Abstract
Provenance is information about entities, activities, and people involved in producing a piece of data or thing, which can be used to form assessments about its quality, reliability or trustworthiness. PROV-DM is the conceptual data model that forms a basis for the W3C provenance (PROV) family of specifications. It defines a concepts for expressing provenance information enabling interchange. This document introduces an XML schema for the PROV data model (PROV-DM), allowing instances of the PROV data model to be serialized in XML.
The PROV Document Overview describes the overall state of PROV, and should be read before other PROV documents.
Status of This Document
This section describes the status of this document at the time of its publication. Other documents may supersede this document. A list of current W3C publications and the latest revision of this technical report can be found in the W3C technical reports index at http://www.w3.org/TR/.
PROV Family of Documents
This document is part of the PROV family of documents, a set of documents defining various aspects that are necessary to achieve the vision of inter-operable
interchange of provenance information in heterogeneous environments such as the Web. These documents are:
- PROV-OVERVIEW (To be published as Note), an overview of the PROV family of documents [PROV-OVERVIEW];
- PROV-PRIMER (To be published as Note), a primer for the PROV data model [PROV-PRIMER];
- PROV-O (Candidate Recommendation), the PROV ontology, an OWL2 ontology allowing the mapping of PROV to RDF [PROV-O];
- PROV-DM (Candidate Recommendation), the PROV data model for provenance [PROV-DM];
- PROV-N (Candidate Recommendation), a notation for provenance aimed at human consumption [PROV-N];
- PROV-CONSTRAINTS (Candidate Recommendation), a set of constraints applying to the PROV data model [PROV-CONSTRAINTS];
- PROV-AQ (To be published as Note), the mechanisms for accessing and querying provenance [PROV-AQ];
- PROV-XML (To be published as Note), an XML schema for the PROV data model (this document).
How to read the PROV Family of Documents
- [PROV-OVERVIEW] overviews the PROV family of documents.
- The primer [PROV-PRIMER] is the entry point to PROV offering an introduction to the provenance model.
- The Linked Data and Semantic Web community should focus on [PROV-O] defining PROV classes and properties specified in an OWL2 ontology. For further details, PROV-DM and [PROV-CONSTRAINTS] specify the constraints applicable to the data model, and its interpretation.
- The XML community should focus on [PROV-XML] defining an XML schema for PROV. Further details can also be found in PROV-DM and [PROV-CONSTRAINTS].
- Developers seeking to retrieve or publish provenance should focus on [PROV-AQ].
- Readers seeking to implement other PROV serializations
should focus on PROV-DM and [PROV-CONSTRAINTS]. [PROV-O], [PROV-N], and [PROV-XML] offer examples of mapping to RDF, text, and XML, respectively.
This document was published by the Provenance Working Group as a First Public Working Draft. If you wish to make comments regarding this document, please send them to public-prov-comments@w3.org (subscribe, archives). All feedback is welcome.
Publication as a Working Draft does not imply endorsement by the W3C Membership. This is a draft document and may be updated, replaced or obsoleted by other documents at any time. It is inappropriate to cite this document as other than work in progress.
This document was produced by a group operating under the 5 February 2004 W3C Patent Policy. The group does not expect this document to become a W3C Recommendation. W3C maintains a public list of any patent disclosures made in connection with the deliverables of the group; that page also includes instructions for disclosing a patent. An individual who has actual knowledge of a patent which the individual believes contains Essential Claim(s) must disclose the information in accordance with section 6 of the W3C Patent Policy.
1. Introduction
For the purpose of this specification, provenance is defined as a record that describes the people, institutions, entities, and activities involved in producing, influencing, or delivering a piece of data or a thing. In particular, the provenance of information is crucial in deciding whether information is to be trusted, how it should be integrated with other diverse information sources, and how to give credit to its originators when reusing it. In an open and inclusive environment such as the Web, where users find information that is often contradictory or questionable, provenance can help those users to make trust judgements.
The PROV data model, PROV-DM, presents a generic data model for provenance that allows domain and application specific representations of provenance to be translated into such a data model and interchanged between systems. Thus, heterogeneous systems can export their native provenance into such a core data model, and applications that need to make sense of provenance can then import it,
process it, and reason over it.
The PROV data model distinguishes core structures from extended structures: core structures form the essence of provenance information, and are commonly found in various domain-specific vocabularies that deal with provenance or similar kinds of information [Mappings]. Extended structures enhance and refine core structures with more expressive capabilities to cater for more advanced uses of provenance. The PROV data model, comprising both core and extended structures, is a domain-agnostic model, but with clear extensibility points allowing further domain-specific and application-specific extensions to be defined.
