Web services provide a standards-based foundation for exchanging
information between distributed software systems. The World-Wide Web
Consortium (W3C) standard Web Services Description Language [WSDL 2.0] specifies a standard way to describe the
interfaces of a Web Service at a syntactic level and how to invoke it. While
the syntactic descriptions provide information about the structure of input
and output messages of an interface and how to invoke them, semantics are
needed to describe what a Web service actual does. These semantics when
expressed in formal languages disambiguate the description of Web services
interfaces paving the way for automatic discovery, composition and
integration of software components. WSDL does not explicitly provide
mechanisms to specify the semantics of a Web service. Semantic Annotations
for WSDL [SAWSDL] is an effort to define mechanisms by
which semantic annotations can be added to WSDL components. Many of the
concepts in SAWSDL are based on an earlier effort WSDL-S [WSDL-S], a W3C submission. This usage guide is an
accompanying document to SAWSDL specification. It
presents examples to illustrate how to associate semantic annotations with a
Web service that could be used for classifying, discovering, matching,
composing, and invoking Web services..
Some of the examples illustrated in this document use RDF [RDF] and OWL Web Ontology Language [OWL]
for representing ontologies. Some knowledge of RDF and OWL is useful for
understanding this document, but not essential.
This section describes the status of this document at the time
of its publication. Other documents may supersede this document.
A list of current W3C publications and the latest
revision of this technical report can be found in the W3C technical reports index at http://www.w3.org/TR/.
This is the 28 September 2006 First Public Working Draft of the Semantic Annotations for
WSDL — Usage Guide, the first publication of this document. This document is
produced by the SAWSDL Working Group, which is part of the W3C Web Services Activity, and it is intended to be published as a
Working Group Note when the Semantic Annotations for WSDL specification
becomes Recommendation.
The public is encouraged to send comments to the public mailing list
public-ws-semann-comments@w3.org (public archive). See W3C mailing list and archive usage guidelines.
This document was produced by a group operating under the 5 February
2004 W3C Patent Policy. The group does not expect this document to become a W3C Recommendation. W3C maintains a public
list of any patent disclosures made in connection with the
deliverables of the group; that page also includes instructions for
disclosing a patent. An individual who has actual knowledge of a patent
which the individual believes contains Essential
Claim(s) must disclose the information in accordance with section
6 of the W3C Patent Policy.
Publication as a Working Draft does not imply endorsement by the W3C Membership. This is a draft document and may be updated, replaced or obsoleted by other documents at any time. It is inappropriate to cite this document as other than work in progress.
1.
Introduction
As the set of available Web Services expands, it becomes increasingly
important to have automated tools to help identify services that match a
requester's requirements. Finding suitable Web services automatically depends
on the facilities available for service providers to describe the
capabilities of their services and for service requesters to describe their
requirements in an unambiguous and ideally, machine-interpretable form.
Adding semantics to represent the requirements and capabilities of Web
services is essential for achieving this unambiguity and
machine-interpretability.
Semantics play an important role in all aspects of the lifecycle of Web
services. During development, a service provider can explicate the intended
semantics by annotating the appropriate parts of the Web service with
concepts from a richer semantic model. Since semantic models provide
agreement on the terms and intended use of terms, and may provide formal and
informal definitions of the entities, there will be less ambiguity in the
intended semantics of the provider. During discovery, a service requestor can
describe the service requirements using terms from the semantic model.
Reasoning techniques can be used to find service descriptions that match the
request. During composition, these annotations can be used to aggregate the
functionality of multiple services to create useful service compositions.
Also, semantics based schema mappings can facilitate data transformations
from which mediation code can be generated to enable Web services invocation.
Therefore, once represented, semantics can be leveraged by tools to automate
service discovery, mediation, composition and monitoring.
The World-Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standard Web Services Description
Language (WSDL) specifies a standard way to describe the interfaces of a Web
Service at a syntactic level and how to invoke it. However, WSDL does not
explicitly provide mechanisms to specify the semantics of a Web service.
Semantic Annotations for WSDL (SAWSDL) is an effort to
define mechanisms by which semantic annotations can be added to WSDL
components. This usage guide is an accompanying document to SAWSDL
specification. It presents examples to illustrate how to associate semantic
annotations with a Web service that could be used for classifying,
discovering, matching, composing, and invoking Web services.
The sections in this document are organized to show how to associate
semantic annotations with a WSDL document for use in service classification,
discovery, matching, composition and invocation in that order.
1.1 Namespaces
The XML namespace names URIs
used by this specification are as follows:
1.2 Running Examples
Throughout this document, we use two Web services and several variations
on these Web services to illustrate how semantic annoations on a WSDL can be
used to do Web service interface matching and composition. One of these two
Web services is presented as a request of a desirable Web service while the
other is used as an advertisement or a service being offered by a service
provider. Some readers may be new to the concept of representing the
requirements of a client as a Web service - WSDL. While there may be
different ways of representing the requirements of a client, in this
document, for illustrative purposes we adopted the notion of a request WSDL
where the requirements of a client are modeled as a Web service - WSDL. The
inputs and outputs of this request WSDL codify the available inputs that a
client can provide and the expected outputs from a service respectively. We
then use the concepts of annotating a request similar to the way that one can
annotate a service provider's WSDL and illustrate how a request WSDL
interface can be matched, composed and transformed to invoke a service
provider's advertised service.
We present these two Web services here so as to allow the reader to get
familiarized with the examples used in the rest of the document. These are
'vanilla' WSDL files with no semantic annotations. In the following sections,
these WSDLs are shown with suitable semantic annotations that suit the
specific illustration. First a WSDL representation of a request WSDL is given
followed by a service provider's advertisement WSDL.
<wsdl:description
targetNamespace="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/CheckAvailabilityRequestService/"
xmlns="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/CheckAvailabilityRequestService/"
xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#">
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/CheckAvailabilityRequestService">
<xs:element name="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceRequest">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="itemCode" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="date" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="qty" type="xs:float"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceResponse type="itemConfirmation"/>
<xs:simpleType name="itemConfirmation">
<xs:restriction base:"xs:boolean"/>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:interface name="CheckAvailabilityRequestService">
<wsdl:operation name="CheckAvailabilityRequestOperation" pattern="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out"
<wsdl:input element="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceRequest"/>
<wsdl:output element="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceResponse"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:interface>
</wsdl:description>
Listing 1.2-1: WSDL excerpt for
CheckAvailabilityRequest service
<wsdl:description
targetNamespace="http://org2.example.com/wsdl/CheckInventoryService/"
xmlns="http://org2.example.com/wsdl/CheckInventoryService/"
xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#">
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://org2.example.com/wsdl/CheckInventoryService">
<xs:element name="CheckInventoryServiceRequest">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="SKU" type="xsd:string"/>
<wsdl:element name="deliveryDate" type="xs:string"/>
<wsdl:element name="numBundles" type="xs:float"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="CheckInventoryServiceResponse">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="conf" type="xsd:boolean"/>
<xs:element name="numBundles_available" type="xsd:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:interface name="CheckInventoryService">
<wsdl:operation name="checkInventoryService" pattern="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out">
<wsdl:input element="CheckInventoryServiceRequest"/>
<wsdl:output element="CheckInventoryServiceResponse"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:interface>
</wsdl:description>
Listing 1.2-2: WSDL excerpt for
CheckInventoryService
A Web service can be semantically annotated to carry categorization
information that could be used to publish it for instance in a service
registry. SAWSDL extension mechanism modelReference can be used to
add this categorization information to Web services. This categorization
information could be used when automatically publishing services in
registries such as UDDI [UDDI]. Below, we illustrate a
couple of ways in which categorization information can be associated with a
Web service.
If a categorization semantic model already exists (for example a
taxonomy), then a modelReference element could be defined either on
an interface or on an operation of a Web service to point to a particular
categorization in the taxonomy. For example, if a purchase order taxonomy was
created as shown in Listing 2.1-1 below (shown in RDF Turtle [Turtle] format for readability), then the interface of
an item availability check Web service (introduced in Listing 1.2-1) could be
annotated with taxonomy information as shown in Listing 2.1-2.
