HTML5
A vocabulary and associated APIs for HTML and XHTML
This is revision 1.5612.
This is revision 1.5612.
An image map allows geometric areas on an image to be associated with hyperlinks.
An image, in the form of an img element or an
object element representing an image, may be associated
with an image map (in the form of a map element) by
specifying a usemap attribute on
the img or object element. The usemap attribute, if specified,
must be a valid hash-name reference to a
map element.
Consider an image that looks as follows:
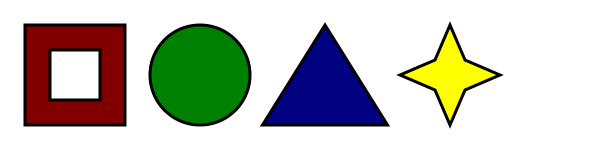
If we wanted just the colored areas to be clickable, we could do it as follows:
<p>
Please select a shape:
<img src="shapes.png" usemap="#shapes"
alt="Four shapes are available: a red hollow box, a green circle, a blue triangle, and a yellow four-pointed star.">
<map name="shapes">
<area shape=rect coords="50,50,100,100"> <!-- the hole in the red box -->
<area shape=rect coords="25,25,125,125" href="red.html" alt="Red box.">
<area shape=circle coords="200,75,50" href="green.html" alt="Green circle.">
<area shape=poly coords="325,25,262,125,388,125" href="blue.html" alt="Blue triangle.">
<area shape=poly coords="450,25,435,60,400,75,435,90,450,125,465,90,500,75,465,60"
href="yellow.html" alt="Yellow star.">
</map>
</p>
If an img element or an object element
representing an image has a usemap attribute specified,
user agents must process it as follows:
First, rules for parsing a hash-name reference
to a map element must be followed. This will return
either an element (the map) or null.
If that returned null, then abort these steps. The image is not associated with an image map after all.
Otherwise, the user agent must collect all the
area elements that are descendants of the map. Let those be the areas.
Having obtained the list of area elements that form
the image map (the areas), interactive user
agents must process the list in one of two ways.
If the user agent intends to show the text that the
img element represents, then it must use the following
steps.
In user agents that do not support images, or that
have images disabled, object elements cannot represent
images, and thus this section never applies (the fallback
content is shown instead). The following steps therefore only
apply to img elements.
Remove all the area elements in areas that have no href attribute.
Remove all the area elements in areas that have no alt attribute, or whose alt attribute's value is the empty
string, if there is another area element in
areas with the same value in the href attribute and with a
non-empty alt attribute.
Each remaining area element in areas represents a hyperlink. Those
hyperlinks should all be made available to the user in a manner
associated with the text of the img.
In this context, user agents may represent area and
img elements with no specified alt attributes, or whose alt
attributes are the empty string or some other non-visible text, in
a user-agent-defined fashion intended to indicate the lack of
suitable author-provided text.
If the user agent intends to show the image and allow interaction
with the image to select hyperlinks, then the image must be
associated with a set of layered shapes, taken from the
area elements in areas, in reverse
tree order (so the last specified area element in the
map is the bottom-most shape, and the first
element in the map, in tree order, is the
top-most shape).
Each area element in areas must
be processed as follows to obtain a shape to layer onto the
image:
Find the state that the element's shape attribute represents.
Use the rules for parsing a list of integers to
parse the element's coords
attribute, if it is present, and let the result be the coords list. If the attribute is absent, let the
coords list be the empty list.
If the number of items in the coords
list is less than the minimum number given for the
area element's current state, as per the following
table, then the shape is empty; abort these steps.
| State | Minimum number of items |
|---|---|
| Circle state | 3 |
| Default state | 0 |
| Polygon state | 6 |
| Rectangle state | 4 |
Check for excess items in the coords
list as per the entry in the following list corresponding to the
shape attribute's state:
If the shape attribute
represents the rectangle
state, and the first number in the list is numerically less
than the third number in the list, then swap those two numbers
around.
If the shape attribute
represents the rectangle
state, and the second number in the list is numerically less
than the fourth number in the list, then swap those two numbers
around.
If the shape attribute
represents the circle
state, and the third number in the list is less than or
equal to zero, then the shape is empty; abort these steps.
Now, the shape represented by the element is the one
described for the entry in the list below corresponding to the
state of the shape
attribute:
Let x be the first number in coords, y be the second number, and r be the third number.
The shape is a circle whose center is x CSS pixels from the left edge of the image and y CSS pixels from the top edge of the image, and whose radius is r pixels.
The shape is a rectangle that exactly covers the entire image.
Let xi be the (2i)th entry in coords, and yi be the (2i+1)th entry in coords (the first entry in coords being the one with index 0).
Let the coordinates be (xi, yi), interpreted in CSS pixels measured from the top left of the image, for all integer values of i from 0 to (N/2)-1, where N is the number of items in coords.
The shape is a polygon whose vertices are given by the coordinates, and whose interior is established using the even-odd rule. [GRAPHICS]
Let x1 be the first number in coords, y1 be the second number, x2 be the third number, and y2 be the fourth number.
The shape is a rectangle whose top-left corner is given by the coordinate (x1, y1) and whose bottom right corner is given by the coordinate (x2, y2), those coordinates being interpreted as CSS pixels from the top left corner of the image.
For historical reasons, the coordinates must be interpreted
relative to the displayed image after any stretching
caused by the CSS 'width' and 'height' properties (or, for non-CSS
browsers, the image element's width and
height attributes — CSS browsers map
those attributes to the aforementioned CSS properties).
Browser zoom features and transforms applied using CSS or SVG do not affect the coordinates.
Pointing device interaction with an image associated with a set
of layered shapes per the above algorithm must result in the
relevant user interaction events being first fired to the top-most
shape covering the point that the pointing device indicated, if any,
or to the image element itself, if there is no shape covering that
point. User agents may also allow individual area
elements representing hyperlinks to
be selected and activated (e.g. using a keyboard).
Because a map element (and its
area elements) can be associated with multiple
img and object elements, it is possible
for an area element to correspond to multiple focusable
areas of the document.
Image maps are live; if the DOM is mutated, then the user agent must act as if it had rerun the algorithms for image maps.