The PROV data model has a modular design and is structured according to six components covering various facets of provenance:
- component 1: entities and activities, and the time at which they were created, used, or ended;
- component 2: derivations of entities from others;
- component 3: agents bearing responsibility for entities that were generated and activities that happened;
- component 4: bundles, a mechanism to support provenance of provenance;
- component 5: properties to link entities that refer to a same thing;
- component 6: collections forming a logical structure for its members.
This specification goal is to provide a succinct definition of the XML form of PROV-DM, thus, we refer the reader to the PROV-DM to provide overall justification and context to the definitions presented here.
1.1 PROV Namespace
The PROV namespace is http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#.
All the concepts, reserved names and attributes introduced in this specification belong to the PROV namespace.
1.2 Conventions
The key words "must", "must not", "required", "shall", "shall
not", "should", "should not", "recommended", "may", and
"optional" in this document are to be interpreted as described in
[RFC2119].
2. XML Schema Design
Several general design principles and patterns were used in the
construction of the PROV XML Schema.
Salami Slice Design Pattern
The general design pattern for the XML schema has been
called Salami Slice Design (cite?). With this design, the
individual components are each defined at the top level as separate
elements with distinct types. This allows the types to be easily
reusable for domain specific extensions.
Elements vs. Attributes
The general PROV-N syntax patterns for expressing provenance
concepts are:
thing(id, elem1, elem2, ..., [attr1=val1, attr2=val2])
concept(id; elem1, elem2, ... [attr1=val2, attr2=val2])
In both cases (required id or optional id), the PROV-N id is
treated as an XML attribute, the PROV-N "elements" are treated as XML
elements, always with the same required order (position) as the
PROV-DM/PROV-N description, and optional PROV-N "attributes", if
allowed, always follow and are also represented by XML elements. As
in PROV-N, the attributes can be specified multiple times, and in any
order, as long as they are all at the end of the encompassing element.
Wherever an "id" is referenced from a later concept, the id is
referenced as a prov:ref attribute of the element within the concept.
This transformation technique yields a general XML pattern:
<prov:thing prov:id="id">
<prov:elem1 />
<prov:elem2 />
...
<prov:attr1>val1</prov:attr1>
<prov:attr2>val2</prov:attr2>
...
</prov:thing>
Most of the concepts described below follow this general pattern.
REVIEW QUESTION:
Is this ordering of elements/attributes reasonable/satisfactory?
Would it be better to loosen the ordering requirement allowing any mix
of elements/attributes, or to tighten the ordering requirement,
requiring all "prov:" namespace attributes to precede all non-"prov:"
namespace attributes when expressed as XML elements?
REVIEW QUESTION:
The current design has mirrored the naming from PROV-N. This often
involves reliance on the "prov:type" attribute to distinguish some
relations. In order to simplify the overall expression of those
concepts in XML, we are considering adding additional explicitly named
top level elements rather than requiring "prov:type".
For example, a Quotation is currently expressed in PROV-N as a type
of Derivation like this:
wasDerivedFrom(a, b, [prov:type='prov:Quotation'])
which is transformed to:
<prov:wasDerivedFrom>
<prov:generatedEntity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:usedEntity prov:ref="b"/>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Quotation</prov:type>
</prov:wasDerivedFrom>
This proposal would replace that with an explicit "Quotation" element:
<prov:Quotation>
<prov:generatedEntity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:usedEntity prov:ref="b"/>
</prov:Quotation>
Other "typed" concepts and relations would be handled similarly.
3. PROV XML Schema
Provenance concepts, expressed as PROV-DM types and relations, are organized according to six components that are defined in this section.
- Component 1: entities and activities. The first component consists of entities, activities, and concepts linking them, such as generation, usage, start, end. The first component is the only one comprising time-related concepts.
- Component 2: derivations. The second component is formed with derivations and derivation subtypes.
- Component 3: agents, responsibility, and influence. The third component consists of agents and concepts ascribing responsibility to agents.
- Component 4: bundles. The fourth component is concerned with bundles, a mechanism to support provenance of provenance.
- Component 5: alternate. The fifth component consists of relations linking entities referring to the same thing.
- Component 6: collections. The sixth component is about collections.
