Status of this Document
This section describes the status of this document at
the time of its publication. Other documents may supersede this
document. A list of current W3C publications and the latest revision
of this technical report can be found in the W3C technical reports index
at http://www.w3.org/TR/.
This is a public
Working Draft
for review by W3C members and other interested parties. This document
is a product of the
XML Processing Model
Working Group which is part of the W3C XML Activity.
The English version of this specification is the only
normative version. However, for translations of this document, see
http://www.w3.org/2003/03/Translations/byTechnology?technology=xproc.
This is a Last Call Working Draft for review by W3C members and
other interested parties. It contains one significant addition to
previous drafts: a discussion of validation, as well as extensive
editorial changes made in response to reviewers comments on our
previous draft. Once again it is the Working Group's intention, since
this specification does not require new implementations, as many
existing XML processors implement one or more of the profiles defined
below, that no Candidate Recommendation version will be published, and
that the next step for this specification will be to Proposed
Recommendation—interested parties please take note and comment
accordingly.
The effective deadline for comments is 29 February 2012. Please send comments on this draft to the public mailing list public-xml-processing-model-comments@w3.org (public
archives are available).
As this specification is intended for use by other specifications
which themselves define one or more XML languages, the Working Group
particularly welcomes input for other Working Groups who are responsible for
such specifications.
Publication as a Working Draft does not imply endorsement by the
W3C Membership. This is a draft document and may be updated, replaced
or obsoleted by other documents at any time. It is inappropriate to
cite this document as other than work in progress.
This document was produced by a group operating under the 5
February 2004 W3C Patent Policy. W3C maintains a public
list of any patent disclosures made in connection with the
deliverables of the group; that page also includes instructions for
disclosing a patent. An individual who has actual knowledge of a
patent which the individual believes contains Essential
Claim(s) must disclose the information in accordance with section
6 of the W3C Patent Policy.
1 Introduction
Few specifications are implemented in their entirety, in exactly the
same way, by every implementor. Many specifications contain optional
features or areas of acknowledged variation and some implementors
choose to ignore required features that aren't needed by the community
they serve, chosing to trade conformance for other benefits.
In the case of XML, there are exists not only optionality in the XML
Recommendation itself, but there are a whole family of additional
specifications which an implementor may choose to support or ignore.
In principle, there are an enormous number of possible variations. In
practice, there are dependencies between the specifications that limit
the number of possible variations and implementors aren't motivated to
implement completely arbitrary selections.
The Infoset gave the community a vocabulary for discussing the items
produced by a parser. This specification
gives the community a vocabulary for describing common
sets of higher level features by
describing profiles, collecting specific sets of features
drawn from the family of specifications, and providing names for them.
One goal of this work is to help establish a lower bound on the number
and nature of features supported. The ability to communicate by sending XML documents back and forth
is predicated on the notion that we have the same understanding of
those documents. While we might
wish for the richest possible understanding, that's not likely to be
supported by the widest range of implementations. Establishing a few
basic profiles, we hope, provides a foundation on which other
specifications can build.
1.1 Background
The XML specification [Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 (Fifth Edition)] defines an XML processor as "a
software module. . .used to read XML documents and provide access to their
content and structure. . .on behalf of another module, called the application."
XML applications are often created by building on top of the [XML Information Set] vocabulary or XML data models such as [XML Path Language (XPath) Version 1.0] or [XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Data Model (XDM)], understood as the output of an XML processor. Such definitions have suffered to some extent from an uncertainty inherent in using that kind of foundation, in that the kind of processing which XML processors carry out on XML documents, as well as the amount of information they provide to applications as a result, is flexible to a certain extent. Some of this flexibility stems from the XML specification itself, which is not always explicit about what information must be passed from processor to application, and which also leaves open the possiblity of reading and interpreting external entities, or not. Another kind of flexibility has arisen from the growth of the XML family of specifications: if the input document includes uses of XInclude, for instance.
This specification addresses this issue by defining several XML processor
profiles, each of which defines how any given XML
document should be processed, both operationally and in
terms of what information must be made available to applications. It is intended as a resource for other specifications, which can by
a single normative reference establish precisely what input processing they
require as well as what information they require.
The profiles presented here are designed for use with respect
to static outcomes, that is, to the result of XML processing as (if) produced by a
batch process.
They do not attempt to address the question of the
preservation or lack thereof of information itself, or of information
invariants, in the course of incremental construction or in the face of
piecemeal modification.
The profiles defined here are appropriate for processing both XML 1.0 [Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 (Fifth Edition)] and XML 1.1 [Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.1 (Second Edition)] documents. References to XML or XML Namespaces below should be understood as references to 1.0 or 1.1 as required by the relevant document or application.