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix owl: <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#> .
@prefix : <http://org1.example.com/taxonomies/POServiceClassification#> .
<http://org1.example.com/taxonomies/POServiceClassification#> rdf:type owl:Ontology .
:PurchaseOrderServices rdf:type owl:Class .
:OrderModification rdf:type owl:Class;
rdfs:subClassOf :PurchaseOrderServices .
:ItemAvailabilityCheck rdf:type owl:Class;
rdfs:subClassOf :PurchaseOrderServices .
:OrderPlacement rdf:type owl:Class;
rdfs:subClassOf :PurchaseOrderServices .
:ProductInfoInquiry rdf:type owl:Class;
rdfs:subClassOf :PurchaseOrderServices .
:OrderTracking rdf:type owl:Class;
rdfs:subClassOf :PurchaseOrderServices .
Listing 2.1-1: A taxonomy to organize Web services
related to checking, placing, and tracking purchase orders
...
<wsdl:interface name="CheckItemAvailabilityRequestService"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/taxonomies/POServiceClassification#ItemAvailabilityCheck">
...
</wsdl:interface>
...
Listing 2.1-2: Shows how a WSDL interface could be
annotated with categorization information that could be used in publishing a
Web service (for example, into a service registry)
Some taxonomies may not provide direct URIs for their categories and may
require multiple pieces of information to identify the categories.In such a
case, users can define such information as per the requirements and associate
a modelReference to point to such user-defined taxonomic
information. For example, if a particular taxonomy specifies three pieces of
information namely, the name of the taxonomy, the specific categorization in
the taxonomy and a unique code for that taxonomy, then, it can be defined as
follows.
@prefix categorization: <http://org1.example.com/taxonomies/categorization#> .
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix xs: <http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
categorization:Category rdf:type rdfs:Class .
categorization:hasValue rdf:type rdf:Property;
rdfs:domain categorization:Category;
rdf:range rdfs:Literal .
categorization:usesTaxonomy rdf:type rdfs:Property;
rdfs:domain categorization:Category;
rdf:range xs:anyUri .
Listing 2.2-1: Schema for defining a taxonomy with
specific properties
Then, an instance such as the one below in listing 2.2-2 that adheres to
the above schema in Listing 2.2-1 can be defined and either imported or
inserted into the WSDL file whose interface (or operation) is to be
annotated.
@prefix categorization: <http://org1.example.com/taxonomies/categorization#> .
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix xs: <http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
categorization:Category rdf:type "urn:Electronics" ;
categorization:hasValue "443112" ;
categorization:usesTaxonomy "http://naics.com/" .
Listing 2.2-2: An instance of a taxonomy defined using
the schema defined in Listing 2.2-1.
The annotation can be associated with the interface of a Web service as
follows.
<wsdl:interface name="CheckAvailabilityRequestService"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/taxonomies/categorization#Electronics">
...
</wsdl:interface>
Listing 2.2-3: A WSDL excerpt showing how a
wsdl:interface could be annotated with taxonomy information from the listing
defined in Listing 2.2-2.
Using similar modelReference annotation operations within an
interface can also be annotated. SAWSDL does not specify any relationship
between the categorization information specified at the level of an interface
and the one that is specified on an operation that is contained within that
interface. The example in listing 2.2-4 below shows how an operation within a
Web service interface could be annotated using the same 'categorization'
scheme.
<wsdl:operation name="CheckAvailabilityRequestOperation" sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/taxonomies/categorization#Electronics"
...
</wsdl:operation>
Listing 2.2-4: A WSDL excerpt showing how a
wsdl:operation could be annotated with taxonomy information from the
listing defined in Listing 2.2-2.
In this subsection, we discuss how one can use the categorization
annotation information defined by using the mechanisms described in section 2
to publish Web services in a UDDI registry. This is provided as an example
for illustrative purpose. One can use similar mechanisms to publish the Web
services in registries or repositories other than UDDI.
Following the example in Listing 2.2-2, one can define taxonomy references
to point to a specific category defined in, say, NAICS [NAICS] taxonomy that is registered in a UDDI registry as
shown in listing 2.3-1. This information can then be reused when a service
(such as the CheckItemAvailability Service whose interface definition is
shown in Listing 2.2-3) is published in the UDDI registry. In the following
example we use the NAICS taxonomy registered in UDDI.
@prefix categorization: <http://org1.example.com/taxonomies/categorization#> .
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix xs: <http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
categorization:Category rdf:type "urn:Electronics" ;
categorization:hasValue "443112" ;
categorization:usesTaxonomy "uddi:uddi.org:ubr:categorization:naics:2002" .
Listing 2.3-1: An instance of a taxonomy defined using
the schema defined in Listing 2.2-1 that refers to NAICS taxonomy registered
in UDDI registry.
To publish a Web service that is represented in SAWSDL in a UDDI registry,
an automatic Web service publishing engine can dereference the taxonomy
information from its interface and use that information to determine which
category of what taxonomy in the registry to publish the service to. For
example, when publishing the service in UDDI V3, a category bag can be
created to classify the service using this information. Listing 2.3-2 below
shows the UDDI categoryBag structure that could be created from the
categorization information in Listing 2.3-1.
<categoryBag>
<keyedReference
tModelKey="uddi:uddi.org:ubr:categorization:naics:2002"
keyName="Electronics"
keyValue="443112"/>
</categoryBag>
Listing 2.3-2: UDDI Category bag structure derived from
the taxonomy instance in Listing 2.3-1.
In this section we have discussed the usage of modelReference concepts on an interface and
operation for associating categorization relation information for
illustrative purposes. Users may choose to use modelReferences on interfaces
and operations for associating other behavioral aspects with a servicel.
One of the main motivations for SAWSDL specification is to provide
mechanisms using which semantic annotations can be added to WSDL documents so
that these semantics can be used to help automate the matching and
composition of Web services. In this section we present some examples to show
how to add such annotations for use during Web service interface matching and
composition. First we present an example to illustrate the use of annotations
in Web service interface matching.
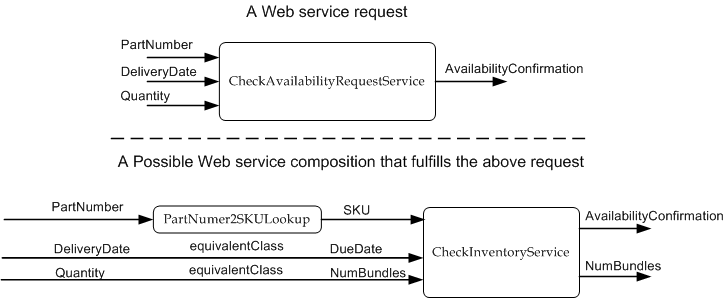
Let's consider the the following scenario. A requestor would like to
submit a request to verify the availability of an item from a preferred
supplier. Say that this request is represented as a CheckAvailabilityRequest
WSDL (introduced in Listing 1.2-1). Also suppose that a service provider has
a service to offer that enables the requesters to check for the availability
of items it offers. This is called CheckInventoryService and is also
represented as a WSDL with the same name (also introduced in Listing 1.2-2).
Specifically, the request
WSDL codifies the inputs it can supply and the outputs it expects of an
item availability check service by the service provider. The service
WSDL specifies the interface of a service that allows requesters to check
for the availability of an inventory item by exposing the inputs it requires
in order to provide item availability confirmation. At a high level the
service offered by the service provider should match the request. However,
the differences in the vocabulary used by the two services to represent their
interfaces may get in the way of making a match. For example, the term
itemCode used by the requester and the term SKU (Stock
Keeping Unit) used by the provider both are meant to uniquely identify the
item in question. Also, the term qty used by the requester and the
term numBundles used by the provider both in this context may refer
to the number of items (in one case, it is the number of items being
requested and in the other case, it is the number of items being offered).
