CERN: The European Particle Physics Laboratory
http://www.w3.org/2007/Talks/1211-whit-tbl/
MIT Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)
Southampton University School of Electronics and Computer Science
World Wide Web Consortium
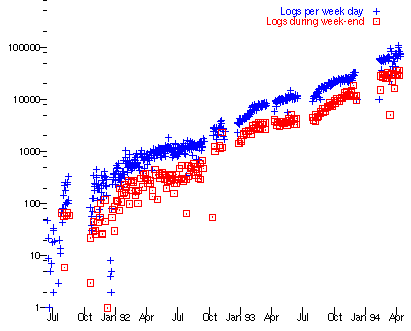
WHIT 3.0 2007now difficult to explain what it was like!

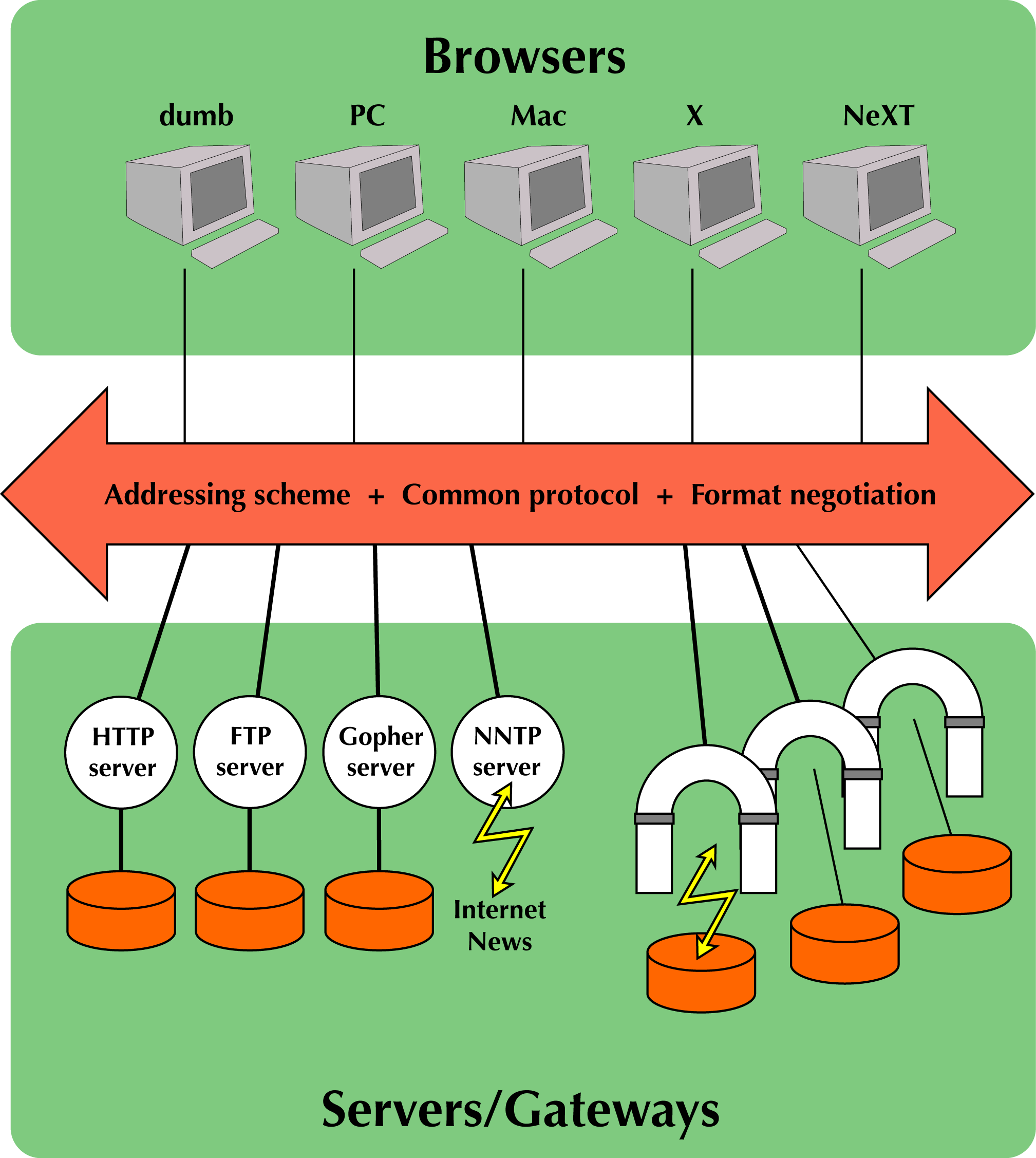
Need to bridge
> ENQUIRE
Enquire V 1.1
Hello!
