
An SVG document fragment consists of any number of SVG elements contained within an 'svg' element.
An SVG document fragment can range from an empty fragment (i.e., no content inside of the 'svg' element), to a very simple SVG document fragment containing a single SVG graphics element such as a 'rect', to a complex, deeply nested collection of container elements and graphics elements.
An SVG document fragment can stand by itself as a self-contained file or resource, in which case the SVG document fragment is an SVG document, or it can be embedded inline as a fragment within a parent XML document.
The following example shows simple SVG content embedded as a fragment within a parent XML document. Note the use of XML namespaces to indicate that the 'svg' and 'ellipse' elements belong to the SVG namespace:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<parent xmlns="http://someplace.org"
xmlns:svg="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg-20000303-stylable">
<!-- parent stuff here -->
<svg:svg width="5cm" height="8cm">
<svg:ellipse rx="200" ry="130" />
</svg:svg>
<!-- ... -->
</parent>
This example shows a slightly more complex (i.e., it contains multiple rectangles) stand-alone, self-contained SVG document:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="4in" height="3in">
<desc>Four separate rectangles
</desc>
<rect width="20" height="60"/>
<rect width="30" height="70"/>
<rect width="40" height="80"/>
<rect width="50" height="90"/>
</svg>
'svg' elements can appear in the middle of SVG content. This is the mechanism by which SVG document fragments can be embedded within other SVG document fragments.
Another use for 'svg' elements within the middle of SVG content is to establish a new viewport and alter the meaning of CSS unit specifiers. See Establishing a new viewport and Redefining the meaning of CSS unit specifiers.
<!ENTITY % svgExt "" > <!ELEMENT svg (%descTitleDefs;,metadata?, (path|text|rect|circle|ellipse|line|polyline|polygon| use|image|svg|g|view|switch|a|altGlyphDef| script|symbol|marker|clipPath|mask| linearGradient|radialGradient|pattern|filter|cursor|font| animate|set|animateMotion|animateColor|animateTransform %StylableSVG-StyleElement; %ExchangeSVG-ColorProfileElement;%ExchangeSVG-FontFaceElement; %ceExt;%svgExt;)*) > <!ATTLIST svg xmlns CDATA #FIXED "%SVGNamespace;" %stdAttrs; %langSpaceAttrs; class %ClassList; #IMPLIED %graphicsElementEvents; %documentEvents; %testAttrs; externalResourcesRequired %Boolean; #IMPLIED x %Coordinate; #IMPLIED y %Coordinate; #IMPLIED width %Length; #REQUIRED height %Length; #REQUIRED viewBox %ViewBoxSpec; #IMPLIED preserveAspectRatio %PreserveAspectRatioSpec; 'xMidYMid meet' enableZoomAndPanControls %Boolean; "true" contentScriptType %ContentType; "text/ecmascript" contentStyleType %ContentType; "text/css" %StylableSVG-StyleAttribute; %ExchangeSVG-ContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-FillStrokeAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GradientAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GraphicsAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-MarkerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextElementAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-ViewportAttrs; > |
Attribute definitions:
The 'g' element is the element for grouping and naming collections of drawing elements. If several drawing elements share similar attributes, they can be collected together using a 'g' element. For example:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="4in" height="3in">
<desc>Two groups, each of two rectangles
</desc>
<g style="fill:red">
<rect x="100" y="100" width="100" height="100" />
<rect x="300" y="100" width="100" height="100" />
</g>
<g style="fill:blue">
<rect x="100" y="300" width="100" height="100" />
<rect x="300" y="300" width="100" height="100" />
</g>
</svg>
Grouping constructs, when used in conjunction with the 'desc' and 'title' elements, provide information about document structure and semantics. Documents that are rich in structure may be rendered graphically, as speech, or as braille. and thus promote accessibility.
A group of drawing elements, as well as individual objects, can be given a name. Named groups are needed for several purposes such as animation and re-usable objects.
The following example organizes the drawing elements into two groups and assigns a name to each group:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="4in" height="3in">
<desc>Two named groups
</desc>
<g id="OBJECT1">
<rect x="100" y="100" width="100" height="100" />
</g>
<g id="OBJECT2">
<circle cx="150" cy="300" r="25" />
</g>
</svg>
A 'g' element can contain other 'g' elements nested within it, to an arbitrary depth. Thus, the following is valid SVG:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="4in" height="3in">
<desc>Groups can nest
</desc>
<g>
<g>
<g>
</g>
</g>
</g>
</svg>
Any drawing element that is not contained within a 'g' is treated (at least conceptually) as if it were in its own group.
