Abstract
This module specifies the text layout model in CSS and the properties
that control it. It covers bidirectional and vertical text.
Status of this document
This section describes the status of this document at the time of
its publication. Other documents may supersede this document. A list of
current W3C publications and the latest revision of this technical report
can be found in the W3C technical reports
index at http://www.w3.org/TR/.
Publication as a Working Draft does not imply endorsement by the W3C
Membership. This is a draft document and may be updated, replaced or
obsoleted by other documents at any time. It is inappropriate to cite this
document as other than work in progress.
The (archived) public
mailing list www-style@w3.org (see
instructions) is preferred
for discussion of this specification. When sending e-mail, please put the
text “css3-writing-modes” in the subject, preferably like
this: “[css3-writing-modes] …summary of
comment…”
This document was produced by the CSS Working Group (part of
the Style Activity).
This document was produced by a group operating under the 5 February
2004 W3C Patent Policy. W3C maintains a public list of any patent disclosures made in
connection with the deliverables of the group; that page also includes
instructions for disclosing a patent. An individual who has actual
knowledge of a patent which the individual believes contains Essential
Claim(s) must disclose the information in accordance with section
6 of the W3C Patent Policy.
This is the first public working draft of the CSS Writing Modes module
as a separate specification. The functionality was split off from the CSS Text module of 14 May 2003.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
This section is non-normative.
This module defines support for various international writing
directions, such as left-to-right (e.g., Latin scripts), right-to-left
(e.g., Hebrew or Arabic), bidirectional (e.g., mixing Latin with Arabic)
and vertical (e.g., Asian scripts).
Inherently bottom-to-top scripts are not handled in this version. See [UTN22] for an
explanation of relevant issues.
1.1. Introduction to
Vertical Text
In addition to extensions to CSS2.1's support for bidirectional text,
this module introduces the rules and properties needed to support vertical
text layout in CSS.
Unlike languages that use the Latin script which are primarily laid out
horizontally, Asian languages such as Chinese and Japanese can be laid
vertically. The Japanese example below shows the same text laid out
horizontally and vertically. In the horizontal case, text is read from
left to right, top to bottom. For the vertical case, the text is read top
to bottom, right to left. Indentation from the left edge in the
left-to-right horizontal case translates to indentation from the top edge
in the top-to-bottom vertical case.
For Chinese and Japanese lines are ordered either right to
left, while for Mongolian and Manchu left to right.
The change from horizontal to vertical writing can affect not just the
layout, but also the typesetting. For example, the position of a
punctuation mark within its spacing box can change from the horizontal to
the vertical case, and in some cases alternate glyphs are used.
Vertical text that includes Latin script text or text from other scripts
normally displayed horizontally can display that text in a number of ways.
For example, Latin words can be rotated sideways, or each letter can be
oriented upright.
In some special cases such as two-digit numbers in dates, text is fit
compactly into a single vertical character box:
Layouts often involve a mixture of vertical and horizontal elements:
Vertical text layouts also need to handle bidirectional text layout;
clockwise-rotated Arabic, for example, is laid out bottom-to-top.
2. Writing Modes and Terminology
A writing mode in CSS is determined by the
‘writing-mode’, ‘direction’, and
‘text-orientation’ properties. It is
defined primarily in terms of its inline base direction and block flow direction:
The inline base direction is the
primary direction in which content is ordered on a line and defines on
which sides the "start" and "end" of a line are. The ‘direction’
property specifies the inline base direction of an element and, together
with the ‘unicode-bidi’ property and the inherent
directionality of any text content, determines the ordering of
inline-level content within a line.
The block flow direction is the
direction in which block-level boxes stack and the direction in which line
boxes stack within a block container. The ‘writing-mode’
property determines the block flow direction.
A horizontal writing mode is one
with horizontal lines of text, i.e. a downward or upward block flow. A
vertical writing mode is one with
vertical lines of text, i.e. a leftward or rightward block flow.
These terms should not be confused with vertical block flow (which is a downward or
upward block flow) and horizontal block
flow (which is leftward or rightward block flow). To avoid
confusion, the CSS specifications avoid this latter set of terms.
Writing systems typically have one or two native writing modes. Some
examples are:
- Latin-based systems are typically written using a left-to-right inline
direction with a downward (top-to-bottom) block flow direction.
- Arabic-based systems are typically written using a right-to-left
inline direction with a downward (top-to-bottom) block flow direction.
- Mongolian-based systems are typically written using a top-to-bottom
inline direction with a rightward (left-to-right) block flow direction.
- Han-based systems are commonly written using a left-to-right inline
direction with a downward (top-to-bottom) block flow direction,
or a top-to-bottom inline direction with a leftward
(right-to-left) block flow direction. Many magazines and newspapers will
mix these two writing modes on the same page.
Some additional characteristics, the line orientation and glyph
orientation, are primarily used to handle scripts placed in a non-native
writing mode. The line orientation
determines which side of the line is the "top" and thus which sides are
under or over the line. This
determines the interpretation of alignment in the transverse dimension of
the line. It also determines the default glyph
orientation for scripts in a non-native orientation. These
characteristics are controlled by the ‘text-orientation’ property.