Opening file (PSK-PCP)VAC-V1:ENQR...
PSB Vacuum Control System (concept) < O>
--- ------ ------- ------
[ 1] described-by: Enquiry System
An experimental system for which this is a test.
[ 2] includes: Vacuum History System
Records and displays slow changes in pressure.
[ 3] includes: Vacuum equipment modules
Perform all the hardware interface
[ 4] includes: Control and status applications programs
Provide operator interaction from the consoles.
[ 5] described-by: Controle du System a Vide du Booster 11-2-80
Operational specification of the software
[ 6] includes: PSB Pump Surveillance System PCP 228
Allows rapid monitoring of pressure changes
[number ]Circles and arrows again...

independence of:
good + fair + fast
w3.orgLeading the web to its full potential
has been the best part

(branches: Historical Roadmap Web Science)
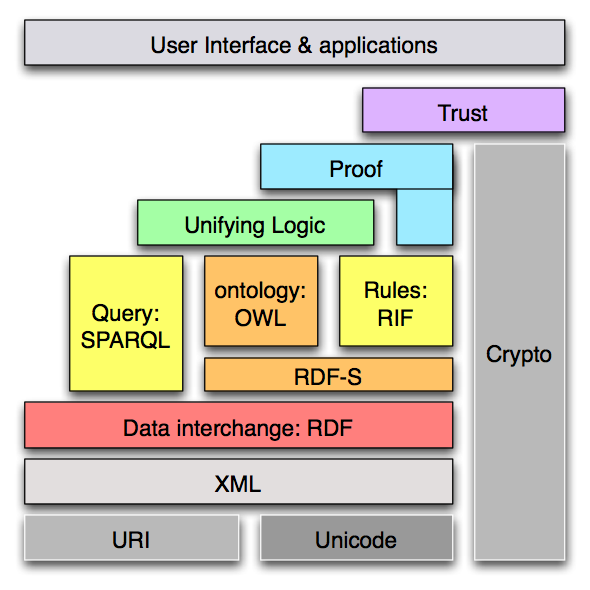
Internet/Web layer separation
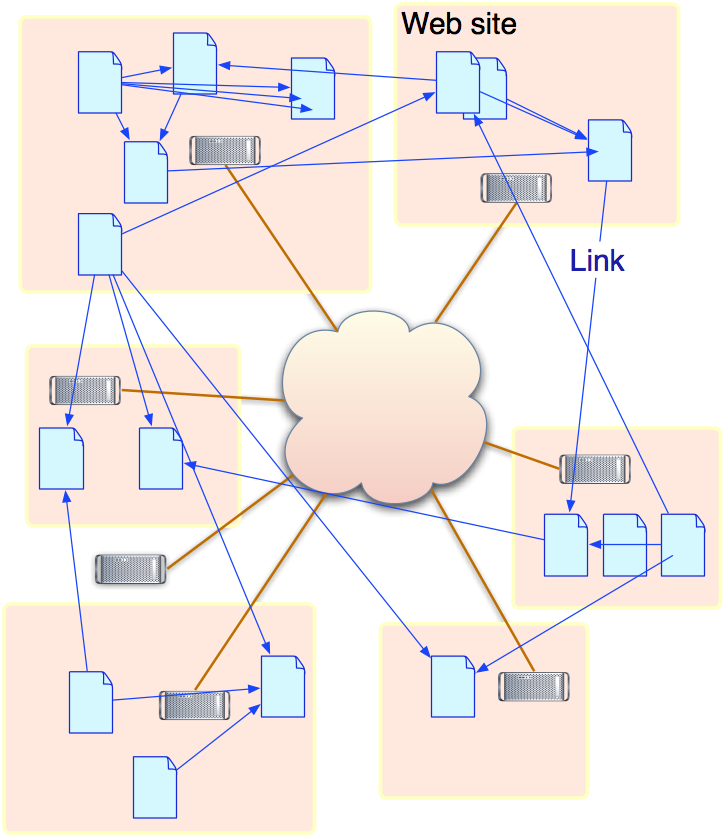


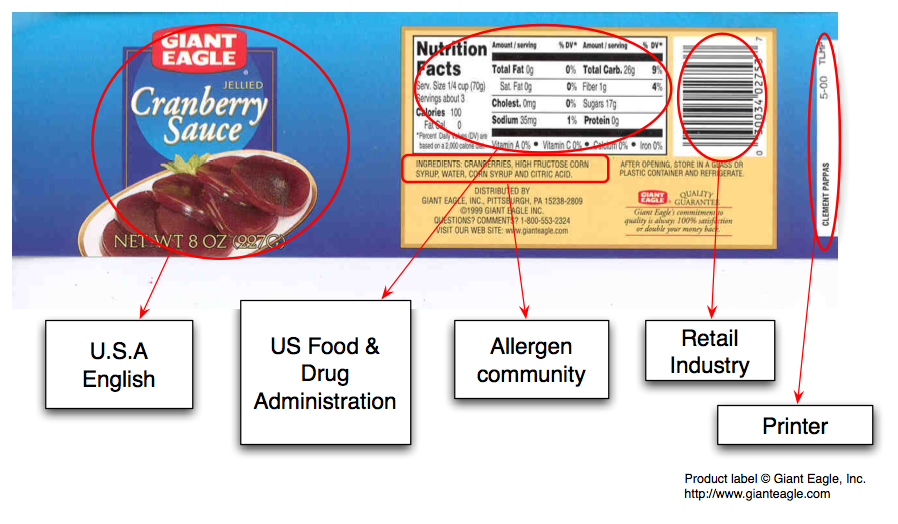
Mixture of international, national, industry and local terms
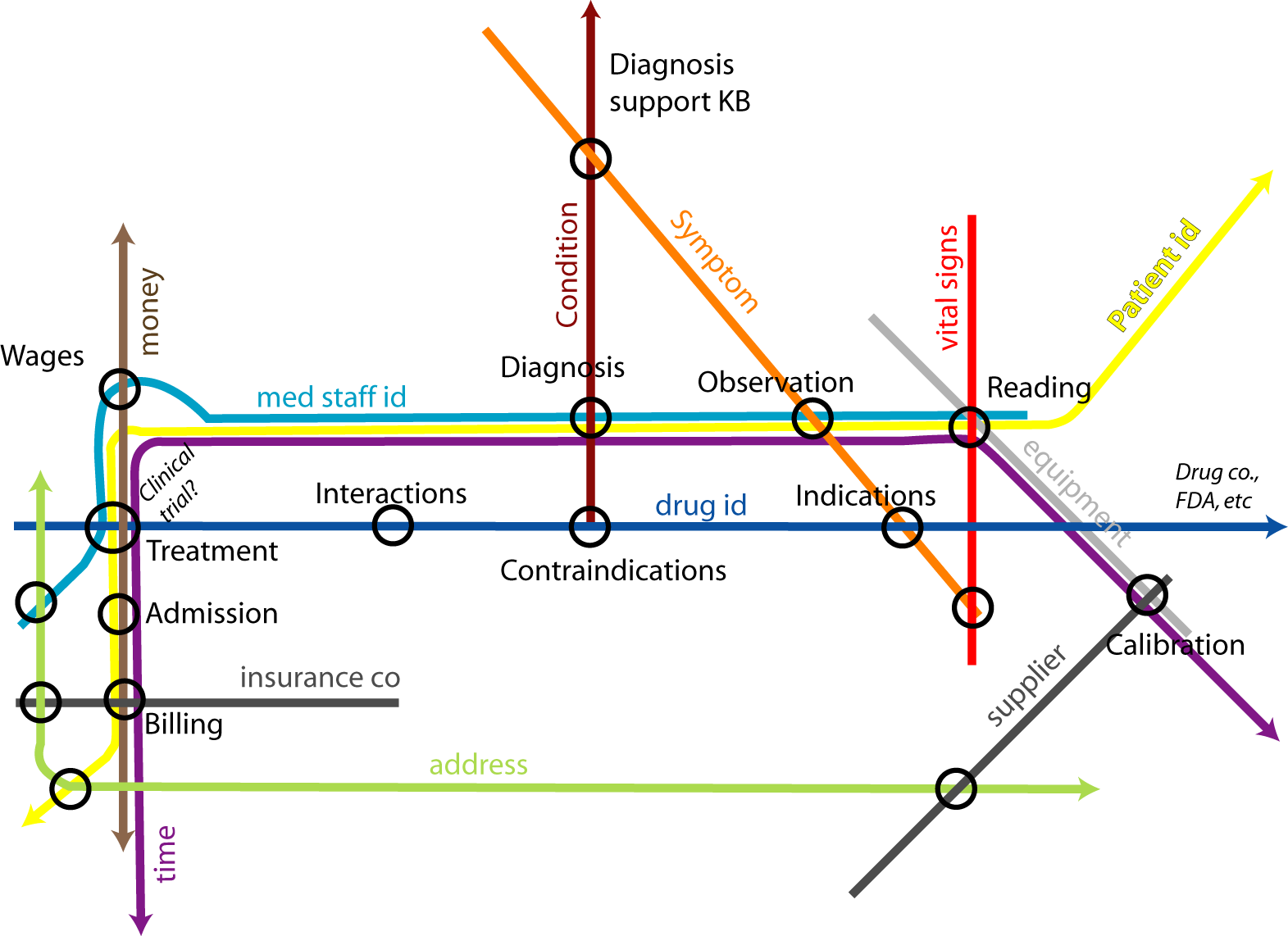
| dc:title | Data Integration and Transparency | ||||||||||