<!ENTITY % gExt "" > <!ELEMENT g (%descTitleDefs;, (path|text|rect|circle|ellipse|line|polyline|polygon| use|image|svg|g|view|switch|a|altGlyphDef| script|symbol|marker|clipPath|mask| linearGradient|radialGradient|pattern|filter|cursor|font| animate|set|animateMotion|animateColor|animateTransform %StylableSVG-StyleElement; %ExchangeSVG-ColorProfileElement;%ExchangeSVG-FontFaceElement; %ceExt;%gExt;)*) > <!ATTLIST g %stdAttrs; %langSpaceAttrs; class %ClassList; #IMPLIED transform %TransformList; #IMPLIED %graphicsElementEvents; %testAttrs; externalResourcesRequired %Boolean; #IMPLIED %StylableSVG-StyleAttribute; %ExchangeSVG-ContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-FillStrokeAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GradientAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GraphicsAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-MarkerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextElementAttrs; > |
SVG makes extensive use of URI references [URI] to other objects. For example, to fill a rectangle with a linear gradient, you first define a 'linearGradient' element and give it an ID, as in:
<linearGradient id="MyGradient">...</linearGradient>
You then reference the linear gradient as the value of the 'fill' property for the rectangle, as in:
<rect style="fill:url(#MyGradient)"/>
In SVG, the following facilities allow URI references:
URI references are defined in either of the following forms:
<URI-reference> = [ <absoluteURI> | <relativeURI> ] [ "#" <elementID> ] -or-
<URI-reference> = [ <absoluteURI> | <relativeURI> ] [ "#xpointer(id(" <elementID> "))" ]
where <elementID> is the ID of the referenced element.
(Note that the two forms above (i.e., #<elementID> and #xpointer(id(<elementID>))) are formulated in syntaxes compatible with "XML Pointer Language (XPointer)" [XPTR]. These two formulations of URI references are the only XPointer formulations that are required in SVG 1.0 user agents.)
SVG supports two types of URI references:
The following rules apply to the processing of URI references:
It is recommended that, wherever possible, referenced elements be defined inside of a 'defs' element. Among the elements that are always referenced: 'altGlyphDef', 'clipPath', 'cursor', 'filter', 'linearGradient', 'marker', 'mask', 'pattern', 'radialGradient' and 'symbol'. Defining these elements inside of a 'defs' element promotes understandability of the SVG content and thus promotes accessibility.
Documents often reference and use the contents of other files (and other web resources) as part of their rendering. In some cases, authors want to specify that particular resources are required for a document to be considered correct.
Attribute externalResourcesRequired is available on all elements which potentially can reference external resources. It specifies whether referenced resources that are not part of the current document are required.
Attribute definition:
This attribute applies to all types of resource references, including style sheets and fonts specified by an @font-face specification. In particular, if an element sets externalResourcesRequired="true", then all style sheets must be available since any style sheet might affect the rendering of that element.
Attribute externalResourcesRequired is inheritable; thus,if set on a container element, its value will apply to the elements within the container which don't specify a value for this attribute.
For externalResourcesRequired: Animatable: yes.
<!ENTITY % xlinkRefAttrs "xmlns:xlink CDATA #FIXED 'http://www.w3.org/2000/xlink/namespace/' xlink:type (simple|extended|locator|arc) 'simple' xlink:role CDATA #IMPLIED xlink:title CDATA #IMPLIED xlink:show (new|embed|replace) 'embed' xlink:actuate (onRequest|onLoad) 'onLoad'" > xlink:href CDATA #REQUIRED |
The 'defs' element is a container element for referenced elements. For understandability and accessibility reasons, it is recommended that, whenever possible, referenced elements be defined inside of a 'defs'.
The content model for 'defs' is the same as for the 'g' element; thus, any element that can be a child of a 'g' can also be a child of a 'defs', and vice versa.
When the current SVG document fragment is rendered as SVG on visual media, graphics elements that are descendants of a 'defs' are not drawn; thus, in this case, the 'display' property does not apply to 'defs' (i.e., there is an implicit 'display:none').
<!ENTITY % defsExt "" > <!ELEMENT defs ( path|text|rect|circle|ellipse|line|polyline|polygon| use|image|svg|g|view|switch|a|altGlyphDef| script|symbol|marker|clipPath|mask| linearGradient|radialGradient|pattern|filter|cursor|font| animate|set|animateMotion|animateColor|animateTransform %StylableSVG-StyleElement; %ExchangeSVG-ColorProfileElement;%ExchangeSVG-FontFaceElement; %ceExt;%defsExt;)* > <!ATTLIST defs %stdAttrs; %langSpaceAttrs; class %ClassList; #IMPLIED transform %TransformList; #IMPLIED %testAttrs; externalResourcesRequired %Boolean; #IMPLIED %StylableSVG-StyleAttribute; %ExchangeSVG-ContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-FillStrokeAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GradientAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GraphicsAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-MarkerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextElementAttrs; > |
To provide some SVG user agents with an opportunity to implement efficient implementations in streaming environments, creators of SVG content are encouraged to place all elements which are targets of local URI references within a 'defs' element which is a direct child of one of the ancestors of the referencing element. For example:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="4in" height="3in">
<desc>Local URI references within ancestor's 'defs' element.</desc>
<defs>
<linearGradient id="Gradient01">
<stop offset="30%" style="color:#39F"/>
</linearGradient>
</defs>
<rect x="0%" y="0%" width="100%" height="100%"
style="fill:url(#Gradient01)" />
</svg>
In the document above, the linear gradient is defined within a 'defs' element which is the direct child of the 'svg' element, which in turn is an ancestor of the 'rect' element which references the linear gradient. Thus, the above document conforms to the guideline.
Each container element or graphics element in an SVG drawing can supply a 'desc' and/or a 'title' description string where the description is text-only. When the current SVG document fragment is rendered as SVG on visual media, 'desc' and 'title' elements are not rendered as part of the graphics. User agents may, however, for example, display the 'title' element as a tooltip, as the pointing device moves over particular elements. Alternate presentations are possible, both visual and aural, which display the 'desc' and 'title' elements but do not display 'path' elements or other graphics elements. This is readilly achieved by using a different (perhaps user) stylesheet. For deep hierarchies, and for following 'use' element references, it is sometimes desirable to allow the user to control how deep they drill down into descriptive text.