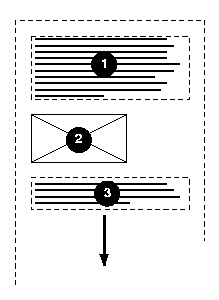
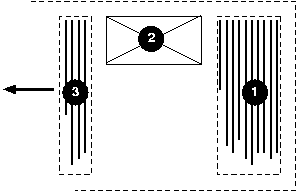
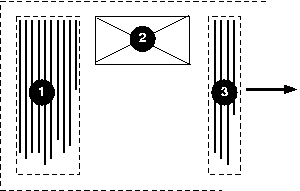
In the following example, two blocks elements (1 and 3) separated by an
image (2) are presented in various flow writing modes.
Here is a diagram of horizontal writing mode (writing-mode:
horizontal-tb):
Here is a diagram for the right-to-left vertical writing mode commonly
used in East Asia (writing-mode: vertical-rl):
And finally, here is a diagram for the left-to-right vertical writing
mode used for Uighur and Mongolian (writing-mode: lr):
See Unicode Technical Note #22 [UTN22] (HTML
version) for a more in-depth introduction to writing modes and
vertical text.
3. Inline Direction and
Bidirectionality
While the characters in most scripts are written from left to right,
certain scripts are written from right to left. In some documents, in
particular those written with the Arabic or Hebrew script, and in some
mixed-language contexts, text in a single (visually displayed) block may
appear with mixed directionality. This phenomenon is called bidirectionality, or "bidi" for short.
The Unicode standard (Unicode Standard Annex #9)
defines a complex algorithm for determining the proper ordering of
bidirectional text. The algorithm consists of an implicit part based on
character properties, as well as explicit controls for embeddings and
overrides. CSS relies on this algorithm to achieve proper bidirectional
rendering. The ‘direction’
and ‘unicode-bidi’ properties allow
authors to specify how the elements and attributes of a document language
map to this algorithm.
User agents that support bidirectional text must apply the Unicode
bidirectional algorithm to every sequence of inline boxes uninterrupted by
a forced (bidi
class B) line break or block boundary. This sequence forms the
"paragraph" unit in the bidirectional algorithm. The paragraph embedding
level is set according to the value of the ‘direction’
property of the containing block rather than by the heuristic given in
steps P2 and P3 of the Unicode algorithm.
Because the base directionality of a text depends on the structure and
semantics of the document, these properties should in most cases be used
only to map bidi information in the markup to its corresponding CSS
styles. If a document language provides markup features to control bidi,
authors and users should use those features and not specify CSS rules to
override them.
The HTML 4 specification ([HTML401], section 8.2) defines
bidirectionality behavior for HTML elements. The HTML 4 specification also
contains more information on bidirectionality issues.
Because HTML UAs can turn off CSS styling, we advise HTML
authors to use the HTML ‘dir’
attribute and <bdo> element to ensure correct bidirectional layout
in the absence of a style sheet.
3.1. Specifying Directionality:
the ‘direction’ property
| Name:
| direction
|
| Value:
| ltr | rtl
|
| Initial:
| ltr
|
| Applies to:
| all elements
|
| Inherited:
| yes
|
| Percentages:
| N/A
|
| Media:
| visual
|
| Computed value:
| specified value
|
This property specifies the base directionality of text and elements on
a line, and the directionality of embeddings and overrides (see ‘unicode-bidi’)
for the Unicode bidirectional algorithm. In addition, it affects the
ordering of table
column layout, the direction of horizontal overflow, and
the default alignment of text within a line, and other things that depend
on the base inline base direction.
Values for this property have the following meanings:
- ltr
- Left-to-right directionality.
- rtl
- Right-to-left directionality.
The ‘direction’ property has no reordering in
inline-level elements whose ‘unicode-bidi’ property's value is
‘normal’.
The value of the ‘direction’ property on the root element is
also propagated to the initial containing block and, together with the
‘writing-mode’ property, determines the
document's principal writing mode. (See below.)
Note that the ‘direction’ property of the HTML BODY
element is not propagated to the viewport. That special behavior
only applies to the background and overflow properties.
The ‘direction’ property, when specified for
table column elements, is not inherited by cells in the column since
columns are not the ancestors of the cells in the document tree. Thus, CSS
cannot easily capture the "dir" attribute inheritance rules described in
[HTML401],
section 11.3.2.1.
3.2. Embeddings and Overrides:
the ‘unicode-bidi’ property
| Name:
| unicode-bidi
|
| Value:
| normal | [ [ embed | isolate ] || [ plaintext | bidi-override ] ]
|
| Initial:
| normal
|
| Applies to:
| all elements, but see prose
|
| Inherited:
| no
|
| Percentages:
| N/A
|
| Media:
| visual
|
| Computed value:
| specified value
|
Values for this property have the following meanings:
- normal
- The element does not open an additional level of embedding with
respect to the bidirectional algorithm. For inline-level elements,
implicit reordering works across element boundaries.
