represent
editable values that can be submitted to a server for processing.
The accept-charset content attribute gives the
character encodings that are to be used for the submission. If specified, the value must be an ordered set of unique space-separated tokens that are ASCII
case-insensitive, and each token must be an ASCII case-insensitive match for
one of the labels of an ASCII-compatible encoding. [ENCODING]
The name content attribute represents the form's name within the forms collection. The
value must not be the empty string, and the value must be unique amongst the form elements in the forms collection that it is in, if any.
The autocomplete content attribute is an enumerated attribute. The attribute has two states. The on keyword maps to the on state, and the off keyword maps to the off state. The attribute may also be omitted. The missing value default is the on state. The off state indicates that by default, form
controls in the form will have their autofill field name set to "off"; the on state indicates that by default, form controls
in the form will have their autofill field name set to "on".
The action, enctype, method, enctype, novalidate, and target attributes are attributes for form submission.
- form .
elements -
Returns an
HTMLFormControlsCollectionof the form controls in the form (excluding image buttons for historical reasons). - form .
length -
Returns the number of form controls in the form (excluding image buttons for historical reasons).
- form[index]
-
Returns the indexth element in the form (excluding image buttons for historical reasons).
- form[name]
-
Returns the form control (or, if there are several, a
RadioNodeListof the form controls) in the form with the given ID orname(excluding image buttons for historical reasons); or, if there are none, returns theimgelement with the given ID.Once an element has been referenced using a particular name, that name will continue being available as a way to reference that element in this method, even if the element’s actual ID or
namechanges, for as long as the element remains in theDocument.If there are multiple matching items, then a
RadioNodeListobject containing all those elements is returned. - form .
submit() -
Submits the form.
- form .
reset() -
Resets the form.
- form .
checkValidity() -
Returns true if the form’s controls are all valid; otherwise, returns false.
- form .
reportValidity() -
Returns true if the form’s controls are all valid; otherwise, returns false and informs the user.
The autocomplete IDL attribute must reflect the content attribute of the same name, limited to only known
values.
The name IDL attribute must reflect the content attribute of the same name.
The acceptCharset IDL attribute must reflect the accept-charset content attribute.
The elements IDL attribute must return an HTMLFormControlsCollection rooted at the form element, whose filter matches listed elements whose form owner is the form element, with the exception of input elements whose type attribute is in the Image Button state, which must, for historical reasons, be
excluded from this particular collection.
The length IDL attribute must return the
number of nodes represented by the elements collection.
The supported property indices at any instant are the indices supported by the
object returned by the elements attribute at that
instant.
When a form element is indexed for indexed property
retrieval, the user agent must return the value returned by the item method on the elements collection, when invoked with the given index as its
argument.
Each form element has a mapping of names to elements called the past names
map. It is used to persist names of controls even when they change names.
The supported property names consist of the names obtained from the following algorithm, in the order obtained from this algorithm:
- Let sourced names be an initially empty ordered list of tuples consisting of a string, an element, a source, where the source is either id, name, or past, and, if the source is past, an age.
-
For each listed element candidate whose form owner is the
formelement, with the exception of anyinputelements whosetypeattribute is in theImage Buttonstate, run these substeps:- If candidate has an
idattribute, add an entry to sourced names with thatidattribute’s value as the string, candidate as the element, and id as the source. - If candidate has a
nameattribute, add an entry to sourced names with thatnameattribute’s value as the string, candidate as the element, and name as the source.
- If candidate has an
-
For each
imgelement candidate whose form owner is theformelement, run these substeps:- If candidate has an
idattribute, add an entry to sourced names with thatidattribute’s value as the string, candidate as the element, and id as the source. - If candidate has a
nameattribute, add an entry to sourced names with thatnameattribute’s value as the string, candidate as the element, and name as the source.
- If candidate has an
-
For each entry past entry in the past names map add an entry to sourced names with the past entry’s name as the string, past entry’s element as the element, past as the source, and the length of time past entry has been in the past names map as the age.
- Sort sourced names by tree order of the element entry of each tuple, sorting entries with the same element by putting entries whose source is id first, then entries whose source is name, and finally entries whose source is past, and sorting entries with the same element and source by their age, oldest first.
- Remove any entries in sourced names that have the empty string as their name.
- Remove any entries in sourced names that have the same name as an earlier entry in the map.
- Return the list of names from sourced names, maintaining their relative order.
The properties exposed in this way must be unenumerable.
When a form element is indexed for named property retrieval, the user agent must
run the following steps:
-
Let candidates be a live
RadioNodeListobject containing all the listed elements whose form owner is theformelement that have either anidattribute or anameattribute equal to name, with the exception ofinputelements whosetypeattribute is in theImage Buttonstate, in tree order. -
If candidates is empty, let candidates be a live
RadioNodeListobject containing all theimgelements that are descendants of theformelement and that have either anidattribute or anameattribute equal to name, in tree order. -
If candidates is empty, name is the name of one of the entries in the
formelement’s past names map: return the object associated with name in that map. -
If candidates contains more than one node, return candidates and abort these steps.
-
Otherwise, candidates contains exactly one node. Add a mapping from name to the node in candidates in the
formelement’s past names map, replacing the previous entry with the same name, if any. -
Return the node in candidates.
If an element listed in a form element’s past names map changes form owner, then
its entries must be removed from that map.
The submit() method, when invoked, must submit the form element from the form element itself, with the submitted from submit() method flag set.
The reset() method, when invoked, must run
the following steps:
- If the
formelement is marked as locked for reset, then abort these steps. - Mark the
formelement as locked for reset. - Reset the
formelement. - Unmark the
formelement as locked for reset.
If the checkValidity() method is
invoked, the user agent must statically validate the constraints of the form element, and return true if the constraint validation return a positive result, and false if it returned a negative result.
If the reportValidity() method is
invoked, the user agent must interactively validate the constraints of the form element, and return true if the constraint validation return a positive result, and false if it returned a negative result.
<form action="https://www.google.com/search" method="get"> <label>Google: <input type="search" name="q"></label> <input type="submit" value="Search..."> </form> <form action="https://www.bing.com/search" method="get"> <label>Bing: <input type="search" name="q"></label> <input type="submit" value="Search..."> </form>
4.10.4. The label element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Phrasing content.
- Interactive content.
- form-associated element.
- Palpable content.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where phrasing content is expected.
- Content model:
- Phrasing content, but with no descendant labelable elements unless it is the element’s labeled control, and no descendant
labelelements. - Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
for- Associate the label with form control- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
- None
- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLLabelElement : HTMLElement { readonly attribute HTMLFormElement? form; attribute DOMString htmlFor; readonly attribute HTMLElement? control; };
The label element represents a caption in a user interface. The
caption can be associated with a specific form control, known as the label element’s labeled control, either using the for attribute,
or by putting the form control inside the label element itself.
Except where otherwise specified by the following rules, a label element has no labeled control.
The for attribute may be specified to indicate a
form control with which the caption is to be associated. If the attribute is specified, the
attribute’s value must be the ID of a labelable element in the same Document as the label element. If the attribute is specified and there is an
element in the Document whose ID is equal to the
value of the for attribute, and the first such element is a labelable element, then that element is the label element’s labeled control.
The following example shows the use of a for attribute, to associate labels
which do not contain the element they label.
<form> <table> <caption>Example, <label>'s for attribute</caption> <tr> <th><label for="name">Customer name: </label></th> <td><input name="name" id="name"></td> </tr> </table> </form>
Note that the id attribute is required to associate the for attribute,
while the name attribute is required so the value of the input will be submitted as
part of the form.
If the for attribute is not specified, but the label element has a labelable element descendant,
then the first such descendant in tree order is the label element’s labeled control.
The label element’s activation behavior should match the platform’s label
behavior. Similarly, any additional presentation hints should match the platform’s
label presentation.
label "Lost" in the following
snippet could trigger the user agent to run synthetic click activation steps on the checkbox, as if the element itself had been triggered by the user, while clicking
the label "Where?" would queue a task that runs the focusing steps for the element to the text input:
<label><input type="checkbox" name="lost"> Lost</label><br> <label>Where? <input type="text" name="where"></label>
If a label element has interactive content other than its labeled control, the activation behavior of the label element for events targeted
at those interactive content descendants and any
descendants of those must be to do nothing.
In the following example, clicking on the link does not toggle the checkbox, even if the platform normally toggles a checkbox when clicking on a label. Instead, clicking the link triggers the normal activation behavior of following the link.
<!-- bad example - link inside label reduces checkbox activation area --> <label><input type=checkbox name=tac>I agree to <a href="tandc.html">the terms and conditions</a></label>
The ability to click or press a label to trigger an event on a control provides
usability and accessibility benefits by increasing the hit area of a control, making it easier for a user to operate.
These benefits may be lost or reduced, if the label element contains an element with its own activation
behavior, such as a link:
<!-- bad example - all label text inside the link reduces activation area to checkbox only --> <label><input type=checkbox name=tac><a href="tandc.html">I agree to the terms and conditions</a></label>
The usability and accessibility benefits can be maintained by placing such elements outside the label element:
<!-- good example - link outside label means checkbox activation area includes the checkbox and all the label text --> <label><input type=checkbox name=tac>I agree to the terms and conditions</label> (read <a href="tandc.html">Terms and Conditions</a>)
<p><label>Full name: <input name=fn> <small>Format: First Last</small></label></p> <p><label>Age: <input name=age type=number min=0></label></p> <p><label>Post code: <input name=pc> <small>Format: AB12 3CD</small></label></p>
- label .
control -
Returns the form control that is associated with this element.
The htmlFor IDL attribute must reflect the for content attribute.
The control IDL attribute must return the label element’s labeled control, if any, or null if there isn’t one.
- control .
labels -
Returns a
NodeListof all thelabelelements that the form control is associated with.
Labelable elements have a NodeList object
associated with them that represents the list of label elements, in tree
order, whose labeled control is the element in question. The labels IDL attribute of labelable elements, on getting, must return that NodeList object.
4.10.5. The input element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Phrasing content.
- If the
typeattribute is not in theHiddenstate: interactive content. - If the
typeattribute is not in theHiddenstate: listed, labelable, submittable, resettable, and reassociateable form-associated element. - If the
typeattribute is in theHiddenstate: listed, submittable, resettable, and reassociateable form-associated element. - If the
typeattribute is not in theHiddenstate: Palpable content. - Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where phrasing content is expected.
- Content model:
- Nothing.
- Tag omission in text/html:
- No end tag
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
accept- Hint for expected file type inFile Uploadcontrolsalt- Replacement text for use when images are not availableautocomplete- Hint for form autofill featureautofocus- Automatically focus the form control when the page is loadedchecked- Whether the command or control is checkeddirname- Name of form field to use for sending the element’s directionality in §4.10.21 Form submissiondisabled- Whether the form control is disabledform- Associates the control with aformelementformaction- URL to use for §4.10.21 Form submissionformenctype- Form data set encoding type to use for §4.10.21 Form submissionformmethod- HTTP method to use for §4.10.21 Form submissionformnovalidate- Bypass form control validation for §4.10.21 Form submissionformtarget- browsing context for §4.10.21 Form submissionheight- Vertical dimensioninputmode- Hint for selecting an input modalitylist- List of autocomplete optionsmax- Maximum valuemaxlength- Maximum length of valuemin- Minimum valueminlength- Minimum length of valuemultiple- Whether to allow multiple valuesname- Name of form control to use for §4.10.21 Form submission and in theform.elementsAPIpattern- Pattern to be matched by the form control’s valueplaceholder- User-visible label to be placed within the form controlreadonly- Whether to allow the value to be edited by the userrequired- Whether the control is required for §4.10.21 Form submissionsize- Size of the controlsrc- Address of the resourcestep- Granularity to be matched by the form control’s valuetype- Type of form controlvalue- Value of the form controlwidth- Horizontal dimension- Also, the
titleattribute has special semantics on this element when used in conjunction with thepatternattribute. - Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
- Depends upon state of the
typeattribute. - Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles. - DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLInputElement : HTMLElement { attribute DOMString accept; attribute DOMString alt; attribute DOMString autocomplete; attribute boolean autofocus; attribute boolean defaultChecked; attribute boolean checked; attribute DOMString dirName; attribute boolean disabled; readonly attribute HTMLFormElement? form; readonly attribute FileList? files; attribute DOMString formAction; attribute DOMString formEnctype; attribute DOMString formMethod; attribute boolean formNoValidate; attribute DOMString formTarget; attribute unsigned long height; attribute boolean indeterminate; attribute DOMString inputMode; readonly attribute HTMLElement? list; attribute DOMString max; attribute long maxLength; attribute DOMString min; attribute long minLength; attribute boolean multiple; attribute DOMString name; attribute DOMString pattern; attribute DOMString placeholder; attribute boolean readOnly; attribute boolean _required; attribute unsigned long size; attribute DOMString src; attribute DOMString step; attribute DOMString type; attribute DOMString defaultValue; [TreatNullAs=EmptyString] attribute DOMString value; attribute object? valueAsDate; attribute unrestricted double valueAsNumber; attribute unsigned long width; void stepUp(optional long n = 1); void stepDown(optional long n = 1); readonly attribute boolean willValidate; readonly attribute ValidityState validity; readonly attribute DOMString validationMessage; boolean checkValidity(); boolean reportValidity(); void setCustomValidity(DOMString error); [SameObject] readonly attribute NodeList labels; void select(); attribute unsigned long? selectionStart; attribute unsigned long? selectionEnd; attribute DOMString? selectionDirection; void setRangeText(DOMString replacement); void setRangeText(DOMString replacement, unsigned long start, unsigned long end, optional SelectionMode selectionMode = "preserve"); void setSelectionRange(unsigned long start, unsigned long end, optional DOMString direction); };
The input element represents a typed data field, usually with a form
control to allow the user to edit the data.
The type attribute controls the data type of the
element. It is an enumerated attribute. The data type is used to select the control to
use for the input. Some data types allow either a text field or combo box control to be used,
based on the absence or presence of a list attribute on the element.
The following table lists the keywords and states for the attribute — the keywords in the
left column map to the state, data type and control(s) in the cells on the same row.
| Keyword | State | Data type | Control type |
|---|---|---|---|
hidden
| | An arbitrary string | n/a |
text
| Text
| Text with no line breaks | A text field or combo box |
search
| Search
| Text with no line breaks | Search field or combo box |
tel
| Telephone
| Text with no line breaks | A text field or combo box |
url
| URL
| An absolute URL | A text field or combo box |
email
| E-mail
| An e-mail address or list of e-mail addresses | A text field or combo box |
password
| Password
| Text with no line breaks (sensitive information) | A text field that obscures data entry |
datetime
| Date and Time
| A date and time (year, month, day, hour, minute, second, fraction of a second) with the time zone set to UTC | A date and time control |
date
| Date
| A date (year, month, day) with no time zone | A date control |
month
| Month
| A date consisting of a year and a month with no time zone | A month control |
week
| Week
| A date consisting of a week-year number and a week number with no time zone | A week control |
time
| Time
| A time (hour, minute, seconds, fractional seconds) with no time zone | A time control |
datetime-local
| Local Date and Time
| A date and time (year, month, day, hour, minute, second, fraction of a second) with no timezone offset | A date and time control |
number
| Number
| A numerical value | A text field or combo box or spinner control |
range
| Range
| A numerical value, with the extra semantic that the exact value is not important | A slider control or similar |
color
| Color
| An sRGB color with 8-bit red, green, and blue components | A color well |
checkbox
| Checkbox
| A set of zero or more values from a predefined list | A checkbox |
radio
| Radio Button
| An enumerated value | A radio button |
file
| File Upload
| Zero or more files each with a MIME type and optionally a file name | A label and a button |
submit
| Submit Button
| An enumerated value, with the extra semantic that it must be the last value selected and initiates form submission | A button |
image
| Image Button
| A coordinate, relative to a particular image’s size, with the extra semantic that it must be the last value selected and initiates form submission | Either a clickable image, or a button |
reset
| Reset Button
| n/a | A button |
button
| Button
| n/a | A button |
The missing value default is the Text state.
Which of the accept, alt, autocomplete, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, list, max, maxlength, min, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, size, src, step, and width content attributes, the checked, files, valueAsDate, valueAsNumber, and list IDL attributes, the select() method, the selectionStart, selectionEnd, and selectionDirection, IDL attributes, the setRangeText() and setSelectionRange() methods, the stepUp() and stepDown() methods, and the input and change events apply to an input element depends on the state of its type attribute.
The subsections that define each type also clearly define in normative "bookkeeping" sections
which of these feature apply, and which do not apply, to each type. The behavior of
these features depends on whether they apply or not, as defined in their various sections (q.v.
for Content attributes, for APIs, for events).
The following table is non-normative and summarizes which of those content attributes, IDL attributes, methods, and events apply to each state:
| Text, Search
| URL, Telephone
| E-mail
| Password
| Date and Time, Date, Month, Week, Time
| Number
| Range
| Color
| Checkbox, Radio Button
| File Upload
| Submit Button
| Image Button
| Reset Button, Button
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content attributes | ||||||||||||||
accept
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | · | · | · |
alt
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | · |
autocomplete
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · |
checked
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | · | · | · | · |
dirname
| · | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
formaction
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | · |
formenctype
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | · |
formmethod
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | · |
formnovalidate
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | · |
formtarget
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | · |
height
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | · |
inputmode
| · | Yes | · | · | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
list
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · |
max
| · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · |
maxlength
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
min
| · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · |
minlength
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
multiple
| · | · | · | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | · | · | · |
pattern
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
placeholder
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
readonly
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
required
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | Yes | Yes | · | · | · |
size
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
src
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | · |
step
| · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · |
width
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | · |
| IDL attributes and methods | ||||||||||||||
checked
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | · | · | · | · |
files
| · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | Yes | · | · | · |
value
| default | value | value | value | value | value | value | value | value | default/on | filename | default | default | default |
valueAsDate
| · | · | · | · | · | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
valueAsNumber
| · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · |
list
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · |
select()
| · | Yes | Yes† | Yes | Yes† | Yes† | Yes† | · | Yes† | · | Yes† | · | · | · |
selectionStart
| · | Yes | Yes | · | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
selectionEnd
| · | Yes | Yes | · | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
selectionDirection
| · | Yes | Yes | · | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
setRangeText()
| · | Yes | Yes | · | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
setSelectionRange()
| · | Yes | Yes | · | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · |
stepDown()
| · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · |
stepUp()
| · | · | · | · | · | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · | · | · | · |
| Events | ||||||||||||||
input event
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · |
change event
| · | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | · | · | · |
† If the control has no text field, the select() method
results in a no-op, with no "InvalidStateError" DOMException.
Some states of the type attribute define a value sanitization algorithm.
Each input element has a value, which is
exposed by the value IDL attribute. Some states define an algorithm to convert a string to a number,
an algorithm to convert a number to a
string, an algorithm to convert a string to a Date object, and an algorithm to
convert a Date object to a string, which are used by max, min, step, valueAsDate, valueAsNumber, stepDown(), and stepUp().
Each input element has a boolean dirty value flag. The dirty value flag must be
initially set to false when the element is created, and must be set to true whenever the user
interacts with the control in a way that changes the value.
(It is also set to true when the value is programmatically changed, as described in the definition
of the value IDL attribute.)
The value content attribute gives the default value of the input element. When the value content attribute is added, set,
or removed, if the control’s dirty value flag is false, the user agent must set the value of the element
to the value of the value content attribute, if there is
one, or the empty string otherwise, and then run the current value sanitization
algorithm, if one is defined.
Each input element has a checkedness,
which is exposed by the checked IDL attribute.
Each input element has a boolean dirty checkedness flag. When it is true, the
element is said to have a dirty checkedness.
The dirty checkedness flag must be initially
set to false when the element is created, and must be set to true whenever the user interacts with
the control in a way that changes the checkedness.
The checked content attribute is a boolean attribute that gives the default checkedness of the input element. When the checked content attribute is added,
if the control does not have dirty checkedness, the
user agent must set the checkedness of the element to
true; when the checked content attribute is removed, if
the control does not have dirty checkedness, the user
agent must set the checkedness of the element to
false.
The reset algorithm for input elements is to set the dirty value flag and dirty checkedness flag back to false, set
the value of the element to the value of the value content attribute, if there is one, or the empty string
otherwise, set the checkedness of the element to true if
the element has a checked content attribute and false if
it does not, empty the list of selected
files, and then invoke the value sanitization algorithm, if the type attribute’s current state defines one.
Each input element can be mutable. Except where
otherwise specified, an input element is always mutable. Similarly, except where otherwise specified, the user
agent should not allow the user to modify the element’s value or checkedness.
When an input element is disabled, it is not mutable.
The readonly attribute can also in some
cases (e.g., for the Date state, but not the Checkbox state) stop an input element from
being mutable.
The cloning steps for input elements
must propagate the value, dirty value flag, checkedness, and dirty checkedness flag from the node being cloned
to the copy.
When an input element is first created, the element’s rendering and behavior must
be set to the rendering and behavior defined for the type attribute’s state, and the value sanitization algorithm, if one is defined for the type attribute’s state, must be invoked.
When an input element’s type attribute
changes state, the user agent must run the following steps:
- If the previous state of the element’s
typeattribute put thevalueIDL attribute in the value mode, and the element’s value is not the empty string, and the new state of the element’stypeattribute puts thevalueIDL attribute in either the default mode or the default/on mode, then set the element’svaluecontent attribute to the element’s value. - Otherwise, if the previous state of the element’s
typeattribute put thevalueIDL attribute in any mode other than the value mode, and the new state of the element’stypeattribute puts thevalueIDL attribute in the value mode, then set the value of the element to the value of thevaluecontent attribute, if there is one, or the empty string otherwise, and then set the control’s dirty value flag to false. - Otherwise, if the previous state of the element’s
typeattribute put thevalueIDL attribute in any mode other than the filename mode, and the new state of the element’stypeattribute puts thevalueIDL attribute in the filename mode, then set the value of the element to the empty string. - Update the element’s rendering and behavior to the new state’s.
- Signal a type change for the element. (The
Radio Buttonstate uses this, in particular.) - Invoke the value sanitization algorithm, if one is defined for the
typeattribute’s new state.
The name attribute represents the element’s name.
The dirname attribute controls how the element’s directionality is submitted.
The disabled attribute is used to make the control non-interactive and to prevent its value from being submitted.
The form attribute is used to explicitly associate the input element with its form owner.
The autofocus attribute controls focus.
The inputmode attribute controls the user interface’s input modality for the control.
The autocomplete attribute controls how the user agent provides autofill behavior.
The indeterminate IDL attribute must
initially be set to false. On getting, it must return the last value it was set to. On setting, it
must be set to the new value. It has no effect except for changing the appearance of checkbox controls.
The accept, alt, max, min, multiple, pattern, placeholder, required, size, src, and step IDL attributes must reflect the respective content attributes of the same name.
The dirName IDL attribute must reflect the dirname content attribute.
The readOnly IDL attribute must reflect the readonly content attribute.
The defaultChecked IDL attribute must reflect the checked content attribute.
The defaultValue IDL attribute must reflect the value content attribute.
The type IDL attribute must reflect the respective content attribute of the same name, limited to only known values.
The inputMode IDL attribute must reflect the inputmode content attribute, limited to only known values.
The maxLength IDL attribute must reflect the maxlength content attribute, limited to only non-negative numbers.
The minLength IDL attribute must reflect the minlength content attribute, limited to only non-negative numbers.
The IDL attributes width and height must return the rendered
width and height of the image, in CSS pixels, if an image is being rendered, and is
being rendered to a visual medium; or else the intrinsic width and height of the image,
in CSS pixels, if an image is available but not being rendered to a visual medium;
or else 0, if no image is available. When the input element’s type attribute is not in the Image Button state,
then no image is available. [CSS-2015]
On setting, they must act as if they reflected the respective content attributes of the same name.
The willValidate, validity, and validationMessage IDL attributes, and
the checkValidity(), reportValidity(), and setCustomValidity() methods, are part of
the constraint validation API.
The labels IDL attribute provides a list of the element’s labels.
The select(), selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods and IDL
attributes expose the element’s text selection.
The autofocus, disabled, form, and name IDL attributes are part of the
element’s forms API.
4.10.5.1. States of the type attribute
4.10.5.1.1. Hidden state (type=hidden)
The input element represents a value that is not intended to be
examined or manipulated by the user.
Constraint validation: If an input element’s type attribute is in the state, it is barred from constraint
validation.
If the name attribute is present and has a value that is a case-sensitive match for the string "_charset_", then the element’s value attribute must be omitted.
The value IDL attribute applies to this element and is
in mode default.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not
apply to the element: accept, alt, autocomplete, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, list, max, maxlength, min, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, size, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the
element: checked, files, list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), setSelectionRange(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The input and change events do not apply.
4.10.5.1.2. Text (type=text) state and Search state (type=search)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
textbox,searchboxwith nolistattribute (default - do not set) or with alistattribute:combobox(default - do not set).- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
When an input element’s type attribute is in
the Text state or the Search state, the rules in this section apply.
The input element represents a one line plain text edit control for
the element’s value.
The difference between the Text state
and the Search state is primarily stylistic: on
platforms where search fields are distinguished from regular text fields, the Search state might result in an appearance consistent with
the platform’s search fields rather than appearing like a regular text field.
If the element is mutable, its value should be editable by the user. User agents must not allow users to insert U+000A LINE FEED (LF) or U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) characters into the element’s value.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the writing direction of the element, setting it either to a left-to-right writing direction or a right-to-left writing direction. If the user does so, the user agent must then run the following steps:
- Set the element’s
dirattribute to "ltr" if the user selected a left-to-right writing direction, and "rtl" if the user selected a right-to-left writing direction. - Queue a task to fire a simple event that bubbles named
inputat theinputelement.
The value attribute, if specified, must have a value that
contains no U+000A LINE FEED (LF) or U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) characters.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: Strip line breaks from the value.
The following common input element content
attributes, IDL attributes, and methods apply to the element: autocomplete, dirname, inputmode, list, maxlength, minlength, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, and size content attributes; list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, and value IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
The value IDL attribute is
in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not
apply to the element: accept, alt, checked, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, max, min, multiple, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the
element: checked, files, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; stepDown() and stepUp() methods.
4.10.5.1.3. Telephone state (type=tel)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
textboxwith nolistattribute (default - do not set) or with alistattribute:combobox(default - do not set).- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
The input element represents a control for editing a telephone number
given in the element’s value.
If the element is mutable, its value should be editable by the user. User agents may change the spacing and, with care, the punctuation of values that the user enters. User agents must not allow users to insert U+000A LINE FEED (LF) or U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) characters into the element’s value.
The value attribute, if specified, must have a value that
contains no U+000A LINE FEED (LF) or U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) characters.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: Strip line breaks from the value.
Unlike the URL and E-mail types, the Telephone type does not enforce a particular syntax. This is
intentional; in practice, telephone number fields tend to be free-form fields, because there are a
wide variety of valid phone numbers. Systems that need to enforce a particular format are
encouraged to use the pattern attribute or the setCustomValidity() method to hook into the client-side
validation mechanism.
The following common input element content
attributes, IDL attributes, and methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, maxlength, minlength, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, and size content attributes; list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, and value IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
The value IDL attribute is
in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not
apply to the element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, max, min, multiple, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the
element: checked, files, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; stepDown() and stepUp() methods.
4.10.5.1.4. URL state (type=url)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
textboxwith nolistattribute (default - do not set) or with alistattribute:combobox(default - do not set).- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
The input element represents a control for editing a single absolute URL given in the element’s value.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the URL represented by its value. User agents may allow the user to set the value to a string that is not a valid absolute URL, but may also or instead automatically escape characters entered by the user so that the value is always a valid absolute URL (even if that isn’t the actual value seen and edited by the user in the interface). User agents should allow the user to set the value to the empty string. User agents must not allow users to insert U+000A LINE FEED (LF) or U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) characters into the value.
The value attribute, if specified and not empty, must
have a value that is a valid URL potentially surrounded by spaces that is also an absolute URL.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: Strip line breaks from the value, then strip leading and trailing white space from the value.
Constraint validation: While the value of the element is neither the empty string nor a valid absolute URL, the element is suffering from a type mismatch.
The following common input element content
attributes, IDL attributes, and methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, maxlength, minlength, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, and size content attributes; list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, and value IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
The value IDL attribute is
in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not
apply to the element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, max, min, multiple, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the
element: checked, files, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; stepDown() and stepUp() methods.
<input type="url" name="location" list="urls"> <datalist id="urls"> <option label="MIME: Format of Internet Message Bodies" value="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2045"> <option label="HTML 4.01 Specification" value="https://www.w3.org/TR/html4/"> <option label="Form Controls" value="https://www.w3.org/TR/xforms/slice8.html#ui-commonelems-hint"> <option label="Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) 1.1 Specification" value="https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG/"> <option label="Feature Sets - SVG 1.1 - 20030114" value="https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG/feature.html"> <option label="The Single UNIX Specification, Version 3" value="https://www.unix-systems.org/version3/"> </datalist>
...and the user had typed "www.w3", and the user agent had also found that the user
had visited https://www.w3.org/Consortium/#membership and https://www.w3.org/TR/XForms/ in the recent past, then the rendering might look
like this:
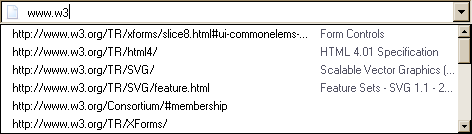
The first four URLs in this sample consist of the four URLs in the author-specified list that match the text the user has entered, sorted in some user agent-defined manner (maybe by how frequently the user refers to those URLs). Note how the user agent is using the knowledge that the values are URLs to allow the user to omit the scheme part and perform intelligent matching on the domain name.
The last two URLs (and probably many more, given the scrollbar’s indications of more values being available) are the matches from the user agent’s session history data. This data is not made available to the page DOM. In this particular case, the user agent has no titles to provide for those values.
4.10.5.1.5. E-mail state (type=email)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
textboxwith nolistattribute (default - do not set) or with alistattribute:combobox(default - do not set).- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
How the E-mail state operates depends on whether the multiple attribute is specified or not.
- When the
multipleattribute is not specified on the element -
The
inputelement represents a control for editing an e-mail address given in the element’s value.If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the e-mail address represented by its value. User agents may allow the user to set the value to a string that is not a valid e-mail address. The user agent should act in a manner consistent with expecting the user to provide a single e-mail address. User agents should allow the user to set the value to the empty string. User agents must not allow users to insert U+000A LINE FEED (LF) or U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) characters into the value. User agents may transform the value for display and editing; in particular, user agents should convert punycode in the domain labels of the value to IDN in the display and vice versa.
Constraint validation: While the user interface is representing input that the user agent cannot convert to punycode, the control is suffering from bad input.
The
valueattribute, if specified and not empty, must have a value that is a single valid e-mail address.The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: Strip line breaks from the value, then strip leading and trailing white space from the value.
Constraint validation: While the value of the element is neither the empty string nor a single valid e-mail address, the element is suffering from a type mismatch.
- When the
multipleattribute is specified on the element -
The
inputelement represents a control for adding, removing, and editing the e-mail addresses given in the element’s values.If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to add, remove, and edit the e-mail addresses represented by its values. User agents may allow the user to set any individual value in the list of values to a string that is not a valid e-mail address, but must not allow users to set any individual value to a string containing U+002C COMMA (,), U+000A LINE FEED (LF), or U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) characters. User agents should allow the user to remove all the addresses in the element’s values. User agents may transform the values for display and editing; in particular, user agents should convert punycode in the domain labels of the value to IDN in the display and vice versa.
Constraint validation: While the user interface describes a situation where an individual value contains a U+002C COMMA (,) or is representing input that the user agent cannot convert to punycode, the control is suffering from bad input.