However, a matching engine may not have sufficient information to identify
them as related terms unless explicitly specified. Semantic annotations, in
cases such as these, could be quite helpful. In the simple case, if there
were to be a common semantic model that one can use to annotate the WSDLs of
the requester and the service provider as shown below (in Listings 3.1-1 and
3.1-2), then a semantic engine could use this information to match the two
Web services. In this example, annotation is done using
modelReference extensibility element defined in SAWSDL.
The WSDL excerpt shown below in listing 3.1-1 represents one of the ways
of semantically annotating WSDL document of the request for checking item
availability.
<wsdl:description
targetNamespace="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/CheckAvailabilityRequestService/"
xmlns="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/CheckAvailabilityRequestService/"
xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#"
xmlns:sawsdl="http://www.w3.org/2002/sw/sawsdl/spec/sawsdl#"
xmlns:SampleOntology="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#>
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/CheckAvailabilityRequestService">
<xs:element name="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceRequest">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="itemCode" type="xs:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#PartNumber"/>
<wsdl:element name="date" type="xs:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#DueDate"/>
<wsdl:element name="qty" type="xs:float"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#Quantity/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceResponse type="itemConfirmation"/>
<xs:simpleType name="itemConfirmation">
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#AvailabilityConfirmation"
<xs:restriction base:"xs:boolean"/>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:interface name="CheckAvailabilityRequestService">
<wsdl:operation name="checkAvailabilityRequestOperation" pattern="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out">
<wsdl:input element="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceRequest"/>
<wsdl:output element="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceResponse"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:interface>
</wsdl:description>
Listing 3.1-1: A WSDL excerpt of a semantically annotated
service request that shows the usage of modelReference.
The WSDL excerpt in listing 3.1-2 represents a way of semantically
annotating the WSDL document of the service offered by the service provider
for checking item availability.
<wsdl:description
targetNamespace="http://org2.example.com/wsdl/CheckInventoryService/"
xmlns="http://org2.example.com/wsdl/CheckInventoryService/"
xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#"
xmlns:sawsdl="http://www.w3.org/2002/sw/sawsdl/spec/sawsdl#"
xmlns:SampleOntology="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#>
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://org2.example.com/wsdl/CheckInventoryService">
<xs:element name="CheckInventoryServiceRequest">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="SKU" type="xsd:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#SKU"/>
<wsdl:element name="deliveryDate" type="xs:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#DueDate"/>
<wsdl:element name="numBundles" type="xs:float"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#Quantity/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="CheckInventoryServiceResponse">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="conf" type="xsd:boolean"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#AvailabilityConfirmation"/>
<xs:element name="numBundles_available" type="xsd:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#Quantity"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:interface name="CheckInventoryService">
<wsdl:operation name="checkInventoryOperation" pattern="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out">
<wsdl:input element="CheckInventoryServiceRequest"/>
<wsdl:output element="CheckInventoryServiceResponse"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:interface>
</wsdl:description>
Listing 3.1-2: A WSDL excerpt of a semantically annotated
service (advertisement) that shows the usage of modelReference.
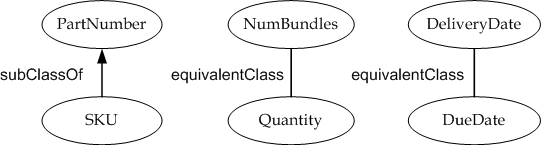
As can be noted, in this example both WSDL documents in this example are
annotated with concepts from the same semantic model – SampleOntology
(shown in listing 3.1-3). In this example, the ontology contains the
relationship between the concepts PartNumber and SKU i.e., a SKU Code is a
subClassOf PartNumber. A semantic engine can infer this relationship during
Web service interface matching by parsing and reasoning over this semantic
model. Therefore, the WSDL elements 'itemCode' in the request WSDL and the
'SKU' in the service WSDL match with one another. In the case of the other
input elements namely'qty' vs 'numBundles' and 'date' vs 'deliveryDate',
since both these sets of elements are annotated with shared semantic concepts
namely 'Quantity' and 'DueDate' respectively the semantic ambiguity can be
resolved by direct matching of semantic annotations. The same applies to
matching outputs as well. The ontology that represents the subClassOf
relationship between the two concepts PartNumber and SKU can be modeled in
OWL as follows.
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix: <http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#> .
@prefix owl: <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#> .
<http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntology#> rdf:type owl:Ontology .
:PartNumber rdf:type owl:Class .
:SKU rdf:type owl:Class;
rdfs:subClassOf :PartNumber .
:Quantity rdf:type owl:Class .
:DueDate rdf:type owl:Class .
:AvailabilityConfirmation rdf:type owl:Class .
Listing 3.1-3: A simple
SampleOntology that captures the subClassOf relationship between PartNumber
and SKU concepts.
In section 3.1 we made a shared ontology assumption between the requester
and service provider domains. This assumption may not always hold good. The
vocabulary differences may result in two different ontologies one for each
side albeit for the same domain. In such a case one can create a mapping
ontology by capturing the relationships between the concepts used in the
different ontologies. Below we annoate the same two request and advertisement
WSDLs using concepts from different ontologies. When a mapping ontology such
as the one shown in listing 3.2-3 is available, then the semantic annotations
extracted from the request and the advertisement WSDL can be matched using
such a mapping ontology.
The WSDL excerpt shown below in listing 3.2-1 represents one of the ways
of semantically annotating WSDL document of the request for checking item
availability.
<wsdl:description
targetNamespace="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/CheckAvailabilityRequestService/"
....
xmlns:Org1Ont="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#>
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/CheckAvailabilityRequestService">
<xs:element name="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceRequest">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="itemCode" type="xs:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#PartNumber"/>
<wsdl:element name="date" type="xs:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#DueDate"/>
<wsdl:element name="qty" type="xs:float"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#Quantity/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceResponse type="itemConfirmation"/>
<xs:simpleType name="itemConfirmation">
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#AvailabilityConfirmation"
<xs:restriction base:"xs:boolean"/>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:interface name="CheckAvailabilityRequestService">
<wsdl:operation name="checkAvailabilityRequestOperation" pattern="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out">
<wsdl:input element="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceRequest"/>
<wsdl:output element="CheckAvailabilityRequestServiceResponse"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:interface>
</wsdl:description>
Listing 3.2-1: A WSDL excerpt of a semantically annotated
service request that shows the usage of modelReference.
The WSDL excerpt shown below in listing 3.2-2 represents a way of
semantically annotating the WSDL document of the service offered by the
service provider for checking item availability.
<wsdl:description
targetNamespace="http://org2.example.com/wsdl/CheckInventoryService/"
.....
xmlns:Org2Ont="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#>
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://org2.example.com/wsdl/CheckInventoryService">
<xs:element name="CheckInventoryServiceRequest">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="SKU" type="xsd:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#SKU"/>
<wsdl:element name="deliveryDate" type="xs:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#DeliveryDate"/>
<wsdl:element name="numBundles" type="xs:float"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#NumBundles/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="CheckInventoryServiceResponse">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="conf" type="xsd:boolean"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#AvailabilityConfirmation"/>
<xs:element name="numBundles_available" type="xsd:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#NumBundles"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:interface name="CheckInventoryService">
<wsdl:operation name="checkInventoryOperation" pattern="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out">
<wsdl:input element="CheckInventoryServiceRequest"/>
<wsdl:output element="CheckInventoryServiceResponse"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:interface>
</wsdl:description>
Listing 3.2-2: A WSDL excerpt of a semantically annotated
service (advertisement) that shows the usage of modelReference.
As noted, in this case the concepts originating from different ontologies
represented in the two WSDLs shown above are mapped in a mapping ontology
such as the one shown below in Listing 3.2-5. It contains relationships
between concepts such as Quantity & NumBundles and Due Date &
DeliveryDate and PartNumber & SKU. Just as in the example in section 3.1,
a semantic matching engine can now be applied to reason over these
relationships during Web service interface matching. The relationships
between the concepts in this mapping ontology are shown pictorially in Figure
1 below.