- embed
- If the element is inline-level, this value opens an additional level
of embedding with respect to the bidirectional algorithm. The direction
of this embedding level is given by the ‘
direction’
property. Inside the element, reordering is done implicitly. This
corresponds to adding a LRE (U+202A; for ‘direction: ltr’) or RLE (U+202B; for ‘direction: rtl’) at the start of the element and a
PDF (U+202C) at the end of the element.
- bidi-override
- For inline-level elements this creates an override. For block-level,
table-cell, table-caption, or inline-block elements this creates an
override for inline-level descendants not within another block-level,
table-cell, table-caption, or inline-block element. This means that
inside the element, reordering is strictly in sequence according to the
‘
direction’ property; the implicit
part of the bidirectional algorithm is ignored. This corresponds to
adding a LRO (U+202D; for ‘direction:
ltr’) or RLO (U+202E; for ‘direction:
rtl’) at the start of the element and a PDF (U+202C) at the
end of the element.
- isolate
- For the purposes of the Unicode bidirectional algorithm, the contents
of the element are considered to be inside a separate, independent
paragraph, and for the purpose of bidi resolution in its containing bidi
paragraph (if any), the element itself is treated as if it were an Object
Replacement Character (U+FFFC). (If the element is broken across multiple
lines, then each box of the element is treated as an Object Replacement
Character.)
- plaintext
-
For the purposes of the Unicode bidirectional algorithm, the base
directionality of each "paragraph" for which the element is the
containing block element is determined not by the element's computed
‘direction’ as usual, but by following
rules P1, P2, and P3 of the Unicode bidirectional algorithm. However, if
no direction-determining character is found in step P2, then the value
of the ‘direction’ property is used instead.
Note this value has no effect on inline elements.
The final order of characters in each block-level element is the same as
if the bidi control codes had been added as described above, markup had
been stripped, and the resulting character sequence had been passed to an
implementation of the Unicode bidirectional algorithm for plain text that
produced the same line-breaks as the styled text. In this process,
non-textual entities such as images are treated as neutral characters,
unless their ‘unicode-bidi’ property has a value
other than ‘normal’, in which case
they are treated as strong characters in the ‘direction’ specified for the
element.
Please note that in order to be able to flow inline boxes in a uniform
direction (either entirely left-to-right or entirely right-to-left), more
inline boxes (including anonymous inline boxes) may have to be created,
and some inline boxes may have to be split up and reordered before
flowing.
Because the Unicode algorithm has a limit of 61 levels of
embedding, care should be taken not to use ‘unicode-bidi’ with a value other
than ‘normal’ unless appropriate.
In particular, a value of ‘inherit’ should be used with extreme caution.
However, for elements that are, in general, intended to be displayed as
blocks, a setting of ‘unicode-bidi:
isolate’ is preferred to keep the element together in case
display is changed to inline (see example below).
The following example shows an XML document with bidirectional text. It
illustrates an important design principle: document language designers
should take bidi into account both in the language proper (elements and
attributes) and in any accompanying style sheets. The style sheets should
be designed so that bidi rules are separate from other style rules, and
such rules should not be overridden by other style sheets so that the
document language's bidi behavior is preserved.
3.3. Example of Bidirectional
Text
In this example, lowercase letters stand for inherently left-to-right
characters and uppercase letters represent inherently right-to-left
characters. The text stream is shown in logical backing store order.
<HEBREW>
<PAR>HEBREW1 HEBREW2 english3 HEBREW4 HEBREW5</PAR>
<PAR>HEBREW6 <EMPH>HEBREW7</EMPH> HEBREW8</PAR>
</HEBREW>
<ENGLISH>
<PAR>english9 english10 english11 HEBREW12 HEBREW13</PAR>
<PAR>english14 english15 english16</PAR>
<PAR>english17 <HE-QUO>HEBREW18 english19 HEBREW20</HE-QUO></PAR>
</ENGLISH>
Since this is arbitrary XML, the style sheet is responsible for setting
the writing direction. This is the style sheet:
/* Rules for bidi */
HEBREW, HE-QUO {direction: rtl; unicode-bidi: embed;}
ENGLISH {direction: ltr; unicode-bidi: embed;}
/* Rules for presentation */
HEBREW, ENGLISH, PAR {display: block;}
EMPH {font-weight: bold;}
The HEBREW element is a block with a right-to-left base direction, the
ENGLISH element is a block with a left-to-right base direction. The PARs
are blocks that inherit the base direction from their parents. Thus, the
first two PARs are read starting at the top right, the final three are
read starting at the top left. Please note that HEBREW and ENGLISH are
chosen as element names for explicitness only; in general, element names
should convey structure without reference to language.
The EMPH element is inline-level, and since its value for ‘unicode-bidi’ is ‘normal’ (the initial value), it has no effect
on the ordering of the text. The HE-QUO element, on the other hand,
creates an embedding.
The formatting of this text might look like this if the line length is
long:
5WERBEH 4WERBEH english3 2WERBEH 1WERBEH
8WERBEH 7WERBEH 6WERBEH
english9 english10 english11 13WERBEH 12WERBEH
english14 english15 english16
english17 20WERBEH english19 18WERBEH
Note that the HE-QUO embedding causes HEBREW18 to be to the right of
english19.