Whenever the user changes the element’s values, the user agent must run the following steps:
- Let latest values be a copy of the element’s values.
- Strip leading and trailing white space from each value in latest values.
- Let the element’s value be the result of concatenating all the values in latest values, separating each value from the next by a single U+002C COMMA character (,), maintaining the list’s order.
The
valueattribute, if specified, must have a value that is a valid e-mail address list.The value sanitization algorithm is as follows:
- Split on commas the element’s value, strip leading and trailing white space from each resulting token, if any, and let the element’s values be the (possibly empty) resulting list of (possibly empty) tokens, maintaining the original order.
- Let the element’s value be the result of concatenating the element’s values, separating each value from the next by a single U+002C COMMA character (,), maintaining the list’s order.
Constraint validation: While the value of the element is not a valid e-mail address list, the element is suffering from a type mismatch.
When the multiple attribute is set or removed, the
user agent must run the value sanitization algorithm.
A valid e-mail address is a string that matches the email production of the following ABNF, the character set for which is Unicode. This ABNF implements the
extensions described in RFC 1123. [ABNF] [RFC5322] [RFC1034] [RFC1123]
email = 1*( atext / "." ) "@" label *( "." label ) label = let-dig [ [ ldh-str ] let-dig ] ; limited to a length of 63 characters by RFC 1034 section 3.5 atext = < as defined in RFC 5322 section 3.2.3 > let-dig = < as defined in RFC 1034 section 3.5 > ldh-str = < as defined in RFC 1034 section 3.5 >
This requirement is a willful violation of RFC 5322, which defines a syntax for e-mail addresses that is simultaneously too strict (before the "@" character), too vague (after the "@" character), and too lax (allowing comments, white space characters, and quoted strings in manners unfamiliar to most users) to be of practical use here.
The following JavaScript- and Perl-compatible regular expression is an implementation of the above definition.
/^[a-zA-Z0-9.!#$%&'*+\/=?^_`{|}~-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9](?:[a-zA-Z0-9-]{0,61}[a-zA-Z0-9])?(?:\.[a-zA-Z0-9](?:[a-zA-Z0-9-]{0,61}[a-zA-Z0-9])?)*$/
A valid e-mail address list is a set of comma-separated tokens, where each token is itself a valid e-mail address. To obtain the list of tokens from a valid e-mail address list, an implementation must split the string on commas.
The following common input element content
attributes, IDL attributes, and methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, maxlength, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, and size content attributes; list and value IDL attributes; select() method.
The value IDL attribute is
in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not
apply to the element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, max, min, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the
element: checked, files, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), setSelectionRange(), stepDown() and stepUp() methods.
4.10.5.1.6. Password state (type=password)
The input element represents a one line plain text edit control for
the element’s value. The user agent should obscure the value
so that people other than the user cannot see it.
If the element is mutable, its value should be editable by the user. User agents must not allow users to insert U+000A LINE FEED (LF) or U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) characters into the value.
The value attribute, if specified, must have a value that
contains no U+000A LINE FEED (LF) or U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) characters.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: Strip line breaks from the value.
The following common input element content
attributes, IDL attributes, and methods apply to the element: autocomplete, inputmode, maxlength, minlength, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, and size content attributes; selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, and value IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
The value IDL attribute is
in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not
apply to the element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, list, max, min, multiple, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the
element: checked, files, list, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; stepDown() and stepUp() methods.
4.10.5.1.7. Date and Time state (type=datetime)
When an input element’s type attribute is in
the Date and Time state, the rules in this section
apply.
The input element represents a control for setting the element’s value to a string representing a specific global date and time. User agents may display
the date and time in whatever time zone is appropriate for the user.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the global date and time represented by its value, as obtained by parsing a floating date and time from it. User agents must not allow the user to set the value to a non-empty string that is not a valid normalized global date and time string, though user agents may allow the user to set and view the time in another time zone and silently translate the time to and from the UTC time zone in the value. If the user agent provides a user interface for selecting a global date and time, then the value must be set to a valid normalized global date and time string representing the user’s selection. User agents should allow the user to set the value to the empty string.
Constraint validation: While the user interface describes input that the user agent cannot convert to a valid normalized global date and time string, the control is suffering from bad input.
See §4.10.1.8 Date, time, and number formats for a discussion of the difference between the input format and submission format for date, time, and number form controls, and the implementation notes regarding localization of form controls.
The value attribute, if specified and not empty, must
have a value that is a valid global date and time string.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: If the value of the element is a valid global date and time string, then adjust the time so that the value represents the same point in time but expressed in the UTC time zone as a valid normalized global date and time string, otherwise, set it to the empty string instead.
The min attribute, if specified, must have a value that is
a valid global date and time string. The max attribute, if specified, must have a value that is a valid global date and time
string.
The step attribute is expressed in seconds. The step scale factor is 1000 (which
converts the seconds to milliseconds, which is the base unit of comparison for the conversion
algorithms below). The default step is 60 seconds.
When the element is suffering from a step mismatch, the user agent may round the element’s value to the nearest global date and time for which the element would not suffer from a step mismatch.
The algorithm to convert a string to a
number, given a string input, is as follows: If parsing a floating date and time from input results in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return the number of
milliseconds elapsed from midnight UTC on the morning of 1970-01-01 (the time represented by the
value "1970-01-01T00:00:00.0Z") to the parsed global date and time, ignoring leap seconds.
The algorithm to convert a number to a
string, given a number input, is as follows: Return a valid normalized global date and time string that represents the global date and time that is input milliseconds after midnight UTC on the morning of 1970-01-01 (the time represented by the value
"1970-01-01T00:00:00.0Z").
The algorithm to convert a string to a Date object, given a string input, is as follows:
If parsing a floating date and time from input results in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return a new Date object representing the parsed global date and time, expressed in UTC.
The algorithm to convert a Date object to a string, given a Date object input, is as follows: Return a valid normalized global date and time string that represents the global date and
time that is represented by input.
The Date and Time state (and other date-related states are not
useful for vague values, and are only useful for dates ranging from recent history through a
few thousand years. For example, "one millisecond after the big bang", "the Ides of March, 44BC",
"the early part of the Jurassic period", or "a winter around 250 BCE", and many other expressions
of time cannot be sensibly expressed in HTML form states.
For the input of dates before the introduction of the Gregorian calendar, authors are
encouraged to not use the Date and Time state (and
the other date- and time-related states described in subsequent sections), as user agents are not
required to support converting dates and times from earlier periods to the Gregorian calendar,
and asking users to do so manually puts an undue burden on users. (This is complicated by the
manner in which the Gregorian calendar was phased in, which occurred at different times in
different countries, ranging from partway through the 16th century all the way to early in the
20th.) Instead, authors are encouraged to provide fine-grained input controls using the select element and input elements with the Number state.
The following common input element content
attributes, IDL attributes, and methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, max, min, readonly, required, and step content attributes; list, value, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The value IDL attribute is
in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not
apply to the element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, maxlength, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, size, src, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the
element: checked, files, selectionStart, selectionEnd, and selectionDirection IDL attributes; setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
<fieldset> <legend>Add Meeting</legend> <p><label>Meeting name: <input type=text name="meeting.label"></label> <p><label>Meeting time: <input type=datetime name="meeting.start"></label> </fieldset>
Had the application used the date and/or time types instead, the calendar application would
have also had to explicitly determine which time zone the user intended.
For events where the precise time is to vary as the user travels (e.g., "celebrate the new
year!"), and for recurring events that are to stay at the same time for a specific geographic
location even though that location may go in and out of daylight savings time (e.g., "bring the
kid to school"), the date and/or time types combined with a select element
(or other similar control) to pick the specific geographic location to which to anchor the time
would be more appropriate.
4.10.5.1.8. Date state (type=date)
The input element represents a control for setting the element’s value to a string representing a specific date.
date values represent a "floating" time and do not include time zone information. Care is needed when converting values of this type to or from date data types in JavaScript and other programming languages. In many cases, an implicit time-of-day and time zone are used to create a global ("incremental") time (an integer value that represents the offset from some arbitrary epoch time). Processing or conversion of these values, particularly across time zones, can change the value of the date itself. [TIMEZONE]
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the date represented by its value, as obtained by parsing a date from it. User agents must not allow the user to set the value to a non-empty string that is not a valid date string. If the user agent provides a user interface for selecting a date, then the value must be set to a valid date string representing the user’s selection. User agents should allow the user to set the value to the empty string.
Constraint validation: While the user interface describes input that the user agent cannot convert to a valid date string, the control is suffering from bad input.
See §4.10.1.8 Date, time, and number formats for a discussion of the difference between the input format and submission format for date, time, and number form controls, and the implementation notes regarding localization of form controls.
The value attribute, if specified and not empty, must
have a value that is a valid date string.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: If the value of the element is not a valid date string, then set it to the empty string instead.
The min attribute, if specified, must have a value that is
a valid date string. The max attribute, if
specified, must have a value that is a valid date string.
The step attribute is expressed in days. The step scale factor is 86,400,000 (which converts the days to milliseconds, which is the base unit of comparison for
the conversion algorithms below). The default step is 1 day.
When the element is suffering from a step mismatch, the user agent may round the element’s value to the nearest date for which the element would not suffer from a step mismatch.
The algorithm to convert a string to a
number, given a string input, is as follows: If parsing a date from input results in an
error, then return an error; otherwise, return the number of milliseconds elapsed from midnight
UTC on the morning of 1970-01-01 (the time represented by the value "1970-01-01T00:00:00.0Z") to midnight UTC on the morning of the parsed date, ignoring leap seconds.
The algorithm to convert a number to a
string, given a number input, is as follows: Return a valid date string that represents the date that, in
UTC, is current input milliseconds after midnight UTC on the morning of
1970-01-01 (the time represented by the value "1970-01-01T00:00:00.0Z").
The algorithm to convert a string to a Date object, given a string input, is as follows:
If parsing a date from input results
in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return a new Date object representing midnight UTC on the morning of the parsed date.
The algorithm to convert a Date object to a string, given a Date object input, is as follows: Return a valid date string that
represents the date current at the time represented by input in the UTC time zone.
See the note on historical dates in the Date and Time state section.
The following common input element content
attributes, IDL attributes, and methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, max, min, readonly, required, and step content attributes; list, value, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The value IDL attribute is
in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not
apply to the element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, maxlength, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, size, src, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the
element: checked, selectionStart, selectionEnd, and selectionDirection IDL attributes; setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
4.10.5.1.9. Month state (type=month)
The input element represents a control for setting the element’s value to a string representing a specific month.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the month represented by its value, as obtained by parsing a month from it. User agents must not allow the user to set the value to a non-empty string that is not a valid month string. If the user agent provides a user interface for selecting a month, then the value must be set to a valid month string representing the user’s selection. User agents should allow the user to set the value to the empty string.
Constraint validation: While the user interface describes input that the user agent cannot convert to a valid month string, the control is suffering from bad input.
See §4.10.1.8 Date, time, and number formats for a discussion of the difference between the input format and submission format for date, time, and number form controls, and the implementation notes regarding localization of form controls.
The value attribute, if specified and not empty, must
have a value that is a valid month string.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: If the value of the element is not a valid month string, then set it to the empty string instead.
The min attribute, if specified, must have a value that is
a valid month string. The max attribute, if
specified, must have a value that is a valid month string.
The step attribute is expressed in months. The step scale factor is 1
(units of whole months are the base unit of comparison for the conversion algorithms below).
The default step is 1 month.
When the element is suffering from a step mismatch, the user agent may round the element’s value to the nearest month for which the element would not suffer from a step mismatch.
The algorithm to convert a string to a number, given a string input, is as follows: If parsing a month from input results in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return the number of months between January 1970 and the parsed month.
The algorithm to convert a number to a string, given a number input, is as follows: Return a valid month string that represents the month that has input months between it and January 1970.
The algorithm to convert a string to a Date object, given a string input, is as follows:
If parsing a month from input results in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return a
new Date object representing midnight UTC on the morning of the first day of
the parsed month.
The algorithm to convert a Date object to a string, given a Date object input, is as follows: Return a valid month string that
represents the month current at the time represented by input in the UTC time zone.
The following common input element content
attributes, IDL attributes, and methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, max, min, readonly, required, and step content attributes; list, value, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The value IDL attribute is
in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not
apply to the element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, maxlength, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, size, src, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the
element: checked, files, selectionStart, selectionEnd, and selectionDirection IDL attributes; setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
4.10.5.1.10. Week state (type=week)
The input element represents a control for setting the element’s value to a string representing a specific week beginning on a Monday, at midnight UTC.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the week represented by its value, as obtained by parsing a week from it. User agents must not allow the user to set the value to a non-empty string that is not a valid week string. If the user agent provides a user interface for selecting a week, then the value must be set to a valid week string representing the user’s selection. User agents should allow the user to set the value to the empty string.
Constraint validation: While the user interface describes input that the user agent cannot convert to a valid week string, the control is suffering from bad input.
See §4.10.1.8 Date, time, and number formats for a discussion of the difference between the input format and submission format for date, time, and number form controls, and the implementation notes regarding localization of form controls.
The value attribute, if specified and not empty, must
have a value that is a valid week string.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: If the value of the element is not a valid week string, then set it to the empty string instead.
The min attribute, if specified, must have a value that is
a valid week string. The max attribute, if
specified, must have a value that is a valid week string.
The step attribute is expressed in weeks. The step scale factor is 604,800,000
(which converts the weeks to milliseconds, which is the base unit of comparison for the conversion
algorithms below). The default step is 1 week. The default step base is -259,200,000
(the start of week 1970-W01 which is the Monday 3 days before 1970-01-01).
When the element is suffering from a step mismatch, the user agent may round the element’s value to the nearest week for which the element would not suffer from a step mismatch.
The algorithm to convert a string to a
number, given a string input, is as follows: If parsing a week string from input results in
an error, then return an error; otherwise, return the number of milliseconds elapsed from midnight
UTC on the morning of 1970-01-01 (the time represented by the value "1970-01-01T00:00:00.0Z") to midnight UTC on the morning of the Monday of the
parsed week, ignoring leap seconds.
The algorithm to convert a number to a
string, given a number input, is as follows: Return a valid week string that represents the week that, in
UTC, is current input milliseconds after midnight UTC on the morning of
1970-01-01 (the time represented by the value "1970-01-01T00:00:00.0Z").
The algorithm to convert a string to a Date object, given a string input, is as follows:
If parsing a week from input results
in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return a new Date object representing midnight UTC on the morning of the Monday of the
parsed week.
The algorithm to convert a Date object to a string, given a Date object input, is as follows: Return a valid week string that
represents the week current at the time represented by input in the UTC time zone.
The following common input element content attributes, IDL attributes, and
methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, max, min, readonly, required, and step content attributes; list, value, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The value IDL attribute is in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, maxlength, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, size, src, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: checked, files, selectionStart, selectionEnd, and selectionDirection IDL attributes; setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
4.10.5.1.11. Time state (type=time)
The input element represents a control for setting the element’s value to a string representing a specific time.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the time represented by its value, as obtained by parsing a time from it. User agents must not allow the user to set the value to a non-empty string that is not a valid time string. If the user agent provides a user interface for selecting a time, then the value must be set to a valid time string representing the user’s selection. User agents should allow the user to set the value to the empty string.
Constraint validation: While the user interface describes input that the user agent cannot convert to a valid time string, the control is suffering from bad input.
See §4.10.1.8 Date, time, and number formats for a discussion of the difference between the input format and submission format for date, time, and number form controls, and the implementation notes regarding localization of form controls.
The value attribute, if specified and not empty, must
have a value that is a valid time string.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: If the value of the element is not a valid time string, then set it to the empty string instead.
The form control has a periodic domain.
The min attribute, if specified, must have a value that is
a valid time string. The max attribute, if
specified, must have a value that is a valid time string.
The step attribute is expressed in seconds. The step scale factor is 1000
(which converts the seconds to milliseconds, which is the base unit of comparison for the
conversion algorithms below). The default step is 60 seconds.
When the element is suffering from a step mismatch, the user agent may round the element’s value to the nearest time for which the element would not suffer from a step mismatch.
The algorithm to convert a string to a number, given a string input, is as follows: If parsing a time from input results in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return the number of milliseconds elapsed from midnight to the parsed time on a day with no time changes.
The algorithm to convert a number to a string, given a number input, is as follows: Return a valid time string that represents the time that is input milliseconds after midnight on a day with no time changes.
The algorithm to convert a string to a Date object, given a string input, is as follows:
If parsing a time from input results
in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return a new Date object representing the parsed time in
UTC on 1970-01-01.
The algorithm to convert a Date object to a string, given a Date object input, is as follows: Return a valid time string that
represents the UTC time component that is represented by input.
The following common input element content attributes, IDL attributes, and
methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, max, min, readonly, required, and step content attributes; list, value, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The value IDL attribute is in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, maxlength, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, size, src, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: checked, files, selectionStart, selectionEnd, and selectionDirection IDL attributes; setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
4.10.5.1.12. Local Date and Time state (type=datetime-local)
When an input element’s type attribute is in
the Local Date and Time state, the rules in
this section apply.
The input element represents a control for setting the element’s value to a string representing a Local Date and Time, with no time-zone offset
information.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the
user to change the Date and Time represented by its value, as obtained by parsing a date and time from it. User agents must not allow the user to set
the value to a non-empty string that is not a valid normalized global date and time string. If the user agent provides a user interface for
selecting a Local Date and Time, then the value must be set to a valid normalized global date and time string representing the user’s selection. User agents should allow the user to set the value to the empty string.
Constraint validation: While the user interface describes input that the user agent cannot convert to a valid normalized global date and time string, the control is suffering from bad input.
See §4.10.1.8 Date, time, and number formats for a discussion of the difference between the input format and submission format for date, time, and number form controls, and the implementation notes regarding localization of form controls.
The value attribute, if specified and not empty, must
have a value that is a valid floating date and time string.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: If the value of the element is a valid floating date and time string, then set it to a valid normalized floating date and time string representing the same date and time; otherwise, set it to the empty string instead.
The min attribute, if specified, must have a value that is
a valid floating date and time string. The max attribute, if specified, must have a value that is a valid floating date and time string.
The step attribute is expressed in seconds. The step scale factor is 1000
(which converts the seconds to milliseconds, which is the base unit of comparison for the
conversion algorithms below). The default step is 60 seconds.
When the element is suffering from a step mismatch, the user agent may round the element’s value to the nearest floating date and time for which the element would not suffer from a step mismatch.
The algorithm to convert a string to a
number, given a string input, is as follows: If parsing a date and time from input results in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return the number of
milliseconds elapsed from midnight on the morning of 1970-01-01 (the time represented by the value
"1970-01-01T00:00:00.0") to the parsed floating date and time, ignoring leap seconds.
The algorithm to convert a number to a
string, given a number input, is as follows: Return a valid normalized floating date and time string that represents the date and time that is input milliseconds after midnight on the morning of 1970-01-01 (the time
represented by the value "1970-01-01T00:00:00.0").
See the note on historical dates in the Date and Time state section.
The following common input element content
attributes, IDL attributes, and methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, max, min, readonly, required, and step content attributes; list, value, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The value IDL attribute is
in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not
apply to the element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, maxlength, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, size, src, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the
element: checked, files, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, and valueAsDate IDL attributes; setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
input element with its type attribute set to datetime-local, and it then interprets the
given date and time in the time zone of the selected airport.
<fieldset> <legend>Destination</legend> <p><label>Airport: <input type=text name=to list=airports></label></p> <p><label>Departure time: <input type=datetime-local name=totime step=3600></label></p> </fieldset> <datalist id=airports> <option value=ATL label="Atlanta"> <option value=MEM label="Memphis"> <option value=LHR label="London Heathrow"> <option value=LAX label="Los Angeles"> <option value=FRA label="Frankfurt"> </datalist>
If the application instead used the datetime type, then the user would have to work out the time-zone conversions themself, which is clearly
not a good user experience!
4.10.5.1.13. Number state (type=number)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
spinbutton(default - do not set).- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
The input element represents a control for setting the element’s value to a string representing a number.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the number represented by its value, as obtained from applying the rules for parsing floating-point number values to it. User agents must not allow the user to set the value to a non-empty string that is not a valid floating-point number. If the user agent provides a user interface for selecting a number, then the value must be set to the best representation of the number representing the user’s selection as a floating-point number. User agents should allow the user to set the value to the empty string.
Constraint validation: While the user interface describes input that the user agent cannot convert to a valid floating-point number, the control is suffering from bad input.
See §4.10.1.8 Date, time, and number formats for a discussion of the difference between the input format and submission format for date, time, and number form controls, and the implementation notes regarding localization of form controls.
The value attribute, if specified and not empty, must
have a value that is a valid floating-point number.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: If the value of the element is not a valid floating-point number, then set it to the empty string instead.
The min attribute, if specified, must have a value that is
a valid floating-point number. The max attribute,
if specified, must have a value that is a valid floating-point number.
The step scale factor is 1. The default step is 1 (allowing only integers to be selected by the user, unless the step base has a non-integer value).
When the element is suffering from a step mismatch, the user agent may round the element’s value to the nearest number for which the element would not suffer from a step mismatch. If there are two such numbers, user agents are encouraged to pick the one nearest positive infinity.
The algorithm to convert a string to a number, given a string input, is as follows: If applying the rules for parsing floating-point number values to input results in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return the resulting number.
The algorithm to convert a number to a string, given a number input, is as follows: Return a valid floating-point number that represents input.
The following common input element content attributes, IDL attributes, and
methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, max, min, placeholder, readonly, required, and step content attributes; list, value, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The value IDL attribute is in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, maxlength, minlength, multiple, pattern, size, src, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: checked, files, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, and valueAsDate IDL attributes; setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
<label>How much do you want to charge? $<input type=number min=0 step=0.01 name=price></label>
As described above, a user agent might support numeric input in the user’s local format, converting it to the format required for submission as described above. This might include handling grouping separators (as in "872,000,000,000") and various decimal separators (such as "3,99" vs "3.99") or using local digits (such as those in Arabic, Devanagari, Persian, and Thai).
The type=number state is not appropriate for input that
happens to only consist of numbers but isn’t strictly speaking a number. For example, it would be
inappropriate for credit card numbers or US postal codes. A simple way of determining whether to
use type=number is to consider whether it would make sense for the input
control to have a spinbox interface (e.g., with "up" and "down" arrows). Getting a credit card
number wrong by 1 in the last digit isn’t a minor mistake, it’s as wrong as getting every digit
incorrect. So it would not make sense for the user to select a credit card number using "up" and
"down" buttons. When a spinbox interface is not appropriate, type=text is
probably the right choice (possibly with a pattern attribute).
4.10.5.1.14. Range state (type=range)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
-
slider(default - do not set). - Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
-
Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
When an input element’s type attribute is in the Range state, the rules in this section apply.
The input element represents a control for setting the element’s value to a string representing a number, but with the caveat that the exact
value is not important, letting user agents provide a simpler interface than they do for the Number state.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the number represented by its value, as obtained from applying the rules for parsing floating-point number values to it. User agents must not allow the user to set the value to a string that is not a valid floating-point number. If the user agent provides a user interface for selecting a number, then the value must be set to a best representation of the number representing the user’s selection as a floating-point number. User agents must not allow the user to set the value to the empty string.
Constraint validation: While the user interface describes input that the user agent cannot convert to a valid floating-point number, the control is suffering from bad input.
The value attribute, if specified, must have a value that is a valid floating-point number.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: If the value of the element is not a valid floating-point number, then set it to the best representation, as a floating-point number, of the default value.
The default value is the minimum plus half the difference between the minimum and the maximum, unless the maximum is less than the minimum, in which case the default value is the minimum.
When the element is suffering from an underflow, the user agent must set the element’s value to the best representation, as a floating-point number, of the minimum.
When the element is suffering from an overflow, if the maximum is not less than the minimum, the user agent must set the element’s value to a valid floating-point number that represents the maximum.
When the element is suffering from a step mismatch, the user agent must round the element’s value to the nearest number for which the element would not suffer from a step mismatch, and which is greater than or equal to the minimum, and, if the maximum is not less than the minimum, which is less than or equal to the maximum, if there is a number that matches these constraints. If two numbers match these constraints, then user agents must use the one nearest to positive infinity.
For example, the markup <input type="range" min=0 max=100 step=20 value=50> results in a range control whose initial value is 60.
list attribute. This could be useful if there are values along the full range of the control that are
especially important, such as preconfigured light levels or typical speed limits in a range
control used as a speed control. The following markup fragment:
<input type="range" min="-100" max="100" value="0" step="10" name="power" list="powers"> <datalist id="powers"> <option value="0"> <option value="-30"> <option value="30"> <option value="++50"> </datalist>
...with the following style sheet applied:
input { height: 75px; width: 49px; background: #D5CCBB; color: black; }
...might render as:
![]()
Note how the user agent determined the orientation of the control from the ratio of the
style-sheet-specified height and width properties. The colors were similarly derived from the
style sheet. The tick marks, however, were derived from the markup. In particular, the step attribute has not affected the placement of tick marks, the user agent deciding
to only use the author-specified completion values and then adding longer tick marks at the
extremes.
Note also how the invalid value ++50 was completely ignored.
<input name=x type=range min=100 max=700 step=9.09090909 value=509.090909>
A user agent could display in a variety of ways, for instance:
Or, alternatively, for instance:

The user agent could pick which one to display based on the dimensions given in the style sheet. This would allow it to maintain the same resolution for the tick marks, despite the differences in width.
<input type="range" name="a" list="a-values"> <datalist id="a-values"> <option value="10" label="Low"> <option value="90" label="High"> </datalist>
With styles that make the control draw vertically, it might look as follows:
In this state, the range and step constraints are enforced even during user input, and there is no way to set the value to the empty string.
The min attribute, if specified, must have a value that is a valid floating-point number. The default minimum is 0. The max attribute,
if specified, must have a value that is a valid floating-point number. The default maximum is 100.
The step scale factor is 1. The default step is 1 (allowing only integers, unless
the min attribute has a non-integer value).
The algorithm to convert a string to a number, given a string input, is as follows: If applying the rules for parsing floating-point number values to input results in an error, then return an error; otherwise, return the resulting number.
The algorithm to convert a number to a string, given a number input, is as follows: Return the best representation, as a floating-point number, of input.
input element content attributes, IDL attributes, and
methods apply to the element: autocomplete, list, max, min, multiple, and step content attributes; list, value, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; stepDown() and stepUp() methods.
The value IDL attribute is in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, maxlength, minlength, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, size, src, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: checked, files, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, and valueAsDate IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods.
4.10.5.1.15. Color state (type=color)
The input element represents a color well control, for setting the
element’s value to a string representing a simple
color.
In this state, there is always a color picked, and there is no way to set the value to the empty string.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the color represented by its value, as obtained from applying the rules for parsing simple color values to it. User agents must not allow the user to set the value to a string that is not a valid lowercase simple color. If the user agent provides a user interface for selecting a color, then the value must be set to the result of using the rules for serializing simple color values to the user’s selection. User agents must not allow the user to set the value to the empty string.
Constraint validation: While the user interface describes input that the user agent cannot convert to a valid lowercase simple color, the control is suffering from bad input.
The value attribute, if specified and not empty, must
have a value that is a valid simple color.
The value sanitization algorithm is as follows: If the value of the element is a valid simple color, then set it to the value of the element in ASCII lowercase; otherwise, set it to
the string "#000000".
The following common input element content attributes and IDL attributes apply to the
element: autocomplete and list content attributes; list and value IDL attributes; select() method.
The value IDL attribute is in mode value.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, alt, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, max, maxlength, min, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, size, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: checked, files, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; setRangeText(), setSelectionRange(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
4.10.5.1.16. Checkbox state (type=checkbox)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
checkbox(default - do not set),menuitemcheckbox,optionorswitch.- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
The input element represents a two-state control that represents the
element’s checkedness state. If the element’s checkedness state is true, the control represents a positive
selection, and if it is false, a negative selection. If the element’s indeterminate IDL attribute is set to true, then the
control’s selection should be obscured as if the control was in a third, indeterminate, state.
The control is never a true tri-state control, even if the element’s indeterminate IDL attribute is set to true. The indeterminate IDL attribute only gives the appearance of a
third state.
If the element is mutable, then: The pre-click
activation steps consist of setting the element’s checkedness to its opposite value (i.e., true if it is false,
false if it is true), and of setting the element’s indeterminate IDL attribute to false. The canceled
activation steps consist of setting the checkedness and the element’s indeterminate IDL attribute back to the values they had
before the pre-click activation steps were run. The activation behavior is to fire a simple event that bubbles named input at the element and then fire a simple event that bubbles named change at the element.
If the element is not mutable, it has no activation behavior.
Constraint validation: If the element is required and its checkedness is false, then the element is suffering from being missing.
- input .
indeterminate[ = value ] -
When set, overrides the rendering of
checkboxcontrols so that the current value is not visible.
The following common input element content attributes and IDL attributes apply to the element: checked, and required content attributes; checked and value IDL attributes.
The value IDL attribute is in mode default/on.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, alt, autocomplete, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, list, max, maxlength, min, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, readonly, size, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: files, list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), setSelectionRange(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
4.10.5.1.17. Radio Button state (type=radio)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
radio(default - do not set) ormenuitemradio.- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
When an input element’s type attribute is in
the Radio Button state, the rules in this section
apply.
The input element represents a control that, when used in conjunction
with other input elements, forms a radio button group in which only one
control can have its checkedness state set to true. If
the element’s checkedness state is true, the control
represents the selected control in the group, and if it is false, it indicates a control in the
group that is not selected.
The radio button group that contains an input element a also contains all the other input elements b that fulfill all
of the following conditions:
- The
inputelement b’stypeattribute is in theRadio Buttonstate. - Either a and b have the same form owner, or they both have no form owner.
- Both a and b are in the same tree.
- They both have a
nameattribute, theirnameattributes are not empty, and the value of a’snameattribute is a compatibility caseless match for the value of b’snameattribute.
A document must not contain an input element whose radio button group contains only that element.
When any of the following phenomena occur, if the element’s checkedness state is true after the occurrence, the checkedness state of all the other elements in the same radio button group must be set to false:
- The element’s checkedness state is set to true (for whatever reason).
- The element’s
nameattribute is set, changed, or removed. - The element’s form owner changes.
- A type change is signalled for the element.
If the element R is mutable, then: The pre-click activation steps for R consist of getting a reference to the
element in R’s radio button group that has its checkedness set to true, if any, and then setting R’s checkedness to true. The canceled
activation steps for R consist of checking if the element to which a reference
was obtained in the pre-click activation steps, if any, is still in what is now R’s radio button group, if it still has one, and if so, setting that
element’s checkedness to true; or else, if there was no
such element, or that element is no longer in R’s radio button group, or
if R no longer has a radio button group, setting R’s checkedness to false. The activation behavior for R is to fire a simple event that bubbles named input at R and then fire a simple event that bubbles named change at R.
If the element is not mutable, it has no activation behavior.
Constraint validation: If an element in the radio button group is required, and all of the input elements in the radio button group have a checkedness that is
false, then the element is suffering from being missing.
If none of the radio buttons in a radio button group are checked when they are inserted into the document, then they will all be initially unchecked in the interface, until such time as one of them is checked (either by the user or by script).
The following common input element content attributes and IDL attributes apply to the element: checked and required content attributes; checked and value IDL attributes.
The value IDL attribute is in mode default/on.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, alt, autocomplete, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, list, max, maxlength, min, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, readonly, size, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: files, list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), setSelectionRange(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
4.10.5.1.18. File Upload state (type=file)
When an input element’s type attribute is in
the File Upload state, the rules in this section
apply.
The input element represents a list of selected files, each file consisting of a file
name, a file type, and a file body (the contents of the file).