| cc:license | <http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/> | ||||||||||
| dc:creator |
|
||||||||||
| tk:event |
|
||||||||||
| tk:slides | <http://www.w3.org/2007/Talks/0618-egov-tbl> | ||||||||||
| tim:slideCount | 12 |
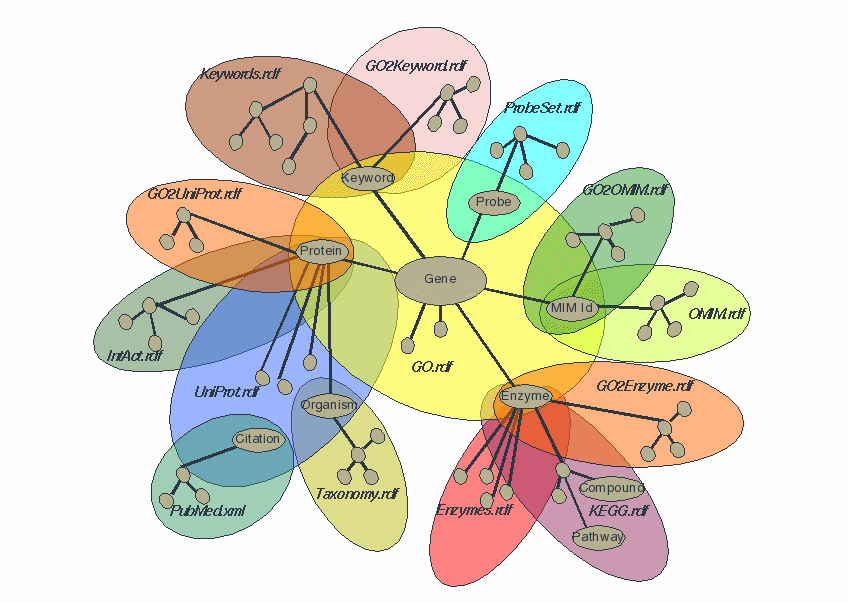
One item may involve data from many ontologies
| Local | Wider |
|---|---|
| Local reuse only | Wider reuse |
| Local terms | Global or shared terms |
| Fast | Takes effort |


Don't say "colour" say <http://example.com/2002/std6#col>
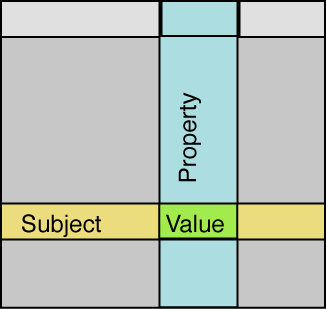