The following is an example. In typical operation, the SVG user agent would not render the 'desc' and 'title' elements but would render the remaining contents of the 'g' element.
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg SYSTEM "http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="4in" height="3in">
<g>
<title>
Company sales by region
</title>
<desc>
This is a bar chart which shows
company sales by region.
</desc>
<!-- Bar chart defined as vector data -->
</g>
</svg>
Description and title elements can contain marked-up text from other namespaces. Here is an example:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<svg width="4in" height="3in"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg-20000303-stylable">
<desc xmlns:mydoc="http://foo.org/mydoc">
<mydoc:title>This is an example SVG file</mydoc:title>
<mydoc:para>The global description uses markup from the
<mydoc:emph>mydoc</mydoc:emph> namespace.</mydoc:para>
</desc>
<g>
<!-- the picture goes here -->
</g>
</svg>
Authors should always provide a 'title' child element to the outermost 'svg' element within a stand-alone SVG document. The 'title' child element to an 'svg' element serves the purposes of identifying the content of the given SVG document fragment. Since users often consult documents out of context, authors should provide context-rich titles. Thus, instead of a title such as "Introduction", which doesn’t provide much contextual background, authors should supply a title such as "Introduction to Medieval Bee-Keeping" instead. For reasons of accessibility, user agents should always make the content of the 'title' child element to the outermost 'svg' element available to users. The mechanism for doing so depends on the user agent (e.g., as a caption, spoken).
The 'symbol' element is used to define graphical template objects which can be instantiated by a 'use' element.
The use of 'symbol' elements for graphics that are used multiple times in the same document adds structure and semantics. Documents that are rich in structure may be rendered graphically, as speech, or as braille. and thus promote accessibility.
The key distinctions between a 'symbol' and a 'g' are:
Closely related to the 'symbol'
element are the 'marker'
and 'pattern' elements.
<!ENTITY % symbolExt "" > <!ELEMENT symbol (%descTitleDefs;, (path|text|rect|circle|ellipse|line|polyline|polygon| use|image|svg|g|switch|a %ceExt;%symbolExt;)*) > <!ATTLIST symbol %stdAttrs; %langSpaceAttrs; class %ClassList; #IMPLIED externalResourcesRequired %Boolean; #IMPLIED viewBox %ViewBoxSpec; #IMPLIED preserveAspectRatio %PreserveAspectRatioSpec; 'xMidYMid meet' %StylableSVG-StyleAttribute; %ExchangeSVG-ContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-FillStrokeAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GradientAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GraphicsAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-MarkerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextElementAttrs; > |
Any 'svg', 'symbol', 'g', graphics element or other 'use' is potentially a template object that can be re-used (i.e., "instanced") in the SVG document via a 'use' element. The 'use' element references another element and indicates that the graphical contents of that element is included/drawn at that given point in the document.
Unlike 'image', the 'use' element cannot reference entire files.
The 'use' element has optional attributes x, y, width and height which are used to map the graphical contents of the referenced element onto a rectangular region within the current coordinate system.
The effect of a 'use' element is as if the contents of the referenced element, along with any property values resulting from the CSS cascade [CSS2-CASCADE] on the referenced element and its contents, were deeply cloned into a separate non-exposed DOM tree which had the 'use' element as its parent and all of the 'use' element's ancestors as its higher-level ancestors. Because the cloned DOM tree is non-exposed, the SVG Document Object Model (DOM) only contains the 'use' element and its attributes. The SVG DOM does not show the referenced element's contents as children of 'use' element.
Property inheritance, however, works as if the referenced element had been textually included as a deeply cloned child of the 'use' element. The referenced element inherits properties from the 'use' element and the 'use' element's ancestors. An instance of a referenced element does not inherit properties from its original parents.
A 'use' element has the same visual effect as if the 'use' element were replaced by the following generated content:
Example Use01 below has a simple 'use' on a 'rect'.
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="10cm" height="3cm">
<desc>Example Use01 - Simple case of 'use' on a 'rect'</desc>
<defs>
<rect id="MyRect" width="6cm" height="1cm"/>
</defs>
<use x="2cm" y="1cm" xlink:href="#MyRect" />
</svg>
 |
View this example as SVG (SVG-enabled browsers only)
The visual effect would be equivalent to the following document:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="10cm" height="3cm">
<desc>Example Use01-GeneratedContent - Simple case of 'use' on a 'rect'</desc>
<!-- 'defs' section left out -->
<!-- Start of generated content. Replaces 'use' -->
<svg x="2cm" y="1cm" width="100%" height="100%">
<rect width="6cm" height="1cm"/>
</svg>
<!-- End of generated content -->
</svg>
View this example as SVG (SVG-enabled browsers only)
Example Use02 below has a 'use' on a 'symbol'.
