Semantic Web: Changing gears
Data on the Web: "Crossing the chasm"
http://www.w3.org/2006/Talks/0521-ac-sw-tbl
AC meeting
Tim Berners-Lee
Director, World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)
This talk
- The Semantic Web adoption phase
- Semantic Web FAQ
Adoption stages "life cycle"
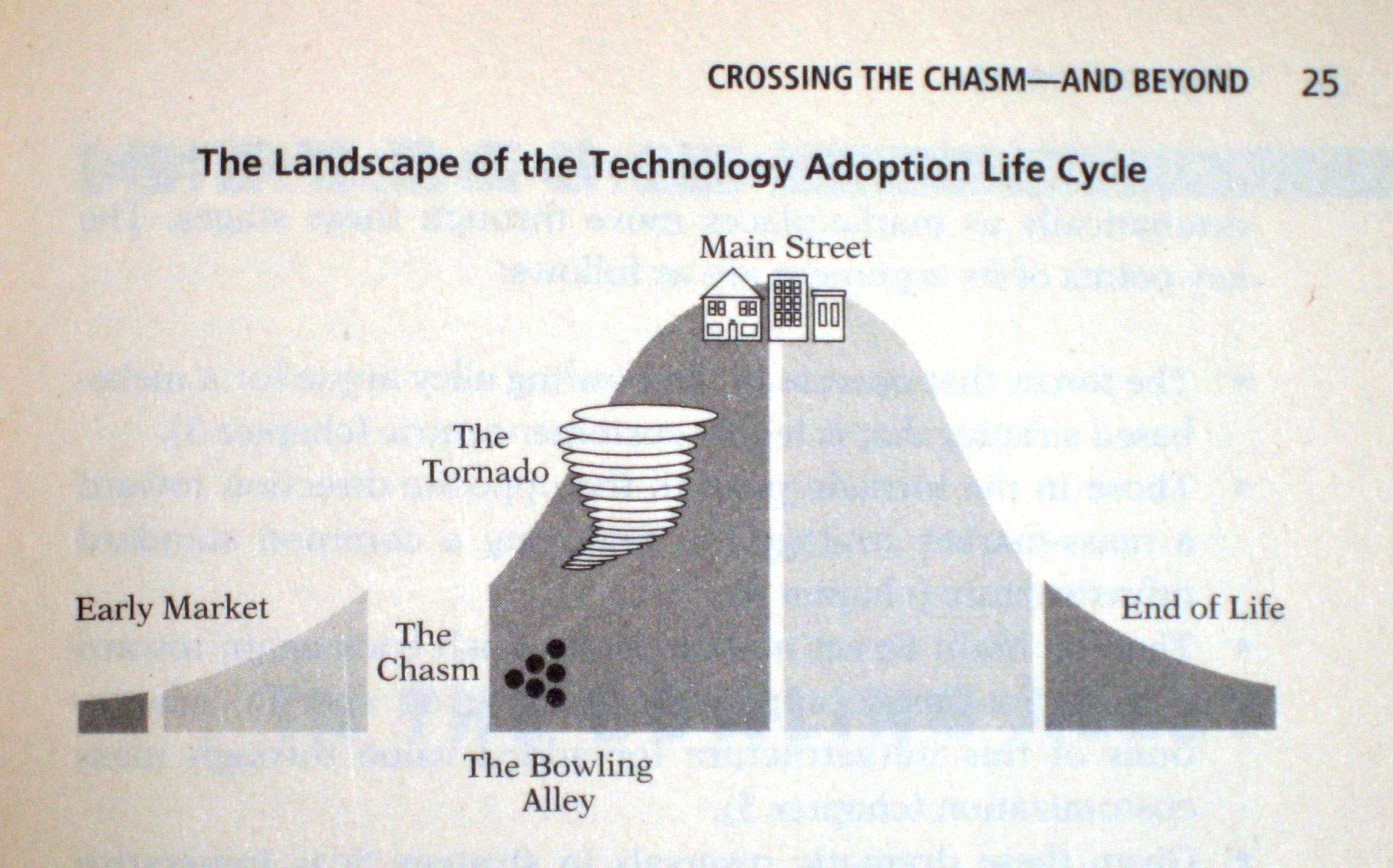
after Geoffrey A Moore, "Crossing the Chasm".
Adoption stages "life cycle"
| Phase |
Who buys |
Technique |
|
| 1 |
Innovators |
|
|
| 2 |
Visionaries, Early adopters |
Concentrate on niche areas |
SW moving from here |
| 3 |
Pragmatists |
Simplify & generalize |
... to here |
| 4 |
Conservatives |
Customize |
|
| 5 |
Laggards |
|
|
The Chasm is between 2 and 3.
That is what SW technology is crossing now.
