1 Introduction
The popularity of VoiceXML 2.0 [VXML2] spurred the development of numerous voice browser implementations
early in the specification process.
[VXML2] has been phenomenally successful
in enabling the rapid deployment of voice applications that handle
millions of phone calls every day. This success has led to the development of additional, innovative features
that help developers build even more powerful voice-activated services.
While it was too late to incorporate these additional features into [VXML2],
the purpose of VoiceXML 2.1 is to formally specify the most common features to ensure their portability
between platforms and at the same time maintain complete backwards-compatibility with [VXML2].
This document defines a set of 8 commonly implemented
additional features to
VoiceXML 2.0 [VXML2].
2 Referencing Grammars Dynamically
As described in section
3.1 of [VXML2],
the <grammar> element allows the specification of a speech recognition or DTMF grammar.
VoiceXML 2.1 extends the <grammar> element to support the following additional attribute:
Table 1: <grammar> Attributes| expr |
Equivalent to src, except that the URI is dynamically determined by evaluating the given ECMAScript expression.
The expression must be evaluated each time the grammar needs to be activated.
|
|---|
Exactly one of "src", "expr", or an inline grammar must be specified;
otherwise, an error.badfetch event is thrown.
The following example dynamically selects the appropriate grammar
and prompt based on whether or not the user is signed in.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml"
version="2.1">
<var name="signedIn" expr="false"/>
<var name="theGrammar" expr="signedIn ? 'loggedin.grxml' : 'anonymous.grxml'"/>
<var name="thePrompt" expr="signedIn ?
'Say balances, trade stocks, or get quote' : 'Say sign in or get quote.' "/>
<form id="main">
<field name="opt">
<grammar type="application/srgs+xml" expr="theGrammar"/>
<prompt><value expr="thePrompt"/></prompt>
<filled>
<prompt>You said <value expr="opt"/></prompt>
</filled>
</field>
</form>
</vxml>
The following example dynamically selects the appropriate grammar and prompt
based on whether the user is a novice or an expert.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml"
version="2.1">
<var name="userLevel" expr="'novice'"/>
<var name="thePrompt" expr="userLevel == 'novice' ?
'To obtain your balances, say balances or press 1. To trade stocks, say stocks or press 2.' :
'Say balances or trade.' "/>
<form id="main">
<field name="opt">
<grammar type="application/srgs+xml" expr="'mainmenu_' + userLevel + '.grxml'"/>
<prompt><value expr="thePrompt"/></prompt>
<filled>
<prompt>You said <value expr="opt"/></prompt>
</filled>
</field>
</form>
</vxml>
3 Referencing Scripts Dynamically
As described in section
5.3.12 of [VXML2],
the <script> element allows the specification of a block of
client-side scripting language code,
and is analogous to the [HTML4] <SCRIPT> element.
VoiceXML 2.1 extends the <script> element to support the following additional attribute:
Table 2: <script> Attributes| expr |
Equivalent to src, except that the URI is dynamically determined by evaluating the given ECMAScript expression.
The expression must be evaluated each time the script needs to be executed. |
|---|
Exactly one of "src", "expr", or an inline script must be specified; otherwise, an error.badfetch event is thrown.
The following example retrieves a parameterized script based on the value of the variable user_id.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml"
version="2.1">
<form>
<var name="user_id" expr="12345"/>
<script expr="'http://acme.passport.net/?id=' + user_id"/>
</form>
</vxml>
4 Using <mark> to Detect Barge-in During Prompt Playback
As described in section 2.3.2
of [SSML], the <mark> element
places a marker into the text/tag sequence. An SSML processor must either allow the
VoiceXML interpreter to retrieve or must inform the interpreter when a <mark> is
executed during audio output.
[SSML] defines a single attribute, name, on the <mark> element, allowing the
programmer to name the mark.
VoiceXML 2.1 extends the <mark> element to support the following additional attribute:
Table 3: <mark> Attributes| nameexpr | An ECMAScript expression which evaluates to the name of the mark.
|
|---|
Exactly one of "name" and "nameexpr" must be specified; otherwise, an error.badfetch event is thrown.
As described in section 4.1.1
of [VXML2], the <mark> element is permitted
in conforming VoiceXML documents, but
[VXML2] does not specify a standard way for VoiceXML processors
to access <mark> element information.