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="10cm" height="3cm">
<desc>Example Use02 - 'use' on a 'symbol'</desc>
<defs>
<symbol id="MySymbol" viewBox="0 0 20 20">
<desc>MySymbol - four rectangles in a grid</desc>
<rect x="1" y="1" width="8" height="8"/>
<rect x="11" y="1" width="8" height="8"/>
<rect x="1" y="11" width="8" height="8"/>
<rect x="11" y="11" width="8" height="8"/>
</symbol>
</defs>
<use x="4.5cm" y="1cm" width="1cm" height="1cm"
xlink:href="#MySymbol" />
</svg>
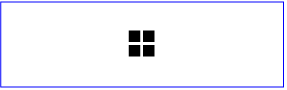 |
View this example as SVG (SVG-enabled browsers only)
The visual effect would be equivalent to the following document:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="10cm" height="3cm">
<desc>Example Use02-GeneratedContent - 'use' on a 'symbol'</desc>
<!-- 'defs' section left out -->
<!-- Start of generated content. Replaces 'use' -->
<svg x="4.5cm" y="1cm" width="1cm" height="1cm" >
<!-- Start of referenced 'symbol'. 'symbol' replaced by 'svg',
with x,y,width,height=0%,0%,100%,100% -->
<svg x="0%" y="0%" width="100%" height="100%"
viewBox="0 0 20 20">
<rect x="1" y="1" width="8" height="8"/>
<rect x="11" y="1" width="8" height="8"/>
<rect x="1" y="11" width="8" height="8"/>
<rect x="11" y="11" width="8" height="8"/>
</svg>
<!-- End of referenced symbol -->
</svg>
<!-- End of generated content -->
</svg>
View this example as SVG (SVG-enabled browsers only)
Example Use03 illustrates what happens when a 'use' has a transform attribute.
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="10cm" height="3cm">
<desc>Example Use03 - 'use' with a 'transform' attribute</desc>
<defs>
<rect id="MyRect" x="0" y="0" width="6cm" height="1cm"/>
</defs>
<use xlink:href="#MyRect"
transform="translate(2cm,.25cm) rotate(10)" />
</svg>
 |
View this example as SVG (SVG-enabled browsers only)
The visual effect would be equivalent to the following document:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="10cm" height="3cm">
<desc>Example Use03-GeneratedContent - 'use' with a 'transform' attribute</desc>
<!-- 'defs' section left out -->
<!-- Start of generated content. Replaces 'use' -->
<g transform="translate(2cm,.25cm) rotate(10)">
<svg x="0%" y="0%" width="100%" height="100%">
<rect x="0" y="0" width="6cm" height="1cm"/>
</svg>
</g>
<!-- End of generated content -->
</svg>
View this example as SVG (SVG-enabled browsers only)
Example Use04 illustrates a 'use' element with various methods of applying CSS styling.
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?> <!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd"> <svg width="12cm" height="3cm" viewBox="0 0 1200 300"> <desc>Example Use04 - 'use' with CSS styling</desc> <defs style="/* rule 9 */ stroke-miterlimit: 10" > <path id="MyPath" d="M300 50 L900 50 L900 250 L300 250" class="MyPathClass" style="/* rule 10 */ stroke-dasharray:300 100" /> </defs> <style type="text/css"> <![CDATA[ /* rule 1 */ #MyUse { fill: blue } /* rule 2 */ #MyPath { stroke: red } /* rule 3 */ use { fill-opacity: .5 } /* rule 4 */ path{ stroke-opacity: .5 } /* rule 5 */ .MyUseClass { stroke-linecap: round } /* rule 6 */ .MyPathClass { stroke-linejoin: bevel } /* rule 7 */ use > path{ shape-rendering: optimizeQuality } /* rule 8 */ svg > path{ visibility: hidden } ]]> </style> <g style="/* rule 11 */ stroke-width: 40"> <use id="MyUse" xlink:href="#MyPath" class="MyUseClass" style="/* rule 12 */ stroke-dashoffset:50" /> </g> </svg>
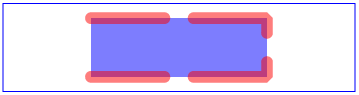 |
View this example as SVG (SVG-enabled browsers only)
The visual effect would be equivalent to the following document. Observe that some of the style rules above apply to the generated content (i.e., rules 1-6, 10-12), whereas others do not (i.e., rules 7-9). The rules which do not affect the generated content are:
In the generated content below, the selectors that yield a match have been transferred into inline 'style' attributes for illustrative purposes.
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="12cm" height="3cm" viewBox="0 0 1200 300">
<desc>Example Use04-GeneratedContent - 'use' with a 'transform' attribute</desc>
<!-- 'style' and 'defs' sections left out -->
<g style="/* rule 11 */ stroke-width:40">
<!-- Start of generated content. Replaces 'use' -->
<svg x="0%" y="0%" width="100%" height="100%"
style="/* rule 1 */ fill:blue;
/* rule 3 */ fill-opacity:.5;
/* rule 5 */ stroke-linecap:round;
/* rule 12 */ stroke-dashoffset:50" >
<path d="M300 50 L900 50 L900 250 L300 250"
style="/* rule 2 */ stroke:red;
/* rule 4 */ stroke-opacity:.5;
/* rule 6 */ stroke-linejoin: bevel;
/* rule 10 */ stroke-dasharray:300 100" />
</svg>
<!-- End of generated content -->
</g>
</svg>
View this example as SVG (SVG-enabled browsers only)
When a 'use' references another element which is another 'use' or whose content contains a 'use' element, then the deep cloning approach described above is recursive.