(
Commercial products,
SPARQL implementations
OWL implementations)
Network effect
Metcalfe's Law: The value of one node is proportional to the number of other nodes
- Rely on: Visionaries who can imagine what it would be like
- and those who do their bit trust that others will do theirs
- Easier with things which are well connected
- Easier to get critical mass in small community
This applies to the Semantic Web maybe more than anything so far
Small community: Niche applications
Connecting: Browsable data
- Don't leave it in data in zip files
- Don't leave URIs are Error 404
- Support URIs with useful data about the things it identifies.
- (This means links in both directions)
- Value of Web = Serendipitous reuse
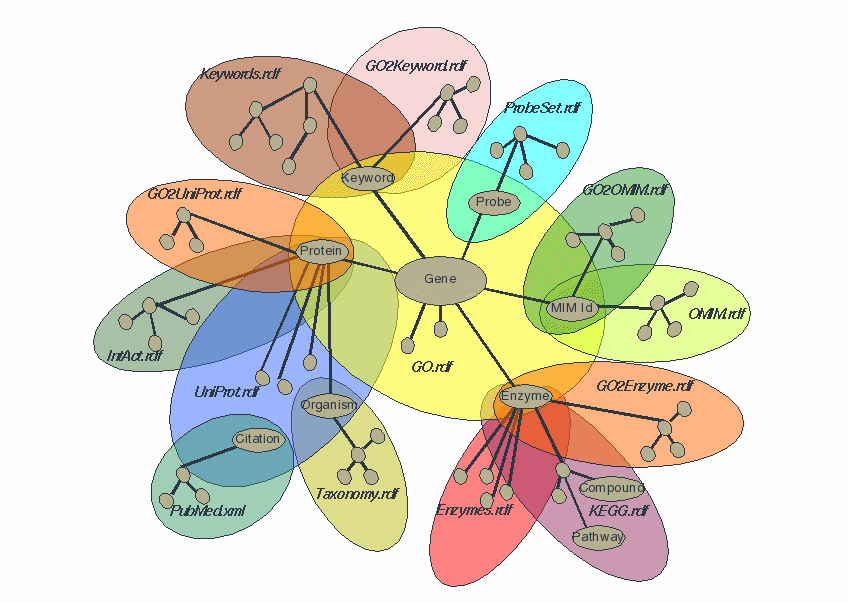
Some RDF deployment areas
|
Library metadata |
Anti-terrorism |
Life sciences |
| Problem to solve? |
Single-domain integration |
Yes. Serious data integration needs |
Yes. Stovepipes between genetics, proteomics, clinical trials,
regulatory etc |
| Willingness to adopt? |
Yes. OCLC push and Dublin Core initiative. |
Yes. Funded early DAML (OWL) work. |
Yes. Intellectual level high, much modeling done already. |
| Motivation |
Light |
Strong. |
Strong. Major cost of delays in drug discovery chain. |
| Links to |
other library data |
Phone calls records, etc |
Chemistry, regulatory, medical, etc |
| Showcase? |
Limited. |
Not at all |
Yes, model for other industries. |
Teranode in Life Sciences
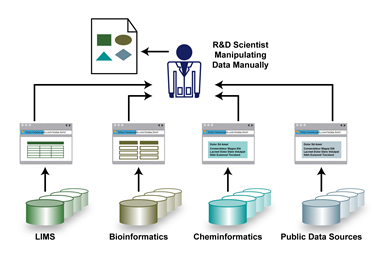
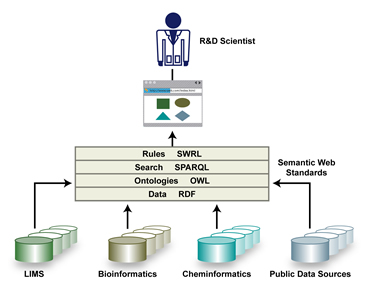
Moving from niche application areas
- Learn from the needs of the markets
- Simplify to make more general (e.g. RDF's old aboutEachPrefix)
- Build on exsiting systems
- Complete the product
Build on existing systems
Innovators have now made lots of exciting new systems, but:
- Practical deployment involves interfacing to existing systems
- Don't change way data is managed
- Put on a thin layer adaptor, such as
- GRDDL adaptor for XML
- Adaptor for SQL (e.g. R2O, SPA-SQL, DBView)
- Adapt to generate RDF and/or support SPARQL
Practical Semantic Web
- A web of data.
- Don't change existing practices
- Instrument and augment
- Use standards: (RDF, OWL, SPARQL*, RIF**)
Practical Semantic Web
- Take inventory of your data to see what you have
- Modeling data to see how it connects
- Map each thing into URI space
- Connect on RDF views, SPARQL services
- Agree on ontologies with others
Bottom-up ontology design
- Start with existing SQL databases
- Add information about how keys and foreign keys connect
- Remove other artifacts of the DB schema
- Note relationships to other people's concepts
RDF views of data
RDF is to data what HTML is to documents
- Technique: PHP scripts accessing relational DB
- XSLT or XQ scripts accessing XML DB
- Looking up a URI for something gives you info about it
- Relations with other things expressed using their URIs
SPARQL access to data
Query interface
- Use the same mapping as the RDF views
- XSLT or XQ scripts accessing XML DB
- Looking up a URI for something gives you info about it
- Relations with other things expressed using their URIs
SPARQL - the universal query service
- How many Web Services ask for info?