If lines have to be broken, it might be more like this:
2WERBEH 1WERBEH
-EH 4WERBEH english3
5WERB
-EH 7WERBEH 6WERBEH
8WERB
english9 english10 en-
glish11 12WERBEH
13WERBEH
english14 english15
english16
english17 18WERBEH
20WERBEH english19
Because HEBREW18 must be read before english19, it is on the line above
english19. Just breaking the long line from the earlier formatting would
not have worked. Note also that the first syllable from english19 might
have fit on the previous line, but hyphenation of left-to-right words in
a right-to-left context, and vice versa, is usually suppressed to avoid
having to display a hyphen in the middle of a line.
3.4. Box model for inline
elements in bidirectional context
For each line box, UAs must take the inline boxes generated for each
element and render the margins, borders and padding in visual order (not
logical order).
When the element's ‘direction’ property is ‘ltr’, the left-most generated box of the first line
box in which the element appears has the left margin, left border and left
padding, and the right-most generated box of the last line box in which
the element appears has the right padding, right border and right margin.
When the element's ‘direction’ property is ‘rtl’, the right-most generated box of the first
line box in which the element appears has the right padding, right border
and right margin, and the left-most generated box of the last line box in
which the element appears has the left margin, left border and left
padding.
4. Block Flow Direction: the
‘writing-mode’ property
| Name:
| writing-mode
|
| Value:
| horizontal-tb | vertical-rl | vertical-lr
|
| Initial:
| horizontal-tb
|
| Applies to:
| All elements except table row groups, table column groups, table
rows, and table columns
|
| Inherited:
| yes
|
| Percentages:
| N/A
|
| Media:
| visual
|
| Computed value:
| specified value
|
This property sets the block flow direction. Possible values:
- horizontal-tb
- Top-to-bottom block flow. The writing mode is horizontal.
- vertical-rl
- Right-to-left block flow. The writing mode is vertical.
- vertical-lr
- Left-to-right block flow. The writing mode is vertical.
SVG1.1 [SVG11]
defines some additional values: ‘lr’,
‘lr-tb’, ‘rl’, ‘rl-tb’,
‘tb’, and ‘tb-rl’. These values are deprecated in any
context except SVG1 documents. Implementations that wish to support them
in the context of CSS must treat these values as follows:
| SVG1
| CSS
|
| lr
| horizontal-tb
|
| lr-tb
|
| rl
|
| tb
| vertical-rl
|
| tb-rl
|
In SVG1.1, these values set the inline progression direction, in
other words, the direction the current text position advances each time a
glyph is added. This is a geometric process that happens after bidi reordering, and thus has no effect
on the interpretation of the ‘direction’ property (which is independent
of ‘writing-mode’). (See Relationship
with bidirectionality. [SVG11]) There are varying
interpretations on whether this process causes "writing-mode: rl" to
merely shift the text string or reverse the order of all glyphs in the
text.
See this demo to
check out your implementation's interpretation! (Note that most SVG
implementations don't support the ‘direction’ property, and thus your results
may be skewed on that account. Examine the red line of text: if the
numbers are not in reverse order, your implementation doesn't support
"direction: rtl".)
The ‘writing-mode’ property determines the
direction of block flow. This determines the progression of block-level
boxes in a block formatting context; the progression of line boxes in a
block container that contains inlines; and the progression of rows in a
table. As a result it also determines which side of a box is its before edge (i.e. the edge that comes earlier in the
progression) and which side is its after edge (i.e.
the edge that comes later in the progression).
The ‘writing-mode’ property, by virtue of
determining the stacking direction of line boxes, determines whether line
boxes and thus the writing mode of text are horizontal or vertical.
However, it does not determine the orientation of the line boxes' contents
or the start and end sides of the line. See Line orientation.
When set on the root element, the ‘writing-mode’ property together with the
‘direction’ property determines the principal writing mode of the document.
This writing mode is used, for example, to determine the default page
progression direction. See [CSS3PAGE] The ‘writing-mode’
value of the root element is also propagated to the initial containing
block and sets the block flow direction of the initial block formatting
context.
Note that the ‘direction’ property of the HTML BODY
element is not propagated to the viewport. That special behavior
only applies to the background and overflow properties.
If an element has a different block flow direction than its containing
block:
- If the element has a specified ‘
display’ of ‘inline’, its ‘display’ computes to ‘inline-block’. [CSS21]
- If the element has a specified ‘
display’ of ‘run-in’, its ‘display’ computes to ‘block’. [CSS21]
If such an element is a block container, then it establishes a new block
formatting context.
The content of replaced elements do not rotate due to the writing mode:
images, for example, remain upright. However replaced content involving
text (such as MathML content or form elements) should match the replaced
element's writing mode and line orientation if the UA supports such a
vertical writing mode for the replaced content.
4.1. Box Layout in Vertical
Writing Modes
CSS box layout in vertical writing modes is analogous to layout in the
horizontal writing modes, following the principles outlined below. See Abstract Box layout for a more complete
discussion.