File names must not contain path components, even
in the case that a user has selected an entire directory hierarchy or multiple files with the same
name from different directories. Path components, for
the purposes of the File Upload state, are those parts
of file names that are separated by U+005C REVERSE SOLIDUS character (\) characters.
Unless the multiple attribute is set, there must be
no more than one file in the list of selected
files.
If the element is mutable, then the element’s activation behavior is to run the following steps:
- If the algorithm is not allowed to show a popup, then abort these steps without doing anything else.
- Return, but continue running these steps in parallel.
- Optionally, wait until any prior execution of this algorithm has terminated.
- Display a prompt to the user requesting that the user specify some files. If the
multipleattribute is not set, there must be no more than one file selected; otherwise, any number may be selected. Files can be from the filesystem or created on the fly, e.g., a picture taken from a camera connected to the user’s device. - Wait for the user to have made their selection.
- Queue a task to first update the element’s selected files so that it represents the user’s
selection, then fire a simple event that bubbles named
inputat theinputelement, and finally fire a simple event that bubbles namedchangeat theinputelement.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the
user to change the files on the list in other ways also, e.g., adding or removing files by
drag-and-drop. When the user does so, the user agent must queue a task to first
update the element’s selected files so that
it represents the user’s new selection, then fire a simple event that bubbles named input at the input element, and finally fire a simple event that bubbles named change at the input element.
If the element is not mutable, it has no activation behavior and the user agent must not allow the user to change the element’s selection.
Constraint validation: If the element is required and the list of selected files is empty, then the element is suffering from being missing.
The accept attribute may be specified to
provide user agents with a hint of what file types will be accepted.
If specified, the attribute must consist of a set of comma-separated tokens, each of which must be an ASCII case-insensitive match for one of the following:
- The string "
audio/*" - Indicates that sound files are accepted.
- The string "
video/*" - Indicates that video files are accepted.
- The string "
image/*" - Indicates that image files are accepted.
- A valid MIME type with no parameters
- Indicates that files of the specified type are accepted.
- A string whose first character is a U+002E FULL STOP character (.)
- Indicates that files with the specified file extension are accepted.
The tokens must not be ASCII case-insensitive matches for any of the other tokens (i.e., duplicates are not allowed). To obtain the list of tokens from the attribute, the user agent must split the attribute value on commas.
User agents may use the value of this attribute to display a more appropriate user interface
than a generic file picker. For instance, given the value image/*, a user
agent could offer the user the option of using a local camera or selecting a photograph from their
photo collection; given the value audio/*, a user agent could offer the user
the option of recording a clip using a headset microphone.
Authors are encouraged to specify both any MIME types and any corresponding extensions when looking for data in a specific format.
<input type="file" accept=".doc,.docx,.xml,application/msword,application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document">
On platforms that only use file extensions to describe file types, the extensions listed here can be used to filter the allowed documents, while the MIME types can be used with the system’s type registration table (mapping MIME types to extensions used by the system), if any, to determine any other extensions to allow. Similarly, on a system that does not have file names or extensions but labels documents with MIME types internally, the MIME types can be used to pick the allowed files, while the extensions can be used if the system has an extension registration table that maps known extensions to MIME types used by the system.
Extensions tend to be ambiguous (e.g., there are an untold number of formats
that use the ".dat" extension, and users can typically quite easily rename
their files to have a ".doc" extension even if they are not Microsoft Word
documents), and MIME types tend to be unreliable (e.g., many formats have no formally registered
types, and many formats are in practice labeled using a number of different MIME types). Authors
are reminded that, as usual, data received from a client should be treated with caution, as it may
not be in an expected format even if the user is not hostile and the user agent fully obeyed the accept attribute’s requirements.
value IDL attribute prefixes
the file name with the string "C:\fakepath\". Some legacy user agents
actually included the full path (which was a security vulnerability). As a result of this,
obtaining the file name from the value IDL attribute in a
backwards-compatible way is non-trivial. The following function extracts the file name in a
suitably compatible manner:
function extractFilename(path) { if (path.substr(0, 12) == "C:\\fakepath\\") return path.substr(12); // modern browser var x; x = path.lastIndexOf('/'); if (x >= 0) // Unix-based path return path.substr(x+1); x = path.lastIndexOf('\\'); if (x >= 0) // Windows-based path return path.substr(x+1); return path; // just the file name }
This can be used as follows:
<p><input type=file name=image onchange="updateFilename(this.value)"></p> <p>The name of the file you picked is: <span id="filename">(none)</span></p> <script> function updateFilename(path) { var name = extractFilename(path); document.getElementById('filename').textContent = name; } </script>
input element content attributes and IDL attributes apply to the element: accept, multiple, and required content attributes; files and value IDL attributes; select() method.
The value IDL attribute is in mode filename.
The input and change events apply.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: alt, autocomplete, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, list, max, maxlength, min, minlength, pattern, placeholder, readonly, size, src, step, and width.
The element’s value attribute must be omitted.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: checked, list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; setRangeText(), setSelectionRange(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
4.10.5.1.19. Submit Button state (type=submit)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
button(default - do not set).- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
When an input element’s type attribute is in
the Submit Button state, the rules in this section
apply.
The input element represents a button that, when activated, submits
the form. If the element has a value attribute, the button’s label must be the value of that attribute; otherwise, it must be an
implementation-defined string that means "Submit" or some such. The element is a button, specifically a submit
button. ![]()
Since the default label is implementation-defined, and the width of the button typically depends on the button’s label, the button’s width can leak a few bits of fingerprintable information. These bits are likely to be strongly correlated to the identity of the user agent and the user’s locale.
If the element is mutable, then the element’s activation behavior is as follows: if the element has a form owner,
and the element’s node document is fully active, submit the form owner from the input element; otherwise, do nothing.
If the element is not mutable, it has no activation behavior.
The formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, and formtarget attributes are attributes for form
submission.
The formnovalidate attribute can be
used to make submit buttons that do not trigger the constraint validation.
The following common input element content attributes and IDL attributes apply to the element: formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, and formtarget content attributes; value IDL attribute.
The value IDL attribute is in mode default.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, alt, autocomplete, checked, dirname, height, inputmode, list, max, maxlength, min, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, size, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: checked, files, list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), setSelectionRange(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The input and change events do not apply.
4.10.5.1.20. Image Button state (type=image)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
button(default - do not set),link,menuitem,menuitemcheckbox,menuitemradioorradio.- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
When an input element’s type attribute is in
the Image Button state, the rules in this section
apply.
The input element represents either an image from which a user can
select a coordinate and submit the form, or alternatively a button from which the user can submit
the form. The element is a button, specifically a Submit Button.
The coordinate is sent to the server during form submission by sending two entries for the element, derived from the name
of the control but with ".x" and ".y" appended to the
name with the x and y components of the coordinate
respectively.
The image is given by the src attribute. The src attribute must be present, and must contain a valid
non-empty URL potentially surrounded by spaces referencing a non-interactive, optionally
animated, image resource that is neither paged nor scripted.
When any of the these events occur
- the
inputelement’stypeattribute is first set to theImage Buttonstate (possibly when the element is first created), and thesrcattribute is present - the
inputelement’stypeattribute is changed back to theImage Buttonstate, and thesrcattribute is present, and its value has changed since the last time thetypeattribute was in theImage Buttonstate - the
inputelement’stypeattribute is in theImage Buttonstate, and thesrcattribute is set or changed
then unless the user agent cannot support images, or its support for images has been disabled,
or the user agent only fetches images on demand, or the src attribute’s value is the empty string, the user agent must parse the value of the src attribute value, relative to the element’s node document, and if that is successful, run these substeps:
- Let request be a new request whose URL is the resulting URL string, client is the element’s node document’s
Windowobject’s environment settings object, type is "image", destination is "subresource", omit-Origin-header flag is set, credentials mode is "include", and whose use-URL-credentials flag is set. - Fetch request.
Fetching the image must delay the load event of the element’s node document until the task that is queued by the networking task source once the resource has been fetched (defined below) has been run.
If the image was successfully obtained, with no network errors, and the image’s type is a supported image type, and the image is a valid image of that type, then the image is said to be available. If this is true before the image is completely downloaded, each task that is queued by the networking task source while the image is being fetched must update the presentation of the image appropriately.
The user agent should apply the image sniffing rules to determine the type of the image, with the image’s associated Content-Type headers giving the official type. If these rules are not applied, then the type of the image must be the type given by the image’s associated Content-Type headers.
User agents must not support non-image resources with the input element. User
agents must not run executable code embedded in the image resource. User agents must only display
the first page of a multipage resource. User agents must not allow the resource to act in an
interactive fashion, but should honor any animation in the resource.
The task that is queued by the networking task source once the resource has been fetched, must, if the
download was successful and the image is available, queue a task to fire a simple event named load at the input element; and otherwise, if the fetching
process fails without a response from the remote server, or completes but the image is not a valid
or supported image, queue a task to fire a simple event named error on the input element.
The alt attribute provides the textual label for
the button for users and user agents who cannot use the image. The alt attribute must be present, and must contain a non-empty string
giving the label that would be appropriate for an equivalent button if the image was
unavailable.
The input element supports dimension attributes.
If the src attribute is set, and the image is available and the user agent is configured to display that image,
then: The element represents a control for selecting a coordinate from the image specified by the src attribute; if the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to select this coordinate, and the element’s activation
behavior is as follows: if the element has a form owner, and the element’s node document is fully active, take the user’s selected coordinate, and submit the input element’s form owner from the input element. If the user activates the control without explicitly
selecting a coordinate, then the coordinate (0,0) must be assumed.
Otherwise, the element represents a submit button whose label is given by the
value of the alt attribute; if the element is mutable, then the element’s activation behavior is as
follows: if the element has a form owner, and the element’s node document is fully active, set the selected
coordinate to (0,0), and submit the input element’s form owner from the input element.
In either case, if the element is mutable but has no form owner or the element’s node document is not fully active, then its activation behavior must be to do nothing. If the element is not mutable, it has no activation behavior.
The selected coordinate must consist of an x-component and a y-component. The coordinates represent the position relative to the edge of the image, with the coordinate space having the positive x direction to the right, and the positive y direction downwards.
The x-component must be a valid integer representing a number x in the range -(borderleft+paddingleft) ≤ x ≤ width+borderright+paddingright, where width is the rendered width of the image, borderleft is the width of the border on the left of the image, paddingleft is the width of the padding on the left of the image, borderright is the width of the border on the right of the image, and paddingright is the width of the padding on the right of the image, with all dimensions given in CSS pixels.
The y-component must be a valid integer representing a number y in the range -(bordertop+paddingtop) ≤ y ≤ height+borderbottom+paddingbottom, where height is the rendered height of the image, bordertop is the width of the border above the image, paddingtop is the width of the padding above the image, borderbottom is the width of the border below the image, and paddingbottom is the width of the padding below the image, with all dimensions given in CSS pixels.
Where a border or padding is missing, its width is zero CSS pixels.
The formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, and formtarget attributes are attributes for form
submission.
- image .
width[ = value ] - image .
height[ = value ] -
These attributes return the actual rendered dimensions of the image, or zero if the dimensions are not known.
They can be set, to change the corresponding content attributes.
The following common input element content attributes and IDL attributes apply to the element: alt, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, src, and width content attributes; value IDL attribute.
The value IDL attribute is in mode default.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, autocomplete, checked, dirname, inputmode, list, max, maxlength, min, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, size, and step.
The element’s value attribute must be omitted.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: checked, files, list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), setSelectionRange(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The input and change events do not apply.
Many aspects of this state’s behavior are similar to the behavior of the img element. Readers are encouraged to read that section, where many of the same
requirements are described in more detail.
<form action="process.cgi"> <input type=image src=map.png name=where alt="Show location list"> </form>
If the user clicked on the image at coordinate (127,40) then the URL used to submit the form
would be "process.cgi?where.x=127&where.y=40".
(In this example, it’s assumed that for users who don’t see the map, and who instead just see a button labeled "Show location list", clicking the button will cause the server to show a list of locations to pick from instead of the map.)
4.10.5.1.21. Reset Button state (type=reset)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
button(default - do not set).- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
When an input element’s type attribute is in
the Reset Button state, the rules in this section
apply.
The input element represents a button that, when activated, resets
the form. If the element has a value attribute, the button’s label must be the value of that attribute; otherwise, it must be an
implementation-defined string that means "Reset" or some such. The element is a button. ![]()
Since the default label is implementation-defined, and the width of the button typically depends on the button’s label, the button’s width can leak a few bits of fingerprintable information. These bits are likely to be strongly correlated to the identity of the user agent and the user’s locale.
If the element is mutable, then the element’s activation behavior, if the element has a form owner and the element’s node document is fully active, is to reset the form owner; otherwise, it is to do nothing.
If the element is not mutable, it has no activation behavior.
Constraint validation: The element is barred from constraint validation.
The value IDL attribute applies to this element and is in mode default.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, alt, autocomplete, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, list, max, maxlength, min, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, size, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: checked, files, list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), setSelectionRange(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The input and change events do not apply.
4.10.5.1.22. Button state (type=button)
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
button(default - do not set),link,menuitem,menuitemcheckbox,menuitemradio,radioorswitch.- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles.
The input element represents a button with no default behavior. A
label for the button must be provided in the value attribute, though it may be the empty string. If the element has a value attribute, the button’s label must be the value of that
attribute; otherwise, it must be the empty string. The element is a button.
If the element is mutable, the element’s activation behavior is to do nothing.
If the element is not mutable, it has no activation behavior.
Constraint validation: The element is barred from constraint validation.
The value IDL attribute applies to this element and is in mode default.
The following content attributes must not be specified and do not apply to the
element: accept, alt, autocomplete, checked, dirname, formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, formtarget, height, inputmode, list, max, maxlength, min, minlength, multiple, pattern, placeholder, readonly, required, size, src, step, and width.
The following IDL attributes and methods do not apply to the element: checked, files, list, selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, valueAsDate, and valueAsNumber IDL attributes; select(), setRangeText(), setSelectionRange(), stepDown(), and stepUp() methods.
The input and change events do not apply.
4.10.5.2. Implementation notes regarding localization of form controls
This section is non-normative.
The formats shown to the user in date, time, and number controls is independent of the format used for form submission.
Browsers should use user interfaces that present locale-affected formats such as dates, times,
and numbers according to the conventions of either the locale implied by the input element’s language or the user’s preferred locale. Using the page’s locale will ensure
consistency with page-provided data.
For example, it would be confusing to users if an American English page claimed that a Cirque De Soleil show was going to be showing on 02/03, but their browser, configured to use the British English locale, only showed the date 03/02 in the ticket purchase date picker. Using the page’s locale would at least ensure that the date was presented in the same format everywhere. (There’s still a risk that the user would end up arriving a month late, of course, but there’s only so much that can be done about such cultural differences...)
4.10.5.3. Common input element attributes
These attributes only apply to an input element if its type attribute is in a state whose definition
declares that the attribute applies. When an attribute doesn’t apply to an input element, user agents must ignore the attribute, regardless of the requirements and definitions below.
4.10.5.3.1. The maxlength and minlength attributes
The maxlength attribute, when it applies, is a form control maxlength attribute controlled by the input element’s dirty value flag.
The minlength attribute, when it applies, is a form control minlength attribute controlled by the input element’s dirty value flag.
If the input element has a maximum allowed value length, then the code-unit length of the value of the element’s value attribute must be equal to or less than the element’s maximum allowed value length.
<label>What are you doing? <input name=status maxlength=140></label>
<p><label>Username: <input name=u required></label> <p><label>Password: <input name=p required minlength=12></label>
4.10.5.3.2. The size attribute
The size attribute gives the number of
characters that, in a visual rendering, the user agent is to allow the user to see while editing
the element’s value.
The size attribute, if specified, must have a value that
is a valid non-negative integer greater than zero.
If the attribute is present, then its value must be parsed using the rules for parsing non-negative integers, and if the result is a number greater than zero, then the user agent should ensure that at least that many characters are visible.
The size IDL attribute is limited to only
non-negative numbers greater than zero and has a default value of 20.
4.10.5.3.3. The readonly attribute
The readonly attribute is a boolean
attribute that controls whether or not the user can edit the form control. When specified, the element is not mutable.
Constraint validation: If the readonly attribute is specified on an input element, the element is barred from constraint validation.
The difference between disabled and readonly is that read-only controls are still focusable, so the
user can still select the text and interact with it, whereas disabled controls are entirely
non-interactive. (For this reason, only text controls can be made read-only: it wouldn’t make
sense for checkboxes or buttons, for instances.)
<form action="products.cgi" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <table> <tr> <th> Product ID <th> Product name <th> Price <th> Action <tr> <td> <input readonly="readonly" name="1.pid" value="H412"> <td> <input required="required" name="1.pname" value="Floor lamp Ulke"> <td> $<input required="required" type="number" min="0" step="0.01" name="1.pprice" value="49.99"> <td> <button formnovalidate="formnovalidate" name="action" value="delete:1">Delete</button> <tr> <td> <input readonly="readonly" name="2.pid" value="FG28"> <td> <input required="required" name="2.pname" value="Table lamp Ulke"> <td> $<input required="required" type="number" min="0" step="0.01" name="2.pprice" value="24.99"> <td> <button formnovalidate="formnovalidate" name="action" value="delete:2">Delete</button> <tr> <td> <input required="required" name="3.pid" value="" pattern="[A-Z0-9]+"> <td> <input required="required" name="3.pname" value=""> <td> $<input required="required" type="number" min="0" step="0.01" name="3.pprice" value=""> <td> <button formnovalidate="formnovalidate" name="action" value="delete:3">Delete</button> </table> <p> <button formnovalidate="formnovalidate" name="action" value="add">Add</button> </p> <p> <button name="action" value="update">Save</button> </p> </form>
4.10.5.3.4. The required attribute
The required attribute is a boolean attribute. When specified, the element is required.
Constraint validation: If the element is required, and its value IDL attribute applies and is in the mode value, and the element is mutable, and the element’s value is the empty string, then the element is suffering
from being missing.
<h1>Create new account</h1> <form action="/newaccount" method=post oninput='up2.setCustomValidity(up2.value != up.value ? "Passwords do not match." : "")'> <p> <label for="username">E-mail address:</label> <input id="username" type=email required name=un> <p> <label for="password1">Password:</label> <input id="password1" type=password required name=up> <p> <label for="password2">Confirm password:</label> <input id="password2" type=password name=up2> <p> <input type=submit value="Create account"> </form>
required attribute is
satisfied if any of the radio buttons in the group is
selected. Thus, in the following example, any of the radio buttons can be checked, not just the
one marked as required:
<fieldset> <legend>Did the movie pass the Bechdel test?</legend> <p><label><input type="radio" name="bechdel" value="no-characters"> No, there are not even two female characters in the movie. </label> <p><label><input type="radio" name="bechdel" value="no-names"> No, the female characters never talk to each other. </label> <p><label><input type="radio" name="bechdel" value="no-topic"> No, when female characters talk to each other it’s always about a male character. </label> <p><label><input type="radio" name="bechdel" value="yes" required> Yes. </label> <p><label><input type="radio" name="bechdel" value="unknown"> I don’t know. </label> </fieldset>
To avoid confusion as to whether a radio button group is required or not, authors are encouraged to specify the attribute on all the radio buttons in a group. Indeed, in general, authors are encouraged to avoid having radio button groups that do not have any initially checked controls in the first place, as this is a state that the user cannot return to, and is therefore generally considered a poor user interface.
4.10.5.3.5. The multiple attribute
The multiple attribute is a boolean attribute that indicates whether the user is to be allowed to specify more than one
value.
<label>Cc: <input type=email multiple name=cc></label>
If the user had, amongst many friends in their user contacts database, two friends "Arthur Dent" (with address "art@example.net") and "Adam Josh" (with address "adamjosh@example.net"), then, after the user has typed "a", the user agent might suggest these two e-mail addresses to the user.
The page could also link in the user’s contacts database from the site:
<label>Cc: <input type=email multiple name=cc list=contacts></label> ... <datalist id="contacts"> <option value="hedral@damowmow.com"> <option value="pillar@example.com"> <option value="astrophy@cute.example"> <option value="astronomy@science.example.org"> </datalist>
Suppose the user had entered "bob@example.net" into this text field, and then started typing a
second e-mail address starting with "a". The user agent might show both the two friends mentioned
earlier, as well as the "astrophy" and "astronomy" values given in the datalist element.
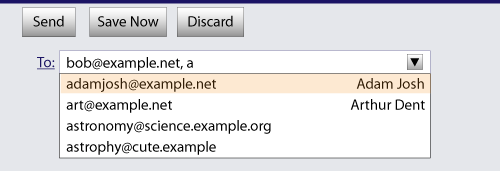
<label>Attachments: <input type=file multiple name=att></label>
4.10.5.3.6. The pattern attribute
The pattern attribute specifies a regular
expression against which the control’s value, or, when the multiple attribute applies and is set, the control’s values, are to be checked.
If specified, the attribute’s value must match the JavaScript Pattern production. [ECMA-262]
If an input element has a pattern attribute specified, and the attribute’s value, when compiled as a JavaScript regular expression
with only the "u" flag specified, compiles successfully, then the resulting regular expression is the element’s compiled pattern regular expression. If the element has no such attribute, or if the
value doesn’t compile successfully, then the element has no compiled pattern regular
expression. [ECMA-262]
If the value doesn’t compile successfully, user agents are encouraged to log this fact in a developer console, to aid debugging.
Constraint validation: If the element’s value is not the empty string, and either the element’s multiple attribute is not specified or it does not apply to the input element given its type attribute’s current state, and the element has a compiled pattern regular expression but that regular expression does not match the
entirety of the element’s value, then the element is suffering from a pattern mismatch.
Constraint validation: If the element’s value is not the empty string, and the element’s multiple attribute is specified and applies to the input element, and the element has
a compiled pattern regular expression but that regular expression does not match the
entirety of each of the element’s values, then the
element is suffering from a pattern mismatch.
The compiled pattern regular expression, when matched against a string, must have its start anchored to the start of the string and its end anchored to the end of the string.
This implies that the regular expression language used for this attribute is the
same as that used in JavaScript, except that the pattern attribute is matched against the entire value, not just any subset (somewhat as if it implied a ^(?: at the start of the pattern and a )$ at the
end).
When an input element has a pattern attribute specified, authors should provide a description of the pattern in text near the
control. Authors may also include a title attribute to give a description of the pattern. User agents may use
the contents of this attribute, if it is present, when informing the
user that the pattern is not matched, or at any other suitable time,
such as in a tooltip or read out by assistive technology when the
control gains focus.
Relying on the title attribute for the visual display
of text content is currently discouraged as many user agents do not expose the attribute in an accessible manner
as required by this specification (e.g., requiring a pointing device such as a mouse to cause a tooltip to appear,
which excludes keyboard-only users and touch-only users, such as anyone with a modern phone or
tablet).
<label> Part number: <input pattern="[0-9][A-Z]{3}" name="part" title="A part number is a digit followed by three uppercase letters."/> </label>
...could cause the user agent to display an alert such as:
A part number is a digit followed by three uppercase letters.You cannot submit this form when the field is incorrect.
When a control has a pattern attribute, the title attribute, if used, must describe the pattern. Additional
information could also be included, so long as it assists the user in filling in the control.
Otherwise, assistive technology would be impaired.
For instance, if the title attribute contained the caption of the control, assistive technology could end up saying something like The text you have entered does not match the required pattern. Birthday, which is not useful.
user agents may still show the title in non-error situations (for
example, as a tooltip when hovering over the control), so authors should be careful not to word titles as if an error has necessarily occurred.
4.10.5.3.7. The min and max attributes
Some form controls can have explicit constraints applied limiting the allowed range of values that the user can provide. Normally, such a range would be linear and continuous. A form control can have a periodic domain, however, in which case the form control’s broadest possible range is finite, and authors can specify explicit ranges within it that span the boundaries.
Specifically, the broadest range of a type=time control is midnight to midnight (24 hours), and
authors can set both continuous linear ranges (such as 9pm to 11pm) and discontinuous ranges
spanning midnight (such as 11pm to 1am).
The min and max attributes indicate the allowed range of values for
the element.
Their syntax is defined by the section that defines the type attribute’s current state.
If the element has a min attribute, and the result of
applying the algorithm to convert a string to a
number to the value of the min attribute is a number,
then that number is the element’s minimum; otherwise, if the type attribute’s current state defines a default minimum, then that is the minimum; otherwise, the element has no minimum.
The min attribute also defines the step base.
If the element has a max attribute, and the result of
applying the algorithm to convert a string to a
number to the value of the max attribute is a number,
then that number is the element’s maximum; otherwise, if the type attribute’s current state defines a default maximum, then that is the maximum; otherwise, the element has no maximum.
If the element does not have a periodic domain, the max attribute’s value
(the maximum) must not be less than the min attribute’s value
(its minimum).
If an element that does not have a periodic domain has a maximum that is less than its minimum, then so long as the element has a value, it will either be suffering from an underflow or suffering from an overflow.
An element has a reversed range if it has a periodic domain and its maximum is less than its minimum.
An element has range limitations if it has a defined minimum or a defined maximum.
How these range limitations apply depends on whether the element has a multiple attribute.
- If the element does not have a
multipleattribute specified or if themultipleattribute does not apply -
Constraint validation: When the element has a minimum and does not have a reversed range, and the result of applying the algorithm to convert a string to a number to the string given by the element’s value is a number, and the number obtained from that algorithm is less than the minimum, the element is suffering from an underflow.
Constraint validation: When the element has a maximum and does not have a reversed range, and the result of applying the algorithm to convert a string to a number to the string given by the element’s value is a number, and the number obtained from that algorithm is more than the maximum, the element is suffering from an overflow.
Constraint validation: When an element has a reversed range, and the result of applying the algorithm to convert a string to a number to the string given by the element’s value is a number, and the number obtained from that algorithm is more than the maximum and less than the minimum, the element is simultaneously suffering from an underflow and suffering from an overflow.
- If the element does have a
multipleattribute specified and themultipleattribute does apply -
Constraint validation: When the element has a minimum, and the result of applying the algorithm to convert a string to a number to any of the strings in the element’s values is a number that is less than the minimum, the element is suffering from an underflow.
Constraint validation: When the element has a maximum, and the result of applying the algorithm to convert a string to a number to any of the strings in the element’s values is a number that is more than the maximum, the element is suffering from an overflow.
<input name=bday type=date max="1979-12-31">
<input name=quantity required="" type="number" min="1" value="1">
<input name="sleepStart" type=time min="21:00" max="06:00" step="60" value="00:00">
4.10.5.3.8. The step attribute
The step attribute indicates the granularity
that is expected (and required) of the value or values, by limiting the allowed values. The
section that defines the type attribute’s current state also
defines the default step, the step scale factor, and in some cases the default step base, which are used in processing the
attribute as described below.
The step attribute, if specified, must either have a
value that is a valid floating-point number that parses to a number that is greater than zero, or must have a
value that is an ASCII case-insensitive match for the string "any".
The attribute provides the allowed value step for the element, as follows:
-
If the
stepattribute is absent, then the allowed value step is the default step multiplied by the step scale factor. -
Otherwise, if the attribute’s value is an ASCII case-insensitive match for the string "
any", then there is no allowed value step. -
Otherwise, let step value be the result of running the rules for parsing floating-point number values, when they are applied to the
stepattribute’s value. -
If the previous step returned an error, or step value is zero, or a number less than zero, then the allowed value step is the default step multiplied by the step scale factor.
-
If the element’s
typeattribute is in theDate and Time,Date,Month,Week, orTimestate, then round step value to the nearest whole number using the "round to nearest + round half up" technique, unless the value is less-than one, in which case let step value be 1. -
The allowed value step is step value multiplied by the step scale factor.
The step base is the value returned by the following algorithm:
-
If the element has a
mincontent attribute, and the result of applying the algorithm to convert a string to a number to the value of themincontent attribute is not an error, then return that result and abort these steps. -
If the element has a
valuecontent attribute, and the result of applying the algorithm to convert a string to a number to the value of thevaluecontent attribute is not an error, then return that result and abort these steps. -
If a default step base is defined for this element given its
typeattribute’s state, then return it and abort these steps. -
Return zero.
How these range limitations apply depends on whether the element has a multiple attribute.
- If the element does not have a
multipleattribute specified or if themultipleattribute does not apply -
Constraint validation: When the element has an allowed value step, and the result of applying the algorithm to convert a string to a number to the string given by the value is a number, and that number is not step aligned, the element is suffering from a step mismatch.
- If the element does have a
multipleattribute specified and themultipleattribute does apply -
Constraint validation: When the element has an allowed value step, and the result of applying the algorithm to convert a string to a number to any of the strings in the values is a number that is not step aligned, the element is suffering from a step mismatch.
<input name=opacity type=range min=0 max=1 step=0.00392156863>
<input name=favtime type=time step=any>
Normally, time controls are limited to an accuracy of one minute.
4.10.5.3.9. The list attribute
The list attribute is used to identify an
element that lists predefined options suggested to the user.
If present, its value must be the ID of a datalist element in the same document.
The suggestions source element is the first element in
the document in tree order to have an ID equal to the
value of the list attribute, if that element is a datalist element. If there is no list attribute,
or if there is no element with that ID, or if the first element
with that ID is not a datalist element, then there is
no suggestions source element.
If there is a suggestions source element, then, when
the user agent is allowing the user to edit the input element’s value, the user agent should offer the suggestions represented by
the suggestions source element to the user in a manner
suitable for the type of control used. The user agent may use the suggestion’s label to identify the suggestion if appropriate.
User agents are encouraged to filter the suggestions represented by the suggestions source element when the number of suggestions is
large, including only the most relevant ones (e.g., based on the user’s input so far). No precise
threshold is defined, but capping the list at four to seven values is reasonable.
User agents that perform filtering should implement substring matching on the label attribute.
Existing user agents filter on either value or label so the behavior may be inconsistent.
How user selections of suggestions are handled depends on whether the element is a control accepting a single value only, or whether it accepts multiple values:
- If the element does not have a
multipleattribute specified or if themultipleattribute does not apply -
When the user selects a suggestion, the
inputelement’s value must be set to the selected suggestion’s value, as if the user had written that value themself. - If the element’s
typeattribute is in theRangestate and the element has amultipleattribute specified -
When the user selects a suggestion, the user agent must identify which value in the element’s values the user intended to update, and must then update the element’s values so that the relevant value is changed to the value given by the selected suggestion’s value, as if the user had themself set it to that value.
- If the element’s
typeattribute is in theE-mailstate and the element has amultipleattribute specified -
When the user selects a suggestion, the user agent must either add a new entry to the
inputelement’s values, whose value is the selected suggestion’s value, or change an existing entry in theinputelement’s values to have the value given by the selected suggestion’s value, as if the user had themself added an entry with that value, or edited an existing entry to be that value. Which behavior is to be applied depends on the user interface in a user-agent-defined manner.
If the list attribute does not apply, there is no suggestions source element.
<label>Homepage: <input name=hp type=url list=hpurls></label> <datalist id=hpurls> <option value="https://www.google.com/" label="Google"> <option value="https://www.reddit.com/" label="Reddit"> </datalist>
Other URLs from the user’s history might show also; this is up to the user agent.
If the autocompletion list is merely an aid, and is not important to the content, then simply
using a datalist element with children option elements is enough. To
prevent the values from being rendered in legacy user agents, they need to be placed inside the value attribute instead of inline.
<p> <label> Enter a breed: <input type="text" name="breed" list="breeds"> <datalist id="breeds"> <option value="Abyssinian"> <option value="Alpaca"> <!-- ... --> </datalist> </label> </p>
However, if the values need to be shown in legacy user agents, then fallback content can be placed
inside the datalist element, as follows:
<p> <label> Enter a breed: <input type="text" name="breed" list="breeds"> </label> <datalist id="breeds"> <label> or select one from the list: <select name="breed"> <option value=""> (none selected) <option>Abyssinian <option>Alpaca <!-- ... --> </select> </label> </datalist> </p>
The fallback content will only be shown in user agents that don’t support datalist. The
options, on the other hand, will be detected by all user agents, even though they are not children of the datalist element.