<!ENTITY % useExt "" > <!ELEMENT use (%descTitle;,(animate|set|animateMotion|animateColor|animateTransform %geExt;%useExt;)*) > <!ATTLIST use %stdAttrs; %langSpaceAttrs; class %ClassList; #IMPLIED transform %TransformList; #IMPLIED %graphicsElementEvents; %testAttrs; externalResourcesRequired %Boolean; #IMPLIED x %Coordinate; #IMPLIED y %Coordinate; #IMPLIED width %Length; #IMPLIED height %Length; #IMPLIED %xlinkRefAttrs; xlink:href %URI; #REQUIRED %StylableSVG-StyleAttribute; %ExchangeSVG-ContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-FillStrokeAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GradientAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GraphicsAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-MarkerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextElementAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-ViewportAttrs; > |
Attribute definitions:
The 'image' element indicates that the contents of a complete file are to be rendered into a given rectangle within the current user coordinate system. The 'image' element can refer to raster image files such as PNG or JPEG or to files with MIME type of "image/svg". Conforming SVG viewers need to support at least PNG, JPEG and SVG format files.
The resource referenced by the 'image' element represents a separate document which generates its own parse tree and document object model (if the resource is XML). Thus, there is no inheritance of properties into the image.
Unlike 'use',
the 'image'
element cannot reference elements within an SVG file.
<!ENTITY % imageExt "" > <!ELEMENT image (%descTitle;,(animate|set|animateMotion|animateColor|animateTransform %geExt;%imageExt;)*) > <!ATTLIST image %stdAttrs; %langSpaceAttrs; class %ClassList; #IMPLIED transform %TransformList; #IMPLIED %graphicsElementEvents; %testAttrs; externalResourcesRequired %Boolean; #IMPLIED x %Coordinate; #IMPLIED y %Coordinate; #IMPLIED width %Length; #REQUIRED height %Length; #REQUIRED %xlinkRefAttrs; xlink:href %URI; #REQUIRED %StylableSVG-StyleAttribute; %ExchangeSVG-ContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-FillStrokeAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GradientAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GraphicsAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-MarkerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextElementAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-ViewportAttrs; > |
Attribute definitions:
A valid example:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<!DOCTYPE svg PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD SVG 20000303 Stylable//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/03/WD-SVG-20000303/DTD/svg-20000303-stylable.dtd">
<svg width="4in" height="3in">
<desc>This graphic links to an external image
</desc>
<image x="200" y="200" width="100px" height="100px"
xlink:href="myimage.png">
<title>My image</title>
</image>
</svg>
A well-formed example:
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<svg width="4in" height="3in"
xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg-20000303-stylable'>
<desc>This links to an external image
</desc>
<image x="200" y="200" width="100px" height="100px"
xlink:type="simple" xlink:show="embed" xlink:actuate="onLoad"
xlink:href="myimage.png">
<title>My image</title>
</image>
</svg>
SVG contains a 'switch' element along with attributes system-required and system-language to provide an ability to specify alternate viewing depending on the capabilities of a given user agent or the user's language. These features operate with the same semantics as the corresponding features within the SMIL 1.0 Recommendation [SMIL1].
<!ENTITY % testAttrs "system-required NMTOKEN #IMPLIED system-language CDATA #IMPLIED" > |
Attributes system-required and system-language act as tests and return either true or false results. The 'switch' renders the first of its children for which both attributes test true.
The 'switch' element evaluates the system-required and system-language attributes on its direct child elements in order, and then processes and renders the first child for which these two attributes evaluate to true. All others will be bypassed and therefore not rendered. If the child element is a container element such as a 'g', then the entire subtree is either processed/rendered or bypassed/not rendered.
<!ENTITY % switchExt "" > <!ELEMENT switch (%descTitleDefs;, (path|text|rect|circle|ellipse|line|polyline|polygon| use|image|svg|g|switch|a|foreignObject| animate|set|animateMotion|animateColor|animateTransform %ceExt;%switchExt;)*) > <!ATTLIST switch %stdAttrs; %langSpaceAttrs; class %ClassList; #IMPLIED transform %TransformList; #IMPLIED %graphicsElementEvents; %testAttrs; externalResourcesRequired %Boolean; #IMPLIED %StylableSVG-StyleAttribute; %ExchangeSVG-ContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-FillStrokeAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GradientAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-GraphicsAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-MarkerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextContainerAttrs; %ExchangeSVG-TextElementAttrs; > |
For more information and an example, see Embedding foreign object types.
Definition of system-required:
All feature strings referring to language capabilities begin with "org.w3c.svg". All feature strings referring to SVG DOM capabilities begin with "org.w3c.dom.svg".
The following are the feature strings for the system-required attribute. These same feature strings apply to the hasFeature method call that is part of the SVG DOM's support for the DOMImplementation interface defined in [DOM2-CORE] (see Feature strings for the hasFeature method call).
If the attribute is not present, then its implicit return value is "true". If a null string or empty string value is given to attribute system-required, the attribute returns "false".
system-required is often used in conjunction with the 'switch' element. If the system-required is used in other situations, then it represented a simple switch on the given element whether to render the element or not.
The attribute value is a comma-separated list of language names as defined in [RFC1766].
Evaluates to "true" if one of the languages indicated by user preferences exactly equals one of the languages given in the value of this parameter, or if one of the languages indicated by user preferences exactly equals a prefix of one of the languages given in the value of this parameter such that the first tag character following the prefix is "-". Evaluates to "false" otherwise.