Below, we list the three ontologies that are used in matching the
checkAvailabilityRequest() request WSDL with the checkInventoryService()
advertisement WSDL. The first ontology shown in listing 3.2-3 is the one used
by the requesting organization (referred to using the name space
http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1) that defined the
checkAvailabilityRequest() request WSDL. The second ontology shown in listing
3.2-4 is the one used by the service advertising organization (referred to
using the namespace ) that defined the checkInventoryService() advertisement
WSDL. The third one shown in listing 3.2-5 is the mapping ontology defined by
a third organization (could possibly be defined by either of the first two
organizations as well) that relates the concepts from the two ontologies
defined by org1 and org2.
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix: <http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#> .
@prefix owl: <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#> .
<http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#> rdf:type owl:Ontology .
:PartNumber rdf:type owl:Class .
:DueDate rdf:type owl:Class .
:Quantity rdf:type owl:Class .
:AvailabilityConfirmation rdf:type owl:Class .
Listing 3.2-3:An RDF
Turtle excerpt of an Ontology used by the organization that defined
checkAvailabilityRequest() request WSDL.
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix: <http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#> .
@prefix owl: <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#> .
<http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#> rdf:type owl:Ontology .
:SKU rdf:type owl:Class .
:DeliveryDate rdf:type owl:Class .
:NumBundles rdf:type owl:Class .
:AvailabilityConfirmation rdf:type owl:Class .
Listing 3.2-4: An RDF Turtle
excerpt of Ontology used by the organization that defined
checkInventoryService() advertisement WSDL
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix: <http://org3.example.com/ontologies/MappingOntology#> .
@prefix Org1Ont: <http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#> .
@prefix Org2Ont: <http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#> .
@prefix owl: <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#> .
<http://org3.example.com/ontologies/MappingOntology#> rdf:type owl:Ontology .
Org2Ont:SKU rdfs:subClassOf Org1Ont:PartNumber .
Org2Ont:NumBundles owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:Quantity .
Org2Ont:DeliveryDate owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:DueDate .
Org2Ont:AvailabilityConfirmation owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:AvailabilityConfirmation .
Listing 3.2-5: An RDF Turtle excerpt showing the mapping
ontology mapping concepts from ontologies in listings 3.2-3 and 3.2-4. This
mapping ontology is used to match the request WSDL in listing 3.2-1 with the
advertisement WSDL in listing 3.2-2.
It is to be noted that SAWSDL specifies mechanisms to annotate WSDLs but
does not say anything about how these annotations are generated. These
annotations can either be created manually or by tools that can infer
relationships between the terms used in the WSDLs and those that are given in
a semantic model. Also, SAWSDL does not say anything about how the semantic
models themselves are created. Just like the creation of annotations, these
semantic models can either be created manually by a human expert or generated
automatically using ontology learning tools or by a combination of both.
In the next section, we extend the above item availability check example
to show how semantic annotations added to a WSDL can be used to compose Web
services.
This section illustrates how semantic annotations can be used to compose
Web services. The request and advertisement WSDLs to be considered in this
scenario are the same as the ones shown in listings 3.2-1 and 3.2-2
respectively. However, we introduce a variation to the mapping ontology from
section 3.2. Suppose that in the item availability checking scenario that we
have been discussing so far, the subClassOf relationship between the concepts
PartNumber and SKU is unspecified in the ontology. In this case, the request
checkAvailabilityRequest() would not match with the service
checkInventoryService() because there is no relationship between PartNumber
and SKU. Also, suppose that there is another Web service called
PartNumber2SKULookup ( ) that can take a PartNumber as input and produce SKU
as output (Listing 3.3-1). Say that a matching engine would be able to find
this service in the appropriate category in a registry - in this case it
would be in 'Utilities/LookupServices' category (because the modelReference
on the operation of this service contains the categorization information. So,
presumably a publishing agent/program would have placed this service in the
appropriate category that is referred to by the modelReference URI). Say, also, that a
mapping ontology such as the one shown in listing 3.3-2 is available for the
matching engine. Now, the service PartNumber2SKULookup() can be composed with
checkInventoryService() to match the request checkAvailabilityRequest() as
shown in Figure 2. This can be achieved by simply extracting the semantic
annotations from the request, and all the advertisement WSDLs and using the
relationships in the mapping ontology to match the corresponding concepts. A
simple Web service composition using the semantics annotations on the request
and advertisement services is illustrated in Figure 2.
<wsdl:description
targetNamespace="http://org3.example.com/wsdl/PartNumber2SKULookupService/"
xmlns="http://org3.example.com/wsdl/PartNumber2SKULookupService/"
xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#"
xmlns:sawsdl="http://www.w3.org/2002/sw/sawsdl/spec/sawsdl#
xmlns:Org3Ont="http://org3.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#">
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://org3.example.com/wsdl/PartNumber2SKULookupService>
<xs:element name="PartNumber2SKULookupServiceRequest" type="partNum"/>
<xs:simpleType name="partNum">
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org3.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#PartNumber">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:element name="PartNumber2SKULookupServiceResponse" type="SKU"/>
<xs:simpleType name="SKU">
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org3.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#SKU">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:interface name="PartNumber2SKULookupService">
<wsdl:operation name="PartNumber2SKULookupService" pattern="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org3.example.com/taxonomies/Utilities#LookupServices" >
<wsdl:input element="PartNumber2SKULookupServiceRequest"/>
<wsdl:output element="PartNumber2SKULookupServiceResponse"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:interface>
</wsdl:description>
Listing 3.3-1: A WSDL excerpt representing
PartNumber2SKULookup service.
Listing 3.3-2 below shows the variation on the mapping ontology discussed
in section 3.2. As noted, this ontology does not contain any relationship
between PartNumber and SKU concepts. The additional differences from listing
3.2-5 are shown below in bold font style. In this example, we assume that the
same organization that provides the PartNumber2SKULookupService() provides
the mapping ontology. In practice, this does not have to be the case. Any of
the three organizations (org1, org2, and org3 referred to in the namespaces)
or an entirely new organization (org4) can provide a mapping ontology. The
namespaces, in such a case, should reflect the change accordingly. The
ontologies that are used to annotate the request WSDL
checkAvailabilityRequest() and the advertisement WSDL checkInventoryService()
are unchanged from those presented in listing 3.2-3 and 3.2-4.
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix: <http://org3.example.com/ontologies/MappingOntology#> .
@prefix Org1Ont: <http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#> .
@prefix Org2Ont: <http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#> .
@prefix Org3Ont: <http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#> .
@prefix owl: <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#> .
<http://org3.example.com/ontologies/MappingOntology#> rdf:type owl:Ontology .
Org2Ont:NumBundles rdf:type owl:Class;
owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:Quantity .
Org2Ont:DeliveryDate rdf:type owl:Class;
owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:DueDate .
Org2Ont:AvailabilityConfirmation rdf:type owl:Class;
owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:AvailabilityConfirmation .
Org3Ont:PartNumber rdf:type owl:Class;
owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:PartNumber .
Org3Ont:SKU rdf:type owl:Class;
owl:equivalentClass Org2Ont:SKU .
Listing 3.3-2: Revised Mapping Ontology that contains
relationships between concepts from three different ontologies.
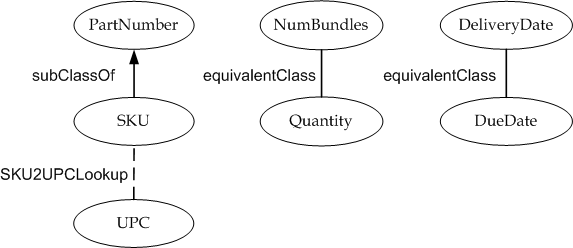
We introduce three variations to our item availability checking scenario
in this section to illustrate how one can use semantic annotations to compose
Web services with ontology reasoning. First, suppose that we have a
checkInventoryService() that takes an UPC as input inplace of SKU ((as
introduced in Listing 1.2-2 but with semantic annotations as in Listing 3.4-1
below). Then, this service will not match the request
checkAvailabilityRequest() (unchanged from Listing 3.2-1) because there is no
relationship between the concepts PartNumber and UPC in the mapping ontology.