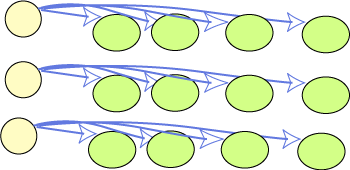
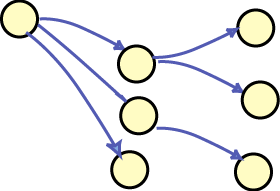
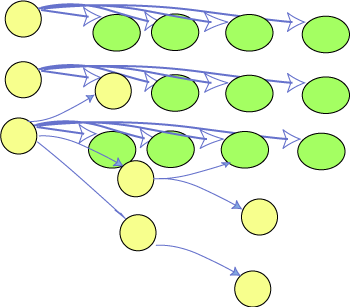
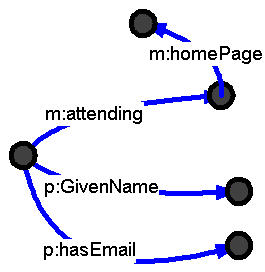
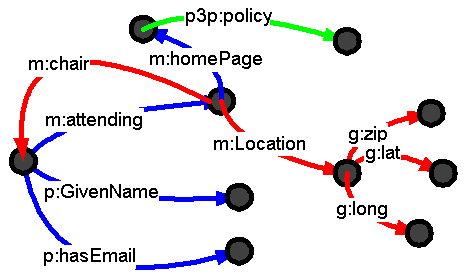
Subject and object node using same URIs
New data applications can be built on top of RDF bus, for example:
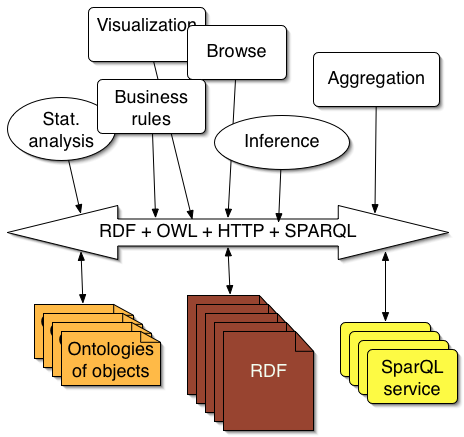
Keep your existing systems running - adapt them
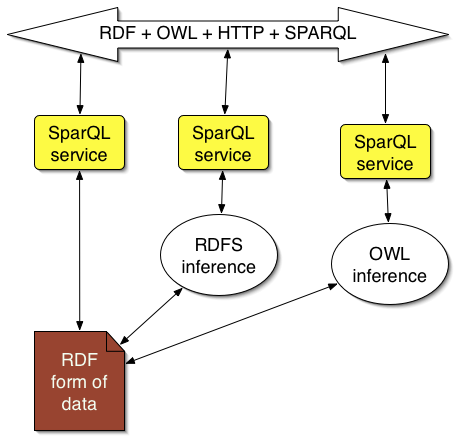
Virtual severs actually figure stuff out as well as look up data
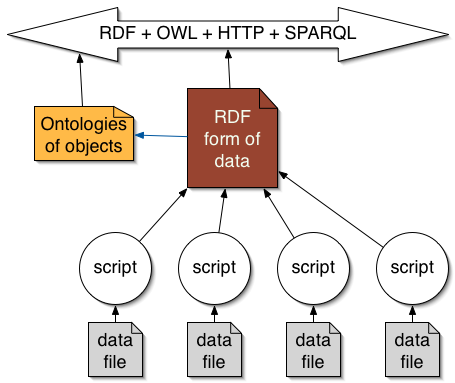