- Each can be SPARQL
- Extensible - without re-architecting
- Independent of database schema/XML schema
- Combinable
- Optimizable - mapping, caching, federating
Clients of the RDF bus
New data applications can be built on top of RDF bus, for example:
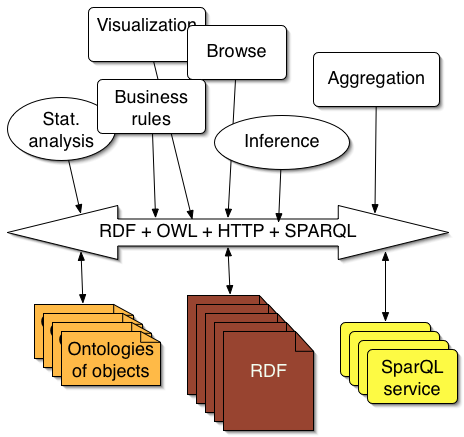
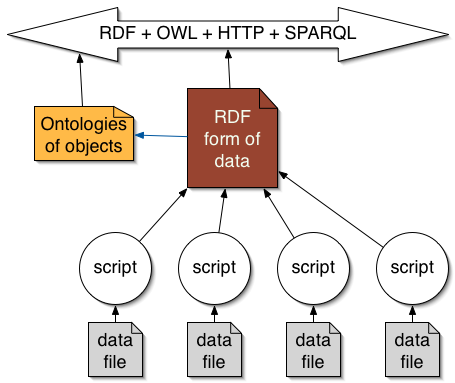
Components: Adapting random files
Keep your existing systems running - adapt them
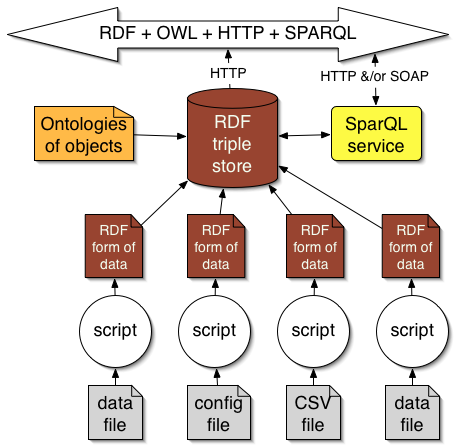
Components: Triple store
Virtual severs actually figure stuff out as well as look up data
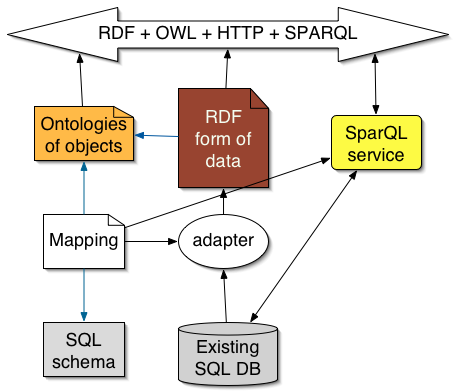
Adapting SQL Databases
Keep your existing systems running - adapt them
Adapting XML
Remember- RDF on an HTTP server can always be virtual
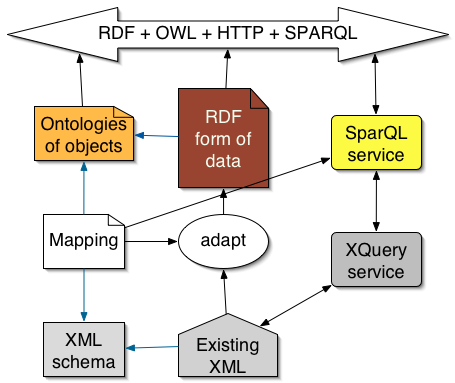
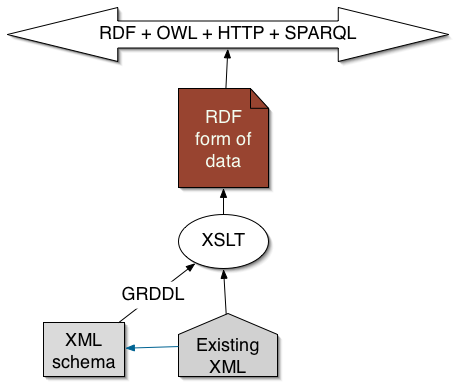
Adapting XML: GRDDL
Remember- RDF on an HTTP server can always be virtual
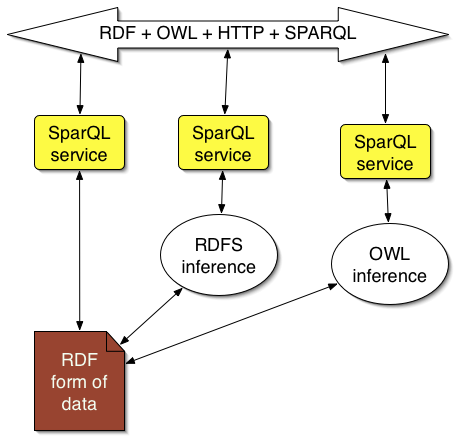
Components: Smart servers
Virtual severs actually figure stuff out as well as look up data
Complete the product
- Needed for general adoption
- SPARQL was a missing link
- What is missing?