Note that if an option element used in a datalist is selected, it will be selected by default by legacy user agents
(because it affects the select), but it will not have any effect on the input element in user agents that support datalist.
4.10.5.3.10. The placeholder attribute
The placeholder attribute represents a short hint (a word or short phrase) intended to aid the user with data entry when the
control has no value. A hint could be a sample value or a brief description of the expected
format. The attribute, if specified, must have a value that contains no U+000A LINE FEED (LF) or
U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) characters.
The placeholder attribute should not be used as a
replacement for a label. For a longer hint or other advisory text, place the text
next to the control.
Use of the placeholder attribute as a replacement for a label can reduce the
accessibility and usability of the control for a range of users including older
users and users with cognitive, mobility, fine motor skill or vision impairments.
While the hint given by the control’s label is shown at all times, the short
hint given in the placeholder attribute is only shown before the user enters a value. Furthermore, placeholder text may be mistaken for
a pre-filled value, and as commonly implemented the default color of the placeholder text
provides insufficient contrast and the lack of a separate visible label reduces the size of the hit region available for setting focus on the control.
User agents should present this hint to the user, after having stripped line breaks from it, when the element’s value is the empty string, especially if the control is not focused.
If a user agent normally doesn’t show this hint to the user when the control is focused, then the user agent should nonetheless show the hint for the control if it
was focused as a result of the autofocus attribute, since
in that case the user will not have had an opportunity to examine the control before focusing
it.
placeholder attribute:
<fieldset> <legend>Mail Account</legend> <p><label>Name: <input type="text" name="fullname" placeholder="John Ratzenberger"></label></p> <p><label>Address: <input type="email" name="address" placeholder="john@example.net"></label></p> <p><label>Password: <input type="password" name="password"></label></p> <p><label>Description: <input type="text" name="desc" placeholder="My Email Account"></label></p> </fieldset>
<input name=t1 type=tel placeholder="‫ رقم الهاتف 1 ‮"> <input name=t2 type=tel placeholder="‫ رقم الهاتف 2 ‮">
For slightly more clarity, here’s the same example using numeric character references instead of inline Arabic:
<input name=t1 type=tel placeholder="‫رقم الهاتف 1‮"> <input name=t2 type=tel placeholder="‫رقم الهاتف 2‮">
4.10.5.4. Common input element APIs
- input .
value[ = value ] -
Returns the current value of the form control.
Can be set, to change the value.
Throws an "
InvalidStateError"DOMExceptionif it is set to any value other than the empty string when the control is aFile Uploadcontrol. - input .
checked[ = value ] -
Returns the current checkedness of the form control.
Can be set, to change the checkedness.
- input .
files -
Returns a
FileListobject listing the selected files of the form control.Returns null if the control isn’t a file control.
- input .
valueAsDate[ = value ] -
Returns a
Dateobject representing the form control’s value, if applicable; otherwise, returns null.Can be set, to change the value.
Throws an "
InvalidStateError"DOMExceptionif the control isn’t date- or time-based. - input .
valueAsNumber[ = value ] -
Returns a number representing the form control’s value, if applicable;
otherwise, returns NaN.
Can be set, to change the value. Setting this to NaN will set the underlying value to the empty string.
Throws an "
InvalidStateError"DOMExceptionif the control is neither date- or time-based nor numeric. - input .
stepUp( [ n ] ) - input .
stepDown( [ n ] ) -
Changes the form control’s value by the value given in the
stepattribute, multiplied by n. The default value for n is 1.Throws "
InvalidStateError"DOMExceptionif the control is neither date- or time-based nor numeric, or if thestepattribute’s value is "any". - input .
list - Returns the
datalistelement indicated by thelistattribute.
The value IDL attribute allows scripts to
manipulate the value of an input element. The
attribute is in one of the following modes, which define its behavior:
- value
-
On getting, it must return the current value of the element. On setting, it must set the element’s value to the new value, set the element’s dirty value flag to true, invoke the value sanitization algorithm, if the element’s
typeattribute’s current state defines one, and then, if the element has a text entry cursor position, should move the text entry cursor position to the end of the text field, unselecting any selected text and resetting the selection direction to none. - default
-
On getting, if the element has a
valueattribute, it must return that attribute’s value; otherwise, it must return the empty string. On setting, it must set the element’svalueattribute to the new value. - default/on
-
On getting, if the element has a
valueattribute, it must return that attribute’s value; otherwise, it must return the string "on". On setting, it must set the element’svalueattribute to the new value. - filename
-
On getting, it must return the string "
C:\fakepath\" followed by the name of the first file in the list of selected files, if any, or the empty string if the list is empty. On setting, if the new value is the empty string, it must empty the list of selected files; otherwise, it must throw an "InvalidStateError"DOMException.This "fakepath" requirement is a sad accident of history. See the example in the
File Uploadstate section for more information.Since path components are not permitted in file names in the list of selected files, the "
\fakepath\" cannot be mistaken for a path component.
The checked IDL attribute allows scripts to
manipulate the checkedness of an input element. On getting, it must return the current checkedness of the element; and on setting, it must set the
element’s checkedness to the new value and set the
element’s dirty checkedness flag to
true.
The files IDL attribute allows scripts to
access the element’s selected files. On
getting, if the IDL attribute applies, it must return a FileList object that represents the current selected files. The same object must be returned
until the list of selected files changes. If
the IDL attribute does not apply, then it must instead return
null. [FILEAPI]
The valueAsDate IDL attribute represents
the value of the element, interpreted as a date.
On getting, if the valueAsDate attribute does not apply, as defined for the input element’s type attribute’s current state, then return null. Otherwise, run
the algorithm to convert a string to a Date object defined for that state to the element’s value; if the algorithm returned a Date object, then
return it, otherwise, return null.
On setting, if the valueAsDate attribute does not apply, as defined for the input element’s type attribute’s current state, then throw an InvalidStateError exception; otherwise, if the new value is not null and not a Date object throw a TypeError exception; otherwise if the new value is null or a Date object representing the NaN time value, then set the value of the element to the empty string; otherwise, run the algorithm to convert a Date object to
a string, as defined for that state, on the new value, and set the value of the element to the resulting string.
The valueAsNumber IDL attribute
represents the value of the element, interpreted as a
number.
On getting, if the valueAsNumber attribute does not apply, as defined for the input element’s type attribute’s current state, then return a Not-a-Number (NaN)
value. Otherwise, if the valueAsDate attribute applies, run the algorithm to convert a string to a Date object defined for that state to the element’s value; if the algorithm returned a Date object, then
return the time value of the object (the number of milliseconds from midnight UTC the
morning of 1970-01-01 to the time represented by the Date object), otherwise, return
a Not-a-Number (NaN) value. Otherwise, run the algorithm to convert a string to a number defined for that state to the element’s value; if the
algorithm returned a number, then return it, otherwise, return a Not-a-Number (NaN) value.
On setting, if the new value is infinite, then throw a TypeError exception.
Otherwise, if the valueAsNumber attribute does not apply, as defined for the input element’s type attribute’s current state, then throw an InvalidStateError exception. Otherwise, if the new value is a Not-a-Number (NaN)
value, then set the value of the element to the empty
string. Otherwise, if the valueAsDate attribute applies, run the algorithm to convert a Date object to a
string defined for that state, passing it a Date object whose time
value is the new value, and set the value of the
element to the resulting string. Otherwise, run the algorithm to convert a number to a string, as
defined for that state, on the new value, and set the value of the element to the resulting string.
The stepDown(n) and stepUp(n) methods, when invoked, must run the following algorithm:
-
If the
stepDown()andstepUp()methods do not apply, as defined for theinputelement’stypeattribute’s current state, then throw an "InvalidStateError"DOMException, and abort these steps. -
If the element has no allowed value step, then throw an "
InvalidStateError"DOMException, and abort these steps. -
If the element has a minimum and a maximum and the minimum is greater than the maximum, then abort these steps.
-
If the element has a minimum and a maximum and there is no step aligned value greater than or equal to the element’s minimum and less than or equal to the element’s maximum, then abort these steps.
-
If applying the algorithm to convert a string to a number to the string given by the element’s value does not result in an error, then let value be the result of that algorithm. Otherwise, let value be zero.
-
Let valueBeforeStepping be value.
-
If value is not step aligned, then:
-
If the method invoked was the
stepDown()method, then step-align value with negative preference. Otherwise step-align value with positive preference. In either case, let value be the result.This ensures that the value first snaps to a step-aligned value when it doesn’t start step-aligned. For example, starting with the followinginputwithvalueof 3:<input type="number" value="3" min="1" max="10" step="2.6">
Invoking the
stepUp()method will snap thevalueto 3.6; subsequent invocations will increment the value by 2.6 (e.g., 6.2, then 8.8). Likewise, the followinginputelement in theWeekstate will also step-align in similar fashion, though in this state, thestepvalue is rounded to 3, per the derivation of the allowed value step.<input type="week" value="2016-W20" min="2016-W01" max="2017-W01" step="2.6">
Invoking
stepUp()will result in avalueof "2016-W22" because the nearest step-aligned value from the step base of "2016-W01" (theminvalue) with 3 weeksteps that is greater than thevalueof "2016-W20" is "2016-W22" (i.e.: W01, W04, W07, W10, W13, W16, W19, W22).
Otherwise (value is step aligned), run the following substeps:
-
Let n be the argument.
-
Let delta be the allowed value step multiplied by n.
-
If the method invoked was the
stepDown()method, negate delta. -
Let value be the result of adding delta to value.
-
-
If the element has a minimum, and value is less than that minimum, then set value to the step-aligned minimum value with positive preference.
-
If the element has a maximum, and value is greater than that maximum, then set value to the step-aligned maximum value with negative preference.
-
If either the method invoked was the
stepDown()method and value is greater than valueBeforeStepping, or the method invoked was thestepUp()method and value is less than valueBeforeStepping, then abort these steps. -
Let value as string be the result of running the algorithm to convert a number to a string, as defined for the
inputelement’stypeattribute’s current state, on value. -
Set the value of the element to value as string.
To determine if a value v is step aligned do the following:
This algorithm checks to see if a value falls along an input element’s
defined step intervals, with the interval’s origin at the step base value. It is
used to determine if the element’s value is suffering from a step mismatch and for various checks in the stepUp() and stepDown() methods.
-
Subtract the step base from v and let the result be relative distance.
-
If dividing the relative distance by the allowed value step results in a value with a remainder then v is not step aligned. Otherwise it is step aligned.
To step-align a value v with either negative preference or positive preference, do the following:
negative preference selects a step-aligned value that is less than or equal to v, while positive preference step-aligns with a value greater than or equal to v.
-
Subtract the step base from v and let the result be relative distance.
-
Let step interval count be the result of integer dividing (or divide and throw out any remainder) relative distance by the allowed value step.
-
Let candidate be the step interval count multiplied by the allowed value step.
-
If this algorithm was invoked with negative preference and the value of v is less than candidate, then decrement candidate by the allowed value step.
Otherwise, if this algorithm was invoked with positive preference and the value of v is greater than candidate, then increment candidate by the allowed value step.
-
The step-aligned value is candidate. Return candidate.
The list IDL attribute must return the
current suggestions source element, if any, or null otherwise.
4.10.5.5. Common event behaviors
When the input and change events apply (which is the case for all input controls other than buttons and those with the type attribute in the state), the events are fired to indicate that the
user has interacted with the control. The input event fires whenever the user has modified the data of the control. The change event fires when the value is committed, if
that makes sense for the control, or else when the control loses focus. In all cases, the input event comes before the corresponding change event (if any).
When an input element has a defined activation behavior, the rules
for dispatching these events, if they apply, are given
in the section above that defines the type attribute’s
state. (This is the case for all input controls with the type attribute in the Checkbox state, the Radio Button state, or the File Upload state.)
For input elements without a defined activation behavior, but to
which these events apply, and for which the user
interface involves both interactive manipulation and an explicit commit action, then when the user
changes the element’s value, the user agent must queue a task to fire a simple event that bubbles named input at the input element, and any time the user
commits the change, the user agent must queue a task to fire a simple
event that bubbles named change at the input element.
An example of a user interface involving both interactive manipulation and a
commit action would be a Range controls that use a
slider, when manipulated using a pointing device. While the user is dragging the control’s knob, input events would fire whenever the position changed,
whereas the change event would only fire when the user
let go of the knob, committing to a specific value.
For input elements without a defined activation behavior, but to
which these events apply, and for which the user
interface involves an explicit commit action but no intermediate manipulation, then any time the
user commits a change to the element’s value, the user
agent must queue a task to first fire a simple event that bubbles named input at the input element, and then fire a simple event that bubbles named change at the input element.
An example of a user interface with a commit action would be a Color control that consists of a single button that brings
up a color wheel: if the value only changes when the dialog
is closed, then that would be the explicit commit action. On the other hand, if manipulating the
control changes the color interactively, then there might be no commit action.
Another example of a user interface with a commit action would be a Date control that allows both text-based user input and user
selection from a drop-down calendar: while text input does not have an explicit commit step,
selecting a date from the drop down calendar and then dismissing the drop down would be a commit
action.
The Range control is also an example of a
user interface that has a commit action when used with a pointing device (rather than a keyboard):
during the time that the pointing device starts manipulating the slider until the time that the
slider is released, no commit action is taken (though input events are fired as the
value is changed). Only after the slider is release is the commit action taken.
For input elements without a defined activation behavior, but to
which these events apply, any time the user causes the
element’s value to change without an explicit commit
action, the user agent must queue a task to fire a simple event that
bubbles named input at the input element. The
corresponding change event, if any, will be fired when
the control loses focus.
Examples of a user changing the element’s value would include the user typing into a text field, pasting a new value into the field, or undoing an edit in that field. Some user interactions do not cause changes to the value, e.g., hitting the "delete" key in an empty text field, or replacing some text in the field with text from the clipboard that happens to be exactly the same text.
A Range control in the form of a
slider that the user has focused and is interacting with using a keyboard would be
another example of the user changing the element’s value without a commit step.
In the case of tasks that just fire an input event, user agents may wait for a suitable break in the
user’s interaction before queuing the tasks; for example, a
user agent could wait for the user to have not hit a key for 100ms, so as to only fire the event
when the user pauses, instead of continuously for each keystroke.
When the user agent is to change an input element’s value on behalf of the user (e.g., as part of a form prefilling
feature), the user agent must queue a task to first update the value accordingly, then fire a simple event that
bubbles named input at the input element,
then fire a simple event that bubbles named change at the input element.
These events are not fired in response to changes made to the values of form controls by scripts. (This is to make it easier to update the values of form controls in response to the user manipulating the controls, without having to then filter out the script’s own changes to avoid an infinite loop.)
The task source for these tasks is the user interaction task source.
4.10.6. The button element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Phrasing content.
- Interactive content.
- listed, labelable, submittable, and reassociateable form-associated element.
- Palpable content.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where phrasing content is expected.
- Content model:
- Phrasing content, but there must be no interactive content descendant.
- Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
autofocus- Automatically focus the form control when the page is loadeddisabled- Whether the form control is disabledform- Associates the control with aformelementformaction- URL to use for §4.10.21 Form submissionformenctype- Form data set encoding type to use for §4.10.21 Form submissionformmethod- HTTP method to use for §4.10.21 Form submissionformnovalidate- Bypass form control validation for §4.10.21 Form submissionformtarget- browsing context for §4.10.21 Form submissionmenu- Specifies the element’s designated pop-up menuname- Name of form control to use for §4.10.21 Form submission and in theform.elementsAPItype- Type of buttonvalue- Value to be used for §4.10.21 Form submission- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
button(default - do not set),link,menuitem,menuitemcheckbox,menuitemradio,radioorswitch.- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles. - DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLButtonElement : HTMLElement { attribute boolean autofocus; attribute boolean disabled; readonly attribute HTMLFormElement? form; attribute DOMString formAction; attribute DOMString formEnctype; attribute DOMString formMethod; attribute boolean formNoValidate; attribute DOMString formTarget; attribute DOMString name; attribute DOMString type; attribute DOMString value; attribute HTMLMenuElement? menu; readonly attribute boolean willValidate; readonly attribute ValidityState validity; readonly attribute DOMString validationMessage; boolean checkValidity(); boolean reportValidity(); void setCustomValidity(DOMString error); [SameObject] readonly attribute NodeList labels; };
The button element represents a control allowing a user to trigger actions, when enabled.
It is labeled by its content.
The element is a button.
The type attribute controls the behavior of
the button when it is activated. It is an enumerated attribute. The following table
lists the keywords and states for the attribute — the keywords in the left column map to the
states in the cell in the second column on the same row as the keyword.
| Keyword | State | Brief description |
|---|---|---|
submit
| submit button | Submits the form. |
reset
| reset button | Resets the form. |
button
| Button | Does nothing. |
menu
| Menu | Shows a menu. |
The missing value default is the submit button state.
If the type attribute is in the submit button state, the element is specifically a submit button.
Constraint validation: If the type attribute is in the reset button state, the Button state, or the Menu state, the element is barred from constrain validation.
When a button element is not disabled,
its activation behavior element is to run the steps defined in the following list for
the current state of the element’s type attribute:
- submit button
- If the element has a form owner and the element’s node document is fully active, the element must submit the form owner from the
buttonelement. - reset button
- If the element has a form owner and the element’s node document is fully active, the element must reset the form owner.
- Button
- Do nothing.
- Menu
-
The element must follow these steps:
- If the
buttonis not being rendered, abort these steps. - If the
buttonelement’s node document is not fully active, abort these steps. - Let menu be the element’s designated pop-up menu, if any. If there isn’t one, then abort these steps.
- Fire a trusted event with the name
showat menu, using theRelatedEventinterface, with therelatedTargetattribute initialized to thebuttonelement. The event must be cancelable. - If the event is not canceled, then build and
show the menu for menu, with the
buttonelement as the subject.
- If the
The form attribute is used to explicitly associate the button element with its form owner. The name attribute represents the element’s name. The disabled attribute is used to make the control non-interactive and
to prevent its value from being submitted. The autofocus attribute controls focus. The formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, and formtarget attributes are attributes for form submission.
The formnovalidate attribute can be
used to make submit buttons that do not trigger the constraint validation.
The formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, and formtarget must not be specified if the element’s type attribute is not in the submit button state.
The value attribute gives the element’s value
for the purposes of form submission. The element’s value is
the value of the element’s value attribute, if there is
one, or the empty string otherwise.
A button (and its value) is only included in the form submission if the button itself was used to initiate the form submission.
If the element’s type attribute is in the Menu state, the menu attribute must be specified to give the element’s
menu. The value must be the ID of a menu element in
the same tree whose type attribute is in
the popup menu state. The attribute must not be specified if
the element’s type attribute is not in the Menu state.
A button element’s designated pop-up menu is the first element in the button's tree whose ID is that given by the button element’s menu attribute, if there is such an element and
its type attribute is in the popup menu state; otherwise, the element has no designated pop-up
menu.
The value and menu IDL attributes must reflect the content attributes of the same name.
The type IDL attribute must reflect the content attribute of the same name, limited to only known values.
The willValidate, validity, and validationMessage IDL attributes, and
the checkValidity(), reportValidity(), and setCustomValidity() methods, are part of
the constraint validation API.
The labels IDL attribute provides a list of the element’s labels.
The autofocus, disabled, form, and name IDL attributes are
part of the element’s forms API.
<button type=button onclick="alert('This 15-20 minute piece was composed by George Gershwin.')"> Show hint </button>
4.10.7. The select element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Phrasing content.
- Interactive content.
- listed, labelable, submittable, resettable, and reassociateable form-associated element.
- Palpable content.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where phrasing content is expected.
- Content model:
- Zero or more
option,optgroup, and script-supporting elements. - Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
autofocus- Automatically focus the form control when the page is loadeddisabled- Whether the form control is disabledform- Associates the control with aformelementmultiple- Whether to allow multiple valuesname- Name of form control to use for §4.10.21 Form submission and in theform.elementsAPIrequired- Whether the control is required for §4.10.21 Form submissionsize- Size of the control- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
listbox(default - do not set) ormenu.- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles. - DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLSelectElement : HTMLElement { attribute DOMString autocomplete; attribute boolean autofocus; attribute boolean disabled; readonly attribute HTMLFormElement? form; attribute boolean multiple; attribute DOMString name; attribute boolean _required; attribute unsigned long size; readonly attribute DOMString type; [SameObject] readonly attribute HTMLOptionsCollection options; attribute unsigned long length; getter Element? item(unsigned long index); HTMLOptionElement? namedItem(DOMString name); void add((HTMLOptionElement or HTMLOptGroupElement) element, optional (HTMLElement or long)? before = null); void remove(); // ChildNode overload void remove(long index); setter void (unsigned long index, HTMLOptionElement? option); [SameObject] readonly attribute HTMLCollection selectedOptions; attribute long selectedIndex; attribute DOMString value; readonly attribute boolean willValidate; readonly attribute ValidityState validity; readonly attribute DOMString validationMessage; boolean checkValidity(); boolean reportValidity(); void setCustomValidity(DOMString error); [SameObject] readonly attribute NodeList labels; };
The select element represents a control for selecting amongst a set of
options.
The multiple attribute is a boolean
attribute. If the attribute is present, then the select element represents a control for selecting zero or more options from the list of options. If the attribute is absent, then the select element represents a control for selecting a single option from
the list of options.
The size attribute gives the number of options
to show to the user. The size attribute, if specified, must
have a value that is a valid non-negative integer greater than zero.
The display size of a select element is the
result of applying the rules for parsing non-negative integers to the value of
element’s size attribute, if it has one and parsing it is
successful. If applying those rules to the attribute’s value is not successful, or if the size attribute is absent, then the element’s display size is 4 if the element’s multiple content attribute is present, and 1 otherwise.
The list of options for a select element consists of all the option element children of the select element, and all the option element children of all the optgroup element
children of the select element, in tree order.
The required attribute is a boolean
attribute. When specified, the user will be required to select a value before submitting
the form.
If a select element has a required attribute specified, does not have a multiple attribute
specified, and has a display size of 1; and if the value of the first option element in the select element’s list of options (if
any) is the empty string, and that option element’s parent node is the select element (and not an optgroup element), then that option is the select element’s placeholder label option.
If a select element has a required attribute specified, does not have a multiple attribute
specified, and has a display size of 1, then the select element must have a placeholder label option.
In practice, the requirement stated in the paragraph above can only apply when a select element does not have a sizes attribute
with a value greater than 1.
Constraint validation: If the element has its required attribute specified, and either none of the option elements in the select element’s list of options have their selectedness set to true, or the only option element in the select element’s list of options with its selectedness set to true is the placeholder label
option, then the element is suffering from being missing.
If the multiple attribute is absent, and the element
is not disabled, then the user agent should allow the
user to pick an option element in its list
of options that is itself not disabled. Upon
this option element being picked (either
through a click, or through unfocusing the element after changing its value, or through a menu command, or through any other mechanism), and before the
relevant user interaction event is queued (e.g., before the click event), the user agent must set the selectedness of the picked option element
to true, set its dirtiness to true, and then send select update notifications.
If the multiple attribute is absent, whenever an option element in the select element’s list of options has its selectedness set to true, and whenever an option element with its selectedness set to true is added to the select element’s list of options,
the user agent must set the selectedness of all
the other option elements in its list of
options to false.
If the multiple attribute is absent and the
element’s display size is greater than 1, then the user
agent should also allow the user to request that the option whose selectedness is true, if any, be unselected. Upon this
request being conveyed to the user agent, and before the relevant user interaction event is queued (e.g., before the click event), the user agent must set the selectedness of that option element to
false, set its dirtiness to true, and then send select update notifications.
If nodes are inserted or nodes are removed causing the list of options to gain or lose one or more option elements, or if an option element in the list of options asks for a reset, then, if the select element’s multiple attribute is absent, the user agent must run the
first applicable set of steps from the following list:
- If the
selectelement’s display size is 1, and nooptionelements in theselectelement’s list of options have their selectedness set to true - Set the selectedness of the first
optionelement in the list of options in tree order that is not disabled, if any, to true. - If two or more
optionelements in theselectelement’s list of options have their selectedness set to true - Set the selectedness of all but the last
optionelement with its selectedness set to true in the list of options in tree order to false.
If the multiple attribute is present, and the
element is not disabled, then the user agent should
allow the user to toggle the selectedness of the option elements in
its list of options that are themselves not disabled. Upon such an element being toggled (either through a click, or through a menu command, or any other mechanism), and before the relevant user
interaction event is queued (e.g., before a related click event), the selectedness of the option element must
be changed (from true to false or false to true), the dirtiness of the element must be set to true, and the
user agent must send select update notifications.
When the user agent is to send select update notifications, queue
a task to first fire a simple event that bubbles named input at the select element, and then fire a simple
event that bubbles named change at the select element, using the user interaction task source as the task
source. If the JavaScript execution context stack was not empty when the user agent was
to send select update notifications, then the resulting input and change events must not be trusted.
The reset algorithm for select elements is to go through all the option elements in the element’s list of options, set their selectedness to true if the option element has a selected attribute, and false otherwise,
set their dirtiness to false, and then have the option elements ask for a reset.
The form attribute is used to explicitly associate the select element with its form owner.
The name attribute represents the element’s name.
The disabled attribute is used to make the control non-interactive and to prevent its value from being submitted.
The autofocus attribute controls focus.
The autocomplete attribute controls how the user agent provides autofill behavior.
A select element that is not disabled is mutable.
- select .
type -
Returns "
select-multiple" if the element has amultipleattribute, and "select-one" otherwise. - select .
options -
Returns an
HTMLOptionsCollectionof the list of options. - select .
length[ = value ] -
Returns the number of elements in the list of options.
When set to a smaller number, truncates the number of
optionelements in theselect.When set to a greater number, adds new blank
optionelements to theselect. - element = select .
item(index) - select[index]
-
Returns the item with index index from the list of options. The items are sorted in tree order.
- element = select .
namedItem(name) -
Returns the first item with ID or
namename from the list of options.Returns null if no element with that ID could be found.
- select .
add(element [, before ] ) -
Inserts element before the node given by before.
The before argument can be a number, in which case element is inserted before the item with that number, or an element from the list of options, in which case element is inserted before that element.
If before is omitted, null, or a number out of range, then element will be added at the end of the list.
This method will throw a
HierarchyRequestErrorexception if element is an ancestor of the element into which it is to be inserted. - select .
selectedOptions -
Returns an
HTMLCollectionof the list of options that are selected. - select .
selectedIndex[ = value ] -
Returns the index of the first selected item, if any, or -1 if there is no selected item.
Can be set, to change the selection.
- select .
value[ = value ] -
Returns the value of the first selected item, if any, or the empty string if there is no selected item.
Can be set, to change the selection.
The type IDL attribute, on getting, must
return the string "select-one" if the multiple attribute is absent, and the string "select-multiple" if the multiple attribute is present.
The options IDL attribute must return an HTMLOptionsCollection rooted at the select node, whose filter matches
the elements in the list of options.
The options collection is also mirrored on the HTMLSelectElement object. The supported property indices at any instant
are the indices supported by the object returned by the options attribute at that instant.
The length IDL attribute must return the
number of nodes represented by the options collection. On setting, it must act like the attribute
of the same name on the options collection.
The item(index) method
must return the value returned by the method of the same
name on the options collection, when invoked with
the same argument.
The namedItem(name) method must return the value returned by the
method of the same name on the options collection,
when invoked with the same argument.
When the user agent is to set the value of a new
indexed property for a given property index index to a new value value, it must instead set the
value of a new indexed property with the given property index index to
the new value value on the options collection.
Similarly, the add() method must act like its
namesake method on that same options collection.
The remove() method must act like its
namesake method on that same options collection when it
has arguments, and like its namesake method on the ChildNode interface implemented by
the HTMLSelectElement ancestor interface Element when it has no
arguments.
The selectedOptions IDL attribute
must return an HTMLCollection rooted at the select node, whose filter
matches the elements in the list of options that
have their selectedness set to true.
The selectedIndex IDL attribute, on
getting, must return the index of the first option element in the list of
options in tree order that has its selectedness set to true, if any. If there isn’t one,
then it must return -1.
On setting, the selectedIndex attribute must set
the selectedness of all the option elements in the list of options to false, and
then the option element in the list of
options whose index is the given new value, if
any, must have its selectedness set to true and
its dirtiness set to true.
This can result in no element having a selectedness set to true even in the case of the select element having no multiple attribute and a display size of 1.
The value IDL attribute, on getting, must
return the value of the first option element in the list of options in tree
order that has its selectedness set to
true, if any. If there isn’t one, then it must return the empty string.
On setting, the value attribute must set the selectedness of all the option elements
in the list of options to false, and then the
first option element in the list of
options, in tree order, whose value is equal to the given new value, if any, must have its selectedness set to true and its dirtiness set to true.
This can result in no element having a selectedness set to true even in the case of the select element having no multiple attribute and a display size of 1.
The multiple, required, and size IDL attributes must reflect the
respective content attributes of the same name. The size IDL
attribute has a default value of zero.
For historical reasons, the default value of the size IDL attribute does not return the actual size used, which, in
the absence of the size content attribute, is either 1 or 4
depending on the presence of the multiple attribute.
The willValidate, validity, and validationMessage IDL attributes, and
the checkValidity(), reportValidity(), and setCustomValidity() methods, are part of
the constraint validation API.
The labels IDL attribute provides a list of the element’s labels.
The autofocus, disabled, form, and name IDL attributes are part of the
element’s forms API.
select element can be used to offer the user
with a set of options from which the user can select a single option. The default option is
preselected.
<div> <label for="unittype">Select unit type:</label> <select id="unittype" name="unittype"> <option value="1"> Miner </option> <option value="2"> Puffer </option> <option value="3" selected> Snipey </option> <option value="4"> Max </option> <option value="5"> Firebot </option> </select> </div>
When there is no default option, a value that provides instructions or a hint (placeholder option) can be used instead:
<select name="unittype" required> <option value=""> Select unit type </option> <option value="1"> Miner </option> <option value="2"> Puffer </option> <option value="3"> Snipey </option> <option value="4"> Max </option> <option value="5"> Firebot </option> </select>
<div> <label for="allowedunits">Select unit types to enable on this map:</label> <select id="allowedunits" name="allowedunits" multiple> <option value="1" selected> Miner </option> <option value="2" selected> Puffer </option> <option value="3" selected> Snipey </option> <option value="4" selected> Max </option> <option value="5" selected> Firebot </option> </select> </div>
<p>Select the songs from that you would like on your Act II Mix Tape:</p> <select multiple required name="act2"> <option value="s1">It Sucks to Be Me (Reprize) <option value="s2">There is Life Outside Your Apartment <option value="s3">The More You Ruv Someone <option value="s4">Schadenfreude <option value="s5">I Wish I Could Go Back to College <option value="s6">The Money Song <option value="s7">School for Monsters <option value="s8">The Money Song (Reprize) <option value="s9">There’s a Fine, Fine Line (Reprize) <option value="s10">What Do You Do With a B.A. in English? (Reprize) <option value="s11">For Now </select>
4.10.8. The datalist element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Phrasing content.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where phrasing content is expected.
- Content model:
- Either: phrasing content.
- Or: Zero or more
optionand script-supporting elements. - Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
listbox(default - do not set).- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles. - DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLDataListElement : HTMLElement { [SameObject] readonly attribute HTMLCollection options; };
The datalist element represents a set of option elements that
represent predefined options for other controls. In the rendering, the datalist element represents nothing and it, along with its children, should
be hidden.