Layout calculation rules (such as those in CSS2.1, Section 10.3) that
apply to the horizontal dimension in horizontal writing modes instead
apply to the vertical dimension in vertical writing modes. Likewise,
layout calculation rules (such as those in CSS2.1, Section 10.6) that
apply to the vertical dimension in horizontal writing modes instead apply
to the horizontal dimension in vertical writing modes. Thus:
-
Layout rules that refer to the width use the height instead, and vice
versa.
-
Layout rules that refer to the ‘*-left’ and ‘*-right’ box properties (border, margin, padding)
use ‘*-top’ and ‘*-bottom’ instead, and vice versa.
Which side of the box the property applies to doesn't
change: only which values are inputs to which layout calculations
changes. The ‘margin-left’
property still affects the lefthand margin, for example; however in a
‘vertical-rl’ writing mode it takes
part in margin collapsing in place of ‘margin-bottom’.
-
Layout rules that depend on the ‘direction’ property to choose between
left and right (e.g. overflow, overconstraint resolution, the initial
value for ‘text-align’, table
column ordering) are abstracted to the start and end sides and applied appropriately.
For features such as text alignment, floating, and list marker
positioning, that primarily reference the left or right sides of the line
box or its longitudinal parallels and therefore have no top or bottom
equivalent, the line left and line right sides are used as the reference for the
left and right sides respectively. See Line-Relative Directions for details.
Likewise for features such as underlining, overlining, and baseline
alignment (the unfortunately-named ‘vertical-align’), that primarily reference the
top or bottom sides of the linebox or its transversal parallels and
therefore have no left or right equivalent, the over
and under sides are used as the reference for the top
and bottom sides respectively. (See Line-Relative Directions.)
5. Line Orientation
Every line box has an orientation. Whether its orientation is horizontal
or vertical is determined by the ‘writing-mode’ property. Given that, which
side is its "top", or over edge, is
determined by the ‘text-orientation’ property on its
containing block, and is independent of the block flow direction.
In addition to its over (ascender side) and under (descender side) edges, a line box, even a
vertically-oriented one, also has a "left" and "right" side, which we will
call the line left and line
right sides of the box to distinguish from the physical left and
physical right sides of the box.
The start edge of a box is nominally the edge from
which text of its inline base direction will start. For boxes with a used
‘direction’ value of ‘ltr’, this means the line
left edge. For boxes with a used ‘direction’ value
of ‘rtl’, this means the line right edge. The edge opposite the start
edge is the end edge.
These directional mappings exist even for boxes that do not contain any
line boxes: they are calculated by the values of the ‘writing-mode’,
‘text-orientation’, and ‘direction’
properties only.
Note that determining the start
and end edges of a box depends not only on its
‘writing-mode’ and ‘direction’
properties, but also its ‘text-orientation’ property.
Note also that while the over and
under directions often map to the same
directions as before and after
respectively, this mapping is reversed for some combinations of ‘writing-mode’
and ‘text-orientation’.
5.1. Orienting Text: the
‘text-orientation’ property
| Name:
| text-orientation
|
| Value:
| vertical-right | upright | rotate-right | rotate-left |
rotate-normal | auto
|
| Initial:
| vertical-right
|
| Applies to:
| all elements except table row groups, rows, column groups, and
columns
|
| Inherited:
| yes
|
| Percentages:
| N/A
|
| Media:
| visual
|
| Computed value:
| specified value
|
This property specifies the orientation of characters in a non-native
‘writing-mode’ and sets the orientation of
the line. Current values only have an effect in vertical writing modes.
Values have the following meanings:
- vertical-right
-
In vertical writing modes, grapheme clusters from scripts that do not
have an intrinsic vertical orientation are rotated 90° clockwise
from their standard orientation in horizontal text. When available,
vertical glyph variants and vertical font metrics are used to set all
punctuation and characters from any script that is not rotated. This
value is typical for layout of primarily vertical-script text.
- upright
-
In vertical writing modes, grapheme clusters that do not have an
intrinsic vertical orientation are rendered upright, i.e. in their
standard horizontal orientation. Shaping characters are shaped in their
isolated forms. When available, vertical glyph variants and vertical
font metrics are used to set the text. The UA should synthesize vertical
font metrics for grapheme clusters that do not have any.
For the purposes of bidi reordering, this value causes all characters
to be treated as strong LTR. This value causes the used value of
‘direction’ to be ‘ltr’.
- rotate-right
-
In vertical writing modes, this causes text to be set as if in a
horizontal layout (using horizontal glyph variants and metrics), but
rotated 90° clockwise. This value is typical for ‘vertical-rl’ text in a primarily
horizontal-script document.
- rotate-left
-
In vertical writing modes, this causes text to be set as if in a
horizontal layout (using horizontal glyph variants and metrics), but
rotated 90° counter-clockwise. This value is typical for
‘vertical-lr’ text in a primarily
horizontal-script document.