Processors of conforming VoiceXML 2.1 documents
must set the following two properties on
the application.lastresult$ object whenever the application.lastresult$
object is assigned (e.g. a <link> is matched) and a <mark> has been executed.
Table 4: <mark>-related application.lastresult$ properties| markname |
The name of the mark last executed
by the SSML processor before barge-in occurred or
the end of audio playback occurred.
If no mark was executed, this variable is undefined.
|
|---|
| marktime |
The number of milliseconds that elapsed since the last mark was
executed by the SSML processor
until barge-in occurred or the end of audio playback occurred.
If no mark was executed, this variable is undefined. |
|---|
When a <mark> is executed during the processing of a form item, the interpreter sets
shadow variables, the names of which correspond to the properties of the application.lastresult$ object.
The value of each shadow variable must be identical to the value of the corresponding application.lastresult$ property.
The following example establishes marks at the beginning and at the end of an advertisement.
In the <filled>, the code checks which mark, if any, was last
executed when bargein occurred.
If the "ad_start" mark is executed but "ad_end" is not,
the code checks that at least 5 seconds of the advertisement has been played
and sets the played_ad variable appropriately.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml"
version="2.1">
<var name="played_ad" expr="false"/>
<form>
<field name="team">
<prompt>
<mark name="ad_start"/>
Baseball scores brought to you by Elephant Peanuts.
There's nothing like the taste of fresh roasted peanuts.
Elephant Peanuts. Ask for them by name.
<mark name="ad_end"/>
<break time="500ms"/>
Say the name of a team. For example, say Boston Red Sox.
</prompt>
<grammar type="application/srgs+xml" src="teams.grxml"/>
<filled>
<if cond="typeof(team$.markname) == 'string' &&
(team$.markname=='ad_end' ||
(team$.markname=='ad_start' &&
team$.marktime >= 5000))">
<assign name="played_ad" expr="true"/>
<else/>
<assign name="played_ad" expr="false"/>
</if>
</filled>
</field>
</form>
</vxml>
5 Using <data> to Fetch XML Without Requiring a Dialog Transition
The <data> element allows a VoiceXML application to fetch arbitrary XML data from
a document server
without transitioning to a new VoiceXML document.
The XML data fetched by the <data> element is bound to ECMAScript
through the named variable that exposes a read-only subset of
the W3C Document Object Model (DOM).
Attributes of <data> are:
Table 5: <data> Attributes| src | The URI specifying the location of the XML data to retrieve. |
|---|
| name | The name of the variable that exposes the DOM. |
|---|
| expr | Like src, except that the URI is dynamically determined
by evaluating the given ECMAScript expression when the data needs to be fetched. |
|---|
| method | The request method: get (the default) or post. |
|---|
| namelist |
The list of variables to submit.
By default, no variables are submitted.
If a namelist is supplied, it may contain individual variable references which are submitted
with the same qualification used in the namelist.
Declared VoiceXML and ECMAScript variables can be referenced.
|
|---|
| enctype | The media encoding type of the submitted document.
The default is application/x-www-form-urlencoded.
Interpreters must also support multipart/form-data and may support additional encoding types. |
|---|
| fetchaudio | See Section 6.1 of
[VXML2]. |
|---|
| fetchhint | See Section 6.1 of
[VXML2]. |
|---|
| fetchtimeout | See Section 6.1 of
[VXML2]. |
|---|
| maxage | See Section 6.1 of
[VXML2]. |
|---|
| maxstale | See Section 6.1 of
[VXML2]. |
|---|
Exactly one of "src" or "expr" must be specified; otherwise, an error.badfetch event is thrown.
Platforms should support parsing the XML data into a DOM.
If an implementation does not support DOM, the name attribute must not be set,
and any retrieved content must be ignored by the interpreter.
If the name attribute is present, these implementations will throw error.unsupported.data.name.
If the name attribute is present,
the VoiceXML interpreter must expose the retrieved content via a read-only subset of the DOM as specified
in Appendix D.
If the content cannot be retrieved, the
interpreter throws
an error
as specified for fetch failures in Section 5.2.6
of [VXML2].
If the retrieved content is not well-formed XML, the interpreter throws error.badfetch.
