About WCAG 2
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) is developed through international collaboration:
- Experts
- Researchers
- Developers
- Industry
- Policy makers
- End-users
Design of WCAG 2
- Technology-independent
- Objectively testable
- Flexible for situations
- Support for developers
WCAG 2 Structure
- Principles (4)
- Guidelines (12)
- Success Criteria - Level A (25)
- Success Criteria - Level AA (13)
- Success Criteria - Level AAA (23)
- Conformance
Note: WCAG 1.0 had 14 Guidelines and 65 Checkpoints
WCAG 2 Principles
Accessibility principles of WCAG 2:
- Perceivable
- Operable
- Understandable
- Robust
To help memorize: P-O-U-R like pouring water.
Example Guidelines
Examples of WCAG 2 Guidelines:
Example Success Criteria
Examples of WCAG 2 Success Criteria:
- 1.1.1 Non-text Content: All non-text content that is presented to the user has a text alternative that serves the equivalent purpose - Level A
- 2.2.4 Interruptions: Interruptions can be postponed or suppressed by the user, except interruptions involving an emergency - Level AAA
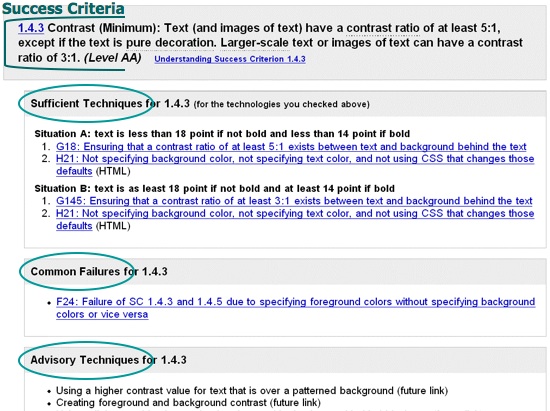
WCAG 2 Techniques
Techniques are documented separately. There are three types of Techniques:
- Sufficient Techniques - minimum requirements
- Advisory Techniques - additional improvements
- Common Failures - often encountered mistakes
Techniques are Technology-specific (e.g. HTML, CSS, AJAX, ...)
Example Test Procedure
Test procedure from WCAG 2 Technique H36:
- Procedure
- For all input elements that have a type attribute value of "image", check for the presence of an alt attribute.
- Check that the alt attribute indicates the button's function.
- Expected Results
- #1 und #2 are true
WCAG 2 Hierarchy
- Principles (POUR)
- Guidelines (12)
- Success Criteria (61)
- Techniques (documented separately)
WCAG 2.0 Quick Reference
Questions?
Quick clarification questions welcome now.
Next: Text Alternatives (after the break).