If set on a non-replaced inline whose parent is not ‘rotate-left’, this
forces ‘isolate’ to be added to the
computed value of ‘unicode-bidi’. Layout of text is exactly
as for ‘rotate-right’ except that the entire text
content and baseline table of the element is mirrored: each box of the
inline is mirrored around a vertical axis such that its content box does
not move. (However the contents of atomic inlines are not mirrored; only
their alignment is changed.) Similarly, if a child of the element has a
‘text-orientation’ value other than
‘rotate-left’, an analogous transformation is
applied.
- rotate-normal
-
This value is equivalent to ‘rotate-right’ in ‘vertical-rl’ writing mode and equivalent to
‘rotate-left’ in ‘vertical-lr’ writing mode.
- auto
-
[SVG11] defines
‘glyph-orientation-vertical’ and
‘glyph-orientation-horizontal’
properties that were intended to control text orientation. These
properties are deprecated and do not apply to non-SVG elements.
If an implementation supports these properties, the ‘auto’ value when set on
SVG elements indicates that the SVG ‘glyph-orientation-vertical’ and ‘glyph-orientation-horizontal’ behavior
control the layout of text. Such UAs must set ‘text-orientation: auto’ on all SVG
text content elements in their default UA style sheet for SVG.
In all other contexts, and for implementations that do not support the
glyph orientation properties, the ‘auto’ behavior is the same as for ‘vertical-right’.
Baseline alignment is not yet defined.
Add section explaining native script orientations. Note that
all wide characters are treated the same as ideographic. Link to
definition of grapheme clusters in [UAX29].
Add appendix that describes interaction with OpenType
features and font layout?
6. Abstract Box Layout
[CSS21] defines
the box layout model of CSS in detail. However, it only defines the box
model for the ‘horizontal-tb’ writing
mode. CSS box layout in writing modes other than ‘horizontal-tb’ is analogous to the box layout
defined in CSS2.1 if boxes and dimensions are abstracted and remapped
appropriately. This module defines the following abstract directional and
dimensional terms and their mappings in order to define box layout for
other writing modes:
6.1. Logical vs Physical
Dimensions
- block flow dimension
- The dimension perpendicular to the flow of text with in a line, the
vertical dimension in horizontal writing modes, and the
horizontal dimension in vertical writing modes.
- inline dimension
- The dimension parallel to the flow of text within a line, i.e. the
horizontal dimension in horizontal writing modes, and the
vertical dimension in vertical writing modes.
- inline-axis
- The axis in the block flow dimension, i.e. the vertical axis in
horizontal writing modes and the horizontal axis in vertical
writing modes.
- block-axis
- The axis in the inline dimension, i.e. the horizontal axis in
horizontal writing modes and the vertical axis in vertical writing
modes.
- length or logical
height
-
- A measurement in the block flow dimension: refers to the physical
height (vertical dimension) in horizontal writing modes, and to the
physical width (horizontal dimension) in vertical writing modes.
- measure or logical
width
-
- A measurement in the inline dimension: refers to the physical width
(horizontal dimension) in horizontal writing modes, and to the physical
height (vertical dimension) in vertical writing modes. (The term measure derives from its use in
typography.)
Certain properties behave logically as follows:
- The first and second values of the ‘
border-spacing’ property represent spacing
between columns and rows respectively, not necessarily the horizontal and
vertical spacing respectively. [CSS21]
- The ‘
line-height’ property
always refers to the logical height. [CSS21]
The height properties (‘height’,
‘min-height’, and ‘max-height’) refer to the physical height, and
the width properties (‘width’,
‘min-width’, and ‘max-width’) refer to the physical width.
However, the rules used to calculate box dimensions and positions are
logical.
For example, the calculation rules in CSS2.1
Section 10.3 are used for the inline dimension measurements: the
logical width (which could be either the physical width or physical
height) and the start and end margins, padding, and border. Likewise the
calculation rules in CSS2.1
Section 10.6 are used for measurements in the block dimension. [CSS21]
As a corollary, percentages on the margin and padding properties, which
are calculated with respect to the containing block width regardless of
their dimension, are calculated with respect to the logical width of the containing block.
6.1.1. Orthogonal Flows
When an element has a different ‘writing-mode’ from its containing block
two cases are possible:
- The two writing modes are parallel to each other. (For example,
‘
vertical-rl’ and ‘vertical-lr’).
- The two writing modes are perpendicular to each other. (For example,
‘
horizontal-tb’ and ‘vertical-rl’).
To handle the second case, for the purposes of calculating the layout of
the box, the dimensions corresponding to the logical height and logical
width of the containing block are determined using the writing mode of the
box under consideration, not the writing mode of the element associated
with the containing block.
What's a reasonable way of calculating ‘auto’ logical widths? The
fallout of the above statements is not reasonable. Three good options are:
use the max-content size; use 100vh margin-box; use the same logical width
that would be calculated if the block flows were parallel.
6.2. Logical vs Physical
Directions
The terms "left", "right", "top", and "bottom" are always interpreted
physically, i.e. with respect to the page independent of writing mode. Two
abstract mappings are possible for these directions: logical and
line-relative. Which one is chosen depends on whether the usage is
primarily with respect to the block, or primarily with respect to the line
box.
6.2.1. Logical Directions
The logical directions are before, after, start, and end. In an LTR ‘horizontal-tb’ writing mode, they correspond to the
top, bottom, left, and right directions, respectively.