Like the <var> element, the <data> element can occur in executable content or as a child of
<form> or <vxml>. In addition, it shares the same scoping rules as the <var> element.
If a <data> element has the same name as a variable already declared in the same scope,
the variable is assigned a reference to the DOM exposed by the <data> element.
If use of the DOM causes a DOMException to be thrown, but the DOMException is not caught by an ECMAScript catch handler,
the VoiceXML interpreter throws error.semantic.
Like the <submit> element, when an ECMAScript variable is submitted to the server
its value is first converted into a string before being submitted.
If the variable is an ECMAScript Object the mechanism by which it is submitted is not currently defined.
If a <data> element's namelist contains a variable which references recorded audio
but does not contain an enctype of multipart/form-data, the behavior is not specified.
It is probably inappropriate to attempt to URL-encode large quantities of data.
In the examples that follow, the XML document fetched by the <data> element is in the following format:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?access-control allow="*.roadrunner.edu *.acme.edu"?>
<quote>
<ticker>F</ticker>
<name>Ford Motor Company</name>
<change>1.00</change>
<last>30.00</last>
</quote>
The following example assigns the value of the "last" element to the ECMAScript variable "price":
<data name="quote" src="quote.xml"/>
<script><![CDATA[
var price = quote.documentElement.getElementsByTagName("last").item(0).firstChild.data;
]]></script>The data is fetched when the <data> element is executed according to the caching rules
established in Section 6.1
of [VXML2].
Before exposing the data in the XML document referenced by the <data> element
via the DOM, the interpreter must check the "access-control" processing instruction included in the XML document indicating the
domains allowed to access the data. If the processing instruction is absent, or the domain, partial domain suffix, or IP address
of the document server that provided the VoiceXML document containing the <data> element is not listed, the
interpreter must throw error.noauthorization. The format of the "access-control" processing instruction is formally described in
Appendix E.
If the VoiceXML interpreter encounters multiple "access-control" processing instructions in the
retrieved XML document, it uses the last one encountered.
The following example retrieves a stock quote in one dialog, caches the DOM in a variable at document scope,
and uses the DOM to playback the quote in another dialog.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml"
version="2.1">
<var name="quote"/>
<var name="ticker" expr="'f'"/>
<form id="get_quote">
<block>
<data name="quote" expr="'http://www.quoteserver.com/getquote?ticker=' + ticker"/>
<assign name="document.quote" expr="quote.documentElement"/>
<goto next="#play_quote"/>
</block>
</form>
<form id="play_quote">
<script><![CDATA[
// retrieve the value contained in the node t from the DOM exposed by d
function GetData(d, t, nodata)
{
try {
return d.getElementsByTagName(t).item(0).firstChild.data;
}
catch(e)
{
// the value could not be retrieved, so return this instead
return nodata;
}
}
]]></script>
<block>
<!-- retrieve the change in the stock's value -->
<var name="change" expr="GetData(quote, 'change', 0)"/>
<!--play the company name -->
<audio expr="ticker + '.wav'"><value expr="GetData(quote, 'name', 'unknown')"/></audio>
<!-- play 'unchanged, 'up', or 'down' based on zero, positive, or negative change -->
<if cond="change == 0">
<audio src="unchanged_at.wav"/>
<else/>
<if cond="change > 0">
<audio src="up.wav"/>
<else/> <!-- negative -->
<audio src="down.wav"/>
</if>
<audio src="by.wav"/>
<!-- play change in value as positive number -->
<audio><value expr="Math.abs(change)"/></audio>
<audio src="to.wav"/>
</if>
<!-- play the current price per share -->
<audio><value expr="GetData(quote, 'last', 0)"/></audio>
</block>
</form>
</vxml>
6 Concatenating Prompts Dynamically Using <foreach>
The <foreach> element
allows a VoiceXML application to iterate through an ECMAScript array
and to execute the content contained within the <foreach>
element for each item in the array.
Attributes of <foreach> are:
Table 6: <foreach> Attributes| array | An ECMAScript expression that must evaluate to an array;
otherwise, an error.semantic event is thrown. |
|---|
| item | The variable that stores each array item upon each iteration
of the loop. A new variable will be declared if it is not already
defined within the parent's scope. |
|---|
The <foreach> element can occur
in executable content and as a child of <prompt>.