Rule Interchange Format.
RDF API? Programmer's interface
Technology for expressing RDB-RDF mapping?
Mainline shallow ontologies?
Trust systems using logic & crypto?
Roadmap: Stack of expressive power
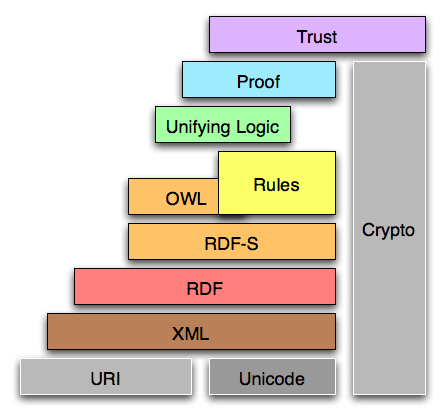
The Semantic Web Wave
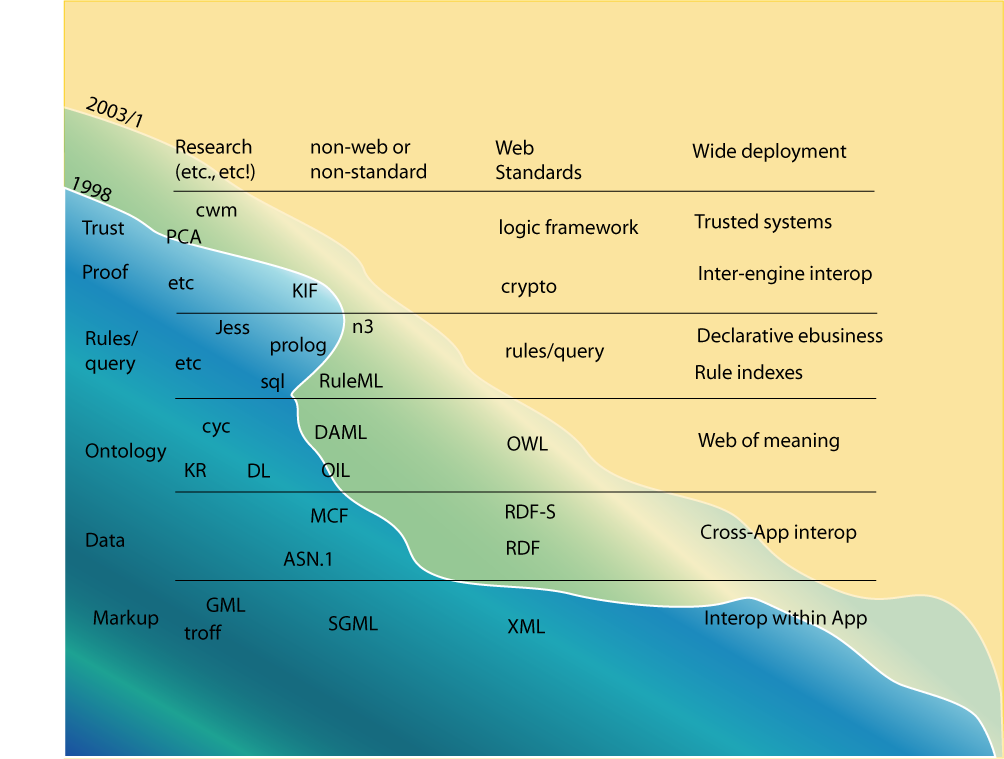
FAQ: Questions about the Semantic Web
Q. What can RDF do which XML can't do?
- For a single application, nothing
- For a simple application, nothing
- As applications grow, working at a high level is quicker.
- Robust against database schema changes
- Robust against XML schema changes
- SQL and XQ expressions get complicated
See Jim Melton's W3C Tech Plenary talk (
slides and XTech paper.)
Q. So can you show me what it looks like?
- No, because semantic web apps will be so varied
- No, because it won't be awesome until masses of data is out there.