The datalist element can be used in two ways. In the simplest case, the datalist element has just option element children.
<label> Sex: <input name=sex list=sexes> <datalist id=sexes> <option value="Female"> <option value="Male"> </datalist> </label>
In the more elaborate case, the datalist element can be given contents that are to
be displayed for down-level clients that don’t support datalist. In this case, the option elements are provided inside a select element inside the datalist element.
<label> Sex: <input name=sex list=sexes> </label> <datalist id=sexes> <label> or select from the list: <select name=sex> <option value=""> <option>Female <option>Male </select> </label> </datalist>
The datalist element is hooked up to an input element using the list attribute on the input element.
Each option element that is a descendant of the datalist element,
that is not disabled, and whose value is a string that isn’t the empty string, represents a
suggestion. Each suggestion has a value and a label.
- datalist .
options - Returns an
HTMLCollectionof theoptionelements of thedatalistelement.
The options IDL attribute must return an HTMLCollection rooted at the datalist node, whose filter matches option elements.
Constraint validation: If an element has a datalist element
ancestor, it is barred from constraint validation.
4.10.9. The optgroup element
- Categories:
- None.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- As a child of a
selectelement. - Content model:
- Zero or more
optionand script-supporting elements. - Tag omission in text/html:
- An
optgroupelement’s end tag may be omitted if theoptgroupelement is immediately followed by anotheroptgroupelement, or if there is no more content in the parent element. - Content attributes:
- Global attributes
disabled- Whether the form control is disabledlabel- User-visible label- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
- None
- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLOptGroupElement : HTMLElement { attribute boolean disabled; attribute DOMString label; };
The optgroup element represents a group of option elements with a common label.
The element’s group of option elements consists of the option elements that are children of the optgroup element.
When showing option elements in select elements, user agents should
show the option elements of such groups as being related to each other and separate
from other option elements.
The disabled content attribute is a boolean attribute and can be used to disable a group of option elements
together.
The label content attribute must be specified. Its
value gives the name of the group, for the purposes of the user interface. User
agents should use this attribute’s value when labeling the group of option elements
in a select element.
The disabled and label IDL attributes must reflect the
respective content attributes of the same name.
There is no way to select an optgroup element. Only option elements can be selected. An optgroup element merely provides a
label for a group of option elements.
select drop-down widget:
<form action="courseselector.dll" method="get"> <p>Which course would you like to watch today? <p><label>Course: <select name="c"> <optgroup label="8.01 Physics I: Classical Mechanics"> <option value="8.01.1">Lecture 01: Powers of Ten <option value="8.01.2">Lecture 02: 1D Kinematics <option value="8.01.3">Lecture 03: Vectors <optgroup label="8.02 Electricity and Magnestism"> <option value="8.02.1">Lecture 01: What holds our world together? <option value="8.02.2">Lecture 02: Electric Field <option value="8.02.3">Lecture 03: Electric Flux <optgroup label="8.03 Physics III: Vibrations and Waves"> <option value="8.03.1">Lecture 01: Periodic Phenomenon <option value="8.03.2">Lecture 02: Beats <option value="8.03.3">Lecture 03: Forced Oscillations with Damping </select> </label> <p><input type=submit value="▶ Play"> </form>
4.10.10. The option element
- Categories:
- None.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- As a child of a
selectelement. - As a child of a
datalistelement. - As a child of an
optgroupelement. - Content model:
- If the element has a
labelattribute and avalueattribute: Nothing. - If the element has a
labelattribute but novalueattribute: Text. - If the element has no
labelattribute: and is not a child of adatalistelement: Text that is not inter-element white space. - If the element has no
labelattribute and is a child of adatalistelement: Text. - Tag omission in text/html:
- An
optionelement’s end tag may be omitted if theoptionelement is immediately followed by anotheroptionelement, or if it is immediately followed by anoptgroupelement, or if there is no more content in the parent element. - Content attributes:
- Global attributes
disabled- Whether the form control is disabledlabel- User-visible labelselected- Whether the option is selected by defaultvalue- Value to be used for §4.10.21 Form submission- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
option(default - do not set),menuitem,menuitemradioorseparator.- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles. - DOM interface:
-
[NamedConstructor=Option(optional DOMString text = "", optional DOMString value, optional boolean defaultSelected = false, optional boolean selected = false)] interface HTMLOptionElement : HTMLElement { attribute boolean disabled; readonly attribute HTMLFormElement? form; attribute DOMString label; attribute boolean defaultSelected; attribute boolean selected; attribute DOMString value; attribute DOMString text; readonly attribute long index; };
The option element represents an option in a select element or as part of a list of
suggestions in a datalist element.
In certain circumstances described in the definition of the select element, an option element can be a select element’s placeholder label option. A placeholder label option does not represent an actual option, but instead represents a
label for the select control.
The disabled content attribute is a boolean attribute. An option element is disabled if its disabled attribute
is present or if it is a child of an optgroup element whose disabled attribute is
present.
An option element that is disabled must prevent any click events
that are queued on the user interaction task source from being dispatched on the
element.
The label content attribute provides a label for
the element. The label of an option element is the value of the label content attribute, if there is one and its value is not the empty string, or, otherwise, the value
of the element’s text IDL attribute if its value is not the empty string.
The label content attribute, if specified, must not be empty.
The value content attribute provides a value for
element. The value of an option element is the value of the value content
attribute, if there is one, or, if there is not, the value of the element’s text IDL attribute (which may be the empty string).
The selected content attribute is a boolean attribute. It represents the default selectedness of the
element.
The dirtiness of an option element is a boolean state, initially
false. It controls whether adding or removing the selected content attribute has any
effect.
The selectedness of an option element is a boolean state,
initially false. Except where otherwise specified, when the element is created, its selectedness must be set to true if the element has a selected attribute. Whenever an option element’s selected attribute is
added, if its dirtiness is false, its selectedness must be set to true. Whenever an option element’s selected attribute is removed, if its dirtiness is
false, its selectedness must be set to false.
The Option() constructor,
when called with three or fewer arguments, overrides the initial state of the selectedness state to always be false even if the third argument is true
(implying that a selected attribute is to be set). The fourth argument can be used to
explicitly set the initial selectedness state when using the
constructor.
A select element whose multiple attribute is not specified must not have more than
one descendant option element with its selected attribute set.
An option element’s index is the number of option elements that are
in the same list of options but that come before it in tree order. If the option element is not in a list of options, then the option element’s index is zero.
- option .
selected -
Returns true if the element is selected, and false otherwise.
Can be set, to override the current state of the element.
- option .
index - Returns the index of the element in its
selectelement’soptionslist. - option .
form - Returns the element’s
formelement, if any, or null otherwise. - option .
text - Same as
textContent, except that spaces are collapsed andscriptelements are skipped. - option = new
Option()( [ text [, value [, defaultSelected [, selected ] ] ] ] ) -
Returns a new
optionelement.The text argument sets the contents of the element.
The value argument sets the
valueattribute.The defaultSelected argument sets the
selectedattribute.The selected argument sets whether or not the element is selected. If it is omitted, even if the defaultSelected argument is true, the element is not selected.
The disabled IDL attribute must reflect the content attribute of the same name. The defaultSelected IDL attribute must reflect the selected content attribute.
The label IDL attribute, on getting, if
there is a label content attribute, must return that attribute’s value; otherwise, it
must return the element’s label. On setting, the element’s label content
attribute must be set to the new value.
The value IDL attribute, on getting,
must return the element’s value. On setting, the element’s value content attribute must be set to the new value.
The selected IDL attribute, on getting,
must return true if the element’s selectedness is true, and false
otherwise. On setting, it must set the element’s selectedness to the new
value, set its dirtiness to true, and then cause the element to ask for a reset.
The index IDL attribute must return the
element’s index.
The text IDL attribute, on getting, must
return the result of stripping and collapsing white space from the child text content of the option element, in tree order,
excluding any that are descendants of descendants of the option element that are themselves script elements in the HTML namespace or script elements in the SVG namespace.
On setting, the text attribute must act as if the textContent IDL
attribute on the element had been set to the new value.
The form IDL attribute’s behavior depends on whether the option element
is in a select element or not. If the option has a select element as its parent, or
has an optgroup element as its parent and that optgroup element has a select element
as its parent, then the form IDL attribute must return the same value as the form IDL attribute on that select element. Otherwise, it must return
null.
A constructor is provided for creating HTMLOptionElement objects (in addition to the factory
methods from DOM such as createElement()): Option(text, value, defaultSelected, selected).
When invoked as a constructor, it must return a new HTMLOptionElement object (a new option element). If the first argument is not the empty string, the new object must have as its only
child a Text node whose data is the value of that argument. Otherwise, it must have no
children. If the value argument is present, the new object must have a value attribute set with the value of the argument as its value. If the defaultSelected argument is true, the new object must have a selected attribute set with no value. If the selected argument is true, the new object must have
its selectedness set to true; otherwise the selectedness must be set to false, even if the defaultSelected argument is true. The element’s node document must be the active document of the browsing context of the Window object on which the
interface object of the invoked constructor is found.
4.10.11. The textarea element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Phrasing content.
- Interactive content.
- listed, labelable, submittable, resettable, and reassociateable form-associated element.
- Palpable content.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where phrasing content is expected.
- Content model:
- Text.
- Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
autocomplete- Hint for form autofill featureautofocus- Automatically focus the form control when the page is loadedcols- Maximum number of characters per linedirname- Name of form field to use for sending the element’s directionality in §4.10.21 Form submissiondisabled- Whether the form control is disabledform- Associates the control with aformelementinputmode- Hint for selecting an input modalitymaxlength- Maximum length of valueminlength- Minimum length of valuename- Name of form control to use for §4.10.21 Form submission and in theform.elementsAPIplaceholder- User-visible label to be placed within the form controlreadonly- Whether to allow the value to be edited by the userrequired- Whether the control is required for §4.10.21 Form submissionrows- Number of lines to showwrap- How the value of the form control is to be wrapped for §4.10.21 Form submission- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
textboxwith thearia-multilineproperty set to "true" (default - do not set).- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles. - DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLTextAreaElement : HTMLElement { attribute DOMString autocomplete; attribute boolean autofocus; attribute unsigned long cols; attribute DOMString dirName; attribute boolean disabled; readonly attribute HTMLFormElement? form; attribute DOMString inputMode; attribute long maxLength; attribute long minLength; attribute DOMString name; attribute DOMString placeholder; attribute boolean readOnly; attribute boolean _required; attribute unsigned long rows; attribute DOMString wrap; readonly attribute DOMString type; attribute DOMString defaultValue; [TreatNullAs=EmptyString] attribute DOMString value; readonly attribute unsigned long textLength; readonly attribute boolean willValidate; readonly attribute ValidityState validity; readonly attribute DOMString validationMessage; boolean checkValidity(); boolean reportValidity(); void setCustomValidity(DOMString error); [SameObject] readonly attribute NodeList labels; void select(); attribute unsigned long? selectionStart; attribute unsigned long? selectionEnd; attribute DOMString? selectionDirection; void setRangeText(DOMString replacement); void setRangeText(DOMString replacement, unsigned long start, unsigned long end, optional SelectionMode selectionMode = "preserve"); void setSelectionRange(unsigned long start, unsigned long end, optional DOMString direction); };
The textarea element represents a multiline plain text edit
control for the element’s raw
value. The contents of the control represent the control’s default value.
The raw value of a textarea control must be initially the empty string.
This element has rendering requirements involving the bidirectional algorithm.
The readonly attribute is a boolean attribute used to control whether the text can be edited by the user or
not.
Filename: <code>/etc/bash.bashrc</code> <textarea name="buffer" readonly> # System-wide .bashrc file for interactive bash(1) shells. # To enable the settings / commands in this file for login shells as well, # this file has to be sourced in /etc/profile. # If not running interactively, don’t do anything [ -z "$PS1" ] && return ...</textarea>
Constraint validation: If the readonly attribute is specified on a textarea element, the element is barred from constraint validation.
A textarea element is mutable if it is
neither disabled nor has a readonly attribute specified.
When a textarea is mutable, its raw value should be editable by the user: the user agent
should allow the user to edit, insert, and remove text, and to insert and remove line breaks in
the form of U+000A LINE FEED (LF) characters. Any time the user causes the element’s raw value to change, the user agent must queue a
task to fire a simple event that bubbles named input at the textarea element. User agents may wait for a
suitable break in the user’s interaction before queuing the task; for example, a user agent could
wait for the user to have not hit a key for 100ms, so as to only fire the event when the user
pauses, instead of continuously for each keystroke.
A textarea element has a dirty value flag, which must be initially
set to false, and must be set to true whenever the user interacts with the control in a way that
changes the raw value.
When the textarea element’s textContent IDL attribute changes value,
if the element’s dirty value flag is false, then the
element’s raw value must be set to the value of
the element’s textContent IDL attribute.
The reset algorithm for textarea elements is to set the dirty value flag back to false, and set the element’s raw value to
the value of the element’s textContent IDL attribute.
When a textarea element is popped off the stack of open elements of
an HTML parser or XML parser, then the user agent must invoke the
element’s reset algorithm.
If the element is mutable, the user agent should allow the user to change the writing direction of the element, setting it either to a left-to-right writing direction or a right-to-left writing direction. If the user does so, the user agent must then run the following steps:
-
Set the element’s
dirattribute to "ltr" if the user selected a left-to-right writing direction, and "rtl" if the user selected a right-to-left writing direction. -
Queue a task to fire a simple event that bubbles named
inputat thetextareaelement.
The cols attribute specifies the expected
maximum number of characters per line. If the cols attribute is specified, its value must be a valid non-negative integer greater than
zero. If applying the rules for parsing non-negative integers to
the attribute’s value results in a number greater than zero, then the element’s character width is that value; otherwise, it is 20.
The user agent may use the textarea element’s character width as a hint to the user as to how many
characters the server prefers per line (e.g., for visual user agents by making the width of the
control be that many characters). In visual renderings, the user agent should wrap the user’s
input in the rendering so that each line is no wider than this number of characters.
The rows attribute specifies the number of
lines to show. If the rows attribute is specified, its
value must be a valid non-negative integer greater than zero. If
applying the rules for parsing non-negative integers to the attribute’s value results
in a number greater than zero, then the element’s character
height is that value; otherwise, it is 2.
Visual user agents should set the height of the control to the number of lines given by character height.
The wrap attribute is an enumerated
attribute with two keywords and states: the soft keyword which maps to the Soft state, and the hard keyword which maps to the Hard state. The missing value default is the Soft state.
The Soft state indicates that the text in the textarea is not to be wrapped when it is submitted (though it can still be wrapped in
the rendering).
The Hard state indicates that the text in the textarea is to have newlines added by the user agent so that the text is wrapped when
it is submitted.
If the element’s wrap attribute is in the Hard state, the cols attribute must be specified.
For historical reasons, the element’s value is normalized in three different ways for three
different purposes. The raw value is the value as
it was originally set. It is not normalized. The API
value is the value used in the value IDL
attribute. It is normalized so that line breaks use U+000A LINE FEED (LF) characters. Finally,
there is the value, as used in form submission and other
processing models in this specification. It is normalized so that line breaks use U+000D CARRIAGE
RETURN U+000A LINE FEED (CRLF) character pairs, and in addition, if necessary given the element’s wrap attribute, additional line breaks are inserted to
wrap the text at the given width.
The element’s API value is defined to be the element’s raw value with the following transformation applied:
- Replace every U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN U+000A LINE FEED (CRLF) character pair from the raw value with a single U+000A LINE FEED (LF) character.
- Replace every remaining U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN character from the raw value with a single U+000A LINE FEED (LF) character.
The element’s value is defined to be the element’s raw value with the textarea wrapping transformation applied. The textarea wrapping transformation is the following algorithm, as applied to a string:
- Replace every occurrence of a U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) character not followed by a U+000A LINE FEED (LF) character, and every occurrence of a U+000A LINE FEED (LF) character not preceded by a U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) character, by a two-character string consisting of a U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN U+000A LINE FEED (CRLF) character pair.
- If the element’s
wrapattribute is in the Hard state, insert U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN U+000A LINE FEED (CRLF) character pairs into the string using a user agent-defined algorithm so that each line has no more than character width characters. For the purposes of this requirement, lines are delimited by the start of the string, the end of the string, and U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN U+000A LINE FEED (CRLF) character pairs.
The maxlength attribute is a form control maxlength attribute controlled
by the textarea element’s dirty value flag.
If the textarea element has a maximum allowed value length, then the
element’s children must be such that the code-unit length of the value of the
element’s textContent IDL attribute with the textarea wrapping
transformation applied is equal to or less than the element’s maximum allowed value
length.
The minlength attribute is a form control minlength attribute controlled by the textarea element’s dirty value flag.
The required attribute is a boolean attribute. When specified, the user will be required to enter a value before
submitting the form.
Constraint validation: If the element has its required attribute specified, and the element is mutable, and the element’s value is the empty string, then the element is suffering
from being missing.
The placeholder attribute represents
a short hint (a word or short phrase) intended to aid the user with data entry when the
control has no value. A hint could be a sample value or a brief description of the expected
format.
The placeholder attribute
should not be used as a replacement for a label. For a
longer hint or other advisory text, place the text next to the control.
Use of the placeholder attribute as a replacement for a label can reduce the
accessibility and usability of the control for a range of users including older
users and users with cognitive, mobility, fine motor skill or vision impairments.
While the hint given by the control’s label is shown at all times, the short
hint given in the placeholder attribute is only shown before the user enters a value. Furthermore, placeholder text may be mistaken for
a pre-filled value, and as commonly implemented the default color of the placeholder text
provides insufficient contrast and the lack of a separate visible label reduces the size of the hit region available for setting focus on the control.
User agents should present this hint to the user when the element’s value is the empty string and the control is not focused (e.g., by displaying it inside a blank unfocused control). All U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN U+000A LINE FEED character pairs (CRLF) in the hint, as well as all other U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) and U+000A LINE FEED (LF) characters in the hint, must be treated as line breaks when rendering the hint.
The name attribute represents the element’s name.
The dirname attribute controls how the element’s directionality is submitted.
The disabled attribute is used to make the control non-interactive and to prevent its
value from being submitted.
The form attribute is used to explicitly associate the textarea element with its form owner.
The autofocus attribute controls focus.
The inputmode attribute controls the user interface’s input
modality for the control.
The autocomplete attribute controls how the user agent provides autofill behavior.
- textarea .
type -
Returns the string "
textarea". - textarea .
value -
Returns the current value of the element.
Can be set, to change the value.
The cols, placeholder, required, rows, and wrap attributes must reflect the respective content attributes of the same name. The cols and rows attributes are limited to only non-negative numbers
greater than zero. The cols attribute’s default value is 20. The rows attribute’s default value is 2. The dirName IDL
attribute must reflect the dirname content attribute. The inputMode IDL attribute must reflect the inputmode content attribute, limited to only known values. The maxLength IDL attribute must reflect the maxlength content attribute, limited to only non-negative numbers. The minLength IDL attribute
must reflect the minlength content attribute, limited to only non-negative numbers. The readOnly IDL attribute
must reflect the readonly content attribute.
The type IDL attribute must return the value "textarea".
The defaultValue IDL attribute must act like the element’s textContent IDL attribute.
The value attribute must, on getting, return the element’s API value; on setting, it must set the element’s raw value to the new value, set
the element’s dirty value flag to true, and should then move the text entry cursor
position to the end of the text field, unselecting any selected text and resetting the selection
direction to none.
The textLength IDL attribute must return the code-unit length of
the element’s API value.
The willValidate, validity, and validationMessage IDL attributes,
and the checkValidity(), reportValidity(), and setCustomValidity() methods, are part of the constraint validation API.
The labels IDL attribute provides a list of the element’s labels.
The select(), selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, setRangeText(), and setSelectionRange() methods and IDL
attributes expose the element’s text selection.
The autofocus, disabled, form, and name IDL attributes are part of the element’s forms API.
textarea being used for unrestricted free-form text input
in a form:
<p>If you have any comments, please let us know: <textarea cols=80 name=comments></textarea></p>
To specify a maximum length for the comments, one can use the maxlength attribute:
<p>If you have any short comments, please let us know: <textarea cols=80 name=comments maxlength=200></textarea></p>
To give a default value, text can be included inside the element:
<p>If you have any comments, please let us know: <textarea cols=80 name=comments>You rock!</textarea></p>
You can also give a minimum length. Here, a letter needs to be filled out by the user; a template (which is shorter than the minimum length) is provided, but is insufficient to submit the form:
<textarea required minlength="500">Dear Madam Speaker, Regarding your letter dated ... ... Yours Sincerely, ...</textarea>
A placeholder can be given as well, to suggest the basic form to the user, without providing an explicit template:
<textarea placeholder="Dear Francine, They closed the parks this week, so we won’t be able to meet your there. Should we just have dinner? Love, Daddy"></textarea>
To have the browser submit the directionality of the element along with the
value, the dirname attribute can be specified:
<p>If you have any comments, please let us know (you may use either English or Hebrew for your comments): <textarea cols=80 name=comments dirname=comments.dir></textarea></p>
4.10.12. The output element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Phrasing content.
- listed, labelable, resettable, and reassociateable form-associated element.
- Palpable content.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where phrasing content is expected.
- Content model:
- Phrasing content.
- Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
for- Specifies controls from which the output was calculatedform- Associates the control with aformelementname- Name of form control to use for §4.10.21 Form submission and in theform.elementsAPI- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
status(default - do not set), Any role value.- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles. - DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLOutputElement : HTMLElement { [SameObject, PutForwards=value] readonly attribute DOMTokenList htmlFor; readonly attribute HTMLFormElement? form; attribute DOMString name; readonly attribute DOMString type; attribute DOMString defaultValue; attribute DOMString value; readonly attribute boolean willValidate; readonly attribute ValidityState validity; readonly attribute DOMString validationMessage; boolean checkValidity(); boolean reportValidity(); void setCustomValidity(DOMString error); [SameObject] readonly attribute NodeList labels; };
The output element represents the result of a calculation performed
by the application, or the result of a user action.
This element can be contrasted with the samp element, which is the
appropriate element for quoting the output of other programs run previously.
The for content attribute allows an explicit
relationship to be made between the result of a calculation and the elements that represent the
values that went into the calculation or that otherwise influenced the calculation. The for attribute, if specified, must contain a string consisting of
an unordered set of unique space-separated tokens that are case-sensitive, each of which must have the value of an ID of an element in the same Document.
The form attribute is used to explicitly associate the output element with its form owner. The name attribute represents the element’s name. The output element is associated with a form so that it can be easily referenced from the event handlers of
form controls; the element’s value itself is not submitted when the form is submitted.
The element has a value mode flag which is either value or default. Initially, the value mode flag must be set to default.
The element also has a default value. Initially, the default value must be the empty string.
When the value mode flag is in mode default, the contents of the element represent both
the value of the element and its default value.
When the value mode flag is in mode value, the contents of the element represent the
value of the element only, and the default value is only accessible using the defaultValue IDL
attribute.
Whenever the element’s descendants are changed in any way, if the value mode flag is in mode default, the element’s default value must be set to the value of the
element’s textContent IDL attribute.
The reset algorithm for output elements is to set the element’s value mode flag to default and then to set the element’s textContent IDL attribute to the value of the element’s default value (thus replacing the element’s child
nodes).
- output .
value[ = value ] -
Returns the element’s current value.
Can be set, to change the value.
- output .
defaultValue[ = value ] -
Returns the element’s current default value.
Can be set, to change the default value.
- output .
type -
Returns the string "
output".
The value IDL attribute must act like the
element’s textContent IDL attribute, except that on setting, in addition, before the
child nodes are changed, the element’s value mode flag must be set to value.
The defaultValue IDL attribute, on
getting, must return the element’s default
value. On setting, the attribute must set the element’s default value, and, if the element’s value mode flag is in the mode default, set the element’s textContent IDL
attribute as well.
The type attribute must return the string
"output".
The htmlFor IDL attribute must reflect the for content attribute.
The willValidate, validity, and validationMessage IDL attributes, and
the checkValidity(), reportValidity(), and setCustomValidity() methods, are part of
the constraint validation API.
The labels IDL attribute provides a list of the element’s labels.
The form and name IDL attributes are
part of the element’s forms API.
output for its display of calculated results:
<form onsubmit="return false" oninput="o.value = a.valueAsNumber + b.valueAsNumber"> <input name=a type=number step=any> + <input name=b type=number step=any> = <output name=o for="a b"></output> </form>
output element is used to report the results of a calculation performed by a remote
server, as they come in:
<output id="result"></output> <script> var primeSource = new WebSocket('ws://primes.example.net/'); primeSource.onmessage = function (event) { document.getElementById('result').value = event.data; } </script>
4.10.13. The progress element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Phrasing content.
- Labelable element.
- Palpable content.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where phrasing content is expected.
- Content model:
- Phrasing content, but there must be no
progresselement descendants. - Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
value- Current value of the elementmax- Upper bound of range- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
progressbar(default - do not set).- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles. - DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLProgressElement : HTMLElement { attribute double value; attribute double max; readonly attribute double position; [SameObject] readonly attribute NodeList labels; };
The progress element represents the completion progress of a task.
The progress is either indeterminate, indicating that progress is being made but that it is not
clear how much more work remains to be done before the task is complete (e.g., because the task is
waiting for a remote host to respond), or the progress is a number in the range zero to a maximum,
giving the fraction of work that has so far been completed.
There are two attributes that determine the current task completion represented by the element.
The value content attribute specifies how much of the
task has been completed, and the max content attribute
specifies how much work the task requires in total. The units are arbitrary and not specified.
To make a determinate progress bar, add a value attribute with the current progress (either a number from
0.0 to 1.0, or, if the max attribute is specified, a number
from 0 to the value of the max attribute). To make an
indeterminate progress bar, remove the value attribute.
Authors are encouraged to also include the current value and the maximum value inline as text inside the element, so that the progress is made available to users of legacy user agents.
<section> <h2>Task Progress</h2> <p>Progress: <progress id="p" max=100><span>0</span>%</progress></p> <script> var progressBar = document.getElementById('p'); function updateProgress(newValue) { progressBar.value = newValue; progressBar.getElementsByTagName('span')[0].textContent = newValue; } </script> </section>
(The updateProgress() method in this example would be called by some
other code on the page to update the actual progress bar as the task progressed.)
The value and max attributes, when present, must have values that are valid floating-point numbers. The value attribute, if present, must have a value equal to or
greater than zero, and less than or equal to the value of the max attribute, if present, or 1.0, otherwise. The max attribute, if present, must have a value greater than
zero.
The progress element is the wrong element to use for something that
is just a gauge, as opposed to task progress. For instance, indicating disk space usage using progress would be inappropriate. Instead, the meter element is available
for such use cases.
User agent requirements: If the value attribute is omitted, then the progress bar is an indeterminate progress bar. Otherwise, it is a
determinate progress bar.
If the progress bar is a determinate progress bar and the element has a max attribute, the user agent must parse the max attribute’s value according to the rules for parsing
floating-point number values. If this does not result in an error, and if the parsed value
is greater than zero, then the maximum value of the
progress bar is that value. Otherwise, if the element has no max attribute, or if it has one but parsing it resulted in an
error, or if the parsed value was less than or equal to zero, then the maximum value of the progress bar is 1.0.
If the progress bar is a determinate progress bar, user agents must parse the value attribute’s value according to the rules for
parsing floating-point number values. If this does not result in an error, and if the
parsed value is less than the maximum value and
greater than zero, then the current value of the
progress bar is that parsed value. Otherwise, if the parsed value was greater than or equal to the maximum value, then the current value of the progress bar is the maximum value of the progress bar. Otherwise, if parsing
the value attribute’s value resulted in an error, or a
number less than or equal to zero, then the current
value of the progress bar is zero.
user agent requirements for showing the progress bar: When representing a progress element to the user, the user agent should indicate whether it is a determinate or
indeterminate progress bar, and in the former case, should indicate the relative position of the current value relative to the maximum value.
- progress .
position -
For a determinate progress bar (one with known current and maximum values), returns the result of dividing the current value by the maximum value.
For an indeterminate progress bar, returns -1.
If the progress bar is an indeterminate progress bar, then the position IDL attribute must return -1.
Otherwise, it must return the result of dividing the current
value by the maximum value.
If the progress bar is an indeterminate progress bar, then the value IDL attribute, on getting, must return 0.
Otherwise, it must return the current value. On
setting, the given value must be converted to the best representation of the number as a floating-point number and then the value content attribute must be set to that string.
Setting the value IDL attribute to itself
when the corresponding content attribute is absent would change the progress bar from an
indeterminate progress bar to a determinate progress bar with no progress.
The max IDL attribute must reflect the content attribute of the same name, limited to numbers greater than
zero. The default value for max is 1.0.
The labels IDL attribute provides a list of the element’s labels.
4.10.14. The meter element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Phrasing content.
- Labelable element.
- Palpable content.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where phrasing content is expected.
- Content model:
- Phrasing content, but there must be no
meterelement descendants. - Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
value- Current value of the elementmin- Lower bound of rangemax- Upper bound of rangelow- High limit of low rangehigh- Low limit of high rangeoptimum- Optimum value in gauge- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
- None
- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLMeterElement : HTMLElement { attribute double value; attribute double min; attribute double max; attribute double low; attribute double high; attribute double optimum; [SameObject] readonly attribute NodeList labels; };
The meter element represents a scalar measurement within a known
range, or a fractional value; for example disk usage, the relevance of a query result, or the
fraction of a voting population to have selected a particular candidate.
This is also known as a gauge.
The meter element should not be used to indicate progress (as in a
progress bar). For that role, HTML provides a separate progress element.
The meter element also does not represent a scalar value of arbitrary
range — for example, it would be wrong to use this to report a weight, or height, unless
there is a known maximum value.
There are six attributes that determine the semantics of the gauge represented by the element.
The min attribute specifies the lower bound of
the range, and the max attribute specifies the
upper bound. The value attribute specifies the
value to have the gauge indicate as the "measured" value.
The other three attributes can be used to segment the gauge’s range into "low", "medium", and
"high" parts, and to indicate which part of the gauge is the "optimum" part. The low attribute specifies the range that is considered to
be the "low" part, and the high attribute
specifies the range that is considered to be the "high" part. The optimum attribute gives the position that is
"optimum"; if that is higher than the "high" value then this indicates that the higher the value,
the better; if it’s lower than the "low" mark then it indicates that lower values are better, and
naturally if it is in between then it indicates that neither high nor low values are good.
Authoring requirements: The value attribute must be specified. The value, min, low, high, max, and optimum attributes,
when present, must have values that are valid
floating-point numbers.
In addition, the attributes' values are further constrained:
Let value be the value attribute’s
number.
If the min attribute is specified, then let minimum be that attribute’s value; otherwise, let it be zero.
If the max attribute is specified, then let maximum be that attribute’s value; otherwise, let it be 1.0.
The following inequalities must hold, as applicable:
- minimum ≤ value ≤ maximum
- minimum ≤
low≤ maximum (iflowis specified) - minimum ≤
high≤ maximum (ifhighis specified) - minimum ≤
optimum≤ maximum (ifoptimumis specified) low≤high(if bothlowandhighare specified)
If no minimum or maximum is specified, then the range is assumed to be 0..1, and the value thus has to be within that range.
Authors are encouraged to include a textual representation of the gauge’s state in the
element’s contents, for users of user agents that do not support the meter element.
When used with microdata, the meter element’s value attribute provides the element’s machine-readable value.