The following example calls a user-defined function GetMovieList
that returns an ECMAScript array. The array is assigned to the variable named 'prompts'.
Upon entering the <field>, if a noinput or a nomatch event occurs, the VoiceXML interpreter reprompts the user
by executing the second <prompt>. The second <prompt> executes the
<foreach> element
by iterating through the ECMAScript array 'prompts' and assigning each array element to the
variable 'thePrompt'.
Upon each iteration of the array, the interpreter executes the <audio> and <break>
elements contained within the <foreach> element.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml"
version="2.1">
<script src="movies.js"/>
<form id="pick_movie">
<!--
GetMovieList returns an array of objects
with properties audio and tts.
The size of the array is undetermined until runtime.
-->
<var name="prompts" expr="GetMovieList()"/>
<field name="movie">
<grammar type="application/srgs+xml" src="movie_names.grxml"/>
<prompt>Say the name of the movie you want.</prompt>
<prompt count="2">
<audio src="prelist.wav">When you hear the name of the movie you want, just say it.</audio>
<foreach item="thePrompt" array="prompts">
<audio expr="thePrompt.audio"><value expr="thePrompt.tts"/></audio>
<break time="300ms"/>
</foreach>
</prompt>
<noinput>
I'm sorry. I didn't hear you.
<reprompt/>
</noinput>
<noinput>
I'm sorry. I didn't get that.
<reprompt/>
</noinput>
</field>
</form>
</vxml>The following is a contrived implementation of the user-defined GetMovieList function:
function GetMovieList()
{
var movies = new Array(3);
movies[0] = new Object();
movies[0].audio = "godfather.wav"; movies[0].tts = "the godfather";
movies[1] = new Object();
movies[1].audio = "high_fidelity.wav"; movies[1].tts = "high fidelity";
movies[2] = new Object();
movies[2].audio = "raiders.wav"; movies[2].tts = "raiders of the lost ark";
return movies;
}When the interpreter queues the second <prompt>,
it expands the <foreach> element
in the previous example to the following:
<audio src="godfather.wav">the godfather</audio>
<break time="300ms"/>
<audio src="high_fidelity.wav">high fidelity</audio>
<break time="300ms"/>
<audio src="raiders.wav">raiders of the lost ark</audio>
<break time="300ms"/>
The following example combines the use of the <mark> and
<foreach> elements
to more precisely identify which item in a list of movies the user has selected.
During each iteration of the movies array, the interpreter
stores the current item in the array to the variable movie.
Upon execution of the <mark> element, the name of the <mark>
is set to the unique identifier of the movie as specified by the id property of the object
referenced by the variable movie.
In the <filled>, if the form item variable mov is set to the value
"more", indicating the user's desire to hear more detail about a movie,
the code retrieves the unique identifier of the desired movie from
mov$.markname. If barge-in occurred within twenty milliseconds
of the mark's execution, the code retrieves the unique identifier of the
preceding movie under the assumption that the user was slow to react.
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml"
version="2.1">
<script src="movies.js"/>
<form id="list_movies">
<!--
GetMovieList returns an array of objects
with properties audio, tts, and id.
The size of the array is undetermined until runtime.
-->
<var name="movies" expr="GetMovieList()"/>
<field name="mov">
<prompt>
Say the name of the movie.
</prompt>
<prompt count="2">
Here's the list of movies.
To hear more about a movie, say 'tell me more'.
<break time="500ms"/>
<foreach item="movie" array="movies">
<mark nameexpr="movie.id"/>
<audio expr="movie.audio"><value expr="movie.tts"/></audio>
<break time="500ms"/>
</foreach>
</prompt>
<grammar type="application/srgs+xml" src="more.grxml"/>
<grammar type="application/srgs+xml" src="movies.grxml"/>
<catch event="nomatch">
Sorry. I didn't get that.
<reprompt/>
</catch>
<catch event="noinput">
<reprompt/>
</catch>
<filled>
<var name="movie_id"/>
<if cond="'more' == mov">
<!-- user wants more detail -->
<if cond="mov$.markname != undefined && mov$.marktime <= 20">
<!-- returns the id of the previous movie (or the first) -->
<assign name="movie_id" expr="GetPreviousMovie(mov$.markname)"/>
<else/>
<assign name="movie_id" expr="mov$.markname"/>
</if>
<else/>
<!-- user said a specific movie -->
<assign name="movie_id" expr="mov"/>
</if>
<!--
Given an id, GetMovieDetail returns an object
with properties audio and tts.