An English (LTR-TB) block:
<---- width / logical width --->
top side/
before side
+------------------------------+ A
left side/ | ---inline direction ---> | right side/ |
start side | | | end side |
| | block * horizontal * | height/
| | direction *writing mode* | logical height
| V | |
+------------------------------+ V
bottom side/
after side
A vertical Japanese block (TTB-RL):
<--- width / logical height --->
top side/
start side
+------------------------------+ A
left side/ | <---block direction--- | right side/ |
after side | | | before side |
| * vertical * inline| | height/
| *writing mode* direction| | logical width
| V | |
+------------------------------+ V
bottom side/
end side
Logical directions are calculated with respect to the writing mode of
the element and used to abstract layout related to padding and border
properties. For example, if an element had computed values of ‘direction: ltr; writing-mode: vertical-lr; text-orientation:
vertical-right’, ‘padding-top’ would give its start padding, and
‘padding-left’ would give its
before padding.
Logical directions are calculated with respect to the writing mode of
the parent of the element and used to abstract layout related to
the margin properties and the ‘top’, ‘bottom’, ‘left’, and ‘right’ properties. (For the root element,
which has no parent, the values of the writing mode of the element is used
instead.)
The margin
collapsing rules apply exactly with the before margin
substituted for the top margin and the after margin substituted
for the bottom margin. Similarly the padding and border on the same side
as the before margin is substituted for the top padding and border, and
the padding and border on the same side as the after margin for the bottom
padding and border. Note this means only before and after margins ever
collapse.
The parent element is used instead of the containing block,
because the benefit of using the containing block is very rare, but the
cost to implement it is rather high for implementations that do
logical-physical mapping at cascade time.
The start and end directions are also used for inline layout as follows:
- The initial value of the ‘
text-align’ property aligns to the start edge
of the line box.
- The ‘
text-indent’ property
indents from the start edge of the line box.
6.2.2. Line-Relative
Directions
The line-relative directions are
over, under, line-left, and line-right.
In an LTR ‘horizontal-tb’ writing mode, they correspond to the
top, bottom, left, and right directions, respectively.
The line right and line left directions are calculated with respect to
the writing mode of the element and used to interpret the ‘left’ and ‘right’ values of the following properties:
The line right and line left directions are calculated with respect to
the writing mode of the containing block of the element and used
to interpret the ‘left’ and
‘right’ values of the following
properties:
The over and under directions are calculated with respect to the writing
mode of the element and used to define the interpretation of the "top"
(over edge) and "bottom" (under edge) of the line box as follows:
- For the ‘
vertical-align’
property, the "top" of the line box is the over edge; the "bottom" of the
line box is the under edge. Positive length and percentage values shift
the baseline towards the over edge. [CSS21]
- For the ‘
text-decoration’
property, the underline is drawn on the under side of the text; the
overline is drawn on the over side of the text. [CSS21] Note that
the CSS Text Module defines this in more detail and provides additional
controls for controlling the position of underlines and overlines. [CSS3TEXT]
6.2.3.
Abstract-to-Physical Mappings
The following table summarizes the abstract-to-physical mappings:
Abstract-Physical Mapping
‘writing-mode’
| ‘horizontal-tb’
| ‘vertical-rl’
| ‘vertical-lr’
|
‘text-orientation’
| —
| ‘rotate-left’
| *right
| ‘rotate-left’
| *right
|
‘direction’
| ‘ltr’
| ‘rtl’
| ‘ltr’
| ‘rtl’
| ‘ltr’
| ‘rtl’
| ‘ltr’
| ‘rtl’
| ‘ltr’
| ‘rtl’
|
| length
| height
| width
|
| measure
| width
| height
|
| before
| top
| right
| left
|
| after
| bottom
| left
| right
|
| start
| left
| right
| bottom
| top
| top
| bottom
| bottom
| top
| top
| bottom
|
| end
| right
| left
| top
| bottom
| bottom
| top
| top
| bottom
| bottom
| top
|
| over
| top
| left
| right
| left
| right
|
| under
| bottom
| right
| left
| right
| left
|
| line-left
| left
| bottom
| top
| bottom
| top
|
| line-right
| right
| top
| bottom
| top
| bottom
|
6.2.4. Purely Physical
Properties
The following values are purely physical in their definitions and do not
respond to changes in writing mode:
- all values of ‘
background-repeat’ other than ‘repeat-y’ and ‘repeat-x’ (described above)
- the ‘
rect()’ notation of the
‘clip’ property [CSS21]
- the offsets of the ‘
box-shadow’ and ‘text-shadow’ properties
6.2.5. The ‘caption-side’ property
This module introduces two new values to the ‘caption-side’ property: ‘before’ and ‘after’, which position the
caption before and after the table box, respectively. For tables with
‘horizontal-tb’ writing mode, they are
equivalent to the existing ‘top’ and
‘bottom’ values, respectively. [CSS21]
Implementations that only support the ‘top’ and ‘bottom’ values of the ‘caption-side’ property must treat them as
‘before’, when
the table is in a vertical writing mode.