- Well, OK then
Some data in HTML microformat (scraped to RDF)
Some data built with RDF reported as HTML

Tabulator: generic data browser
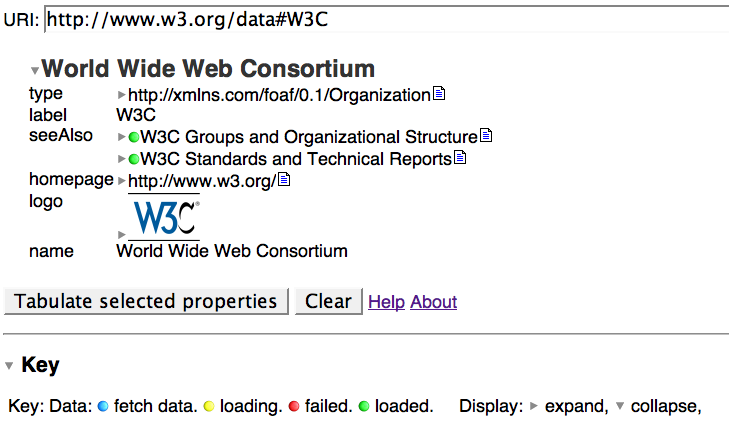
Starting only with a URI
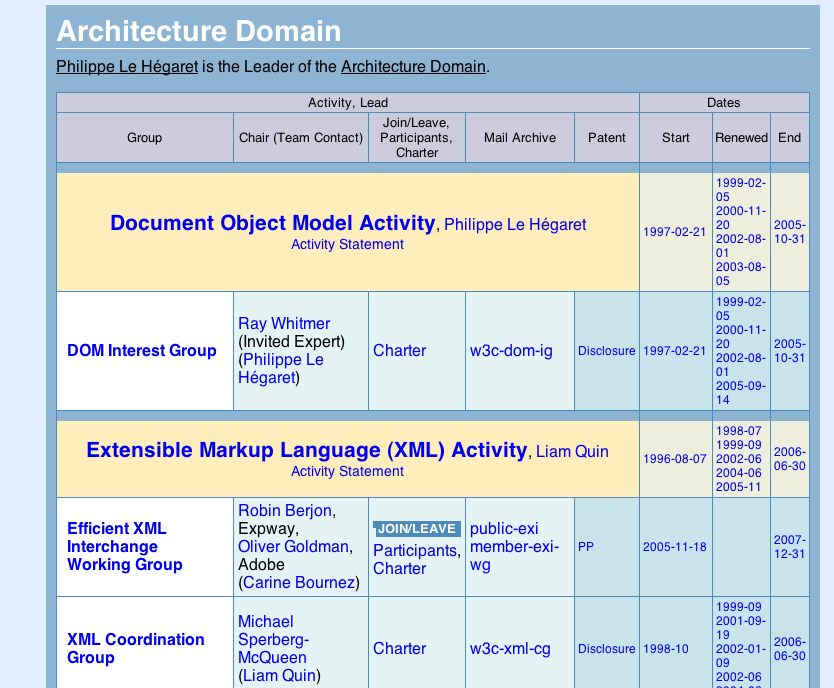
Tabulating around W3C -
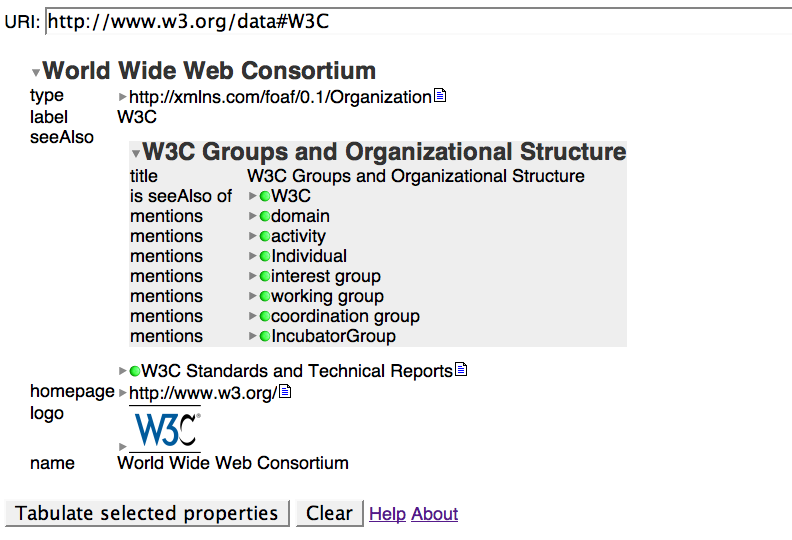