-->
<var name="detail" expr="GetMovieDetail(movie_id)"/>
<audio expr="detail.audio"><value expr="detail.tts"/></audio>
</filled>
</field>
</form>
</vxml>The following is a contrived implementation of the user-defined GetMovieList function:
function GetMovieList()
{
var movies = new Array(3);
movies[0] = new Object(); movies[0].id = "m0010";
movies[0].audio = "godfather.wav"; movies[0].tts = "the godfather";
movies[1] = new Object(); movies[1].id = "m0052";
movies[1].audio = "high_fidelity.wav"; movies[1].tts = "high fidelity";
movies[2] = new Object(); movies[2].id = "m0027";
movies[2].audio = "raiders.wav"; movies[2].tts = "raiders of the lost ark";
return movies;
}When the interpreter queues the second <prompt>,
it expands the <foreach> element
in the previous example to the following:
<mark name="m0010"/>
<audio src="godfather.wav">the godfather</audio>
<break time="300ms"/>
<mark name="m0052"/>
<audio src="high_fidelity.wav">high fidelity</audio>
<break time="300ms"/>
<mark name="m0027"/>
<audio src="raiders.wav">raiders of the lost ark</audio>
<break time="300ms"/>
7 Recording User Utterances While Attempting Recognition
Several elements defined in [VXML2] can instruct the interpreter to accept user input during execution.
These elements include <field>, <initial>, <link>, <menu>, <record>, and <transfer>.
VoiceXML 2.1 extends these elements to allow the interpreter to conditionally
enable recording while simultaneously gathering input from the user.
To enable recording during recognition, set the value of the recordutterance property to true.
If the recordutterance property is set to true
in the current scope
, the following three
shadow variables are set on the appropriate form item variable:
Table 7: recordutterance-related shadow variables| recording |
The variable that stores a reference to the recording, or undefined if no audio is collected.
|
|---|
| recordingsize |
The size of the recording in bytes, or undefined if no audio is collected.
|
|---|
| recordingduration |
The duration of the recording in milliseconds, or undefined if no audio is collected.
|
|---|
The interpreter sets the corresponding properties on the application.lastresult$ object, and the value
of each property must be identical to the value of the corresponding shadow variable.
In the case of <link> and <menu>, the interpreter only sets the application.lastresult$ properties.
Support for this feature is optional on <record>, and <transfer>.
Platforms that support it set the aforementioned shadow variables on the associated form item variable
and the corresponding properties on the application.lastresult$ object
when the recordutterance property is set to true in an encompassing scope.
Like recordings created using the <record> tag, utterance recordings can be submitted to a document server
via HTTP POST using the namelist attribute of the <submit> and <subdialog> elements.
The enctype attribute must be set to "multipart/form-data", and the method attribute must be set to "post".
In the following example, the dialog requests a city and state from the user.
On the third recognition failure, the recording of the user's utterance is submitted to a Web server.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml"
version="2.1">
<form>
<property name="recordutterance" value="true"/>
<field name="city_state">
<prompt>
Say a city and state.
</prompt>
<grammar type="application/srgs+xml" src="citystate.grxml"/>
<nomatch>
I'm sorry. I didn't get that.
<reprompt/>
</nomatch>
<nomatch count="3">
<submit method="post"
enctype="multipart/form-data"
next="upload.cgi"
namelist="lastresult$.recording"/>
</nomatch>
</field>
</form>
</vxml>
7.1 Specifying the Media Format of Utterance Recordings
To specify the media format of the resulting recording, set the recordutterancetype property.
Platforms must support the audio file formats specified in Appendix E of [VXML2].
Other formats may also be supported. The recordutterancetype property defaults to a platform-specific
format which should be one of the required formats.
Note that the recordutterancetype property does not affect the <record> element.
8 Adding namelist to <disconnect>
As described in section
5.3.11 of [VXML2],
the <disconnect> element causes the interpreter context to disconnect from the user.
