Scope of the Web
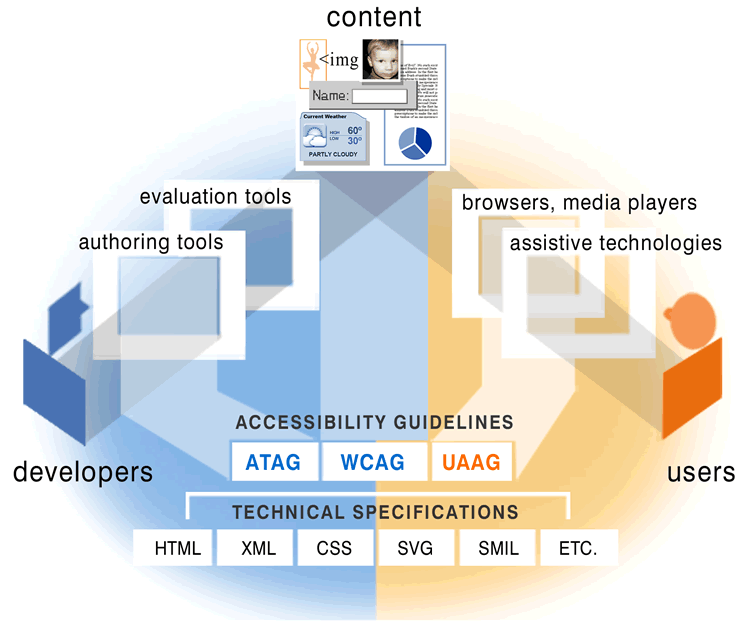
The Web consists of several components that work together:
- Content - websites, web applications, documents, ...
- Browsers - media players, assistive technology, ...
- Authoring Tools - content management systems, ...
- Technologies - HTML, CSS, XML, SVG, SMIL, ...
Web Accessibility Guidelines
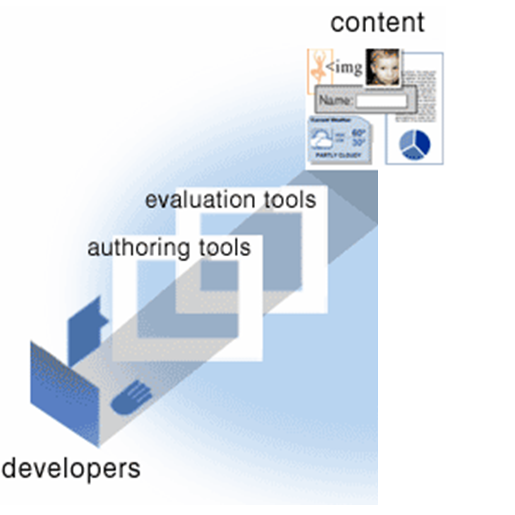
Authoring Tools
ATAG
Authoring Tool Accessibility Guidelines (ATAG) defines:
- Production of accessible web content
- Accessibility of web authoring tools
http://www.w3.org/WAI/intro/atag
User Agents
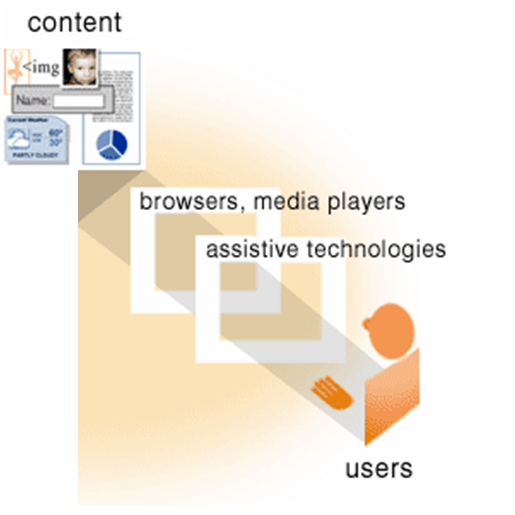
UAAG
User Agent Accessibility Guidelines (UAAG) defines:
- Accessibility of browsers and media players
- Compatibility with assistive technologies
http://www.w3.org/WAI/intro/uaag
Web content
Web content has different forms including:
- natural information such as text, images, and sounds
- code or markup that defines structure, presentation, etc.
WCAG
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) defines:
- Accessibility requirements for web content
- Techniques for meeting these requirements
http://www.w3.org/WAI/intro/wcag
Simple Example
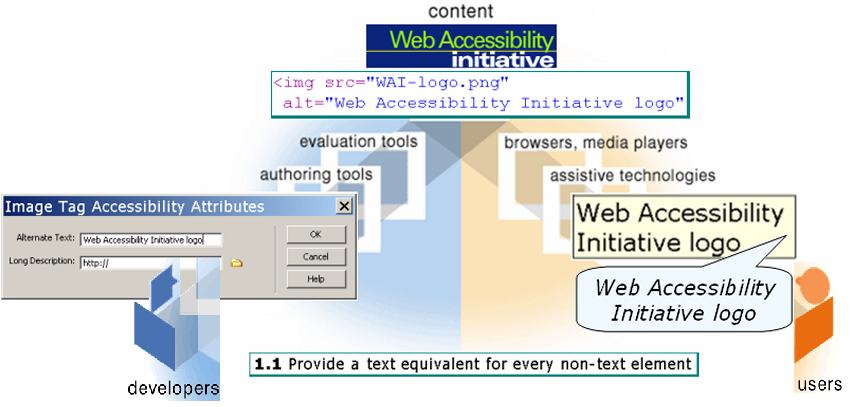
When Components Are Weak...
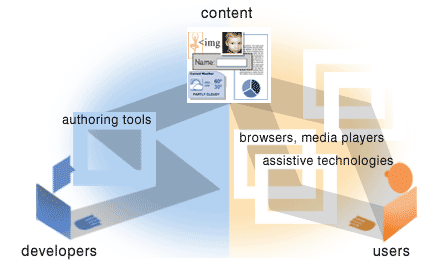
Sometimes components can compensate through "work-arounds"
- require much more effort
- not good solutions overall
- often not implemented
Summary
W3C/WAI develops international accessibility standards:
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
- Authoring Accessibility Guidelines (ATAG)
- User Agent Accessibility Guidelines (UAAG)
- Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA)