Storage space usage: <meter value=6 max=8>6 blocks used (out of 8 total)</meter> Voter turnout: <meter value=0.75><img alt="75%" src="graph75.png"></meter> Tickets sold: <meter min="0" max="100" value="75"></meter>
The following example is incorrect use of the element, because it doesn’t give a range (and since the default maximum is 1, both of the gauges would end up looking maxed out):
<p>The grapefruit pie had a radius of <meter value=12>12cm</meter>and a height of <meter value=2>2cm</meter>.</p> <!-- BAD! -->
Instead, one would either not include the meter element, or use the meter element with a defined range to give the dimensions in context compared to other pies:
<p>The grapefruit pie had a radius of 12cm and a height of 2cm.</p> <dl> <dt>Radius: <dd> <meter min=0 max=20 value=12>12cm</meter> <dt>Height: <dd> <meter min=0 max=10 value=2>2cm</meter> </dl>
There is no explicit way to specify units in the meter element, but the units may
be specified in the title attribute in free-form text.
<dl> <dt>Radius: <dd> <meter min=0 max=20 value=12 title="centimeters">12cm</meter> <dt>Height: <dd> <meter min=0 max=10 value=2 title="centimeters">2cm</meter> </dl>
User agent requirements: User agents must parse the min, max, value, low, high, and optimum attributes using the rules for parsing floating-point number values.
User agents must then use all these numbers to obtain values for six points on the gauge, as follows. (The order in which these are evaluated is important, as some of the values refer to earlier ones.)
- The minimum value
-
If the
minattribute is specified and a value could be parsed out of it, then the minimum value is that value. Otherwise, the minimum value is zero. - The maximum value
-
If the
maxattribute is specified and a value could be parsed out of it, then the candidate maximum value is that value. Otherwise, the candidate maximum value is 1.0.If the candidate maximum value is greater than or equal to the minimum value, then the maximum value is the candidate maximum value. Otherwise, the maximum value is the same as the minimum value.
- The actual value
-
If the
valueattribute is specified and a value could be parsed out of it, then that value is the candidate actual value. Otherwise, the candidate actual value is zero.If the candidate actual value is less than the minimum value, then the actual value is the minimum value.
Otherwise, if the candidate actual value is greater than the maximum value, then the actual value is the maximum value.
Otherwise, the actual value is the candidate actual value.
- The low boundary
-
If the
lowattribute is specified and a value could be parsed out of it, then the candidate low boundary is that value. Otherwise, the candidate low boundary is the same as the minimum value.If the candidate low boundary is less than the minimum value, then the low boundary is the minimum value.
Otherwise, if the candidate low boundary is greater than the maximum value, then the low boundary is the maximum value.
Otherwise, the low boundary is the candidate low boundary.
- The high boundary
-
If the
highattribute is specified and a value could be parsed out of it, then the candidate high boundary is that value. Otherwise, the candidate high boundary is the same as the maximum value.If the candidate high boundary is less than the low boundary, then the high boundary is the low boundary.
Otherwise, if the candidate high boundary is greater than the maximum value, then the high boundary is the maximum value.
Otherwise, the high boundary is the candidate high boundary.
- The optimum point
-
If the
optimumattribute is specified and a value could be parsed out of it, then the candidate optimum point is that value. Otherwise, the candidate optimum point is the midpoint between the minimum value and the maximum value.If the candidate optimum point is less than the minimum value, then the optimum point is the minimum value.
Otherwise, if the candidate optimum point is greater than the maximum value, then the optimum point is the maximum value.
Otherwise, the optimum point is the candidate optimum point.
All of which will result in the following inequalities all being true:
- minimum value ≤ actual value ≤ maximum value
- minimum value ≤ low boundary ≤ high boundary ≤ maximum value
- minimum value ≤ optimum point ≤ maximum value
user agent requirements for regions of the gauge: If the optimum point is equal to the low boundary or the high boundary, or anywhere in between them, then the region between the low and high boundaries of the gauge must be treated as the optimum region, and the low and high parts, if any, must be treated as suboptimal. Otherwise, if the optimum point is less than the low boundary, then the region between the minimum value and the low boundary must be treated as the optimum region, the region from the low boundary up to the high boundary must be treated as a suboptimal region, and the remaining region must be treated as an even less good region. Finally, if the optimum point is higher than the high boundary, then the situation is reversed; the region between the high boundary and the maximum value must be treated as the optimum region, the region from the high boundary down to the low boundary must be treated as a suboptimal region, and the remaining region must be treated as an even less good region.
user agent requirements for showing the gauge: When representing a meter element to the user, the user agent should indicate the relative position of the actual value to the
minimum and maximum values, and the relationship between the actual value and the three regions of
the gauge.
<h3>Suggested groups</h3> <menu type="toolbar"> <a href="?cmd=hsg" onclick="hideSuggestedGroups()">Hide suggested groups</a> </menu> <ul> <li> <p><a href="/group/comp.infosystems.www.authoring.stylesheets/view">comp.infosystems.www.authoring.stylesheets</a> - <a href="/group/comp.infosystems.www.authoring.stylesheets/subscribe">join</a></p> <p>Group description: <strong>Layout/presentation on the WWW.</strong></p> <p><meter value="0.5">Moderate activity,</meter> Usenet, 618 subscribers</p> </li> <li> <p><a href="/group/netscape.public.mozilla.xpinstall/view">netscape.public.mozilla.xpinstall</a> - <a href="/group/netscape.public.mozilla.xpinstall/subscribe">join</a></p> <p>Group description: <strong>Mozilla XPInstall discussion.</strong></p> <p><meter value="0.25">Low activity,</meter> Usenet, 22 subscribers</p> </li> <li> <p><a href="/group/mozilla.dev.general/view">mozilla.dev.general</a> - <a href="/group/mozilla.dev.general/subscribe">join</a></p> <p><meter value="0.25">Low activity,</meter> Usenet, 66 subscribers</p> </li> </ul>
Might be rendered as follows: 
User agents may combine the value of the title attribute and the other attributes to provide context-sensitive
help or inline text detailing the actual values.
<meter min=0 max=60 value=23.2 title=seconds></meter>
...might cause the user agent to display a gauge with a tooltip saying "Value: 23.2 out of 60." on one line and "seconds" on a second line.
The value IDL attribute, on getting, must
return the actual value. On setting, the given value
must be converted to the best representation of the number as a floating-point number and then the value content attribute must be set to that string.
The min IDL attribute, on getting, must return
the minimum value. On setting, the given value must be
converted to the best representation of the number as a floating-point number and then the min content attribute must be set to that string.
The max IDL attribute, on getting, must return
the maximum value. On setting, the given value must be
converted to the best representation of the number as a floating-point number and then the max content attribute must be set to that string.
The low IDL attribute, on getting, must return
the low boundary. On setting, the given value must be
converted to the best representation of the number as a floating-point number and then the low content attribute must be set to that string.
The high IDL attribute, on getting, must return
the high boundary. On setting, the given value must be
converted to the best representation of the number as a floating-point number and then the high content attribute must be set to that string.
The optimum IDL attribute, on getting, must
return the optimum value. On setting, the given value
must be converted to the best representation of the number as a floating-point number and then the optimum content attribute must be set to that string.
The labels IDL attribute provides a list of the element’s labels.
<p>Disk usage: <meter min=0 value=170261928 max=233257824>170 261 928 bytes used out of 233 257 824 bytes available</meter></p>
4.10.15. The fieldset element
- Categories:
- Flow content.
- Sectioning root.
- listed and reassociateable form-associated element.
- Palpable content.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- Where flow content is expected.
- Content model:
- Optionally a
legendelement, followed by flow content. - Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
disabled- Whether the form control is disabledform- Associates the control with aformelementname- Name of form control to use for §4.10.21 Form submission and in theform.elementsAPI- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
grouporpresentation.- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- Any
aria-*attributes applicable to the allowed roles. - DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLFieldSetElement : HTMLElement { attribute boolean disabled; readonly attribute HTMLFormElement? form; attribute DOMString name; readonly attribute DOMString type; [SameObject] readonly attribute HTMLCollection elements; readonly attribute boolean willValidate; [SameObject] readonly attribute ValidityState validity; readonly attribute DOMString validationMessage; boolean checkValidity(); boolean reportValidity(); void setCustomValidity(DOMString error); };
The fieldset element represents a set of form controls optionally
grouped under a common name.
The name of the group is given by the first legend element that is a child of the fieldset element, if any. The remainder of the descendants form the group.
The disabled attribute, when specified,
causes all the form control descendants of the fieldset element, excluding those that
are descendants of the fieldset element’s first legend element child, if
any, to be disabled.
A fieldset element is a disabled fieldset if it matches any of the following conditions:
- Its
disabledattribute is specified - It is a descendant of another
fieldsetelement whosedisabledattribute is specified, and is not a descendant of thatfieldsetelement’s firstlegendelement child, if any.
The form attribute is used to explicitly associate the fieldset element with its form owner. The name attribute represents the element’s name.
- fieldset .
type -
Returns the string "fieldset".
- fieldset .
elements -
Returns an
HTMLCollectionof the form controls in the element.
The disabled IDL attribute must reflect the content attribute of the same name.
The type IDL attribute must return the string
"fieldset".
The elements IDL attribute must return an HTMLCollection rooted at the fieldset element, whose filter
matches listed elements.
The willValidate, validity, and validationMessage attributes, and the checkValidity(), reportValidity(), and setCustomValidity() methods, are part of
the constraint validation API. The form and name IDL attributes are part of the
element’s forms API.
fieldset element being used to group a set of related
controls:
<fieldset> <legend>Display</legend> <p><label><input type=radio name=c value=0 checked> Black on White</label> <p><label><input type=radio name=c value=1> White on Black</label> <p><label><input type=checkbox name=g> Use grayscale</label> <p><label>Enhance contrast <input type=range name=e list=contrast min=0 max=100 value=0 step=1></label> <datalist id=contrast> <option label=Normal value=0> <option label=Maximum value=100> </datalist> </fieldset>
<fieldset name="clubfields" disabled> <legend> <label> <input type=checkbox name=club onchange="form.clubfields.disabled = !checked"> Use Club Card </label> </legend> <p><label>Name on card: <input name=clubname required></label></p> <p><label>Card number: <input name=clubnum required pattern="[-0-9]+"></label></p> <p><label>Expiry date: <input name=clubexp type=month></label></p> </fieldset>
fieldset elements. Here is an example expanding on the previous
one that does so:
<fieldset name="clubfields" disabled> <legend> <label> <input type=checkbox name=club onchange="form.clubfields.disabled = !checked"> Use Club Card </label> </legend> <p><label>Name on card: <input name=clubname required></label></p> <fieldset name="numfields"> <legend> <label> <input type=radio checked name=clubtype onchange="form.numfields.disabled = !checked"> My card has numbers on it </label> </legend> <p><label>Card number: <input name=clubnum required pattern="[-0-9]+"></label></p> </fieldset> <fieldset name="letfields" disabled> <legend> <label> <input type=radio name=clubtype onchange="form.letfields.disabled = !checked"> My card has letters on it </label> </legend> <p><label>Card code: <input name=clublet required pattern="[A-Za-z]+"></label></p> </fieldset> </fieldset>
In this example, if the outer "Use Club Card" checkbox is not checked, everything inside the
outer fieldset, including the two radio buttons in the legends of the two nested fieldsets, will be disabled. However, if the checkbox is checked, then the radio
buttons will both be enabled and will let you select which of the two inner fieldsets is to be enabled.
4.10.16. The legend element
- Categories:
- None.
- Contexts in which this element can be used:
- As the first child of a
fieldsetelement. - Content model:
- Phrasing content and headings (
h1-h6elements). - Tag omission in text/html:
- Neither tag is omissible
- Content attributes:
- Global attributes
- Allowed ARIA role attribute values:
- None
- Allowed ARIA state and property attributes:
- Global aria-* attributes
- DOM interface:
-
interface HTMLLegendElement : HTMLElement { readonly attribute HTMLFormElement? form; };
The legend element represents a caption for the rest of the contents
of the legend element’s parent fieldset element, if
any.
- legend .
form -
Returns the element’s
formelement, if any, or null otherwise.
The form IDL attribute’s behavior depends on
whether the legend element is in a fieldset element or not. If the legend has a fieldset element as its parent, then the form IDL attribute must return the same value as the form IDL attribute on that fieldset element. Otherwise,
it must return null.
4.10.17. Form control infrastructure
4.10.17.1. A form control value
Most form controls have a value and a checkedness. (The latter is only used by input elements.) These are used to describe how the user interacts with the control.
A control’s value is its internal state. As such, it might not match the user’s current input.
For instance, if a user enters the word "three" into a numeric field that expects digits, the user’s input would
be the string "three" but the control’s value would remain
unchanged. Or, if a user enters the email address " awesome@example.com"
(with leading white space) into an email field, the
user’s input would be the string " awesome@example.com" but the browser’s UI for
email fields might translate that into a value of "awesome@example.com" (without the leading white space).
To define the behavior of constraint validation in the face of the input element’s multiple attribute, input elements
can also have separately defined values.
The select element does not have a value;
the selectedness of its option elements is what is used instead.
4.10.17.2. Mutability
A form control can be designated as mutable.
This determines (by means of definitions and requirements in this specification that rely on whether an element is so designated) whether or not the user can modify the value or checkedness of a form control, or whether or not a control can be automatically prefilled.
4.10.17.3. Association of controls and forms
A form-associated element can have a relationship with a form element, which is called the element’s form owner. If a form-associated
element is not associated with a form element, its form owner is
said to be null.
A form-associated element is, by default, associated with its nearest ancestor form element (as described
below), but, if it is reassociateable, may have a form attribute specified to override this.
This feature allows authors to work around the lack of support for nested form elements.
If a reassociateable form-associated
element has a form attribute specified, then that
attribute’s value must be the ID of a form element
in the element’s owner Document.
The rules in this section are complicated by the fact that although conforming
documents will never contain nested form elements, it is quite possible (e.g., using a
script that performs DOM manipulation) to generate documents that have such nested elements. They
are also complicated by rules in the HTML parser that, for historical reasons, can result in a form-associated element being associated with a form element that is not
its ancestor.
When a form-associated element is created, its form owner must be initialized to null (no owner).
When a form-associated element is to be associated with a form, its form owner must be set to that form.
When a form-associated element or one of its ancestors is inserted into a Document, then the user agent must reset the form owner of that form-associated element. The HTML parser overrides this requirement when inserting form
controls.
When an element changes its parent node resulting in a form-associated element and its form owner (if any) no longer being in the same tree, then the user agent must reset the form owner of that form-associated element.
When a reassociateable form-associated
element’s form attribute is set, changed, or removed,
then the user agent must reset the form owner of that element.
When a reassociateable form-associated
element has a form attribute and the ID of any of the elements in the Document changes, then
the user agent must reset the form owner of that form-associated
element.
When a reassociateable form-associated
element has a form attribute and an element with an ID is inserted into or removed from the Document, then the user agent must reset the form owner of that form-associated element.
When the user agent is to reset the form owner of a form-associated element, it must run the following steps:
- If the element’s form owner is not null, and either the element is not reassociateable or its
formcontent attribute is not present, and the element’s form owner is its nearestformelement ancestor after the change to the ancestor chain, then do nothing, and abort these steps. - Let the element’s form owner be null.
-
If the element is reassociateable, has a
formcontent attribute, and is itself in aDocument, then run these substeps:- If the first element in the
Documentto have an ID that is case-sensitively equal to the element’sformcontent attribute’s value is aformelement, then associate the form-associated element with thatformelement. - Abort the "reset the form owner" steps.
- If the first element in the
- Otherwise, if the form-associated element in question has an ancestor
formelement, then associate the form-associated element with the nearest such ancestorformelement. - Otherwise, the element is left unassociated.
... <form id="a">
<div id="b"></div>
</form>
<script>
document.getElementById('b').innerHTML =
'<table><tr><td></form><form id="c"><input id="d"></table>' +
'<input id="e">';
</script>
...
The form owner of "d" would be the inner nested form "c", while the form owner of "e" would be the outer form "a".
This happens as follows: First, the "e" node gets associated with "c" in the HTML
parser. Then, the innerHTML algorithm moves the nodes
from the temporary document to the "b" element. At this point, the nodes see their ancestor chain
change, and thus all the "magic" associations done by the parser are reset to normal ancestor
associations.
This example is a non-conforming document, though, as it is a violation of the content models
to nest form elements, and there is a parse error for the </form> tag.
- element .
form -
Returns the element’s form owner.
Returns null if there isn’t one.
form IDL attribute, which, on getting, must return the element’s form owner, or null if there
isn’t one. 4.10.18. Attributes common to form controls
4.10.18.1. Naming form controls: the name attribute
The name content attribute gives the name of the form control, as used in §4.10.21 Form submission and
in the form element’s elements object. If the attribute is specified, its value
must not be the empty string.
Any non-empty value for name is allowed, but the name
"_charset_" is special:
_charset_-
This value, if used as the name of a
control with novalueattribute, is automatically given a value during submission consisting of the submission character encoding.
4.10.18.2. Submitting element directionality: the dirname attribute
The dirname attribute on a form control
element enables the submission of the directionality of the element, and gives the name of
the field that contains this value during §4.10.21 Form submission. If such an attribute is
specified, its value must not be the empty string.
<form action="addcomment.cgi" method=post> <p><label>Comment: <input type=text name="comment" dirname="comment.dir" required></label></p> <p><button name="mode" type=submit value="add">Post Comment</button></p> </form>
When the user submits the form, the user agent includes three fields, one called "comment", one called "comment.dir", and one called "mode"; so if the user types "Hello", the submission body might be something like:
comment=Hello&comment.dir=ltr&mode=add
If the user manually switches to a right-to-left writing direction and enters "مرحبا", the submission body might be something like:
comment=%D9%85%D8%B1%D8%AD%D8%A8%D8%A7&comment.dir=rtl&mode=add
4.10.18.3. Limiting user input length: the maxlength attribute
A form control maxlength attribute,
controlled by a dirty value flag, declares a limit on the number of characters
a user can input.
If an element has its form control maxlength attribute specified, the attribute’s value must be a valid
non-negative integer. If the attribute is specified and applying the rules for
parsing non-negative integers to its value results in a number, then that number is the
element’s maximum allowed value length. If the attribute is omitted or parsing its
value results in an error, then there is no maximum allowed value length.
Constraint validation: If an element has a maximum allowed value length, its dirty value flag is true, its value was last changed by a user edit (as opposed to a change made by a script), and the code-unit length of the element’s value is greater than the element’s maximum allowed value length, then the element is suffering from being too long.
User agents may prevent the user from causing the element’s value to be set to a value whose code-unit length is greater than the element’s maximum allowed value length.
In the case of textarea elements, this is the value, not the raw
value, so the textarea wrapping transformation is applied before the maximum allowed value length is checked.
4.10.18.4. Setting minimum input length requirements: the minlength attribute
A form control minlength attribute,
controlled by a dirty value flag, declares a lower bound on the number of
characters a user can input.
The minlength attribute does not imply the required attribute. If the form control has no required attribute, then the value can still be omitted; the minlength attribute only kicks in once the user has entered
a value at all. If the empty string is not allowed, then the required attribute also needs to be set.
If an element has its form control minlength attribute specified, the attribute’s value must be a valid
non-negative integer. If the attribute is specified and applying the rules for
parsing non-negative integers to its value results in a number, then that number is the
element’s minimum allowed value length. If the attribute is omitted or parsing its
value results in an error, then there is no minimum allowed value length.
If an element has both a maximum allowed value length and a minimum allowed value length, the minimum allowed value length must be smaller than or equal to the maximum allowed value length.
Constraint validation: If an element has a minimum allowed value length, its dirty value flag is true, its value was last changed by a user edit (as opposed to a change made by a script), its value is not the empty string, and the code-unit length of the element’s value is less than the element’s minimum allowed value length, then the element is suffering from being too short.
<form action="/events/menu.cgi" method="post"> <p><label>Name of Event: <input required minlength=5 maxlength=50 name=event></label></p> <p><label>Describe what you would like for breakfast, if anything: <textarea name="breakfast" minlength="10"></textarea></label></p> <p><label>Describe what you would like for lunch, if anything: <textarea name="lunch" minlength="10"></textarea></label></p> <p><label>Describe what you would like for dinner, if anything: <textarea name="dinner" minlength="10"></textarea></label></p> <p><input type=submit value="Submit Request"></p> </form>
4.10.18.5. Enabling and disabling form controls: the disabled attribute
The disabled content attribute is a boolean attribute.
A form control is disabled if any of the following conditions are met:
- The element is a
button,input,select, ortextareaelement, and thedisabledattribute is specified on this element (regardless of its value). - The element is a descendant of a
fieldsetelement whosedisabledattribute is specified, and is not a descendant of thatfieldsetelement’s firstlegendelement child, if any.
A form control that is disabled must prevent any click events that are queued on the user interaction task source from being dispatched on the element.
Constraint validation: If an element is disabled, it is barred from constraint validation.
The disabled IDL attribute must reflect the disabled content attribute.
4.10.18.6. Form submission
Attributes for form submission can be specified both on form elements
and on submit buttons (elements that represent buttons
that submit forms, e.g., an input element whose type attribute is in the Submit Button state).
The attributes for form submission that may be specified on form elements are action, enctype, method, novalidate, and target.
The corresponding attributes for form submission that may be specified on submit buttons are formaction, formenctype, formmethod, formnovalidate, and formtarget. When omitted, they default to the values given on
the corresponding attributes on the form element.
The action and formaction content attributes, if specified, must
have a value that is a valid non-empty URL potentially surrounded by spaces.
The action of an element is the value of the element’s formaction attribute, if the element is a Submit Button and has such an attribute, or the value of its form owner’s action attribute, if it has
one, or else the empty string.
The method and formmethod content attributes are enumerated attributes with the following keywords and
states:
- The keyword
get, mapping to the state GET, indicating the HTTP GET method. - The keyword
post, mapping to the state POST, indicating the HTTP POST method. - The keyword
dialog, mapping to the state dialog, indicating that submitting theformis intended to close thedialogbox in which the form finds itself, if any, and otherwise not submit.
The invalid value default for these attributes is the GET state. The missing value default for the method attribute is also the GET state. (There is no missing value default for the formmethod attribute.)
The method of an element is one of those states. If the element is a Submit Button and has a formmethod attribute, then the element’s method is that attribute’s state; otherwise, it
is the form owner’s method attribute’s state.
method attribute is used to explicitly specify
the default value, "get", so that the search
query is submitted in the URL:
<form method="get" action="/search.cgi"> <p><label>Search terms: <input type=search name=q></label></p> <p><input type=submit></p> </form>
method attribute is used to
specify the value "post", so that the user’s
message is submitted in the HTTP request’s body:
<form method="post" action="/post-message.cgi"> <p><label>Message: <input type=text name=m></label></p> <p><input type=submit value="Submit message"></p> </form>
form is used with a dialog. The method attribute’s "dialog" keyword is used to have the dialog
automatically close when the form is submitted.
<dialog id="ship"> <form method=dialog>
<p>A ship has arrived in the harbour.</p>
<button type=submit value="board">Board the ship</button>
<button type=submit value="call">Call to the captain</button>
</form>
</dialog>
<script>
var ship = document.getElementById('ship');
ship.showModal();
ship.onclose = function (event) {
if (ship.returnValue == 'board') {
// ...
} else {
// ...
}
};
</script>
The enctype and formenctype content attributes are enumerated attributes with the following keywords and
states:
- The "
application/x-www-form-urlencoded" keyword and corresponding state. - The "
multipart/form-data" keyword and corresponding state. - The "
text/plain" keyword and corresponding state.
The invalid value default for these attributes is the application/x-www-form-urlencoded state. The missing value default for the enctype attribute is also the application/x-www-form-urlencoded state. (There is no missing value default for the formenctype attribute.)
The enctype of an element is one of those three states.
If the element is a Submit Button and has a formenctype attribute, then the element’s enctype is that attribute’s state; otherwise, it is the form owner’s enctype attribute’s state.
The target and formtarget content attributes, if specified, must
have values that are valid browsing context
names or keywords.
The target of an element is the value of the element’s formtarget attribute, if the element is a Submit Button and has such an attribute; or the value of its form owner’s target attribute, if it has
such an attribute; or, if the Document contains a base element with a target attribute, then the value of the target attribute of the first such base element; or,
if there is no such element, the empty string.
The novalidate and formnovalidate content attributes are boolean attributes. If present, they indicate that the form is
not to be validated during submission.
The no-validate state of an element is true if the
element is a Submit Button and the element’s formnovalidate attribute is present, or if the element’s form owner’s novalidate attribute is present,
and false otherwise.
<form action="editor.cgi" method="post"> <p><label>Name: <input required name=fn></label></p> <p><label>Essay: <textarea required name=essay></textarea></label></p> <p><input type=submit name=submit value="Submit essay"></p> <p><input type=submit formnovalidate name=save value="Save essay"></p> <p><input type=submit formnovalidate name=cancel value="Cancel"></p> </form>
The action IDL attribute must reflect the
content attribute of the same name, except that on getting, when the content attribute is missing
or its value is the empty string, the document’s URL must be returned instead.
The target IDL attribute must reflect the
content attribute of the same name.
The method and enctype IDL attributes must reflect the
respective content attributes of the same name, limited to only known values.
The encoding IDL attribute must reflect the enctype content attribute, limited to only known values.
The noValidate IDL attribute must reflect the novalidate content attribute.
The formAction IDL attribute must reflect the formaction content attribute, except that on getting, when the content attribute is
missing or its value is the empty string, the document’s URL must be returned instead.
The formEnctype IDL attribute must reflect the formenctype content attribute, limited to only known values.
The formMethod IDL attribute must reflect the formmethod content attribute, limited to only known values.
The formNoValidate IDL attribute must reflect the formnovalidate content attribute.
The formTarget IDL attribute must reflect the formtarget content attribute.
4.10.18.6.1. Autofocusing a form control: the autofocus attribute
The autofocus content attribute allows the
author to indicate that a control is to be focused as soon as the page is loaded or as soon as the dialog within which it finds itself is shown, allowing the user to just start typing
without having to manually focus the main control.
Use of the autofocus attribute can reduce usability and accessibility
for users. Users of assistive technology can be adversively affected, because its use overrides
the default behaviour of assistive technology to display content at the top of a document in the
viewport, or announce content from the start of the document. Users with cognitive disabilities can
also be disorientated by unexpected focus movement upon page load.
User agents should provide a method for users to disable the autofocus attribute behaviour.
The autofocus attribute is a boolean attribute.
An element’s nearest ancestor autofocus scoping document element is the element itself
if the element is a dialog element, or else is the element’s nearest ancestor dialog element, if any, or else is the element’s document element.
There must not be two elements with the same nearest ancestor autofocus scoping document element that both have the autofocus attribute specified.
When an element with the autofocus attribute specified
is inserted into a document, user agents
should run the following steps:
- Let target be the element’s node document.
- If target has no browsing context, abort these steps.
- If target’s browsing context has no top-level browsing context (e.g., it is a nested browsing context with no parent browsing context), abort these steps.
- If target’s active sandboxing flag set has the sandboxed automatic features browsing context flag, abort these steps.
- If target’s origin is not the same as the origin of the node document of the currently focused element in target’s top-level browsing context, abort these steps.
- If target’s origin is not the same as the origin of the active document of target’s top-level browsing context, abort these steps.
- If the user agent has already reached the last step of this list of steps in response to
an element being inserted into a
Documentwhose top-level browsing context’s active document is the same as target’s top-level browsing context’s active document, abort these steps. - If the user has indicated (for example, by starting to type in a form control) that he does not wish focus to be changed, then optionally abort these steps.
- Queue a task that runs the focusing steps for the element. User agents may also change the scrolling position of the document, or perform some other action that brings the element to the user’s attention. The task source for this task is the user interaction task source.
This handles the automatic focusing during document load. The show() and showModal() methods of dialog elements also processes the autofocus attribute.
Focusing the control does not imply that the user agent must focus the browser window if it has lost focus.
The autofocus IDL attribute must reflect the content attribute of the same name.
<input maxlength="256" name="q" value="" autofocus> <input type="submit" value="Search">
4.10.18.7. Input modalities: the inputmode attribute
The inputmode content attribute is an enumerated attribute that specifies what kind of input mechanism would be most
helpful for users entering content into the form control.
User agents must recognize all the keywords and corresponding states given below, but need not support all of the corresponding states. If a keyword’s state is not supported, the user agent must act as if the keyword instead mapped to the given state’s fallback state, as defined below. This fallback behavior is transitive.
For example, if a user agent with a QWERTY keyboard layout does not support text
prediction and automatic capitalization, then it could treat the latin-prose keyword in the same way as the verbatim keyword, following the chain Latin Prose → Latin Text → Latin Verbatim.
The possible keywords and states for the attributes are listed in the following table. The keywords are listed in the first column. Each maps to the state given in the cell in the second column of that keyword’s row, and that state has the fallback state given in the cell in the third column of that row.
| Keyword | State | Fallback state | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
verbatim
| Latin Verbatim | Default | Alphanumeric Latin-script input of non-prose content, e.g., usernames, passwords, product codes. |
latin
| Latin Text | Latin Verbatim | Latin-script input in the user’s preferred language(s), with some typing aids enabled (e.g., text prediction). Intended for human-to-computer communications, e.g., free-form text search fields. |
latin-name
| Latin Name | Latin Text | Latin-script input in the user’s preferred language(s), with typing aids intended for entering human names enabled (e.g., text prediction from the user’s contact list and automatic capitalization at every word). Intended for situations such as customer name fields. |
latin-prose
| Latin Prose | Latin Text | Latin-script input in the user’s preferred language(s), with aggressive typing aids intended for human-to-human communications enabled (e.g., text prediction and automatic capitalization at the start of sentences). Intended for situations such as e-mails and instant messaging. |
full-width-latin
| Full-width Latin | Latin Prose | Latin-script input in the user’s secondary language(s), using full-width characters, with aggressive typing aids intended for human-to-human communications enabled (e.g., text prediction and automatic capitalization at the start of sentences). Intended for latin text embedded inside CJK text. |
kana
| Kana | Default | Kana or romaji input, typically hiragana input, using full-width characters, with support for converting to kanji. Intended for Japanese text input. |
kana-name
| Kana Name | Kana | Kana or romaji input, typically hiragana input, using full-width characters, with support for converting to kanji, and with typing aids intended for entering human names enabled (e.g., text prediction from the user’s contact list). Intended for situations such as customer name fields. |
katakana
| Katakana | Kana | Katakana input, using full-width characters, with support for converting to kanji. Intended for Japanese text input. |
numeric
| Numeric | Default | Numeric input, including keys for the digits 0 to 9, the user’s preferred thousands
separator character, and the character for indicating negative numbers. Intended for numeric
codes, e.g., credit card numbers. (For numbers, prefer "<input type=number>".)
|
tel
| Telephone | Numeric | Telephone number input, including keys for the digits 0 to 9, the "#" character, and the
"*" character. In some locales, this can also include alphabetic mnemonic labels (e.g., in the
US, the key labeled "2" is historically also labeled with the letters A, B, and C). Rarely necessary; use "<input
type=tel>" instead.
|
email
| Default | Text input in the user’s locale, with keys for aiding in the input of e-mail addresses,
such as that for the "@" character and the "." character. Rarely
necessary; use "<input type=email>" instead.
| |
url
| URL | Default | Text input in the user’s locale, with keys for aiding in the input of Web addresses, such
as that for the "/" and "." characters and for quick input of strings commonly found in domain
names such as "www." or ".co.uk". Rarely necessary; use "<input type=url>" instead.
|
The last three keywords listed above are only provided for completeness, and are rarely necessary, as dedicated input controls exist for their usual use cases (as described in the table above).
User agents must all support the Default input mode state, which corresponds to the user agent’s default input modality. This specification does not define how the user agent’s default modality is to operate. The missing value default is the Default input mode state.
User agents should use the input modality corresponding to the state of the inputmode attribute when exposing a user interface for editing
the value of a form control to which the attribute applies. An input modality corresponding to a state is one
designed to fit the description of the state in the table above. This value can change
dynamically; user agents should update their interface as the attribute changes state, unless that
would go against the user’s wishes.