VoiceXML 2.1 extends the <disconnect> element to support the following attribute:
Table 8: <disconnect> Attributes| namelist |
Variable names to be returned to interpreter context.
The default is to return no variables;
this means the interpreter context will receive an empty ECMAScript object.
|
|---|
9 Adding type to <transfer>
As described in section
2.3.7 of [VXML2],
the <transfer> element directs the interpreter to connect the caller to another entity.
VoiceXML 2.1 extends the <transfer> element to support the following additional attribute:
Table 9: <transfer> Attributes| type |
The type of transfer. The value can be "bridge", "blind", or "consultation".
|
|---|
Exactly one of "bridge" or "type" may be specified; otherwise an error.badfetch event is thrown.
As specified in 2.3.7 of [VXML2],
the <transfer> element is optional, though platforms should support it.
Platforms that support <transfer> may support any combination of bridge, blind,
or consultation transfer types.
If the value of the type attribute is set to "bridge", the interpreter's behavior must be identical to its behavior
when the value of the bridge attribute is set to "true".
If the value of the type attribute is set to "blind", the interpreter's behavior must be identical to its behavior
when the bridge attribute is set to "false". The behavior of the bridge attribute is fully specified in
section 2.3.7 of [VXML2].
If the type attribute is specified and the bridge attribute is absent,
the value of the type attribute takes precedence over the default value of the bridge attribute.
The bridge attribute is maintained for backwards compatiblity with [VXML2].
Since all of the functionality of the bridge attribute has been incorporated into the type attribute,
developers are encouraged to use the type attribute on platforms that implement it.
The connecttimeout attribute of <transfer> applies if the type attribute is set to "bridge" or
"consultation".
The maxtime attribute of <transfer> applies if the type attribute is set to "bridge".
9.1 Consultation Transfer
The consultation transfer is similar
to a blind transfer except that the outcome of the transfer call setup
is known and the caller is not dropped as a result of an unsuccessful transfer attempt.
When performing a consultation transfer,
the platform monitors the progress of the transfer until the connection
is established between caller and callee.
If the connection cannot be established (e.g. no answer, line busy, etc.),
the session remains active and returns control to the application.
As in the case of a blind transfer, if the connection is established,
the interpreter disconnects from the session, connection.disconnect.transfer is thrown,
and document interpretation continues normally.
Any connection between the caller and the callee remains in place regardless of document execution.
Issue (xfer1):
The Voice Browser Working Group
would like to solicit feedback on the proposed value: "consultation".
Alternative proposals should consider the specified transfer functionality
in comparison to existing standards.
Resolution:
None recorded.
Figure 1: Audio Connections during a consultation transfer: <transfer type="consultation"/>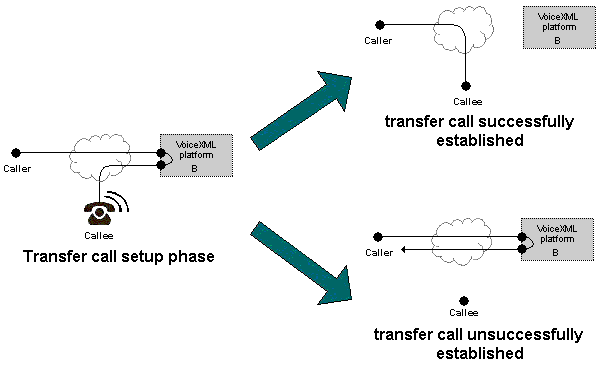 |
The possible outcomes for a consultation transfer before the connection to the callee is established are:
Table 10: Consultation Transfer Outcomes Prior to Connection Being Established| Action | Value of form item variable | Event | Reason |
|---|
| caller disconnects | | connection.disconnect.hangup | The caller hung up. |
| caller cancels transfer before outgoing call begins | near_end_disconnect | | The caller cancelled the transfer attempt via a DTMF or voice command
before the outgoing call begins (during playback of queued audio). |
| callee busy | busy | | The callee was busy. |
| network busy | network_busy | | An intermediate network refused the call. |
| callee does not answer | noanswer | | There was no answer within the time specified by the connecttimeout attribute. |