So, even semantic annotations will not be able to help in matching the
request checkAvailabilityRequest() and the advertisement
checkInventoryService(). Second, say that there is another Web service
called SKU2UPCLookup( ) that can take an SKU as input and
produce UPC (Universal Product Code) as output (Listing 3.4-2).
Third, the original mapping ontology introduced in Listing 3.2-3 has an
addition of UPC concept. But it is to be noted that the ontology does not
specify any relationship between SKU and UPC codes. Figure 3 summarizes the
relationships between the concepts PartNumber, SKU, and UPC in
SampleOntology. Now with these three variations, we have enough information
to see how a semantic engine can compose Web services to match the request
checkAvailabilityRequest() with checkInventoryService().
<wsdl:description
targetNamespace="http://org2.example.com/wsdl/CheckInventoryService/"
....
xmlns:Org2Ont="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#>
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://org2.example.com/wsdl/CheckInventoryService">
<xs:element name="CheckInventoryServiceRequest">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="UPC" type="xsd:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#UPC"/>
<wsdl:element name="deliveryDate" type="xs:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#DeliveryDate"/>
<wsdl:element name="numBundles" type="xs:float"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#NumBundles/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="CheckInventoryServiceResponse">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="conf" type="xsd:boolean"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#AvailabilityConfirmation"/>
<xs:element name="numBundles_available" type="xsd:string"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#NumBundles"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:interface name="CheckInventoryService">
<wsdl:operation name="checkInventoryOperation" pattern="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out">
<wsdl:input element="CheckInventoryServiceRequest"/>
<wsdl:output element="CheckInventoryServiceResponse"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:interface>
</wsdl:description>
Listing 3.4-1: CheckInventoryService() WSDL excerpt with
a variation where the input SKU is replaced by UPC for the purpose of
illustrating Web service composition with ontology reasoning.
A WSDL excerpt of SKU2UPCLookupService() is shown below.
<wsdl:description
targetNamespace="http://org3.example.com/wsdl/SKU2UPCLookupService/"
.....
xmlns:Org3Ont="http://org3.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#>
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://org3.example.com/wsdl/SKU2UPCLookupService>
<xs:element name="SKU2UPCLookupServiceRequest" type="SKU"/>
<xs:simpleType name="SKU">
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org3.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#SKU">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:element name="SKU2UPCLookupServiceResponse" type="UPC"/>
<xs:simpleType name="UPC">
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org3.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#UPC">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:interface name="SKU2UPCLookupService">
<wsdl:operation name="SKU2UPCLookupService" pattern="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org3.example.com/taxonomies/Utilities#LookupServices">
<wsdl:input element="SKU2UPCLookupServiceRequest"/>
<wsdl:output element="SKU2UPCLookupServiceResponse"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:interface>
</wsdl:description>
Listing 3.4-2: A WSDL excerpt representing SKU2UPCLookup
service.
Below, we list the three ontologies that are used in matching the
checkAvailabilityRequest() request WSDL with the checkInventoryService()
advertisement WSDL according to the scenario described in this section. The
first ontology shown in listing 3.4-3 is the one used by the requesting
organization (referred to using the name space
http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1) that defined the
checkAvailabilityRequest() request WSDL. Please note that this differs from
the listing in 3.2-3 because this ontology contains the 'subClassOf'
relationship between SKU and PartNumber concepts. The second ontology shown
in listing 3.4-4 is the one used by the service advertising organization
(referred to using the namespace ) that defined the checkInventoryService()
advertisement WSDL. Please note that this differs from the listing in 3.2-4
because this contains the concept UPC instead of SKU. The third one shown in
listing 3.2-5 is the mapping ontology defined by a third organization (could
possibly be defined by either of the first two organizations as well) that
relates the concepts from the two ontologies defined by org1 and org2.
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix: <http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#> .
@prefix owl: <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#> .
<http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#> rdf:type owl:Ontology .
:PartNumber rdf:type owl:Class .
:SKU rdf:type owl:Class;
rdfs:subClassOf :PartNumber .
:DueDate rdf:type owl:Class .
:Quantity rdf:type owl:Class .
:AvailabilityConfirmation rdf:type owl:Class .
Listing 3.4-3:An RDF
Turtle excerpt of an Ontology used by the organization that defined
checkAvailabilityRequest() request WSDL.
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix: <http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#> .
@prefix owl: <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#> .
<http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#> rdf:type owl:Ontology .
:UPC rdf:type owl:Class;
:DeliveryDate rdf:type owl:Class .
:NumBundles rdf:type owl:Class .
:AvailabilityConfirmation rdf:type owl:Class .
Listing 3.4-4: An RDF Turtle excerpt of Ontology used by the
organization that defined checkInventoryService() advertisement
WSDL
Listing 3.4-5 represents the updated sample ontology that enables
composition in this example. It relates the concepts in the ontologies shown
in listings 3.4-3 and 3.4-4. Note that the ontology as such does not specify
any relationship between SKU and UPC. Given an SKU, its corresponding UPC
code is retrieved by the Web service SKU2UPCLookup(). Here also, we assume
that the organization that is providing the SKU2UPCLookupService() is
providing the mapping ontology as well. As mentioned earlier in section 3.3,
this does not always have to be the case.
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix: <http://org3.example.com/ontologies/MappingOntology#> .
@prefix Org1Ont: <http://org1.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg1#> .
@prefix Org2Ont: <http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg2#> .
@prefix Org3Ont: <http://org2.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#> .
@prefix owl: <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#> .
<http://org3.example.com/ontologies/MappingOntology#> rdf:type owl:Ontology .
Org2Ont:NumBundles owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:Quantity .
Org2Ont:DeliveryDate owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:DueDate .
Org2Ont:AvailabilityConfirmation owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:AvailabilityConfirmation .
Org3Ont:SKU rdf:type owl:Class;
owl:equivalentClass Org1Ont:SKU .
Org3Ont:UPC rdf:type owl:Class;
owl:equivalentClass Org2Ont:UPC .
Listing 3.4-5: Revised Mapping Ontology that contains
relationships between concepts PartNumber, SKU, and UPC among other things
that is used in this section to illustrate Web service composition using
ontology reasoning.
Figure 3 represents an altered version of the ontology that enables
composition in this example.
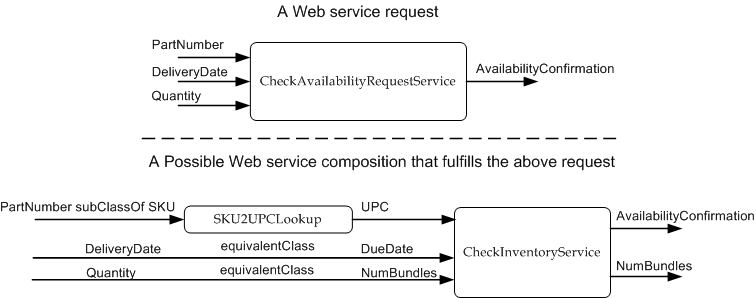
Figure 4 shows how Web service composition can be achieved by using the
semantic annotations in the WSDL files discussed in this example. As can be
noted, in this scenario, a semantic engine retrieves the semantic annotations
from checkAvailabilityRequest() for element itemCode namely PartNumber and
for the element SKU in SKU2UPCLookup() service namely SKU. The annotation
PartNumber doesnot match lexically with the concept SKU. So, the semantic
engine could then consult the MappingOntology to see if there is any
relationship between PartNumber and SKU. The ontology reasoner can return the
existance of 'subClassOf' relationship between SKU and PartNumber. This
information can then be used in composing SKU2UPCLookup() with
CheckInventoryService() as shown in Figure 4 to match the request
CheckAvailabilityRequest(). Again, as mentioned earlier in Section 3.3, a
matching engine would be able to find a utility service such as
SKU2UPCLookup() in the appropriate category in a registry - in this case it
would be in 'Utilities/LookupServices' category because the modelReference on
the operation of this service contains the categorization information. So,
presumably a publishing agent/program would have placed this service in the
appropriate category that is referred to by the modelReference URI.