1.2 Terminology
[Definition: The key words
must, must not, required,
shall, shall not, should,
should not, recommended, may,
and optional in this specification are to be interpreted
as described in [RFC 2119].]
The term base URI is used in this specification as it is defined in [RFC 3986].
2 XML processor profiles
The profile
definitions which follow all assume that the starting point is a well-formed and namespace well-formed XML document. This specification does not consider documents
that are not namespace well-formed. Documents which are not well-formed are not XML.
Each profile is defined in terms of conformance requirements on processors
with respect to various XML-family specifications, and in terms of requirements
on the information they provide to applications. Information provision requirements are specified by
reference to classes of information items and properties, as further defined in 3 Classes of Information.
It is the information itself which is required, not the
particular packaging of it implied by the items and properties used to define
those information classes. Processors typically package information in terms of
more-or-less standardized data models or application program
interfaces (APIs). How the information
required for conformance to a particular profile defined below is conveyed by a
data model or API need
not correspond point-for-point to the Infoset terminology. For example, a data model may expose element
content as an array of strings. That does not prevent it from conforming to
the requirements expressed below in terms of the [XML Information Set]'s
Character Information Items, for example requirement (3) of 2.1 The basic XML processor profile.
The four profiles defined here identify four increasingly rich
profiles, in terms of kinds of processing and amount of information
provided to applications, starting from a profile very close to what many XML
processors do already in their minimal configuration:
The Basic profile adds only support for xml:base processing to
the minimum expected of all processors, in order to allow for
correct resolution of relative URIs;
The Id profile adds xml:id processing in order to identify
IDs in the possible absence of complete attribute type declaration
information;
The External Declarations
profile adds mandatory external
markup declaration processing in order to guarantee all
information-affecting declarations are processed;
The Full profile adds xi:include processing, in order to
transclude linked infosets as parsed XML or as text, recursively as
required.
The precise nature of each of these profiles is described in the sections which follow.
3 Classes of Information
For the profile definitions above and the invariants below, we
categorize the information expressed in XML documents, which
may be made available to applications, into a number of
(overlapping) classes. What follows is a complete tabulation of all the
information items and their properties from [XML Information Set], annotated
with one or more class labels.
Note:
The glosses which follow immediately below here are explanatory: the
actual class definitions are given in the subsequent table
- Class Core
Items and properties which are fundamental for
all XML applications and so must be provided by all profiles.
- Class Extended
Items and properties which depend on declarations and so must be provided by 2.3 The external declarations XML processor profile and 2.4 The full XML processor profile only
- Class Signal
Items and properties which only are relevant when entity declarations are not available and so must be provided by 2.1 The basic XML processor profile and 2.2 The id XML processor profile only
- Class Decl
Items and properties which depend on declarations.
For 2.1 The basic XML processor profile and 2.2 The id XML processor profile, they will not be provided if the relevant declaration
is in an unprocessed external entity, or is after the first reference to an external entity
which is not processed.
- Class Validated
Items and properties which will be present for
validating processors, but for which support by non-validating processors is
implementation-defined. Non-validating processors must document whether they
provide this information to applications or not. For the definition of
implementation-defined, and the contrasting term
implementation-determined, see the XPath 2.0 specification
- Class ImplDef
Items and properties for which support is
implementation-defined. Processors must document whether they
provide this information to applications or not.
The tabulation which follows defines the information classes by
enumerating their membership in terms of information items and their
properties—each class contains all and only those items and properties
against which its name appears below.
- Document Information Item
- Element Information Item
- Attribute Information Item
| the item itself | Core |
| [namespace name] | Core |
| [local name] | Core |
| [prefix] | Core |
| [normalized value] | Extended, Decl |
| [specified] | Core |
| [attribute type] | Extended, Decl |
| [references] to Element Information Items, i.e. for attributes of types IDREF and IDREFS | Extended, Decl |
| [references] to Notation and Unparsed Entity Information Items, i.e. for attributes of types ENTITY, ENTITIES and NOTATION | ImplDef |
| [owner element] | Core |
- Processing Instruction Information Item
- Unexpanded Entity Reference Information Item
Note:
This type of information item will not occur at all if standalone="yes"
- Character Information Item
- Comment Information Item
- Document Type Declaration Information Item
- Unparsed Entity Information Item
- Notation Information Item
- Namespace Information Item
4 Relations and Invariants
Whenever a
document is processed in conformance with one of the profiles defined
above, the information made available to applications will
be guaranteed to have certain properties. The relation between the profiles and information classes
defined above is summarized in the illustration below (PNG,SVG), then the sub-sections which follow describe
this in terms of invariants with respect to the information made available.