Further description of the system-language attribute can be found at [SMIL10-SYSLANG].
If the attribute is not present, then its implicit return value is "true". If a null string or empty string value is given to attribute system-required, the attribute returns "false".
The id attribute is available on all SVG elements:
<!ENTITY % stdAttrs "id ID #IMPLIED" > |
Attribute definitions:
Attribute definitions:
The class attribute assigns one or more class names to an element. The element may be said to belong to these classes. A class name may be shared by several element instances. The class attribute has several roles:
In the following example, the 'text' element is used in conjunction with the class attributes to markup document messages. Messages appear in both English and French versions.
<!-- English messages --> <text class="info" lang="en">Variable declared twice</text> <text class="warning" lang="en">Undeclared variable</text> <text class="error" lang="en">Bad syntax for variable name</text> <!-- French messages --> <text class="info" lang="fr">Variable déclarée deux fois</text> <text class="warning" lang="fr">Variable indéfinie</text> <text class="error" lang="fr">Erreur de syntaxe pour variable</text>
In an SVG user agent that supports CSS styling, the following CSS style rules would tell visual user agents to display informational messages in green, warning messages in yellow, and error messages in red:
text.info { color: green }
text.warning { color: yellow }
text.error { color: red }
<!ENTITY % langSpaceAttrs "xml:lang NMTOKEN #IMPLIED xml:space (default|preserve) #IMPLIED" > |
Attribute definitions:
The following interfaces are defined below: SVGDocument, SVGElement, SVGSVGElement, SVGGElement, SVGDefsElement, SVGDescElement, SVGTitleElement, SVGUseElement, SVGImageElement, SVGSymbolElement, SVGSwitchElement, SVGLangSpace, SVGTests, SVGURIReference, GetSVGDocument.
When an 'svg' element is embedded inline as a component of a document from another namespace, such as when an 'svg' element is embedded inline within an XHTML document [XHTML], then an SVGDocument object will not exist; instead, the root object in the document object hierarchy will be a Document object of a different type, such as an HTMLDocument object.
However, an SVGDocument object will indeed exist when the root element of the XML document hierarchy is an 'svg' element, such as when viewing a standalone SVG file (i.e., a file with MIME type "image/svg"). In this case, the SVGDocument object will be the the root object of the document object model hierarchy.
In the case where an SVG document is embedded by reference, such as when an XHTML document has an 'object' element whose href attribute references an SVG document (i.e., a document whose MIME type is "image/svg" and whose root element is thus an 'svg' element), there will exist two distinct DOM hierarchies. The first DOM hierarchy will be for the referencing document (e.g., an XHTML document). The second DOM hierarchy will be for the referenced SVG document. In this second DOM hierarchy, the root object of the document object model hierarchy is an SVGDocument object.
The SVGDocument interface contains a similar list of attributes and methods to the HTMLDocument interface described in Document Object Model (HTML) Level 1 chapter of the [DOM1] specification.
interface SVGDocument : Document, DocumentEvent {
attribute DOMString title;
readonly attribute DOMString referrer;
readonly attribute DOMString domain;
readonly attribute DOMString URL;
readonly attribute SVGSVGElement rootElement;
Element getElementById ( in DOMString elementId );
};
| in DOMString elementId |
The unique id value for an element. |
| Element | The matching element. |
All of the SVG DOM interfaces that correspond directly to elements in the SVG language (e.g., the SVGPathElement interface corresponds directly to the 'path' element in the language) are derivative from base class SVGElement.
interface SVGElement : Element {
attribute DOMString id;
readonly attribute SVGSVGElement ownerSVGElement;
readonly attribute SVGElement viewportElement;
};
A key interface definition is the SVGSVGElement interface, which is the interface that corresponds to the 'svg' element. This interface contains various miscellaneous commonly-used utility methods, such as matrix operations and the ability to control the time of redraw on visual rendering devices.
interface SVGSVGElement : SVGElement, SVGLangSpace, SVGTests, SVGFitToViewBox, DocumentEvent, EventTarget {
attribute DOMString className;
readonly attribute SVGRect viewport;
readonly attribute float CSSPixelToMillimeterX;
readonly attribute float CSSPixelToMillimeterY;
readonly attribute float ScreenPixelToMillimeterX;
readonly attribute float ScreenPixelToMillimeterY;
attribute boolean useCurrentView;
readonly attribute SVGViewSpec currentView;
attribute boolean enableZoomAndPanControls;
attribute float currentScale;
attribute SVGPoint currentTranslate;
attribute SVGLength x;
attribute SVGLength y;
attribute SVGLength width;
attribute SVGLength height;
#ifdef STYLABLESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Stylable SVG.
STYLABLESVGStyleAttribute;
#endif STYLABLESVG
#ifdef EXCHANGESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Exchange SVG.
EXCHANGESVGContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGFillStrokeAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGradientAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGraphicsAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGMarkerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextElementAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGViewportAttrs;
#endif EXCHANGESVG
unsigned long suspendRedraw ( in unsigned long max_wait_milliseconds );
void unsuspendRedraw ( in unsigned long suspend_handle_id )
raises( DOMException );
void unsuspendRedrawAll ( );
void forceRedraw ( );
void pauseAnimations ( );
void unpauseAnimations ( );
boolean animationsPaused ( );
float getCurrentTime ( );
void setCurrentTime ( in float seconds );
NodeList getIntersectionList ( in SVGRect rect, in SVGElement referenceElement )
raises( SVGException );
NodeList getEnclosureList ( in SVGRect rect, in SVGElement referenceElement )
raises( SVGException );
boolean checkIntersection ( in SVGElement element, in SVGRect rect )
raises( SVGException );
boolean checkEnclosure ( in SVGElement element, in SVGRect rect )
raises( SVGException );
void deSelectAll ( );
SVGNumber createSVGNumber ( );
SVGLength createSVGLength ( );
SVGLengthList createSVGLengthList ( );
SVGAngle createSVGAngle ( );
SVGPoint createSVGPoint ( );
SVGPointList createSVGPointList ( );
SVGMatrix createSVGMatrix ( );
SVGPreserveAspectRatio createSVGPreserveAspectRatio ( );
SVGRect createSVGRect ( );
SVGTransformList createSVGTransformList ( );
SVGTransformList createSVGTransformListFromMatrix ( in SVGMatrix matrix );
SVGTransform createSVGTransform ( );
SVGTransform createSVGTransformFromMatrix ( in SVGMatrix matrix );
SVGICCColor createSVGICCColor ( );
SVGColor createSVGColor ( );
SVGPaint createSVGPaint ( );
Element getElementById ( in DOMString elementId );
};
The position and size of the viewport (implicit or explicit) that corresponds to this 'svg' element. When the user agent is actually rendering the content, then the position and size values represent the actual values when rendering. The position and size values are unit-less values in the coordinate system of the parent element. If no parent element exists (i.e., 'svg' element represents the root of the document tree), if this SVG document is embedded as part of another document (e.g., via the HTML 'object' element), then the position and size are unitless values in the coordinate system of the parent document. (If the parent uses CSS layout, then values represent CSS pixels in the coordinate system of the current CSS viewport.) If the parent element does not have a coordinate system, then the user agent should provide reasonable default values for this attribute.
| in unsigned long max_wait_milliseconds | The amount of time in milliseconds to hold off before redrawing the device. Values greater than 60 seconds will be truncated down to 60 seconds. |
| unsigned long | A number which acts as a unique identifier for the given suspendRedraw() call. This value must be passed as the parameter to the corresponding unsuspendRedraw() method call. |
| in unsigned long suspend_handle_id | A number which acts as a unique identifier for the desired suspendRedraw() call. The number supplied must be a value returned from a previous call to suspendRedraw() |
| DOMException |
This method will raise a DOMException with value NOT_FOUND_ERR if an
invalid value (i.e., no such suspend_handle_id is active)
for suspend_handle_id is provided.
|
| boolean | Boolean indicating whether this SVG document fragment is in a paused state. |
| float | The current time in seconds. |
| in float seconds | The new current time in seconds relative to the start time for the current SVG document fragment. |
| in SVGRect rect | The test rectangle. The values are in the initial coordinate system for the current 'svg' element. | |
| in SVGElement referenceElement | If not null, then only return elements whose drawing order has them below the given reference element. |
| SVGException |
SVG_WRONG_TYPE_ERR: Raised if the parameter is of the wrong type.
|
| in SVGRect rect | The test rectangle. The values are in the initial coordinate system for the current 'svg' element. | |
| in SVGElement referenceElement | If not null, then only return elements whose drawing order has them below the given reference element. |
| SVGException |
SVG_WRONG_TYPE_ERR: Raised if the parameter is of the wrong type.
|
| in SVGElement element | The element on which to perform the given test. | |
| in SVGRect rect | The test rectangle. The values are in the initial coordinate system for the current 'svg' element. |
| SVGException |
SVG_WRONG_TYPE_ERR: Raised if the parameter is of the wrong type.
|
| in SVGElement element | The element on which to perform the given test. | |
| in SVGRect rect | The test rectangle. The values are in the initial coordinate system for the current 'svg' element. |
| SVGException |
SVG_WRONG_TYPE_ERR: Raised if the parameter is of the wrong type.
|
| SVGNumber | An SVGNumber object. |
| SVGLength | An SVGLength object. |
| SVGLengthList | An SVGLengthList object. |
| SVGAngle | An SVGAngle object. |
| SVGPoint | An SVGPoint object. |
| SVGPointList | An SVGPointList object. |
| SVGMatrix | An SVGMatrix object. |
| SVGPreserveAspectRatio | An SVGPreserveAspectRatio object. |
| SVGRect | An SVGRect object. |
| SVGTransformList | An SVGTransformList object. |
| in SVGMatrix matrix | The initial transform matrix. |
| SVGTransformList | An SVGTransformList object. |
| SVGTransform | An SVGTransform object. |
| in SVGMatrix matrix | The transform matrix. |
| SVGTransform | An SVGTransform object. |
| SVGICCColor | An SVGICCColor object. |
| SVGColor | An SVGColor object. |
| SVGPaint | An SVGPaint object. |
| in DOMString elementId |
The unique id value for an element. |
| Element | The matching element. |
The SVGGElement interface corresponds to the 'g' element.
interface SVGGElement : SVGElement, SVGTransformable, SVGLangSpace, SVGTests, EventTarget {
attribute DOMString className;
#ifdef STYLABLESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Stylable SVG.