The example presented in this section was a variation of the one discussed
in section 3.4. It illustrated how Web service composition can be achieved
usng the relationships between concepts in an ontology even when the semantic
annotations on the services don't match directly.
SAWSDL allows multiple annotations to be associated with those WSDL
elements that can have a modelReference extension. These annotations
could be pointing to different concepts from the same semantic model or from
different models altogether. For example, a WSDL element with the name
itemCode can be associated with SampleOntology#PartNumber
and SampleOntology#SKU concepts. SAWSDL does not specify any
relationship between these multiple annotations other than saying that they
all apply. It is upto the consumers of these annotated WSDLs to use the ones
that are relevant to them or to figure out the relationship between the
concepts, if they so choose, by consulting the ontology that defines them.
The following example in Listing 3.5-1 shows the annotation of
itemCode with multiple annotations. If a requesting WSDL is
annotated with multiple concepts like shown in listing 3.5-1, this increases
the likelihood of matching this request with other advertisement/service
WSDLs. Similarly, if a service WSDL is annotated with multiple concepts,
possibly more request WSDLs will match it.
...
<xs:simpleType name="itemCode"
sawsdl:modelReference="http://org3.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#PartNumber http://org3.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#SKU"/>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
...
Listing 3.5-1: A WSDL excerpt showing multiple
annotations to a simple type
The example given in this section so far illustrated multiple annotations
that come from the same ontology. It is possible for elements to be annotated
with concepts from different ontologies as well. The mechanism for doing so
is exactly the same as the one employed in Listing 3.5-1 except in the latter
case, the namespaces for the concepts coming from different ontolgies would
be different.
In the examples that we discussed so far, all annotations are added at the
member element levels of a complex type. SAWSDL allows annotations to be
added either at the complex type level (top level) or at the member element
level (bottom level) or both. In cases where both complex type and the member
elements have annotations, SAWSDL does not specify any relationship between
the modelReferences on a complex type and those on the elements
contained within a complex type. The listing below (Listing 3.6-1)
illustrates the usage of modelReference for annotating the complex
type 'ItemRequest' as well as the member elements.
<wsdl:types>
...
<xs:element name="ItemRequest" sawsdl:modelReference="http://org3.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#OrderItem">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="itemCode" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="date" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="qty" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
...
</wsdl:types>
Listing 3.6-1: WSDL excerpt from
CheckAvailabilityRequest() showing the annotation of a
complexType.
Here is one possible way in which the annotation on a complex type can be
used. The annotation on the complex type 'itemRequest' such as the one in
3.6-1 which is part of checkAvailabilityRequest() can be used to match
another complex type such as the one in checkInventoryService() shown in
Listing 3.6-2 below. The annotation on a complex type can be used a first
level of matching in structure matching i.e., a semantic matching engine
could use these annotations to see if two complex types have any relationship
at all. If they do, perhaps spending more time on matching the member
elements of complex types may be worth the time. If not, perhaps there is no
need to do detailed matching of complex structures. Therefore, the
annotations on complex types can be used for first level of structure
matching.
<wsdl:types>
...
<xs:element name="Item" sawsdl:modelReference="http://org3.example.com/ontologies/SampleOntologyOrg3#OrderItem">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="SKU" type="xsd:string"/>
<xs:element name="deliveryDate" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="numBundles" type="xs:float"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
...
</wsdl:types>
Listing 3.6-2: WSDL excerpt from CheckInventoryService()
showing the annotation of a compex type.
So far, we have discussed how to annotate WSDL documents with semantic
concepts for use in Web service discovery, matching and composition.These
annotations that can be added to a WSDL using modelReferences are meant to
add semantic clarity to WSDL elements by pointing to concepts in a semantic
model that describes the larger context. They help understand whether a
service matches clients' requests at a semantic level. However, there may
still be mismatches at the data level that would need to be addressed and
captured to enable the invocation of a Web service. In the following section,
we discuss the mechanisms defined in SAWSDL to capture such data
transformation maps (knowns as schema mappings) to enable Web service
invocation.
Consider the example where a client/requester may have a 'first name' and
'last name' among its data as shown in listing 4-1 and the advertisement
service requires a 'full name' as shown in listing 4-2. In this case, when
the client invokes the Web service of the service provider, the data values
of firstName and lastName need to be concatenated in the
message to the advertisement Web service to pass the correct values for the
fullName element.
..
<xs:element name="firstName" type=xs:string/>
<xs:element name="lastName" type=xs:string/>
..
Listing 4-1: An XML excerpt showing two elements
firstName and lastName.
..
<xs:element name="fullName" type=xs:string/>
..
Listing 4-2: An XML excerpt showing two elements
fullName.
To facilitate the association of such types of data transformations with
Web services, SAWSDL provides a mechanism called schemaMapping. A
schemaMapping concept is provided to allow the specification of
transformation functions on the WSDL elements to map instance data defined by
that XML schema document to the semantic data of the concepts in a semantic
model. Conversely, it allows the specification of transformation functions
that map the semantic data of ontological concepts to the instance data
values that adheres to the XML schema document that is being annotated. In
the former case, the transformation functions are referred to using the
extensibility feature liftingSchemaMapping and in the latter case it
is called loweringSchemaMapping. These kinds of mappings are useful
in general when the structure of the instance data does not correspond
directly to the organization of the semantic data. Also, these types of
mappings can be used to generate mediation code to support invocation of a
Web service.
Consider the scenario where a client/requester is able to supply the
parameters 'firstName', 'lastName' and 'middleName'. Say that the semantic
model that the that the client would like to use to annotate it's parameters
contains 'fullName' and 'middleName' concepts. Then the client can specify a
lifting schema mapping to map it's 'firstName' and 'lastName' concepts with
'fullName' via concatenation. 'middleName' concepts would be mapped directly
in this case since no transformation is required. Now, let's consider that a
service provider has an advertisement service that expects a parameter
'completeName'. This 'completeName' is meant to be a string consisting of
'firstName lastName middleInitial'. Say that the servide provider is using
the same semantic model as the one that the client is using for simplifying
the discussion. Then, the service provider can provide a lowering schema
mapping from the semantic data of the semantic model to create an XML
instance for 'completeName'. This lowering schemaMapping would essentially
concatenate the 'fullName' concept with the first letter of the concept
'middleName' to create an instance of 'completeName'. In this case, together
the lifting and lowering schema mapping transformation functions can enable
the client to invoke the service provider's service.
In the remaining part of this section, we illustrate this lifting and
lowering schema mappings in the context of a purchase order scenario. The
purchase order scenario is very similar to the check availability scenario we
have been discussing throughout this document so far.
Editor's note: TODO: The remaining part of this section and the following SPARQL and XSLT examples will be revised to make it complete.
In their current form, they do not work.
The following example in Listing 4-2 illustrates lifting schema mapping
notion with XSLT.
<wsdl:description>
...
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema
targetNamespace="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/order#" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:element name="OrderRequest">
<xs:complexType sawsdl:liftingSchemaMapping="http://org1.example.com/mapping/OrderRequest.xslt">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="firstName" type="xs:integer" />
<xs:element name="lastName" type="xs:integer" />
<xs:element name="item" type="item" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="item">
<xs:all>
<xs:element name="itemCode" type="xs:string" />
<xs:element name="quantity" type="xs:float"/>
<xs:element name="dueDate" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="billingInfo" type="xsd1:POBilling"/>
</xs:all>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:element name="OrderResponse" type="Confirmation"/>
<xs:simpleType name="Confirmation">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="Confirmed"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Pending"/>
<xs:enumeration value="Rejected"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:interface name="Order">
<wsdl:operation name="order" pattern="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out">
<wsdl:input element="OrderRequest"/>
<wsdl:output element="OrderResponse"/>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:interface>
</wsdl:description>
...
Listing 4-2: A WSDL excerpt showing
liftingSchemaMapping notion.
Listing 4-2 refers to OrderRequest.xslt. This XSLT maps the elements of
OrderRequest complex type with the corresponding ones in the ontology. The
part where an XSLT would be of most value in this example is where the values
of firstName and lastName are concatenated to match with the semantic data of
the concept 'FullName' in the SampleOntology. An excerpt of such a
transformation in XSLT [XSLT] is shown Listing 4-3
below.