| --- | unknown | | The transfer ended but the reason is not known. |
The possible outcomes for a consultation
transfer once the connection to the callee is established are:
Table 11: Consultation Transfer Outcomes After Connection Has Been Established| Action | Value of form item variable | Event | Reason |
|---|
| transfer begins | undefined | connection.disconnect.transfer | The caller was transferred to another line and will not return. |
|---|
| transfer ends | unknown | | The transfer ended but the reason is not known. |
|---|
9.2 Consultation Transfer Errors and Events
One of the following events may be thrown during a consultation transfer:
Table 12: Events thrown during consultation transfer| Event | Reason |
|---|
| connection.disconnect.hangup | The caller hung up. |
|---|
| connection.disconnect.transfer | The caller was transferred to another line and will not return. |
|---|
If a consultation transfer could not be made,
one of the following errors will be thrown:
Table 13: Consultation transfer attempt error events| Error | Reason |
|---|
| error.connection.noauthorization | The caller is not allowed to call the destination. |
|---|
| error.connection.baddestination | The destination URI is malformed. |
|---|
| error.connection.noroute | The platform is not able to place a call to the destination. |
|---|
| error.connection.noresource | The platform cannot allocate resources to place the call. |
|---|
| error.connection.protocol.nnn | The protocol stack for this connection raised an exception
that does not correspond to one of the other error.connection events. |
|---|
| error.unsupported.transfer.consultation | The platform does not support consultation transfer. |
|---|
| error.unsupported.uri |
The platform does not support the URI format used.
The special variable _message
(section 5.2.2 of [VXML2])
will contain the string "The URI x is not a supported URI format"
where x is the URI from the dest or destexpr <transfer> attributes.
|
|---|
9.3 Example of a Consultation Transfer
The following example attempts to perform a consultation
transfer of the caller to a another party.
Prompts may be included before or within the <transfer> element.
This may be used to inform the caller of what is happening,
with a notice such as "Please wait while we transfer your call."
The <prompt> within the <block>, and the <prompt> within <transfer>
are queued and played before actually performing the transfer.
After the prompt queue is flushed, the outgoing call is initiated.
The "transferaudio" attribute specifies an audio file to be played to the caller in place of
audio from the far-end until the far-end answers. If the audio source is longer than the connect time,
the audio will stop playing immediately upon far-end answer.
Figure 2: Sequence and timing during an example of a consultation transfer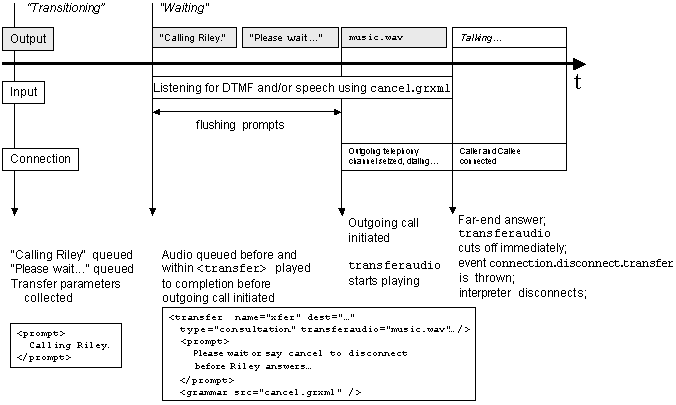 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<vxml version="2.1"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/vxml"
<catch event="connection.disconnect.transfer">
<!-- far-end answered -->
<log> Connection with the callee established: transfer executed.</log>
</catch>
<form id="consultation_xfer">
<block>
<!-- queued and played before starting the transfer -->
<prompt>
Calling Riley.
</prompt>
</block>
<!-- Play music while attempting to connect to far-end -->
<!-- Wait up to 60 seconds for the far end to answer -->
<transfer name="mycall" dest="tel:+1-555-123-4567"
transferaudio="music.wav" connecttimeout="60s" type="consultation">
<!-- queued and played before starting the transfer -->
<prompt>
Please wait...
</prompt>
<filled>
<if cond="mycall == 'busy'">
<prompt>
Riley's line is busy. Please call again later.
</prompt>
<elseif cond="mycall == 'noanswer'"/>
<prompt>
Riley can't answer the phone now. Please call
again later.
</prompt>
</if>
</filled>
</transfer>
<!-- submit call statistics to server -->
<block>
<submit namelist="mycall" next="/cgi-bin/report"/>
</block>
</form>
</vxml> 
