Essential Components of Web Accessibility
Shawn Lawton Henry, W3C WAI
9 May 2005
World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)
- International, vendor-neutral consortium
- Promotes evolution, interoperability, universality
- Develops core Web standards: HTML, XML, etc.
- Internationally hosted
- Keio University in Japan
- MIT in North America
- ERCIM in Europe
- 14 outreach offices around the world
- Only industry consortium with consensus-based multi-stakeholder accessibility
effort
Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI)
- International forum
- Multi-stakeholder
- Industry
- Disability organizations
- Accessibility researchers
- Government
- Education
- Consensus-based solutions
- Collaborative W3C working groups
- Opportunities for public comment
- Cross-disability requirements: Visual, auditory, physical, speech, cognitive,
neurological
WAI Activities
- Accessibility in W3C technologies
- Accessibility Guidelines
- Evaluation
- Education and outreach
- Advanced research and development
Essential Components Interdependent
- Myth: Web accessibility is mainly the responsibility of the Web content
producer
- Web accessibility depends on several components working together
- Improvements in components could substantially improve Web accessibility
- WAI guidelines address these components
How the Components Relate - Content
Web content - the information in a Web page or Web application,
including:
- natural information such as text, images, and sounds
- code or markup that defines structure, presentation, etc.
How the Components Relate - Content Developer Side
Web developers usually use authoring tools
and evaluation tools to create Web content.
- developers - content producers, designers, coders, authors,
etc., including developers with disabilities and users who contribute content
- authoring tools - software that creates Web sites
- evaluation tools - Web accessibility evaluation tools,
HTML validators, CSS validators, etc.
How the Components Relate - Users Side
People ("users") use Web browsers,
media players, assistive technologies, or other "user agents"
to get and interact with the content.
- Web browsers, media players, and other "user agents"
- assistive technology, in some cases - screen readers, alternative
keyboards, switches, scanning software, etc.
- users' knowledge, experiences, and in some cases, adaptive
strategies using the Web
Interdependencies Between Components, Example

Interdependencies Between Components, Example
- Significant interdependencies between the components
- Example, for alternative text on images
- Technical specifications address alternative text
- For example, HTML defines alternative text attribute (alt) of image
element (img))
- WAI guidelines define how to implement alternative
text for accessibility
- Developers provide appropriate alternative text wording
- Authoring tools enable, facilitate, and promote providing
alternative text in Web content
- Evaluation tools help check alternative text exists in
content
- User agents provide human and machine interface to alternative
text
- Assistive technologies provide human interface to alternative
text in various modalities
- Users know how to get the alternative text from user
agent and/or assistive technology
When One Component is Weak
Sometimes other components can compensate through "work-arounds"
- require much more effort
- not good for accessibility overall
- often not implemented, result poor accessibility
- sometimes no way to work around, result is impossible for some people with
disabilities to use Web site, page, or feature
Weak Authoring Tool Accessibility Support
- developers do more work
- for example, coding markup directly
- less accessible Web sites
- people with disabilities cannot contribute content
Weak Browsers, Media Players, Assistive Technology, or Content Accessibility Support
- users can do more work
- for example, using different browsers or assistive technologies to overcome
different accessibility issues
- or not accessible at all
Accessibility Feature Implementation Cycle
- If not in one component, other components less likely to implement it
- Example: developers not implement feature if authoring tools do not
support and browsers or assistive technologies do not implement consistently
- When one implements, others more likely to implement:
- When Web browsers, media players, assistive technologies, and
other user agents support accessibility feature, users demand
it and developers implement it
- When developers want accessibility feature, they demand authoring
tool make it easy
- When authoring tools make it easy, developers implement
it
- When in most content, developers and users demand that
user agents support it
Guidelines for Different Components
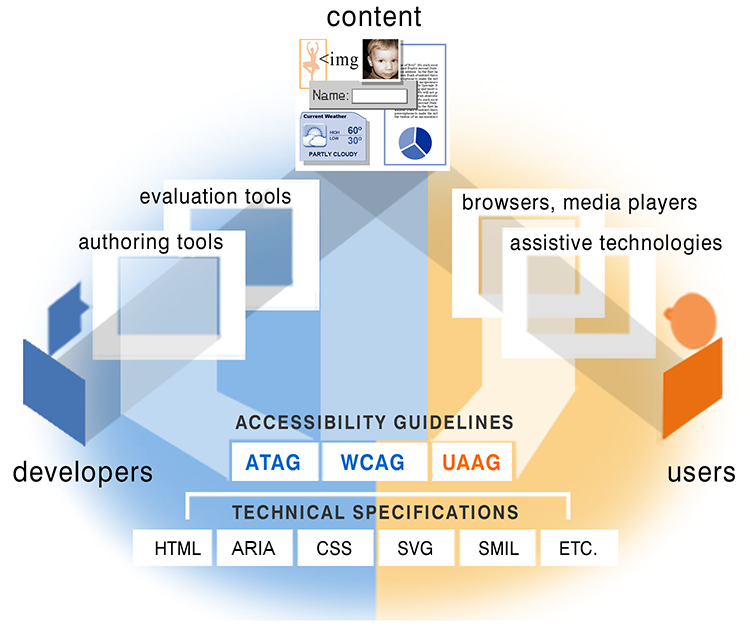
Guidelines for Different Components
Developed by World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Web Accessibility
Initiative (WAI):
- Authoring Tool Accessibility Guidelines (ATAG)
addresses authoring tools
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
addresses Web content, used by developers, authoring tools, accessibility
evaluation tools
- User Agent Accessibility Guidelines (UAAG)
addresses Web browsers and media players, including some aspects of assistive
technologies
- Based on the fundamental technical specifications Web, in coordination with
W3C technical specifications (HTML, XML, CSS, SVG, SMIL,
etc.)
International Standards Harmonization
Next: WCAG 2.0
Questions?