Keep your existing systems running - adapt them
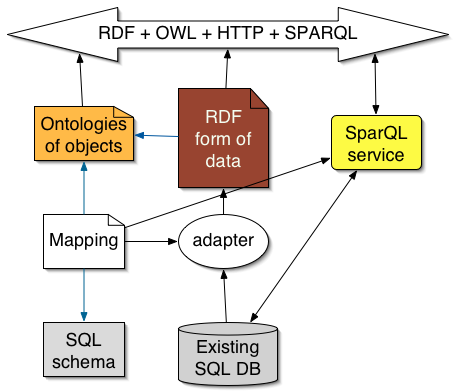
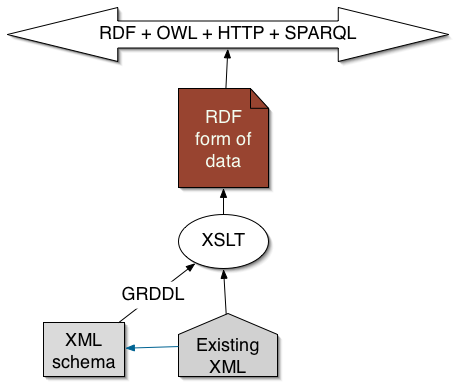
Remember- RDF on an HTTP server can always be virtual
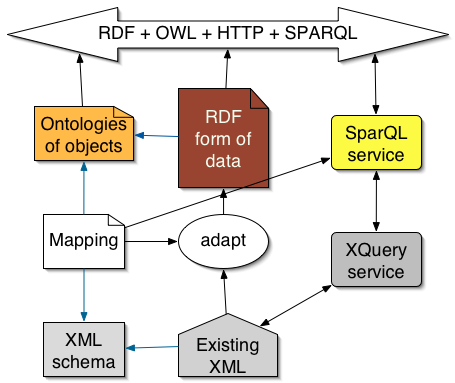
Remember- RDF on an HTTP server can always be virtual
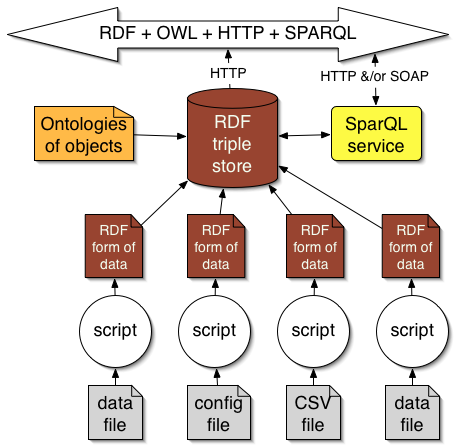
Virtual severs actually figure stuff out as well as look up data
Linking out is to use in your data URIs for objects as described on sites
Incentive: kudos, reuse
W3C: w3.org
Thank you for your attention
Slides: http://www.w3.org/2007/Talks/1211-whit-tbl/