<xsl:transform version="2.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:po="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/order#"
xmlns:POOntology="http://org1.example.com/ontology/purchaseorder#">
<xsl:output method="xml" version="1.0" encoding="iso-8859-1" indent="yes" />
<xsl:variable name="firstName" select="wsdl:description/xs:element[@name='OrderRequest']/xs:complexType/xs:sequence/xs:element[@name='firstName']"/>
<xsl:variable name="lastName" select="wsdl:description/xs:element[@name='OrderRequest']/xs:complexType/xs:sequence/xs:element[@name='lastName']"/>
<xsl:variable name="fullName" select="concat($firstName,' ', $lastName)"/>
<xsl:template match="/">
<xsl:apply-templates/>
<xsl:template>
</xsl:transform>
Listing 4-3: An XSLT excerpt that concatenates the values
of firstName and lastName elements to form the semantic data of the concept
FullName in the ontology.
When specifying a liftingSchemaMapping, an XSLT transform can create a
specific XML that can be treated as the representation of semantic data for
an RDF/OWL ontology. While specifying loweringSchemaMapping, on the other
hand, it may not be clear what format the semantic data of the ontology is
expressed in (since there are many variations of RDF semantic data
representation format as defined by XML schema). To overcome this, SAWSDL
proposes the use of SPARQL language to query the semantic data of the
ontology to obtain a specific XML format for the semantic data of the
ontology so that it can then be used to formulate an XSLT transform to obtain
an XML that could correspond with the instance of a Web service. A sample
semantic data is shown in Listing 4-4 and a sample SPARQL query that could be
used in loweringSchemaMapping is shown in Listing 4-5 below.
<!DOCTYPE rdf:RDF[
<!ENTITY xsd "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#" >
]> <rdf:RDF
xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:owl="http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#"
xmlns="http://org1.example.com/ontology/purchaseorder#"
xml:base="http://org1.example.com/ontology/purchaseorder#">
<owl:Ontology />
<OrderRequest>
<hasLineItems>
<LineItem>
<hasPart>
<part>
<hasPartCode>
<partNum>
<hasLexicalRespresentation>348290187318</hasLexicalRespresentation>
</partNum>
</hasPartCode>
</part>
</hasPart>
<hasDueDate>
<date>
<dueDate>
<hasLexicalRespresentation>20060906</hasLexicalRespresentation>
</dueDate>
</date>
</hasDueDate>
<hasQuantity rdf:datatype="&xsd;float">12</hasQuantity>
<hasQuantity rdf:billingInfo="&xsd1;POBilling">23 XYZ Road</hasQuantity>
</LineItem>
</hasLineItems>
<hasCustomer>
<Customer>
<hasCustomerName>
<Name>
<hasLexicalRespresentation>ABC DEF</hasLexicalRespresentation>
</Name>
</hasCustomerName>
</Customer>
</hasCustomer>
</OrderRequest>
</rdf:RDF>
Listing 4-4: An excerpt of semantic
data that adheres to the variation on SampleOntology.
<lowering>
<sparqlQuery>
PREFIX po: <http://org1.example.com/ontology/purchaseorder#>
SELECT ?name ?partNum ?quantity ?dueDate ?billingInfo
WHERE {
?order po:hasCustomer ?customer .
?customer po:hasCustomerName ?Name .
?Name po:hasLexicalRespresentation ?name .
?order po:hasLineItems ?item .
?item po:hasQuantity ?quantity .
?item po:hasBillingInfo ?billingInfo .
?item po:hasDueDate ?Date .
?date po:hasLexicalRepresentation ?dueDate .
?item po:hasPart ?part .
?part po:hasPartCode ?code .
?code po:hasLexicalRespresentation ?partNum }
</sparqlQuery>
Listing 4-5: A SPARQL query on the
semantic data (of an ontology) to obtain an XML that could be used to specify
XSLT transform in loweringSchemaMapping
When SPARQL [SPARQL] is applied to the RDF graph in
Listing 4-4, the following XML will be generated as query answer.
<sparql xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/sparql-results#">
<head>
<variable name="quantity" />
<variable name="partNum" />
<variable name="name" />
<variable name="dueDate" />
<variable name="billingInfo" />
</head>
<results>
<result>
<binding name="quantity">
<literal>12</literal>
</binding>
<binding name="partNum">
<literal>348290187318</literal>
</binding>
<binding name="name">
<literal>ABC DEF</literal>
</binding>
<binding name="billingInfo">
<literal>23 XYZ Road</literal>
</binding>
<binding name="dueDate">
<literal>20060925</literal>
</binding>
</result>
</results>
</sparql>
Listing 4-6: Result of applying SPARQL from Listing 4-5
to RDF in Listing 4-4.
Once an XML is obtained from SPARQL query an XSLT transform can be
created. Listing 4.7 shows such an XSLT transform.
<xsl:transform version="2.0"
xmlns:po="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/order#"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:sp="http://www.w3.org/2005/sparql-results#">
<xsl:output method="xml" version="1.0" encoding="iso-8859-1" indent="yes" />
<xsl:template match="/sp:sparql">
<po:OrderRequest>
<po:Name>
<xsl:value-of
select="sp:results/sp:result[position()=1]/sp:binding[@name='name']/sp:literal" />
</po:Name>
<xsl:apply-templates select="sp:results/sp:result" />
</po:OrderRequest>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="sp:result">
<po:orderItem>
<xsl:attribute name="quantity">
<xsl:value-of select="sp:binding[@name='quantity']/sp:literal" />
</xsl:attribute>
<po:partNum>
<xsl:value-of select="sp:binding[@name='partNum']/sp:literal" />
</po:partNum>
<po:dueDate>
<xsl:value-of select="sp:binding[@name='dueDate']/sp:literal" />
</po:dueDate>
<po:billingInfo>
<xsl:value-of select="sp:binding[@name='billingInfo']/sp:literal" />
</po:billingInfo>
</po:orderItem>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:transform>
</lowering>
Listing 4-7: An XSLT excerpt that shows
loweringSchemaMapping notion.
The result of executing the above XSLT (in Listing 4-7) is shown below in
Listing 4-8. This XML could be used in invoking the advertised service (on
whose interface a loweringSchemaMapping is specified) from a requester (on
whose request interface a liftingSchemaMapping is specified).
<ex:OrderRequest
xmlns:POOntology="http://org1.example.org/ontologies/purchaseorder#"
xmlns:sp="http://www.w3.org/2005/sparql-results#"
xmlns:po="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/order#"
xmlns:ex="http://org1.example.com/wsdl/order#"
xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<ex:name>ABC DEF</ex:name>
<ex:orderItem quantity="12">
<ex:partNum>348290187318</ex:partNum>
<ex:dueDate>20060925</ex:dueDate>
<ex:billingInfo>23 XYZ Road</ex:dueDate>
</ex:orderItem>
</ex:OrderRequest>
Listing 4-8: Result of applying XSLT from Listing 4-7 to
SPARQL result of Listing 4-6.
In summary, the lifting and lower schema mapping notions together enable
the transformation of data between Web services which can be an important
part of enabling the invocation of Web services.
Just as multiple annotations can be associated using modelReference
concept, multiple schema mappings can be associated with elements as well.
When multiple URIs are specified on liftingSchemaMapping or
loweringSchemaMapping, SAWSDL specifies that the schema mappings they
reference are to be treated as alternatives, i.e. the client processor should
choose one of them to apply, and the choice is fully at the client
processor's discretion. For example, a mapping can be selected based on what
mapping language the processor supports (different alternatives can use
different languages), based on the availability of the mapping document, or
by other preferences.Just as SAWSDL does not prescribe any particular
ontology representation language for specifying modelReferences, it does not
prescribe any particular schema mapping representation language. In this user
guide XSLT is used for illustrative purposes. Users are welcome to use
transformation language of their choice to specify lifting and lowering
schema mappings.