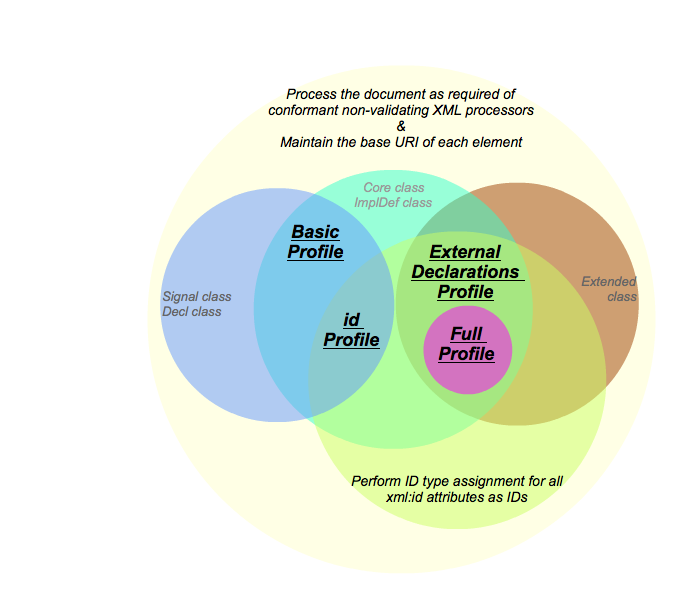
Note: in an effort to maintain consistent
relationships in the diagram, the label for the inner-most circle,
around “Full Profile”, has been omitted. It should be read as if it was
labeled “Perform XInclude processing”.
4.1 Information invariants within a given profile
Every instance of processing a given namespace-well-formed XML
document in conformance with the
same profile will make available
exactly the same information with respect to the information items and
properties which
that profile is required to provide accurately, as tabulated above.
4.2 Information variation between profiles
In comparing two cases when a given namespace-well-formed XML
document is processed in conformance with
two different profiles, the information made available will in some cases (depending on
the specifics of the document in question) differ with repect to the following information items and
properties (leaving aside the items and
properties classified as implementation-defined above):
4.2.1 Between basic and richer profiles
- Attribute Information Items
[normalized value],
[attribute type],
[references]—These properties may vary for xml:id attributes
And all the differences listed in the next two sections.
4.2.2 Between id and richer profiles
Where an id processor reports an Unexpanded Entity
Reference, richer ones will report the entity expansion, that is, they will report
some number of information items and their associated properties. For this reason,
the information reported from an id processor may differ from that reported by
a processor conforming to a richer profile with respect to any or all of
Element, Attribute, Character, Comment, Namespace, Processing Instruction and
Unexpanded Entity Reference Information Items.
- Attribute Information Items
With respect to [normalized value],
[specified],
[attribute type] and
[references] where an id processor has not processed the relevant
declaration, but a richer one has.
And all the differences listed in the next section.
4.2.3 Between external declarations and full profiles
Parallel to the case for expanding entity references in the previous
section, XInclude processing in conformance with the full profile may replace
some (XInclude) Element Information Items reported by processing in conformance
to other profiles with some amount of different
information, corresponding to Element, Attribute, Character, Comment,
Namespace and Processing Instruction Information Items.
5 Other profiles (non-normative)
The profiles defined here can be used as a starting point for the definition of further profiles. For example, the media type registrations for stylesheet languages applicable to XML such as application/xslt+xml or text/css might define a profile specifying appropriate <?xml-stylesheet type="[their media type]" . . .?> processing in addition to the processing required by 2.2 The id XML processor profile.
6 Conformance
Conformance to this specification means conformance by XML processors to profiles, as specified in 2 XML processor profiles.
Which profile or profiles an XML processor conforms to may depend on how it is configured. The conformance conditions for any specific
processor configuration with respect to each profile are specified in the
corresponding sub-section of 2 XML processor profiles.
Accordingly, any specification which references this one
normatively
is recommended to do so in terms such as "Conforming implementations
must process XML documents and make information available as
required by the id
XML processor profile."
7 Validation (Non-normative)
Specifying desired information outcomes is not sufficient to completely
determine XML processor behaviour. In particular, if validation is performed
and errors detected, the result may be no outcome at all.
A range of schema languages and approaches to validation
exist. Some may provide for additional information items and/or properties
which are not addressed by this specification. Also, the validation-dependent [element content whitespace] property of Character Information Items
may only be
reliably provided in conjunction with some approaches
to validation, specifically DTD validation.
Furthermore, not all of the profiles defined above can be combined with all forms of validation: in particular, DTD
validation requires that all external markup declarations be read and processed, and so cannot be required in conjunction with 2.1 The basic XML processor profile or 2.2 The id XML processor profile.
Accordingly, specifications referencing this one should also specify
whether validation is forbidden, optional or required, with respect to which
schema language(s) with what validation control settings, if
any. If the 2.4 The full XML processor profile is involved,
careful consideration is required as to whether validation is to happen before XInclude processing, or after, or both.