4.10.18.8. Autofill
4.10.18.8.1. Autofilling form controls: the autocomplete attribute
User agents sometimes have features for helping users fill forms in, for example prefilling the
user’s address based on earlier user input. The autocomplete content attribute can be used to hint
to the user agent how to, or indeed whether to, provide such a feature.
There are two ways this attribute is used. When wearing the autofill expectation
mantle, the autocomplete attribute describes what
input is expected from users. When wearing the autofill anchor mantle, the autocomplete attribute describes the meaning of the given
value.
On an input element whose type attribute is
in the state, the autocomplete attribute wears the autofill anchor
mantle. In all other cases, it wears the autofill expectation mantle.
When wearing the autofill expectation mantle, the autocomplete attribute, if specified, must have a value that
is an ordered set of space-separated tokens consisting of either a single token that
is an ASCII case-insensitive match for the string "off", or a single token
that is an ASCII case-insensitive match for the string "on",
or autofill detail tokens.
When wearing the autofill anchor
mantle, the autocomplete attribute, if specified, must have a value that is an ordered set of
space-separated tokens consisting of just autofill detail tokens (i.e., the
"on" and "off" keywords are not allowed).
Autofill detail tokens are the following, in the order given below:
-
Optionally, a token whose first eight characters are an ASCII case-insensitive match for the string "
section-", meaning that the field belongs to the named group.For example, if there are two shipping addresses in the form, then they could be marked up as:<fieldset> <legend>Ship the blue gift to...</legend> <div> <label> Address: <input name=ba autocomplete="section-blue shipping street-address"> </label> </div> <div> <label> City: <input name=bc autocomplete="section-blue shipping address-level2"> </label></div> <div> <label> Postal Code: <input name=bp autocomplete="section-blue shipping postal-code"> </label></div> </fieldset> <fieldset> <legend>Ship the red gift to...</legend> <div> <label> Address: <input name=ra autocomplete="section-red shipping street-address"> </label></div> <div> <label> City: <input name=rc autocomplete="section-red shipping address-level2"> </label></div> <div> <label> Postal Code: <input name=rp autocomplete="section-red shipping postal-code"> </label></div> </fieldset>
-
Optionally, a token that is an ASCII case-insensitive match for one of the following strings:
-
Either of the following two options:
-
A token that is an ASCII case-insensitive match for one of the following autofill field names, excluding those that are inappropriate for the control:
- "
name" - "
honorific-prefix" - "
given-name" - "
additional-name" - "
family-name" - "
honorific-suffix" - "
nickname" - "
username" - "
new-password" - "
current-password" - "
organization-title" - "
organization" - "
street-address" - "
address-line1" - "
address-line2" - "
address-line3" - "
address-level4" - "
address-level3" - "
address-level2" - "
address-level1" - "
country" - "
country-name" - "
postal-code" - "
cc-name" - "
cc-given-name" - "
cc-additional-name" - "
cc-family-name" - "
cc-number" - "
cc-exp" - "
cc-exp-month" - "
cc-exp-year" - "
cc-csc" - "
cc-type" - "
transaction-currency" - "
transaction-amount" - "
language" - "
bday" - "
bday-day" - "
bday-month" - "
bday-year" - "
sex" - "
url" - "
photo"
(See the table below for descriptions of these values.)
- "
-
The following, in the given order:
-
Optionally, a token that is an ASCII case-insensitive match for one of the following strings:
- "
home", meaning the field is for contacting someone at their residence - "
work", meaning the field is for contacting someone at their workplace - "
mobile", meaning the field is for contacting someone regardless of location - "
fax", meaning the field describes a fax machine’s contact details - "
pager", meaning the field describes a pager’s or beeper’s contact details
- "
-
A token that is an ASCII case-insensitive match for one of the following autofill field names, excluding those that are inappropriate for the control:
- "
tel" - "
tel-country-code" - "
tel-national" - "
tel-area-code" - "
tel-local" - "
tel-local-prefix" - "
tel-local-suffix" - "
tel-extension" - "
email" - "
impp"
(See the table below for descriptions of these values.)
- "
-
-
As noted earlier, the meaning of the attribute and its keywords depends on the mantle that the attribute is wearing.
- When wearing the autofill expectation mantle...
-
The "
off" keyword indicates either that the control’s input data is particularly sensitive (for example the activation code for a nuclear weapon); or that it is a value that will never be reused (for example a one-time-key for a bank login) and the user will therefore have to explicitly enter the data each time, instead of being able to rely on the user agent to prefill the value for him; or that the document provides its own autocomplete mechanism and does not want the user agent to provide autocompletion values.The "
on" keyword indicates that the user agent is allowed to provide the user with autocompletion values, but does not provide any further information about what kind of data the user might be expected to enter. User agents would have to use heuristics to decide what autocompletion values to suggest.The autofill field listed above indicate that the user agent is allowed to provide the user with autocompletion values, and specifies what kind of value is expected. The meaning of each such keyword is described in the table below.
If the
autocompleteattribute is omitted, the default value corresponding to the state of the element’s form owner’sautocompleteattribute is used instead (either "on" or "off"). If there is no form owner, then the value "on" is used. - When wearing the autofill anchor mantle...
-
The autofill field listed above indicate that the value of the particular kind of value specified is that value provided for this element. The meaning of each such keyword is described in the table below.
In this example the page has explicitly specified the currency and amount of the transaction. The form requests a credit card and other billing details. The user agent could use this information to suggest a credit card that it knows has sufficient balance and that supports the relevant currency.<form method=post action="step2.cgi"> <input type=hidden autocomplete=transaction-currency value="CHF"> <input type=hidden autocomplete=transaction-amount value="15.00"> <p><label>Credit card number: <input type=text inputmode=numeric autocomplete=cc-number></label> <p><label>Expiry Date: <input type=month autocomplete=cc-exp></label> <p><input type=submit value="Continue..."> </form>
The autofill field keywords relate to each other as described in the table below. Each field name
listed on a row of this table corresponds to the meaning given in the cell for that row in the
column labeled "Meaning". Some fields correspond to subparts of other fields; for example, a
credit card expiry date can be expressed as one field giving both the month and year of expiry
("cc-exp"), or as two fields, one giving the
month ("cc-exp-month") and one the year
("cc-exp-year"). In such cases, the names of
the broader fields cover multiple rows, in which the narrower fields are defined.
Generally, authors are encouraged to use the broader fields rather than the narrower fields, as the narrower fields tend to expose Western biases. For example, while it is common in some Western cultures to have a given name and a family name, in that order (and thus often referred to as a first name and a surname), many cultures put the family name first and the given name second, and many others simply have one name (a mononym). Having a single field is therefore more flexible.
Some fields are only appropriate for certain form controls. An autofill field name is inappropriate for a control if the control does not belong to the group listed for that autofill field in the fifth column of the first row describing that autofill field in the table below. What controls fall into each group is described below the table.
| Field name | Meaning | Canonical Format | Canonical Format Example | Control group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
"name"
| Full name | Free-form text, no newlines | Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee, OM, KBE, FRS, FREng, FRSA | Text
| |||
"honorific-prefix"
| Prefix or title (e.g., "Mr.", "Ms.", "Dr.", "Mlle") | Free-form text, no newlines | Sir | Text
| |||
"given-name"
| Given name (in some Western cultures, also known as the first name) | Free-form text, no newlines | Timothy | Text
| |||
"additional-name"
| Additional names (in some Western cultures, also known as middle names, forenames other than the first name) | Free-form text, no newlines | John | Text
| |||
"family-name"
| Family name (in some Western cultures, also known as the last name or surname) | Free-form text, no newlines | Berners-Lee | Text
| |||
"honorific-suffix"
| Suffix (e.g., "Jr.", "B.Sc.", "MBASW", "II") | Free-form text, no newlines | OM, KBE, FRS, FREng, FRSA | Text
| |||
"nickname"
| Nickname, screen name, handle: a typically short name used instead of the full name | Free-form text, no newlines | Tim | Text
| |||
"organization-title"
| Job title (e.g., "Software Engineer", "Senior Vice President", "Deputy Managing Director") | Free-form text, no newlines | Professor | Text
| |||
"username"
| A username | Free-form text, no newlines | timbl | Text
| |||
"new-password"
| A new password (e.g., when creating an account or changing a password) | Free-form text, no newlines | GUMFXbadyrS3 | Password
| |||
"current-password"
| The current password for the account identified by the username field (e.g., when logging in)
| Free-form text, no newlines | qwerty | Password
| |||
"organization"
| Company name corresponding to the person, address, or contact information in the other fields associated with this field | Free-form text, no newlines | World Wide Web Consortium | Text
| |||
"street-address"
| Street address (multiple lines, newlines preserved) | Free-form text | 32 Vassar Street MIT Room 32-G524 | Multiline | |||
"address-line1"
| Street address (one line per field) | Free-form text, no newlines | 32 Vassar Street | Text
| |||
"address-line2"
| Free-form text, no newlines | MIT Room 32-G524 | Text
| ||||
"address-line3"
| Free-form text, no newlines | Text
| |||||
"address-level4"
| The most fine-grained administrative level, in addresses with four administrative levels | Free-form text, no newlines | Text
| ||||
"address-level3"
| The third administrative level, in addresses with three or more administrative levels | Free-form text, no newlines | Text
| ||||
"address-level2"
| The second administrative level, in addresses with two or more administrative levels; in the countries with two administrative levels, this would typically be the city, town, village, or other locality within which the relevant street address is found | Free-form text, no newlines | Cambridge | Text
| |||
"address-level1"
| The broadest administrative level in the address, i.e., the province within which the locality is found; for example, in the US, this would be the state; in Switzerland it would be the canton; in the UK, the post town | Free-form text, no newlines | MA | Text
| |||
"country"
| Country code | Valid ISO 3166-1-alpha-2 country code [ISO3166] | US | Text
| |||
"country-name"
| Country name | Free-form text, no newlines; derived from country in some cases
| US | Text
| |||
"postal-code"
| Postal code, post code, ZIP code, CEDEX code (if CEDEX, append "CEDEX", and the dissement, if relevant, to the address-level2 field)
| Free-form text, no newlines | 02139 | Text
| |||
"cc-name"
| Full name as given on the payment instrument | Free-form text, no newlines | Tim Berners-Lee | Text
| |||
"cc-given-name"
| Given name as given on the payment instrument (in some Western cultures, also known as the first name) | Free-form text, no newlines | Tim | Text
| |||
"cc-additional-name"
| Additional names given on the payment instrument (in some Western cultures, also known as middle names, forenames other than the first name) | Free-form text, no newlines | Text
| ||||
"cc-family-name"
| Family name given on the payment instrument (in some Western cultures, also known as the last name or surname) | Free-form text, no newlines | Berners-Lee | Text
| |||
"cc-number"
| Code identifying the payment instrument (e.g., the credit card number) | ASCII digits | 4114360123456785 | Text
| |||
"cc-exp"
| Expiration date of the payment instrument | Valid month string | 2014-12 | Month
| |||
"cc-exp-month"
| Month component of the expiration date of the payment instrument | valid integer in the range 1..12 | 12 | Numeric
| |||
"cc-exp-year"
| Year component of the expiration date of the payment instrument | valid integer greater than zero | 2014 | Numeric
| |||
"cc-csc"
| Security code for the payment instrument (also known as the card security code (CSC), card validation code (CVC), card verification value (CVV), signature panel code (SPC), credit card ID (CCID), etc) | ASCII digits | 419 | Text
| |||
"cc-type"
| Type of payment instrument | Free-form text, no newlines | Visa | Text
| |||
"transaction-currency"
| The currency that the user would prefer the transaction to use | ISO 4217 currency code [ISO4217] | GBP | Text
| |||
"transaction-amount"
| The amount that the user would like for the transaction (e.g., when entering a bid or sale price) | Valid floating-point number | 401.00 | Numeric
| |||
"language"
| Preferred language | Valid BCP 47 language tag [BCP47] | en | Text
| |||
"bday"
| Birthday | Valid date string | 1955-06-08 | Date
| |||
"bday-day"
| Day component of birthday | valid integer in the range 1..31 | 8 | Numeric
| |||
"bday-month"
| Month component of birthday | valid integer in the range 1..12 | 6 | Numeric
| |||
"bday-year"
| Year component of birthday | valid integer greater than zero | 1955 | Numeric
| |||
"sex"
| Gender identity (e.g., Female, Fa’afafine) | Free-form text, no newlines | Male | Text
| |||
"url"
| Home page or other Web page corresponding to the company, person, address, or contact information in the other fields associated with this field | Valid URL | https://www.w3.org/People/Berners-Lee/ | URL
| |||
"photo"
| Photograph, icon, or other image corresponding to the company, person, address, or contact information in the other fields associated with this field | Valid URL | https://www.w3.org/Press/Stock/Berners-Lee/2001-europaeum-eighth.jpg | URL
| |||
"tel"
| Full telephone number, including country code | ASCII digits and U+0020 SPACE characters, prefixed by a U+002B PLUS SIGN character (+) | +1 617 253 5702 | Tel | |||
"tel-country-code"
| Country code component of the telephone number | ASCII digits prefixed by a U+002B PLUS SIGN character (+) | +1 | Text
| |||
"tel-national"
| Telephone number without the county code component, with a country-internal prefix applied if applicable | ASCII digits and U+0020 SPACE characters | 617 253 5702 | Text
| |||
"tel-area-code"
| Area code component of the telephone number, with a country-internal prefix applied if applicable | ASCII digits | 617 | Text
| |||
"tel-local"
| Telephone number without the country code and area code components | ASCII digits | 2535702 | Text
| |||
"tel-local-prefix"
| First part of the component of the telephone number that follows the area code, when that component is split into two components | ASCII digits | 253 | Text
| |||
"tel-local-suffix"
| Second part of the component of the telephone number that follows the area code, when that component is split into two components | ASCII digits | 5702 | Text
| |||
"tel-extension"
| Telephone number internal extension code | ASCII digits | 1000 | Text
| |||
"email"
| E-mail address | Valid e-mail address | timbl@w3.org | E-mail
| |||
"impp"
| URL representing an instant messaging protocol endpoint (for example, "aim:goim?screenname=example" or "xmpp:fred@example.net")
| Valid URL | irc://example.org/timbl,isuser | URL
| |||
The groups correspond to controls as follows:
- Text
inputelements with atypeattribute in theHiddenstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theTextstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theSearchstatetextareaelementsselectelements- Multiline
inputelements with atypeattribute in theHiddenstatetextareaelementsselectelements- Password
inputelements with atypeattribute in theHiddenstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theTextstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theSearchstateinputelements with atypeattribute in thePasswordstatetextareaelementsselectelements- URL
inputelements with atypeattribute in theHiddenstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theTextstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theSearchstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theURLstatetextareaelementsselectelementsinputelements with atypeattribute in theHiddenstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theTextstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theSearchstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theE-mailstatetextareaelementsselectelements- Tel
inputelements with atypeattribute in theHiddenstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theTextstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theSearchstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theTelephonestatetextareaelementsselectelements- Numeric
inputelements with atypeattribute in theHiddenstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theTextstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theSearchstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theNumberstatetextareaelementsselectelements- Month
inputelements with atypeattribute in theHiddenstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theTextstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theSearchstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theMonthstatetextareaelementsselectelements- Date
inputelements with atypeattribute in theHiddenstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theTextstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theSearchstateinputelements with atypeattribute in theDatestatetextareaelementsselectelements
Address levels: The "address-level1" – "address-level4" fields are used to describe
the locality of the street address. Different locales have different numbers of levels. For
example, the US uses two levels (state and town), the UK uses one or two depending on the address
(the post town, and in some cases the locality), and China can use three (province, city,
district). The "address-level1" field
represents the widest administrative division. Different locales order the fields in different
ways; for example, in the US the town (level 2) precedes the state (level 1); while in Japan the
prefecture (level 1) precedes the city (level 2) which precedes the district (level 3). Authors
are encouraged to provide forms that are presented in a way that matches the country’s conventions
(hiding, showing, and rearranging fields accordingly as the user changes the country).
4.10.18.8.2. Processing model
Each input element to which the autocomplete attribute applies, each select element, and each textarea element, has an autofill hint set, an autofill scope, an autofill field name, and
an IDL-exposed autofill value.
The autofill field name specifies the specific kind of data expected in the field,
e.g., "street-address" or "cc-exp".
The autofill hint set identifies what address or contact information type the user
agent is to look at, e.g., "shipping fax" or "billing".
The autofill scope identifies the group of fields that are to be filled with the
information from the same source, and consists of the autofill hint set with, if
applicable, the "section-*" prefix, e.g., "billing", "section-parent shipping", or "section-child
shipping home".
These values are defined as the result of running the following algorithm:
- If the element has no
autocompleteattribute, then jump to the step labeled default. - Let tokens be the result of splitting the attribute’s value on spaces.
- If tokens is empty, then jump to the step labeled default.
- Let index be the index of the last token in tokens.
-
If the indexth token in tokens is not an ASCII case-insensitive match for one of the tokens given in the first column of the following table, or if the number of tokens in tokens is greater than the maximum number given in the cell in the second column of that token’s row, then jump to the step labeled default. Otherwise, let field be the string given in the cell of the first column of the matching row, and let category be the value of the cell in the third column of that same row.
Token Maximum number of tokens Category " off"1 Off " on"1 Automatic " name"3 Normal " honorific-prefix"3 Normal " given-name"3 Normal " additional-name"3 Normal " family-name"3 Normal " honorific-suffix"3 Normal " nickname"3 Normal " organization-title"3 Normal " username"3 Normal " new-password"3 Normal " current-password"3 Normal " organization"3 Normal " street-address"3 Normal " address-line1"3 Normal " address-line2"3 Normal " address-line3"3 Normal " address-level4"3 Normal " address-level3"3 Normal " address-level2"3 Normal " address-level1"3 Normal " country"3 Normal " country-name"3 Normal " postal-code"3 Normal " cc-name"3 Normal " cc-given-name"3 Normal " cc-additional-name"3 Normal " cc-family-name"3 Normal " cc-number"3 Normal " cc-exp"3 Normal " cc-exp-month"3 Normal " cc-exp-year"3 Normal " cc-csc"3 Normal " cc-type"3 Normal " transaction-currency"3 Normal " transaction-amount"3 Normal " language"3 Normal " bday"3 Normal " bday-day"3 Normal " bday-month"3 Normal " bday-year"3 Normal " sex"3 Normal " url"3 Normal " photo"3 Normal " tel"4 Contact " tel-country-code"4 Contact " tel-national"4 Contact " tel-area-code"4 Contact " tel-local"4 Contact " tel-local-prefix"4 Contact " tel-local-suffix"4 Contact " tel-extension"4 Contact " email"4 Contact " impp"4 Contact - If category is Off or Automatic but the element’s
autocompleteattribute is wearing the autofill anchor mantle, then jump to the step labeled default. - If category is Off, let the element’s autofill field name be the string "
off", let its autofill hint set be empty, and let its IDL-exposed autofill value be the string "off". Then, abort these steps. - If category is Automatic, let the element’s autofill field
name be the string "
on", let its autofill hint set be empty, and let its IDL-exposed autofill value be the string "on". Then, abort these steps. - Let scope tokens be an empty list.
- Let hint tokens be an empty set.
- Let IDL value have the same value as field.
- If the indexth token in tokens is the first entry, then skip to the step labeled done.
- Decrement index by one.
-
If category is Contact and the indexth token in tokens is an ASCII case-insensitive match for one of the strings in the following list, then run the substeps that follow:
- "
home" - "
work" - "
mobile" - "
fax" - "
pager"
The substeps are:
- Let contact be the matching string from the list above.
- Insert contact at the start of scope tokens.
- Add contact to hint tokens.
- Let IDL value be the concatenation of contact, a U+0020 SPACE character, and the previous value of IDL value (which at this point will always be field).
- If the indexth entry in tokens is the first entry, then skip to the step labeled done.
- Decrement index by one.
- "
-
If the indexth token in tokens is an ASCII case-insensitive match for one of the strings in the following list, then run the substeps that follow:
- "
shipping" - "
billing"
The substeps are:
- Let mode be the matching string from the list above.
- Insert mode at the start of scope tokens.
- Add mode to hint tokens.
- Let IDL value be the concatenation of mode, a U+0020 SPACE character, and the previous value of IDL value (which at this point will either be field or the concatenation of contact, a space, and field).
- If the indexth entry in tokens is the first entry, then skip to the step labeled done.
- Decrement index by one.
- "
- If the indexth entry in tokens is not the first entry, then jump to the step labeled default.
- If the first eight characters of the indexth token in tokens are not
an ASCII case-insensitive match for the string "
section-", then jump to the step labeled default. - Let section be the indexth token in tokens, in ASCII lowercase.
- Insert section at the start of scope tokens.
- Let IDL value be the concatenation of section, a U+0020 SPACE character, and the previous value of IDL value.
- Done: Let the element’s autofill hint set be hint tokens.
- Let the element’s autofill scope be scope tokens.
- Let the element’s autofill field name be field.
- Let the element’s IDL-exposed autofill value be IDL value.
- Abort these steps.
- Default: Let the element’s IDL-exposed autofill value be the empty string, and its autofill hint set and autofill scope be empty.
- If the element’s
autocompleteattribute is wearing the autofill anchor mantle, then let the element’s autofill field name be the empty string and abort these steps. - Let form be the element’s form owner, if any, or null otherwise.
-
If form is not null and form’s
autocompleteattribute is in the off state, then let the element’s autofill field name be "off".Otherwise, let the element’s autofill field name be "
on".
For the purposes of autofill, a control’s data depends on the kind of control:
- An
inputelement with itstypeattribute in theE-mailstate and with themultipleattribute specified - The element’s values.
- Any other
inputelement - A
textareaelement - The element’s value.
- A
selectelement with itsmultipleattribute specified - The
optionelements in theselectelement’s list of options that have their selectedness set to true. - Any other
selectelement - The
optionelement in theselectelement’s list of options that has its selectedness set to true.
How to process the autofill hint set, autofill scope, and autofill field name depends on the mantle that the autocomplete attribute is wearing.
- When wearing the autofill expectation mantle...
-
When an element’s autofill field name is "
off", the user agent should not remember the control’s data, and should not offer past values to the user.In addition, when an element’s autofill field name is "
off", values are reset when traversing the history.Banks frequently do not want user agents to prefill login information:<p><label>Account: <input type="text" name="ac" autocomplete="off"></label></p> <p><label>PIN: <input type="password" name="pin" autocomplete="off"></label></p>
When an element’s autofill field name is not "
off", the user agent may store the control’s data, and may offer previously stored values to the user.For example, suppose a user visits a page with this control:<select name="country"> <option>Afghanistan <option>Albania <option>Algeria <option>Andorra <option>Angola <option>Antigua and Barbuda <option>Argentina <option>Armenia <!-- ... --> <option>Yemen <option>Zambia <option>Zimbabwe </select>
This might render as follows:
Suppose that on the first visit to this page, the user selects "Zambia". On the second visit, the user agent could duplicate the entry for Zambia at the top of the list, so that the interface instead looks like this:
When the autofill field name is "
on", the user agent should attempt to use heuristics to determine the most appropriate values to offer the user, e.g., based on the element’snamevalue, the position of the element in the document’s DOM, what other fields exist in the form, and so forth.When the autofill field name is one of the names of the autofill fields described above, the user agent should provide suggestions that match the meaning of the field name as given in the table earlier in this section. The autofill hint set should be used to select amongst multiple possible suggestions.
For example, if a user once entered one address into fields that used the "
shipping" keyword, and another address into fields that used the "billing" keyword, then in subsequent forms only the first address would be suggested for form controls whose autofill hint set contains the keyword "shipping". Both addresses might be suggested, however, for address-related form controls whose autofill hint set does not contain either keyword. - When wearing the autofill anchor mantle...
-
When the autofill field name is not the empty string, then the user agent must act as if the user had specified the control’s data for the given autofill hint set, autofill scope, and autofill field name combination.
When the user agent autofills form controls, elements
with the same form owner and the same autofill scope must use data
relating to the same person, address, payment instrument, and contact details. When a user agent autofills "country" and "country-name" fields with the same form
owner and autofill scope, and the user agent has a value for the country" field(s), then the "country-name" field(s) must be filled using a
human-readable name for the same country. When a user agent fills in multiple fields at
once, all fields with the same autofill field name, form owner and autofill scope must be filled with the same value.
Suppose a user agent knows of two phone numbers, +1 555 123 1234 and +1 555 666 7777. It would
not be conforming for the user agent to fill a field with autocomplete="shipping tel-local-prefix" with the value "123" and another field in
the same form with autocomplete="shipping tel-local-suffix" with the value "7777".
The only valid prefilled values given the aforementioned information would be "123" and "1234",
or "666" and "7777", respectively.
Similarly, if a form for some reason contained both a "cc-exp" field and a
"cc-exp-month" field, and the user agent prefilled the form, then the month
component of the former would have to match the latter.
<form> <input type=hidden autocomplete="nickname" value="TreePlate"> <input type=text autocomplete="nickname"> </form>
The only value that a conforming user agent could suggest in the text field is
"TreePlate", the value given by the hidden input element.
The "section-*" tokens in the autofill scope are opaque;
user agents must not attempt to derive meaning from the precise values of these tokens.
For example, it would not be conforming if the user agent decided that it
should offer the address it knows to be the user’s daughter’s address for "section-child" and the addresses it knows to be the user’s spouses' addresses for
"section-spouse".
The autocompletion mechanism must be implemented by the user agent acting as if the user had modified the control’s data, and must be done at a time where the element is mutable (e.g., just after the element has been inserted into the document, or when the user agent stops parsing). User agents must only prefill controls using values that the user could have entered.
For example, if a select element only has option elements with values "Steve" and "Rebecca", "Jay", and "Bob", and has an autofill field
name "given-name", but the user
agent’s only idea for what to prefill the field with is "Evan", then the user agent cannot prefill
the field. It would not be conforming to somehow set the select element to the value
"Evan", since the user could not have done so themselves.
A user agent prefilling a form control’s value must not cause that control to suffer from a type mismatch, suffer from being too long, suffer from being too short, suffer from an underflow, suffer from an overflow, suffer from a step mismatch, or suffer from a pattern mismatch. Where possible given the control’s constraints, user agents must use the format given as canonical in the aforementioned table. Where it’s not possible for the canonical format to be used, user agents should use heuristics to attempt to convert values so that they can be used.
<input name=middle-initial maxlength=1 autocomplete="additional-name">
...then the user agent could convert "Ines" to "I" and prefill it that way.
<input name=b type=month autocomplete="bday"> | 2012-07 | The day is dropped since the Month state only accepts a month/year combination. |
<select name=c autocomplete="bday"> <option>Jan <option>Feb ... <option>Jul <option>Aug ... </select> | July | The user agent picks the month from the listed options, either by noticing there are twelve options and picking the 7th, or by recognizing that one of the strings (three characters "Jul" followed by a newline and a space) is a close match for the name of the month (July) in one of the user agent’s supported languages, or through some other similar mechanism. |
<input name=a type=number min=1 max=12 autocomplete="bday-month"> | 7 | User agent converts "July" to a month number in the range 1..12, like the field. |
<input name=a type=number min=0 max=11 autocomplete="bday-month"> | 6 | User agent converts "July" to a month number in the range 0..11, like the field. |
<input name=a type=number min=1 max=11 autocomplete="bday-month"> | User agent doesn’t fill in the field, since it can’t make a good guess as to what the form expects. |
A user agent may allow the user to override an element’s autofill field name, e.g.,
to change it from "off" to "on" to allow values to be remembered and prefilled despite
the page author’s objections, or to always "off",
never remembering values.
More specifically, user agents may in particular consider replacing the autofill field
name of form controls that match the description given in the first column of the following
table, when their autofill field name is either "on" or "off", with the value given in the second cell of that
row. If this table is used, the replacements must be done in tree order, since all
but the first row references the autofill field name of earlier elements. When the
descriptions below refer to form controls being preceded or followed by others, they mean in the
list of listed elements that share the same form owner.
| Form control | New autofill field name |
|---|---|
|
an |
" |
|
an |
" |
|
an |
" |
|
an |
" |
The autocomplete IDL attribute, on getting,
must return the element’s IDL-exposed autofill value, and on setting, must reflect the content attribute of the same name.
4.10.19. APIs for text field selections
The input and textarea elements define the following members in their
DOM interfaces for handling their selection: select(), selectionStart, selectionEnd, selectionDirection, setRangeText(replacement), setSelectionRange(start, end)
The setRangeText() method uses the following enumeration:
enum SelectionMode {
"select",
"start",
"end",
"preserve" // default
};
These methods and attributes expose and control the selection of input and textarea text fields.
- element .
select() -
Selects everything in the text field.
- element .
selectionStart[ = value ] -
Returns the offset to the start of the selection.
Can be set, to change the start of the selection.
- element .
selectionEnd[ = value ] -
Returns the offset to the end of the selection.
Can be set, to change the end of the selection.
- element .
selectionDirection[ = value ] -
Returns the current direction of the selection.
Can be set, to change the direction of the selection.
The possible values are "
forward", "backward", and "none". - element . setSelectionRange(start, end [, direction] )
-
Changes the selection to cover the given substring in the given direction. If the direction is omitted, it will be reset to be the platform default (none or forward).
- element . setRangeText(replacement [, start, end [, selectionMode ] ] )
-
Replaces a range of text with the new text. If the start and end arguments are not provided, the range is assumed to be the selection.
The final argument determines how the selection should be set after the text has been replaced. The possible values are:
- "
select" -
Selects the newly inserted text.
- "
start" -
Moves the selection to just before the inserted text.
- "
end" -
Moves the selection to just after the selected text.
- "
preserve" -
Attempts to preserve the selection. This is the default.
- "
For input elements, calling these methods while they don’t apply, and getting or setting these attributes while they don’t apply, must throw an InvalidStateError exception. Otherwise, they
must act as described below.
For input elements, these methods and attributes must operate on the element’s value. For textarea elements, these methods and
attributes must operate on the element’s raw value.
Where possible, user interface features for changing the text selection in input and textarea elements must be implemented in terms of the DOM API described in this
section, so that, e.g., all the same events fire.
The selections of input and textarea elements have a direction, which is either forward, backward, or none. This direction
is set when the user manipulates the selection. The exact meaning of the selection direction
depends on the platform.
On Windows, the direction indicates the position of the caret relative to the selection: a forward selection has the caret at the end of the selection and a backward selection has the caret at the start of the selection. Windows has no none direction. On Mac, the direction indicates which end of the selection is affected when the user adjusts the size of the selection using the arrow keys with the Shift modifier: the forward direction means the end of the selection is modified, and the backwards direction means the start of the selection is modified. The none direction is the default on Mac, it indicates that no particular direction has yet been selected. The user sets the direction implicitly when first adjusting the selection, based on which directional arrow key was used.
The select() method must cause the
contents of the text field to be fully selected, with the selection direction being none, if the
platform support selections with the direction none, or otherwise forward. The user
agent must then queue a task to fire a simple event that bubbles named select at the element, using the user interaction task
source as the task source.
In the case of input elements, if the control has no text field, then the method
must do nothing.
For instance, in a user agent where <input type=color> is rendered as a color well with a
picker, as opposed to a text field accepting a hexadecimal color code, there would be no text
field, and thus nothing to select, and thus calls to the method are ignored.
The selectionStart attribute
must, on getting, return the offset (in logical order) to the character that immediately follows
the start of the selection. If there is no selection, then it must return the offset (in logical
order) to the character that immediately follows the text entry cursor.
On setting, it must act as if the setSelectionRange() method had been called,
with the new value as the first argument; the current value of the selectionEnd attribute as the second argument,
unless the current value of the selectionEnd is less than the new value, in which case the second argument must also be the new value; and the
current value of the selectionDirection as the third argument.