The SAWSDL Usage Guide is an accompanying document to SAWSDL specification. This
guide presented examples to illustrate how to associate semantic annotations
to a Web service (represented in SAWSDL format) and how to use these
annotations for classifying, discovering, matching, composing, and invoking
Web services. Arguably, this usage guide presents only some of the ways in
which the annotations that can be associated with a WSDL document can be
used.
- [NAICS]
- North
American Industry Classification System. Available at
http://www.census.gov/epcd/www/naics.html.
- [OWL]
- OWL
Web Ontology Language Reference, Mike Dean and Guus
Schreiber, Editors. W3C Recommendation, 10 February
2004,http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/REC-owl-ref-20040210/.
Latest version available at
http://www.w3.org/TR/owl-ref/.
- [RDF]
- Resource
Description Framework, Dave Beckett, Editor. World Wide Web
Consortium, 10th February 2004. This version is
http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-syntax-grammar/
- [RDF Turtle]
- Terse RDF
Triple Language, Dave Beckett, Editor. World Wide Web
Consortium, 4th April 2004. This version is
http://www.dajobe.org/2004/01/turtle/
- [SAWSDL]
- Semantic
Annotations for WSDL, Joel Farrell and Holger Lauson,
Editors. World Wide Web Consortium, 28th Sept 2006. This version is
http://www.w3.org/TR/2006/WD-sawsdl-20060928/.
- [SPARQL]
- SPARQL Query
Language for RDF, Eric Prud'hommeaux and Andy Seaborne,
Editors. World Wide Web Consortium, 6 April 2006. This version is
http://www.w3.org/TR/2006/CR-rdf-sparql-query-20060406/. The latest version is
available at http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-sparql-query/.
- [UDDI]
- UDDI Version
3.0.2, Luc Clement, Andrew Hately, Claus von Riegen, and
Tony Rogers, Editors. Organization for the Advancement of Structured
Information Standards (OASIS). Available at
http://uddi.org/pubs/uddi_v3.htm.
- [WSDL 2.0]
- Web
Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 2.0 Part 1: Core
Language, R. Chinnici, J-J. Moreau, A. Ryman, S.
Weerawarana, Editors. World Wide Web Consortium, 27 March 2006. This
version of the "Web Services Description Language (WSDL) Version 2.0
Part 1: Core Language" Specification is available is available at
http://www.w3.org/TR/2006/CR-wsdl20-20060327. The latest version of "Web Services
Description Language (WSDL) Version 2.0 Part 1: Core Language" is
available at http://www.w3.org/TR/wsdl20.
- [WSDL-S]
- W3C Member
Submission, Web Service Semantics - WSDL-S, Rama Akkiraju,
Joel Farrell, John Miller, Meenakshi Nagarajan, Marc-Thomas Schmidt,
Amit Sheth, and Kunal Verma, Authors. World Wide Web Consortium, 7
November 2005. Available at http://www.w3.org/Submission/WSDL-S/.
- [XSLT]
- XSL Transformations
(XSLT) Version 2.0, Michael Kay, Editor. World Wide Web
Consortium, 3 Nov 2005. This version is
http://www.w3.org/TR/2005/CR-xslt20-20051103/. The latest version is available at
http://www.w3.org/TR/xslt20/.
A version of the WSDL files and the ontology used in this document are
given below. Please note that these WSDLs and the OWL files do not contain
all the variations that have been discussed in the examples.
Editor's note: TODO: These examples will be made more complete.
Check Availability Request: Please see http://www.w3.org/TR/sawsdl-guide/wsdl/CheckAvailability-req-sem.wsdl
Check Inventory Service: Please see http://www.w3.org/TR/sawsdl-guide/wsdl/CheckInventory-sem.wsdl,
Sample Ontology: Please see http://www.w3.org/TR/sawsdl-guide/wsdl/ElectronicsOntology.owl
This document is the work of the W3C Semantic Annotations for Web
Service Description Language Working Group.
Members of the Working Group are (at the time of
writing, and by alphabetical order): Rama Akkiraju (IBM Corporation), Carine
Bournez (W3C), J.B. Domingue (The Open University), Joel Farrell (IBM
Corporation), Laura Ferrari (Telecom Italia SpA), Laurent Henocque (ILOG,
S.A.), Mathias Kleiner (ILOG, S.A.), Jacek Kopecký (DERI Innsbruck at the
Leopold-Franzens-Universität Innsbruck, Austria), Holger Lausen (DERI
Innsbruck at the Leopold-Franzens-Universität Innsbruck, Austria), John
Miller (University of Georgia Research Foundation, Inc (UGARF)) Carlos
Pedrinaci (The Open University), Eric Prud'hommeaux (W3C), Brahmananda
Sapkota (DERI Galway at the National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland),
Amit Sheth (Fortent), Claudio Venezia (Telecom Italia SpA), Tomas Vitvar
(DERI Galway at the National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland).
Table B-1. Summary of Changes Related to
Semantic Annotations for WSDL Specification — Use Cases and
Examples
| Date |
Author |
Description |
| 20060508 |
BNS |
Initial skeleton created from Rama's
document |
| 20060515 |
BNS |
WSDL-S files attached to Sections 4.1, 5.1
and 5.2 sent by Rama
Section 6 added from Rama's document |
| 20060614 |
BNS, RA |
Best Practices Section 7 added. |
| 20060814 |
RA |
Completely revamped and rewrote the
document. The focus of the document is now on how to associate
semantic annotations with a WSDL document for use in , composition
and invocation NOT on how to do matching, composition and invocation
using semantic annotations.
Still some sections need some more work. |
| 20060815 |
BNS |
Some clean ups. |
| 20060816 |
RA |
Many more cleanups. Writeups for some more
sections. Examples are much cleaner now and there is really only one
running example that we keep building throughout the document. More
Todos to be finished up still. |
| 20060819 |
BNS |
Added schemaMapping examples. |
| 20060821 |
BNS |
Added PartNumber2EANLookup SAWSDL
examples. |
| 20060823 |
RA |
Many more cleanups and additions to the
sections. Created more images and text throughout the document to
explain things better. Added a better example in the schemaMapping
section. This should be more amenable to creating schema mappings (in
XSLT or RDF). The placement of images need some cleanup. Some how
things are getting justified to be in the middle. Even if I change it
to left justification, it doesn't seem to work. The formatting needs
cleanup as well. |
| 20060824 |
BNS |
Clean up, and some additions in section
4. |
| 20060831 |
RA |
Some clean up.
implemented comments from 2nd F2F meeting throughout the
document. |
| 20060909 |
BNS |
Some clean up.
implemented comments from 2nd F2F meeting, in section 3. |
| 20060910 |
BNS |
Converted OWL examples to RDF - Turtle
format. |
| 20060918 |
BNS |
Implemented comments from Laura
Added Section on Mapping Choices from main spec. |
| 20060922 |
RA |
Many more cleanups. Added new sections 1.2,
2.1, 3.1 and many more updates throughout the document . |
| 20060923 |
BNS |
Addition to Appendix,
XSLT and SPARQL examples added. |
| 20060924 |
RA |
Major Revisions to sections 3 and 4. Added
References. |
| 20060925 |
RA |
Updated SampleOntology. Commented out the
Mapping Choices section. I don't think it belongs here in this
document. It is in WSDL-S and we have a pointer to WSDL-S from here.
That should suffice. |
| 20060926 |
EGP |
fixed the formatting of listings 3.2-3 and
4-3 per Jacek's
comment # 6 |
| 20060926 |
RA |
Addressed many of the issues in Jacek's
feedback note |
| 20060927 |
RA |
Made significant revisions to section 3 and
4. Addressed more the remaining issues from Jacek's
feedback note. Also addressed Joel's comments sent in a mail on
Sept 25th 2006. |
Table C-1. Summary of Editors' Semantic Annotations for WSDL
Specification — Use Cases and Examples Work Items
| Item |
Description |
| Item 3 |
To update SampleOntology so that it
contains all the concepts and their relationships |
| Item 5 |
Need to clean up SPARQL and XSLT
examples |