For implementations that support side captions (i.e. the ‘left’ and ‘right’ values), this module also introduces the
‘start’ and
‘end’ values, which
behave similarly and which position the caption on the start and end sides
of the table box, calculated with respect to the writing mode of the table
element. For such implementations, the ‘top’ and ‘bottom’ values must place the caption on the top
and bottom sides of the table box, respectively.
7. Glyph Composition: the
‘text-combine’ property
| Name:
| text-combine
|
| Value:
| none | [ horizontal <number>? ]
|
| Initial:
| none
|
| Applies to:
| non-replaced inline elements
|
| Inherited:
| no
|
| Percentages:
| N/A
|
| Media:
| visual
|
| Computed value:
| specified value
|
This property allows the combination of multiple characters into the
space of a single character. For text layout purposes, e.g. bidi ordering,
line-breaking, emphasis marks, text-decoration, etc. the resulting
composition is treated as a single glyph representing the Object
Replacement Character U+FFFC. Values have the following meanings:
- none
- No special processing.
- horizontal
-
In vertical writing mode, attempt to display the text contents of the
element horizontally within the vertical line box, ideally within the
space of one ideographic character (1em square), as follows:
If the UA has compressed glyphs available for the contents of the
element, then it should use those glyphs to attempt sizing the contents
to 1em square. For example, a two digit number should use halfwidth or
proportional glyphs, a three-digit number use 1/3-em glyphs (if
available, else halfwidth glyphs), etc. The glyphs are stacked
horizontally (similar to the contents of an inline-box with a horizontal
writing mode and a line-height of 1em) and the baseline of the resulting
composition chosen such that it is centered between the content edges of
its parent inline box.
If the size of the composed glyph exceeds the element's used
line-height, then { the UA may scale the
contents to fit (else overflow the line) | the contents are
instead rendered as if ‘text-combine’ were ‘none’ }
In horizontal mode, or if the number of grapheme clusters in the
element exceeds the number specified (if any), this value is equivalent
to ‘none’.
In East Asian documents, the ‘text-combine:
upright’ effect is often used to display Latin-based strings
such as components of a date or letters of an initialism, always in a
horizontal writing mode regardless of the writing mode of the line:
In Japanese, this effect is known as tate-chu-yoko.
Some people have requested a way to have numbers
automatically text-combine'd. Maybe a text-auto-combine property? Note
that whether a number should be tate-chu-yoko'd is often
context-sensitive: this would give very weird results when applied to an
arbitrary paragraph.
Acknowledgements
John Daggett, Martin Heijdra, Paul Nelson, Michel Suignard, Steve Zilles
Appendix B: Bidi Rules for HTML
The style sheet rules that would achieve the bidi behaviors specified in
[HTML401] for the
HTML Strict doctype are given below:
/* HTML dir attribute creates an embedding */
*[dir="ltr"] { direction: ltr; unicode-bidi: embed; }
*[dir="rtl"] { direction: rtl; unicode-bidi: embed; }
/* BDO element creates an override */
bdo[dir="ltr"] { direction: ltr; unicode-bidi: bidi-override; }
bdo[dir="rtl"] { direction: rtl; unicode-bidi: bidi-override; }
/* HTML4.01:8.2.6 - preserve bidi behavior if 'display' is changed */
html, body,
div, address, blockquote, p,
ul, ol, li, dl, dt, dd,
fieldset, form,
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6,
{ unicode-bidi: isolate; }
References
Normative references
-
- [CSS21]
- Bert Bos; et al. Cascading Style
Sheets Level 2 Revision 1 (CSS 2.1) Specification. 8 September
2009. W3C Candidate Recommendation. (Work in progress.) URL: http://www.w3.org/TR/2009/CR-CSS2-20090908
- [SVG11]
- Erik Dahlström; et al. Scalable Vector
Graphics (SVG) 1.1 (Second Edition). 22 June 2010. W3C Working
Draft. (Work in progress.) URL: http://www.w3.org/TR/2010/WD-SVG11-20100622
- [UAX29]
- Mark Davis. Text
Boundaries. 25 March 2005. Unicode Standard Annex #29. URL: http://www.unicode.org/unicode/reports/tr29/tr29-9.html
Other references
-
- [CSS3PAGE]
- Melinda Grant; Håkon Wium Lie. CSS3 Module:
Paged Media. 10 October 2006. W3C Working Draft. (Work in
progress.) URL: http://www.w3.org/TR/2006/WD-css3-page-20061010
- [CSS3TEXT]
- Paul Nelson; Elika J. Etemad. CSS Text
Level 3. 6 March 2007. W3C Working Draft. (Work in progress.)
URL: http://www.w3.org/TR/2007/WD-css3-text-20070306
- [HTML401]
- David Raggett; Ian Jacobs; Arnaud Le Hors. HTML 4.01
Specification. 24 December 1999. W3C Recommendation. URL: http://www.w3.org/TR/1999/REC-html401-19991224
- [UTN22]
- Elika J. Etemad. Robust
Vertical Text Layout. 25 April 2005. Unicode Technical Note
#22. URL: http://unicode.org/notes/tn22/