Tabulating around W3C -

Tabulating around W3C -
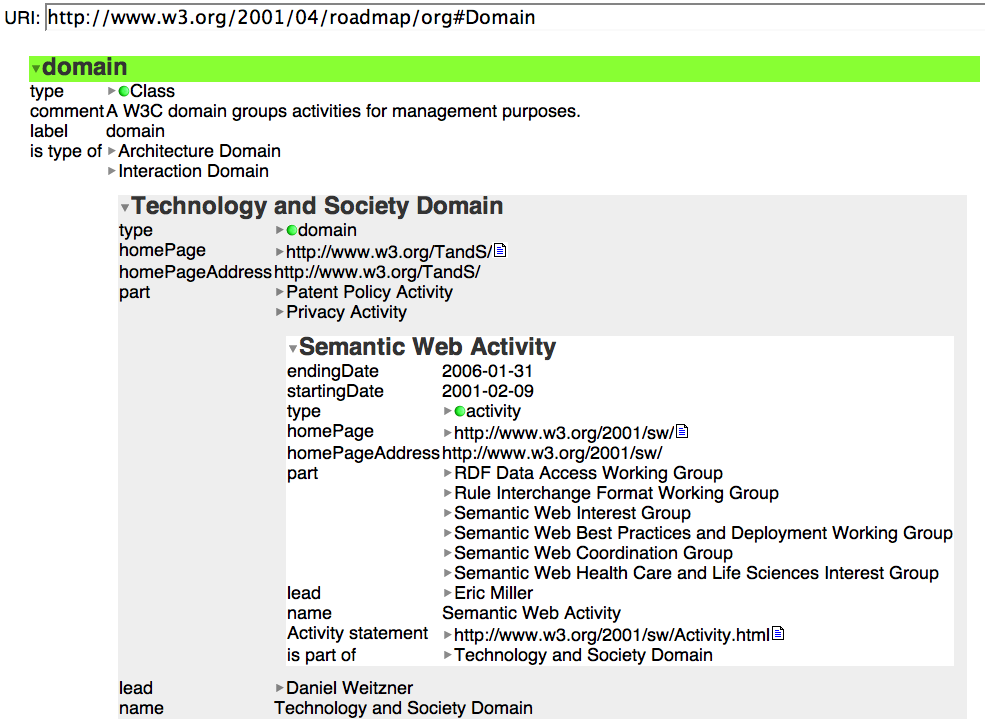
Tabulating around W3C - Crossing the application boundary
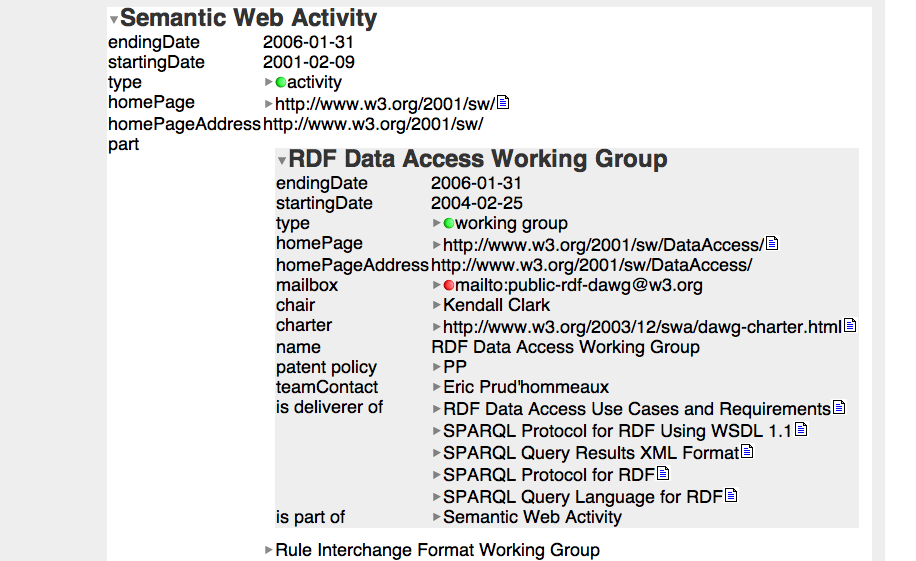
Tabulating around W3C -
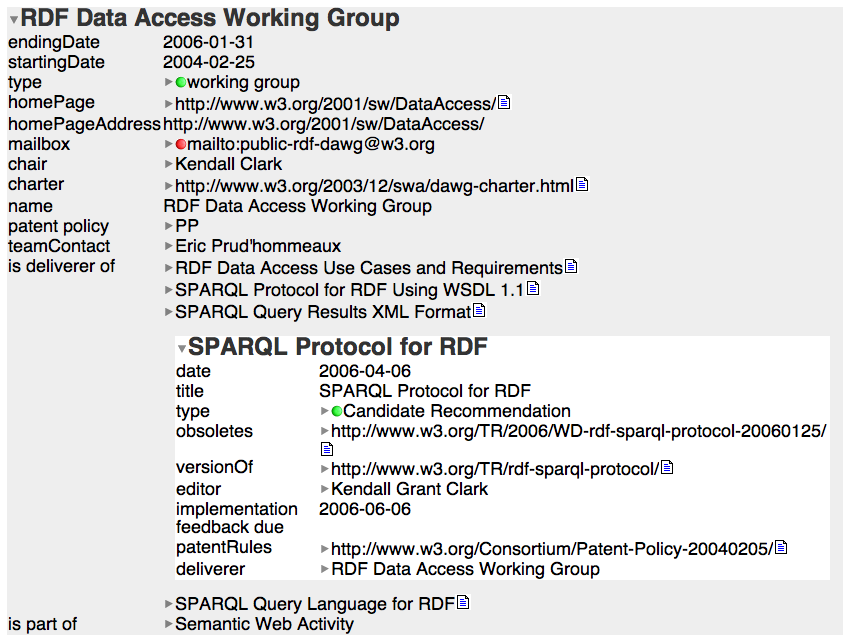
Tabulating around W3C -