The selectionEnd attribute
must, on getting, return the offset (in logical order) to the character that immediately follows
the end of the selection. If there is no selection, then it must return the offset (in logical
order) to the character that immediately follows the text entry cursor.
On setting, it must act as if the setSelectionRange() method had been called,
with the current value of the selectionStart attribute as the first argument,
the new value as the second argument, and the current value of the selectionDirection as the third argument.
The selectionDirection attribute must, on getting, return the string corresponding to the current selection direction: if
the direction is forward, "forward"; if the direction is backward, "backward"; and otherwise, "none".
On setting, it must act as if the setSelectionRange() method had been called,
with the current value of the selectionStart IDL attribute as the first argument,
the current value of the selectionEnd IDL
attribute as the second argument, and the new value as the third argument.
The setSelectionRange(start, end, direction) method
must set the selection of the text field to the sequence of characters starting with the character
at the startth position (in logical order) and ending with the character at
the (end-1)th position. Arguments greater than the
length of the value of the text field must be treated as pointing at the end of the text field. If end is less than or equal to start then the start of the
selection and the end of the selection must both be placed immediately before the character with
offset end. In user agents where there is no concept of an empty selection, this must
set the cursor to be just before the character with offset end. The direction
of the selection must be set to backward if direction is a case-sensitive match for the string "backward", forward if direction is a case-sensitive match for the string "forward" or if the platform does not support selections with the direction none, and none otherwise (including if the argument is omitted). The user agent must
then queue a task to fire a simple event that bubbles named select at the element, using the user interaction task
source as the task source.
The setRangeText(replacement, start, end, selectMode) method must run the following steps:
-
If the method has only one argument, then let start and end have the values of the
selectionStartIDL attribute and theselectionEndIDL attribute respectively.Otherwise, let start, end have the values of the second and third arguments respectively.
- If start is greater than end, then throw an
IndexSizeErrorexception and abort these steps. - If start is greater than the length of the value of the text field, then set it to the length of the value of the text field.
- If end is greater than the length of the value of the text field, then set it to the length of the value of the text field.
- Let selection start be the current value of the
selectionStartIDL attribute. - Let selection end be the current value of the
selectionEndIDL attribute. - If start is less than end, delete the sequence of characters starting with the character at the startth position (in logical order) and ending with the character at the (end-1)th position.
- Insert the value of the first argument into the text of the value of the text field, immediately before the startth character.
- Let new length be the length of the value of the first argument.
- Let new end be the sum of start and new length.
-
Run the appropriate set of substeps from the following list:
- If the fourth argument’s value is "
select" -
Let selection start be start.
Let selection end be new end.
- If the fourth argument’s value is "
start" -
Let selection start and selection end be start.
- If the fourth argument’s value is "
end" -
Let selection start and selection end be new end.
- If the fourth argument’s value is "
preserve" (the default) -
- Let old length be end minus start.
- Let delta be new length minus old length.
-
If selection start is greater than end, then increment it by delta. (If delta is negative, i.e., the new text is shorter than the old text, then this will decrease the value of selection start.)
Otherwise: if selection start is greater than start, then set it to start. (This snaps the start of the selection to the start of the new text if it was in the middle of the text that it replaced.)
-
If selection end is greater than end, then increment it by delta in the same way.
Otherwise: if selection end is greater than start, then set it to new end. (This snaps the end of the selection to the end of the new text if it was in the middle of the text that it replaced.)
- If the fourth argument’s value is "
-
Set the selection of the text field to the sequence of characters starting with the character at the selection startth position (in logical order) and ending with the character at the (selection end-1)th position. In user agents where there is no concept of an empty selection, this must set the cursor to be just before the character with offset end. The direction of the selection must be set to forward if the platform does not support selections with the direction none, and none otherwise.
- Queue a task to fire a simple event that bubbles named
selectat the element, using the user interaction task source as the task source.
All elements to which this API applies have either a selection or a text entry cursor position at all times (even for elements that are not being rendered). User agents should follow platform conventions to determine their initial state.
Characters with no visible rendering, such as U+200D ZERO WIDTH JOINER, still count as characters. Thus, for instance, the selection can include just an invisible character, and the text insertion cursor can be placed to one side or another of such a character.
var selectionText = control.value.substring(control.selectionStart, control.selectionEnd);
var oldStart = control.selectionStart; var oldEnd = control.selectionEnd; var oldDirection = control.selectionDirection; var prefix = "https://"; control.value = prefix + control.value; control.setSelectionRange(oldStart + prefix.length, oldEnd + prefix.length, oldDirection);
4.10.20. Constraints
4.10.20.1. Definitions
A submittable element is a candidate for constraint validation except when a condition has barred the element from constraint validation. (For example, an element is barred from
constraint validation if it is an object element.)
An element can have a custom validity error message defined. Initially, an element
must have its custom validity error message set to the empty string. When its value
is not the empty string, the element is suffering from a custom error. It can be set
using the setCustomValidity() method. The user
agent should use the custom validity error message when alerting the user to the
problem with the control.
An element can be constrained in various ways. The following is the list of validity states that a form control can be in, making the control invalid for the purposes of constraint validation. (The definitions below are non-normative; other parts of this specification define more precisely when each state applies or does not.)
- Suffering from being missing
-
When a control has no value but has a
requiredattribute (inputrequired,textarearequired); or, in the case of an element in a radio button group, any of the other elements in the group has arequiredattribute; or, forselectelements, none of theoptionelements have their selectedness set (selectrequired). - Suffering from a type mismatch
-
When a control that allows arbitrary user input has a value that is not in the correct syntax (
E-mail,URL). - Suffering from a pattern mismatch
-
When a control has a value that doesn’t satisfy the
patternattribute. - Suffering from being too long
-
When a control has a value that is too long for the form control
maxlengthattribute (inputmaxlength,textareamaxlength). - Suffering from being too short
-
When a control has a value that is too short for the form control
minlengthattribute (inputminlength,textareaminlength). - Suffering from an underflow
-
When a control has a value that is not the empty string and is too low for the
minattribute. - Suffering from an overflow
-
When a control has a value that is not the empty string and is too high for the
maxattribute. - Suffering from a step mismatch
-
When a control has a value that doesn’t fit the rules given by the
stepattribute. - Suffering from bad input
-
When a control has incomplete input and the user agent does not think the user ought to be able to submit the form in its current state.
- Suffering from a custom error
-
When a control’s custom validity error message (as set by the element’s
setCustomValidity()method) is not the empty string.
An element can still suffer from these states even when the element is disabled; thus these states can be represented in the DOM even if validating the form during submission wouldn’t indicate a problem to the user.
An element satisfies its constraints if it is not suffering from any of the above validity states.
4.10.20.2. Constraint validation
When the user agent is required to statically validate the constraints of form element form, it must run the following steps, which return
either a positive result (all the controls in the form are valid) or a negative result (there are invalid controls) along with a (possibly empty) list of elements that are
invalid and for which no script has claimed responsibility:
- Let controls be a list of all the submittable elements whose form owner is form, in tree order.
- Let invalid controls be an initially empty list of elements.
-
For each element field in controls, in tree order, run the following substeps:
- If field is not a candidate for constraint validation, then move on to the next element.
- Otherwise, if field satisfies its constraints, then move on to the next element.
- Otherwise, add field to invalid controls.
- If invalid controls is empty, then return a positive result and abort these steps.
- Let unhandled invalid controls be an initially empty list of elements.
-
For each element field in invalid controls, if any, in tree order, run the following substeps:
- Fire a simple event named
invalidthat is cancelable at field. - If the event was not canceled, then add field to unhandled invalid controls.
- Fire a simple event named
- Return a negative result with the list of elements in the unhandled invalid controls list.
If a user agent is to interactively validate the constraints of form element form, then the user agent must run the following steps:
- Statically validate the constraints of form, and let unhandled invalid controls be the list of elements returned if the result was negative.
- If the result was positive, then return that result and abort these steps.
- Report the problems with the constraints of at least one of the elements given in unhandled invalid controls to the user. User agents may focus one of those elements in
the process, by running the focusing steps for that element, and may change the
scrolling position of the document, or perform some other action that brings the element to the
user’s attention. User agents may report more than one constraint violation. User agents may
coalesce related constraint violation reports if appropriate (e.g., if multiple radio buttons in a group are marked as required, only one error need be
reported). If one of the controls is not being rendered (e.g., it has the
attribute set) then user agents may report a script error. - Return a negative result.
4.10.20.3. The constraint validation API
- element .
willValidate -
Returns true if the element will be validated when the form is submitted; false otherwise.
- element .
setCustomValidity() -
Sets a custom error, so that the element would fail to validate. The given message is the message to be shown to the user when reporting the problem to the user.
If the argument is the empty string, clears the custom error.
- element .
validity.valueMissing -
Returns true if the element has no value but is a required field; false otherwise.
- element .
validity.typeMismatch -
Returns true if the element’s value is not in the correct syntax; false otherwise.
- element .
validity.patternMismatch -
Returns true if the element’s value doesn’t match the provided pattern; false otherwise.
- element .
validity.tooLong -
Returns true if the element’s value is longer than the provided maximum length; false otherwise.
- element .
validity.tooShort -
Returns true if the element’s value, if it is not the empty string, is shorter than the provided minimum length; false otherwise.
- element .
validity.rangeUnderflow -
Returns true if the element’s value is lower than the provided minimum; false otherwise.
- element .
validity.rangeOverflow -
Returns true if the element’s value is higher than the provided maximum; false otherwise.
- element .
validity.stepMismatch -
Returns true if the element’s value doesn’t fit the rules given by the
stepattribute; false otherwise. - element .
validity.badInput -
Returns true if the user has provided input in the user interface that the user agent is unable to convert to a value; false otherwise.
- element .
validity.customError -
Returns true if the element has a custom error; false otherwise.
- element .
validity.valid -
Returns true if the element’s value has no validity problems; false otherwise.
- valid = element .
checkValidity() -
Returns true if the element’s value has no validity problems; false otherwise. Fires an
invalidevent at the element in the latter case. - valid = element .
reportValidity() -
Returns true if the element’s value has no validity problems; otherwise, returns false, fires an
invalidevent at the element, and (if the event isn’t canceled) reports the problem to the user. - element .
validationMessage -
Returns the error message that would be shown to the user if the element was to be checked for validity.
The willValidate IDL attribute must return
true if an element is a candidate for constraint validation, and false otherwise
(i.e., false if any conditions are barring it from
constraint validation).
The setCustomValidity(message),
when invoked, must set the custom validity error message to the value of the given message argument.
setCustomValidity() method to set an appropriate
message.
<label>Feeling: <input name=f type="text" oninput="check(this)"></label> <script> function check(input) { if (input.value == "good" || input.value == "fine" || input.value == "tired") { input.setCustomValidity('"' + input.value + '" is not a feeling.'); } else { // input is fine -- reset the error message input.setCustomValidity(""); } } </script>
The validity IDL attribute must return a ValidityState object that represents
the validity states of the element.
This object is live.
interface ValidityState { readonly attribute boolean valueMissing; readonly attribute boolean typeMismatch; readonly attribute boolean patternMismatch; readonly attribute boolean tooLong; readonly attribute boolean tooShort; readonly attribute boolean rangeUnderflow; readonly attribute boolean rangeOverflow; readonly attribute boolean stepMismatch; readonly attribute boolean badInput; readonly attribute boolean customError; readonly attribute boolean valid; };
A ValidityState object has the following attributes. On getting, they must return
true if the corresponding condition given in the following list is true, and false otherwise.
valueMissing, of type boolean, readonly-
The control is suffering from being missing.
typeMismatch, of type boolean, readonly-
The control is suffering from a type mismatch.
patternMismatch, of type boolean, readonly-
The control is suffering from a pattern mismatch.
tooLong, of type boolean, readonly-
The control is suffering from being too long.
tooShort, of type boolean, readonly-
The control is suffering from being too short.
rangeUnderflow, of type boolean, readonly-
The control is suffering from an underflow.
rangeOverflow, of type boolean, readonly-
The control is suffering from an overflow.
stepMismatch, of type boolean, readonly-
The control is suffering from a step mismatch.
badInput, of type boolean, readonly-
The control is suffering from bad input.
customError, of type boolean, readonly-
The control is suffering from a custom error.
valid, of type boolean, readonly-
None of the other conditions are true.
When the checkValidity() method is
invoked, if the element is a candidate for constraint validation and does not satisfy its constraints, the user agent must fire a simple event named invalid that is cancelable (but in this case
has no default action) at the element and return false. Otherwise, it must only return true
without doing anything else.
When the reportValidity() method is
invoked, if the element is a candidate for constraint validation and does not satisfy its constraints, the user agent must: fire a simple
event named invalid that is cancelable at the element,
and if that event is not canceled, report the problems with the constraints of that element to the
user; then, return false. Otherwise, it must only return true without doing anything else. When
reporting the problem with the constraints to the user, the user agent may run the focusing
steps for that element, and may change the scrolling position of the document, or perform
some other action that brings the element to the user’s attention. User agents may report more
than one constraint violation, if the element suffers from multiple problems at once. If the
element is not being rendered, then the user agent may, instead of notifying the
user, report a script error.
The validationMessage attribute must
return the empty string if the element is not a candidate for constraint validation or if it is one but it satisfies its constraints; otherwise,
it must return a suitably localized message that the user agent would show the user if this were
the only form control with a validity constraint problem. If the user agent would not actually
show a textual message in such a situation (e.g., it would show a graphical cue instead), then the
attribute must return a suitably localized message that expresses (one or more of) the validity
constraint(s) that the control does not satisfy. If the element is a candidate for
constraint validation and is suffering from a custom error, then the custom validity error message should be present in the return value.
4.10.20.4. Security
Servers should not rely on client-side validation. Client-side validation can be intentionally bypassed by hostile users, and unintentionally bypassed by users of older user agents or automated tools that do not implement these features. The constraint validation features are only intended to improve the user experience, not to provide any kind of security mechanism.
4.10.21. Form submission
4.10.21.1. Introduction
This section is non-normative.
When a form is submitted, the data in the form is converted into the structure specified by the enctype, and then sent to the destination specified by the action using the given method.
For example, take the following form:
<form action="/find.cgi" method=get> <input type=text name=t> <input type=search name=q> <input type=submit> </form>
If the user types in "cats" in the first field and "fur" in the second, and then hits the
submit button, then the user agent will load /find.cgi?t=cats&q=fur.
On the other hand, consider this form:
<form action="/find.cgi" method=post enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type=text name=t> <input type=search name=q> <input type=submit> </form>
Given the same user input, the result on submission is quite different: the user agent instead does an HTTP POST to the given URL, with as the entity body something like the following text:
------kYFrd4jNJEgCervEContent-Disposition: form-data; name="t" cats ------kYFrd4jNJEgCervE Content-Disposition: form-data; name="q" fur ------kYFrd4jNJEgCervE--
4.10.21.2. Implicit submission
A form element’s default button is the first Submit Button in tree order whose form
owner is that form element.
If the user agent supports letting the user submit a form implicitly (for example, on some platforms hitting the "enter" key while a text field is focused implicitly submits the form), then doing so for a form whose default button has a defined activation behavior must cause the user agent to run synthetic click activation steps on that default button.
Consequently, if the default button is disabled, the form is not submitted when such an implicit submission mechanism is used. (A button has no activation behavior when disabled.)
There are pages on the Web that are only usable if there is a way to implicitly submit forms, so user agents are strongly encouraged to support this.
If the form has
no Submit Button, then the implicit submission
mechanism must do nothing if the form has more than one field that blocks implicit
submission, and must submit the form element from the form element itself otherwise.
For the purpose of the previous paragraph, an element is a field that blocks implicit
submission of a form element if it is an input element whose form owner is that form element and whose type attribute is in one of the following states: Text, Search, URL, Telephone, E-mail, Password, Date and Time, Date, Month, Week, Time, Number
4.10.21.3. Form submission algorithm
When a form element form is submitted from an element submitter (typically a button), optionally with a submitted from submit() method flag set, the user agent must run the
following steps:
- Let form document be the form’s node document.
- If form document has no associated browsing context or its active sandboxing flag set has its sandboxed forms browsing context flag set, then abort these steps without doing anything.
- Let form browsing context be the browsing context of form document.
- If the submitted from
submit()method flag is not set, and the submitter element’s no-validate state is false, then interactively validate the constraints of form and examine the result: if the result is negative (the constraint validation concluded that there were invalid fields and probably informed the user of this) then fire a simple event namedinvalidat the form element and then abort these steps. - If the submitted from
submit()method flag is not set, then fire a simple event that bubbles and is cancelable namedsubmit, at form. If the event’s default action is prevented (i.e., if the event is canceled) then abort these steps. Otherwise, continue (effectively the default action is to perform the submission). - Let form data set be the result of constructing the form data set for form in the context of submitter.
- Let action be the submitter element’s action.
-
If action is the empty string, let action be the document’s URL of the form document.
- Parse the URL action, relative to the submitter element’s node document. If this fails, abort these steps.
- Let action be the resulting URL string.
- Let action components be the resulting URL record.
- Let scheme be the scheme of the resulting URL record.
- Let enctype be the submitter element’s enctype.
- Let method be the submitter element’s method.
- Let target be the submitter element’s target.
- If the user indicated a specific browsing context to use when submitting the form, then let target browsing context be that browsing context. Otherwise, apply the rules for choosing a browsing context given a browsing context name using target as the name and form browsing context as the context in which the algorithm is executed, and let target browsing context be the resulting browsing context.
- If target browsing context was created in the previous step, or,
alternatively, if the form document has not yet completely
loaded and the submitted from
submit()method flag is set, then let replace be true. Otherwise, let it be false. -
If the value of method is dialog then jump to the submit dialog steps.
Otherwise, select the appropriate row in the table below based on the value of scheme as given by the first cell of each row. Then, select the appropriate cell on that row based on the value of method as given in the first cell of each column. Then, jump to the steps named in that cell and defined below the table.
GET POST httpMutate action URL Submit as entity body httpsMutate action URL Submit as entity body ftpGet action URL Get action URL javascriptGet action URL Get action URL dataGet action URL Post to data: mailtoMail with headers Mail as body If scheme is not one of those listed in this table, then the behavior is not defined by this specification. User agents should, in the absence of another specification defining this, act in a manner analogous to that defined in this specification for similar schemes.
Each
formelement has a planned navigation, which is either null or a task; when theformis first created, its planned navigation must be set to null. In the behaviors described below, when the user agent is required to plan to navigate to a particular resource destination, it must run the following steps:- If the
formhas a non-null planned navigation, remove it from its task queue. -
Let the
form's planned navigation be a new task that consists of running the following steps:- Let the
form's planned navigation be null. - Navigate target browsing context to destination. If replace is true, then target browsing context must be navigated with replacement enabled.
For the purposes of this task, target browsing context and replace are the variables that were set up when the overall form submission algorithm was run, with their values as they stood when this planned navigation was queued.
- Let the
-
Queue a task that is the
form's new planned navigation.The task source for this task is the DOM manipulation task source.
The behaviors are as follows:
- Mutate action URL
-
Let query be the result of encoding the form data set using the
application/x-www-form-urlencodedencoding algorithm, interpreted as a US-ASCII string.Set parsed action’s query component to query.
Let destination be a new URL formed by applying the URL serializer algorithm to parsed action.
Plan to navigate to destination.
- Submit as entity body
-
Let entity body be the result of encoding the form data set using the appropriate form encoding algorithm.
Let MIME type be determined as follows:
- If enctype is
application/x-www-form-urlencoded -
Let MIME type be "
application/x-www-form-urlencoded". - If enctype is
multipart/form-data -
Let MIME type be the concatenation of the string "
multipart/form-data;", a U+0020 SPACE character, the string "boundary=", and themultipart/form-databoundary string generated by themultipart/form-dataencoding algorithm. - If enctype is
text/plain -
Let MIME type be "
text/plain".
Otherwise, plan to navigate to a new request whose URL is action, method is method, header list consists of
Content-Type/MIME type, and body is entity body. - If enctype is
- Get action URL
-
Plan to navigate to action.
The form data set is discarded.
- Post to data:
-
Let data be the result of encoding the form data set using the appropriate form encoding algorithm.
If action contains the string "
%%%%" (four U+0025 PERCENT SIGN characters), then percent encode all bytes in data that, if interpreted as US-ASCII, are not characters in the URL default encode set, and then, treating the result as a US-ASCII string, UTF-8 percent encode all the U+0025 PERCENT SIGN characters in the resulting string and replace the first occurrence of "%%%%" in action with the resulting doubly-escaped string. [URL]Otherwise, if action contains the string "
%%" (two U+0025 PERCENT SIGN characters in a row, but not four), then UTF-8 percent encode all characters in data that, if interpreted as US-ASCII, are not characters in the URL default encode set, and then, treating the result as a US-ASCII string, replace the first occurrence of "%%" in action with the resulting escaped string. [URL]Plan to navigate to the potentially modified action (which will be a
data:URL). - Mail with headers
-
Let headers be the resulting encoding the form data set using the
application/x-www-form-urlencodedencoding algorithm, interpreted as a US-ASCII string.Replace occurrences of U+002B PLUS SIGN characters (+) in headers with the string "
%20".Let destination consist of all the characters from the first character in action to the character immediately before the first U+003F QUESTION MARK character (?), if any, or the end of the string if there are none.
Append a single U+003F QUESTION MARK character (?) to destination.
Append headers to destination.
Plan to navigate to destination.
- Mail as body
-
Let body be the resulting of encoding the form data set using the appropriate form encoding algorithm and then percent encoding all the bytes in the resulting byte string that, when interpreted as US-ASCII, are not characters in the URL default encode set. [URL]
Let destination have the same value as action.
If destination does not contain a U+003F QUESTION MARK character (?), append a single U+003F QUESTION MARK character (?) to destination. Otherwise, append a single U+0026 AMPERSAND character (&).
Append the string "
body=" to destination.Append body, interpreted as a US-ASCII string, to destination.
Plan to navigate to destination.
- Submit dialog
-
Let subject be the nearest ancestor
dialogelement of form, if any.If there isn’t one, or if it does not have an
openattribute, do nothing. Otherwise, proceed as follows:If submitter is an
inputelement whosetypeattribute is in theImage Buttonstate, then let result be the string formed by concatenating the selected coordinate’s x-component, expressed as a base-ten number using ASCII digits, a U+002C COMMA character (,), and the selected coordinate’s y-component, expressed in the same way as the x-component.Otherwise, if submitter has a value, then let result be that value.
Otherwise, there is no result.
Then, close the dialog subject. If there is a result, let that be the return value.
The appropriate form encoding algorithm is determined as follows:
- If enctype is
application/x-www-form-urlencoded -
Use the
application/x-www-form-urlencodedencoding algorithm. - If enctype is
multipart/form-data - If enctype is
text/plain -
Use the
text/plainencoding algorithm.
- If the
4.10.21.4. Constructing the form data set
The algorithm to construct the form data set for a form form optionally in the context of a submitter submitter is as follows. If not specified otherwise, submitter is null.
- Let controls be a list of all the submittable elements whose form owner is form, in tree order.
- Let the form data set be a list of name-value-type tuples, initially empty.
-
Loop: For each element field in controls, in tree order, run the following substeps:
-
If any of the following conditions are met, then skip these substeps for this element:
- The field element has a
datalistelement ancestor. - The field element is disabled.
- The field element is a button but it is not submitter.
- The field element is an
inputelement whosetypeattribute is in theCheckboxstate and whose checkedness is false. - The field element is an
inputelement whosetypeattribute is in theRadio Buttonstate and whose checkedness is false. - The field element is not an
inputelement whosetypeattribute is in theImage Buttonstate, and either the field element does not have anameattribute specified, or itsnameattribute’s value is the empty string. - The field element is an
objectelement that is not using a plugin.
Otherwise, process field as follows:
- The field element has a
- Let type be the value of the
typeIDL attribute of field. -
If the field element is an
inputelement whosetypeattribute is in theImage Buttonstate, then run these further nested substeps:- If the field element has a
nameattribute specified and its value is not the empty string, let name be that value followed by a single U+002E FULL STOP character (.). Otherwise, let name be the empty string. - Let namex be the string consisting of the concatenation of name and a single U+0078 LATIN SMALL LETTER X character (x).
- Let namey be the string consisting of the concatenation of name and a single U+0079 LATIN SMALL LETTER Y character (y).
- The field element is submitter, and before this algorithm was invoked the user indicated a coordinate. Let x be the x-component of the coordinate selected by the user, and let y be the y-component of the coordinate selected by the user.
- Append an entry to the form data set with the name namex, the value x, and the type type.
- Append an entry to the form data set with the name namey and the value y, and the type type.
- Skip the remaining substeps for this element: if there are any more elements in controls, return to the top of the loop step, otherwise, jump to the end step below.
- If the field element has a
- Let name be the value of the field element’s
nameattribute. - If the field element is a
selectelement, then for eachoptionelement in theselectelement’s list of options whose selectedness is true and that is not disabled, append an entry to the form data set with the name as the name, the value of theoptionelement as the value, and type as the type. -
Otherwise, if the field element is an
inputelement whosetypeattribute is in theCheckboxstate or theRadio Buttonstate, then run these further nested substeps:- If the field element has a
valueattribute specified, then let value be the value of that attribute; otherwise, let value be the string "on". - Append an entry to the form data set with name as the name, value as the value, and type as the type.
- If the field element has a
- Otherwise, if the field element is an
inputelement whosetypeattribute is in theFile Uploadstate, then for each file selected in theinputelement, append an entry to the form data set with the name as the name, the file (consisting of the name, the type, and the body) as the value, and type as the type. If there are no selected files, then append an entry to the form data set with the name as the name, the empty string as the value, andapplication/octet-streamas the type. - Otherwise, if the field element is an
objectelement: try to obtain a form submission value from the plugin, and if that is successful, append an entry to the form data set with name as the name, the returned form submission value as the value, and the string "object" as the type. - Otherwise, append an entry to the form data set with name as the name, the value of the field element as the value, and type as the type.
-
If the element has a
dirnameattribute, and that attribute’s value is not the empty string, then run these substeps:- Let dirname be the value of the element’s
dirnameattribute. - Let dir be the string "
ltr" if the directionality of the element is 'ltr', and "rtl" otherwise (i.e., when the directionality of the element is 'rtl'). - Append an entry to the form data set with dirname as the name, dir as the value, and the string
"
direction" as the type.
An element can only have a
dirnameattribute if it is atextareaelement or aninputelement whosetypeattribute is in either theTextstate or theSearchstate. - Let dirname be the value of the element’s
-
-
End: For the name of each entry in the form data set, and for the value of each entry in the form data set whose type is not "
file" or "textarea", replace every occurrence of a U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) character not followed by a U+000A LINE FEED (LF) character, and every occurrence of a U+000A LINE FEED (LF) character not preceded by a U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) character, by a two-character string consisting of a U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN U+000A LINE FEED (CRLF) character pair.In the case of the value of
textareaelements, this newline normalization is already performed during the conversion of the control’s raw value into the control’s value (which also performs any necessary line wrapping). In the case ofinputelementstypeattributes in theFile Uploadstate, the value is not normalized. - Return the form data set.
4.10.21.5. Selecting a form submission encoding
If the user agent is to pick an encoding for a form, it must run the following steps:
-
Let encoding be the document’s character encoding.
-
If the
formelement has anaccept-charsetattribute, set encoding to the return value of running these substeps:-
Let input be the value of the
formelement’saccept-charsetattribute. -
Let candidate encoding labels be the result of splitting input on spaces.
-
Let candidate encodings be an empty list of character encodings.
-
For each token in candidate encoding labels in turn (in the order in which they were found in input), get an encoding for the token and, if this does not result in failure, append the encoding to candidate encodings.
-
If candidate encodings is empty, return UTF-8.
-
Return the first encoding in candidate encodings.
-
-
Return the result of getting an output encoding from encoding.
4.10.21.6. URL-encoded form data
See the WHATWG URL specification for details on application/x-www-form-urlencoded. [URL]
The application/x-www-form-urlencoded encoding algorithm is as follows:
-
Let encoding be the result of picking an encoding for the form.
-
Let serialized be the result of running the
application/x-www-form-urlencodedserializer given form data set and encoding. -
Return the result of encoding serialized.
4.10.21.7. Multipart form data
The multipart/form-data encoding algorithm is as follows:
- Let result be the empty string.
-
If the algorithm was invoked with an explicit character encoding, let the selected character encoding be that encoding. (This algorithm is used by other specifications, which provide an explicit character encoding to avoid the dependency on the
formelement described in the next paragraph.)Otherwise, if the
formelement has anaccept-charsetattribute, let the selected character encoding be the result of picking an encoding for the form.Otherwise, if the
formelement has noaccept-charsetattribute, but the document’s character encoding is an ASCII-compatible encoding, then that is the selected character encoding.Otherwise, let the selected character encoding be UTF-8.
- Let charset be the name of the selected character encoding.
-
For each entry in the form data set, perform these substeps:
- If the entry’s name is "
_charset_" and its type is "hidden", replace its value with charset. - For each character in the entry’s name and value that cannot be expressed using the selected character encoding, replace the character by a string consisting of a U+0026 AMPERSAND character (&), a U+0023 NUMBER SIGN character (#), one or more ASCII digits representing the Unicode code point of the character in base ten, and finally a U+003B SEMICOLON character (;).
- If the entry’s name is "
-
Encode the (now mutated) form data set using the rules described by RFC 7578, Returning Values from Forms:
multipart/form-data, and return the resulting byte stream. [RFC7578]Each entry in the form data set is a field, the name of the entry is the field name and the value of the entry is the field value.
The order of parts must be the same as the order of fields in the form data set. Multiple entries with the same name must be treated as distinct fields.
The parts of the generated
multipart/form-dataresource that correspond to non-file fields must not have aContent-Typeheader specified. Their names and values must be encoded using the character encoding selected above.File names included in the generated
multipart/form-dataresource (as part of file fields) must use the character encoding selected above, though the precise name may be approximated if necessary (e.g., newlines could be removed from file names, quotes could be changed to "%22", and characters not expressible in the selected character encoding could be replaced by other characters).The boundary used by the user agent in generating the return value of this algorithm is the
multipart/form-databoundary string. (This value is used to generate the MIME type of the form submission payload generated by this algorithm.)
For details on how to interpret multipart/form-data payloads, see RFC 7578. [RFC7578]
4.10.21.8. Plain text form data
The text/plain encoding algorithm is as follows:
- Let result be the empty string.
- Let encoding be the result of picking an encoding for the form.
- Let charset be the name of encoding.
- If the entry’s name is "
_charset_" and its type is "hidden", replace its value with charset. - If the entry’s type is "
file", replace its value with the file’s name only. -
For each entry in the form data set, perform these substeps:
- Append the entry’s name to result.
- Append a single U+003D EQUALS SIGN character (=) to result.
- Append the entry’s value to result.
- Append a U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN (CR) U+000A LINE FEED (LF) character pair to result.
- Return the result of encoding result using encoding.
Payloads using the text/plain format are intended to be human readable. They are
not reliably interpretable by computer, as the format is ambiguous (for example, there is no way
to distinguish a literal newline in a value from the newline at the end of the value).
4.10.22. Resetting a form
When a form element form is reset, the user agent must fire a simple event named reset, that bubbles and is cancelable, at form, and then, if that event is not canceled, must invoke the reset algorithm of each resettable element whose form owner is form.
When the reset algorithm is invoked by the reset() method, the reset event
fired by the reset algorithm must not be trusted.
Each resettable element defines its own reset algorithm. Changes made to form controls as part of
these algorithms do not count as changes caused by the user (and thus, e.g., do not cause input events to fire).