STYLABLESVGStyleAttribute;
#endif STYLABLESVG
#ifdef EXCHANGESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Exchange SVG.
EXCHANGESVGContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGFillStrokeAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGradientAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGraphicsAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGMarkerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextElementAttrs;
#endif EXCHANGESVG
};
The SVGDefsElement interface corresponds to the 'defs' element.
interface SVGDefsElement : SVGElement, SVGTransformable, SVGLangSpace {
attribute DOMString className;
#ifdef STYLABLESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Stylable SVG.
STYLABLESVGStyleAttribute;
#endif STYLABLESVG
#ifdef EXCHANGESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Exchange SVG.
EXCHANGESVGContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGFillStrokeAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGradientAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGraphicsAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGMarkerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextElementAttrs;
#endif EXCHANGESVG
};
The SVGDescElement interface corresponds to the 'desc' element.
interface SVGDescElement : SVGElement, SVGLangSpace {
attribute DOMString className;
#ifdef STYLABLESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Stylable SVG.
STYLABLESVGStyleAttribute;
#endif STYLABLESVG
};
The SVGTitleElement interface corresponds to the 'title' element.
interface SVGTitleElement : SVGElement, SVGLangSpace {
attribute DOMString className;
#ifdef STYLABLESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Stylable SVG.
STYLABLESVGStyleAttribute;
#endif STYLABLESVG
};
The SVGUseElement interface corresponds to the 'use' element.
interface SVGUseElement : SVGElement, SVGTransformable, SVGLangSpace, SVGTests, SVGURIReference, EventTarget {
attribute DOMString className;
attribute SVGLength x;
attribute SVGLength y;
attribute SVGLength width;
attribute SVGLength height;
#ifdef STYLABLESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Stylable SVG.
STYLABLESVGStyleAttribute;
#endif STYLABLESVG
#ifdef EXCHANGESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Exchange SVG.
EXCHANGESVGContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGFillStrokeAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGradientAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGraphicsAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGMarkerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextElementAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGViewportAttrs;
#endif EXCHANGESVG
};
The SVGImageElement interface corresponds to the 'image' element.
interface SVGImageElement : SVGElement, SVGTransformable, SVGLangSpace, SVGTests, SVGURIReference, EventTarget {
attribute DOMString className;
attribute SVGLength x;
attribute SVGLength y;
attribute SVGLength width;
attribute SVGLength height;
#ifdef STYLABLESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Stylable SVG.
STYLABLESVGStyleAttribute;
#endif STYLABLESVG
#ifdef EXCHANGESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Exchange SVG.
EXCHANGESVGContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGFillStrokeAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGradientAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGraphicsAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGMarkerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextElementAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGViewportAttrs;
#endif EXCHANGESVG
};
The SVGSymbolElement interface corresponds to the 'symbol' element.
interface SVGSymbolElement : SVGElement, SVGLangSpace, SVGFitToViewBox {
attribute DOMString className;
#ifdef STYLABLESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Stylable SVG.
STYLABLESVGStyleAttribute;
#endif STYLABLESVG
#ifdef EXCHANGESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Exchange SVG.
EXCHANGESVGContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGFillStrokeAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGradientAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGraphicsAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGMarkerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextElementAttrs;
#endif EXCHANGESVG
};
The SVGSwitchElement interface corresponds to the 'switch' element.
interface SVGSwitchElement : SVGElement, SVGTransformable, SVGLangSpace, SVGTests, EventTarget {
attribute DOMString className;
#ifdef STYLABLESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Stylable SVG.
STYLABLESVGStyleAttribute;
#endif STYLABLESVG
#ifdef EXCHANGESVG
// The following pre-defined attribute collections are only
// available in the DOM for Exchange SVG.
EXCHANGESVGContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGFillStrokeAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGradientAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGGraphicsAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGMarkerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextContainerAttrs;
EXCHANGESVGTextElementAttrs;
#endif EXCHANGESVG
};
Interface SVGLangSpace defines an interface which applies to all elements which have attributes xml:lang and xml:space.
interface SVGLangSpace {
attribute DOMString xmllang;
attribute DOMString xmlspace;
};
Interface SVGTests defines an interface which applies to all elements which have attributes system-required and system-language.
interface SVGTests {
attribute DOMString systemRequired;
attribute DOMString systemLanguage;
};
Interface SVGURIReference defines an interface which applies to all elements which have the collection of XLink attributes, such as xlink:href, which define a URI reference.
interface SVGURIReference {
attribute DOMString xlinkType;
attribute DOMString xlinkRole;
attribute DOMString xlinkTitle;
attribute DOMString xlinkShow;
attribute DOMString xlinkActuate;
attribute DOMString href;
};
In the case where an SVG document is embedded by reference, such as when an XHTML document has an 'object' element whose href (or equivalent) attribute references an SVG document (i.e., a document whose MIME type is "image/svg" and whose root element is thus an 'svg' element), the SVG user agent is required to implement the GetSVGDocument interface for the element which references the SVG document (e.g., the HTML 'object' or comparable referencing elements).
interface GetSVGDocument {
SVGDocument getSVGDocument ( )
raises( DOMException );
};
Returns the SVGDocument object for the referenced SVG document.
| SVGDocument | The SVGDocument object for the referenced SVG document. |
| DOMException |
NOT_SUPPORTED_ERR: No SVGDocument object is available.
|