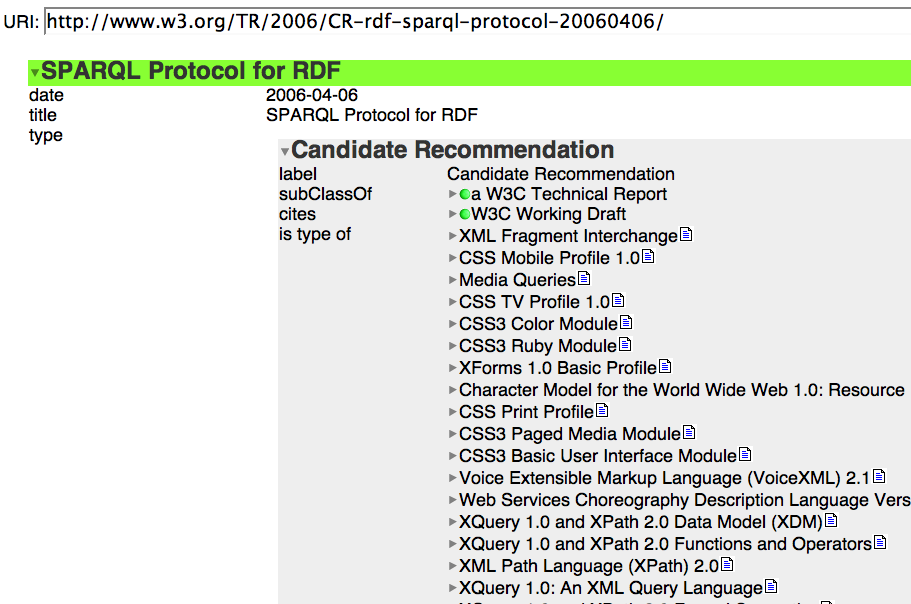
Tabulating around W3C - This is not a tree
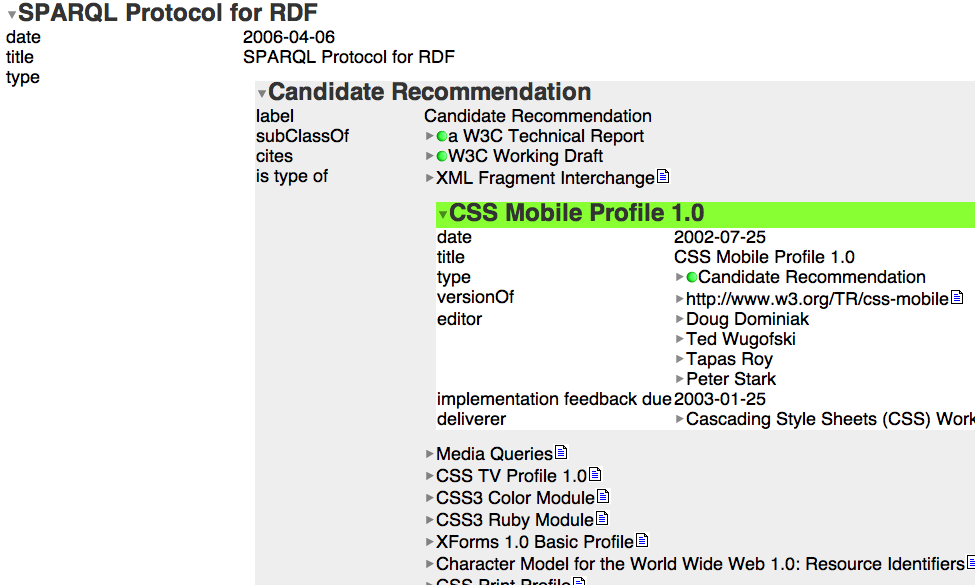
Tabulating around W3C - Query by example

Tabulating around W3C - Graph to table
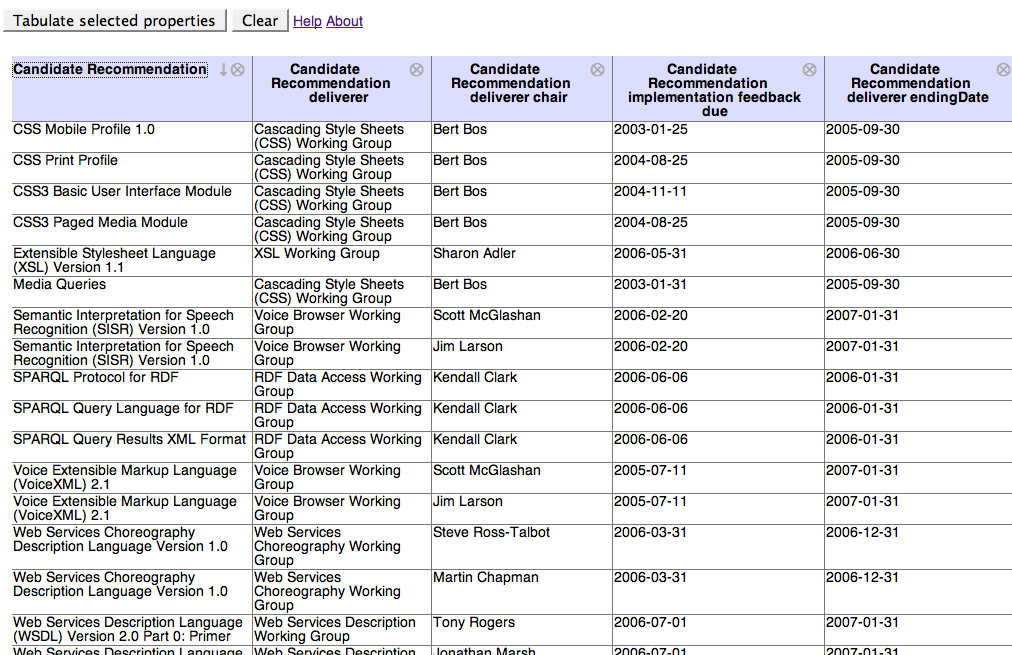
Q: What about the cost of making all the ontologies?
Communities and Vocabularies
Universal WWW must include communities on many scales
- Communities communicate with languages
- Languages form barriers
- Barriers are essential to the community
- Communicating with other communities is expensive
- Developing wider languages is expensive
- For data web, communities map to ontologies
Applications connected by concepts
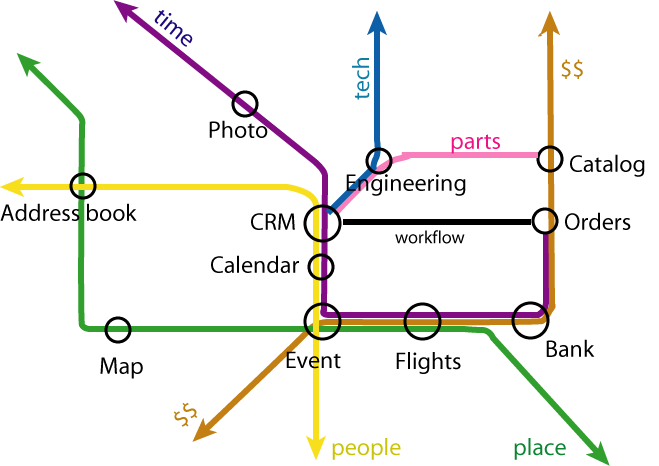
Fractal Web of concepts
- Across boundaries of scale -- personal, group, global
- Varying access levels
- Tension between local and global standards
- Society is a fractal tangle, so must SW be.
- Personal interactions on multiple scales
The semantic web is about allowing data systems to change by evolution not
revolution
Total Cost of Ontologies (TCO)
Assume :-) ontologies evenly spread across orders of magnitude; committee
size as log(community), time as committee^2, cost shared across
community.
| Scale |
Eg |
Committee size |
Cost per ontology (weeks) |
My share of cost |
| 0 |
Me |
1 |
1 |
1 |
| 10 |
My team |
4 |
16 |
1.6 |
| 100 |
Group |
7 |
49 |
0.49 |
| 1000 |
|
10 |
100 |
0.10 |
| 10k |
Enterprise |
13 |
169 |
0.017 |
| 100k |
Business area |
16 |
256 |
0.0026 |
| 1M |
|
19 |
361 |
0.00036 |
| 10M |
|
22 |
484 |
0.000048 |
| 100M |
National, State |
25 |
625 |
0.000006 |
| 1G |
EU, US |
28 |
784 |
0.000001 |
| 10G |
Planet |
31 |
961 |
0.000000 |
Total cost of 10 ontologies: 3.2 weeks. Serious project: 30 ontologies, TCO =
10 weeks.
Lesson:
Do your bit. Others will do
theirs.
Thank those who do working groups!
"Crossing the chasm": Timing strawman
- 2006. Have your data modelled. Build RDF and SPARQL access for
analytics and CEO questions as a start.
- 2007. Build added value on top of your data
web:
- Analysis - using rules, programs on RDF
API
- Visualization
- Sanity checks - OWL, Rule-based, etc.
- Offer filtered RDF data to partners
- 2008 demand your partners give you RDF for data which is important to
the relationship
- 2009 Build new applications on top of semantic web base
- 2011 Start to replace legacy systems with semantic-web native
systems
Summary
- Moving from early adopter to pragmatic buyers
- Niche areas demonstrate missing features
- Total Cost of Ontologies is finite
- Building on existing systems is key
- Major vendors are moving it into products
- We have some ideas about actually making a user interface!
Thank You
Thank you for your attention
http://www.w3.org/2006/Talks/0404-mit-tbl
Random links
Tabulator demo (experts only with signed): W3C,