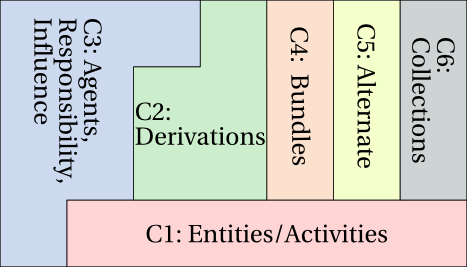
Figure 1 ◊: PROV-DM Components (Informative)
Table 1 is a mapping of PROV-DM types and relations in PROV-XML schema XML types and elements.
This mapping table is still under discussion and it's structure is subject to change.
In the rest of the section, each type is defined, in English initially, followed by its XML schema definition and some example.
3.1 Component 1: Entities and Activities
The first component of PROV-DM is concerned with entities and activities, and their inter-relations: Usage, Generation, Start, End, and Communication.
3.1.1 Entity
An entity is a physical, digital, conceptual, or other kind of thing with some fixed aspects; entities may be real or imaginary.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Entity">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:value"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="entity" type="prov:Entity"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#"
xmlns:tr="http://example.com/ns/tr#">
<prov:entity prov:id="tr:WD-prov-dm-20111215">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">document</prov:type>
<ex:version>2</ex:version>
</prov:entity>
</prov:document>
3.1.2 Activity
An activity is something that occurs over a period of time and acts upon or with entities; it may include consuming, processing, transforming, modifying, relocating, using, or generating entities.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Activity">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="startTime" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="endTime" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="activity" type="prov:Activity"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:activity prov:id="a1">
<prov:startTime>2011-11-16T16:05:00</prov:startTime>
<prov:endTime>2011-11-16T16:06:00</prov:endTime>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">ex:edit</prov:type>
<ex:host>server.example.org</ex:host>
</prov:activity>
</prov:document>
3.1.3 Generation
Generation is the completion of production of a new entity by an activity. This entity did not exist before generation and becomes available for usage after this generation.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Generation">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="time" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="wasGeneratedBy" type="prov:Generation"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:entity prov:id="e1"/>
<prov:activity prov:id="a1"/>
<prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:entity prov:ref="e1"/>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a1"/>
<prov:time>2001-10-26T21:32:52</prov:time>
<ex:port>p1</ex:port>
</prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:entity prov:id="e2"/>
<prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:entity prov:ref="e2"/>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a1"/>
<prov:time>2001-10-26T10:00:00</prov:time>
<ex:port>p2</ex:port>
</prov:wasGeneratedBy>
</prov:document>
3.1.4 Usage
Usage is the beginning of utilizing an entity by an activity. Before usage, the activity had not begun to utilize this entity and could not have been affected by the entity.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Usage">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:EntityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="time" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="used" type="prov:Usage"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:activity prov:id="a1"/>
<prov:entity prov:id="e1"/>
<prov:entity prov:id="e2"/>
<prov:used>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a1"/>
<prov:entity prov:ref="e1"/>
<prov:time≶2011-11-16T16:00:00</prov:time>
<ex:parameter>p1</ex:parameter>
</prov:used>
<prov:used>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a1"/>
<prov:entity prov:ref="e2"/>
<prov:time>2011-11-16T16:00:01</prov:time>
<ex:parameter>p2</ex:parameter>
</prov:used>
</prov:document>
3.1.5 Communication
Communication is the exchange of some unspecified entity by two activities, one activity using some entity generated by the other.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Communication">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="informed" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:element name="informant" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="wasInformedBy" type="prov:Communication"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#">
<prov:activity prov:id="a1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:string">traffic regulations enforcing<prov:type>
</prov:activity>
<prov:activity prov:id="a2">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:string">fine paying, check writing, and mailing</prov:type>
</prov:activity>
<prov:wasInformedBy>
<prov:informed prov:ref="a2"/>
<prov:informant prov:ref="a1"/>
</prov:wasInformedBy>
</prov:document>
3.1.6 Start
Start is when an activity is deemed to have been started by an entity, known as trigger. The activity did not exist before its start. Any usage, generation, or invalidation involving an activity follows the activity's start. A start may refer to a trigger entity that set off the activity, or to an activity, known as starter, that generated the trigger.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Start">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:element name="trigger" type="prov:EntityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="starter" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="time" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="wasStartedBy" type="prov:Start"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:entity prov:id="e1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:string">email message</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:activity prov:id="a1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">Discuss</prov:type>
</prov:activity>
<prov:wasStartedBy>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a1"/>
<prov:trigger prov:ref="e1"/>
<prov:time>2011-11-16T16:05:00</prov:time>
</prov:wasStartedBy>
<prov:used>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a1"/>
<prov:entity prov:ref="e1"/>
</prov:used>
<prov:activity prov:id="a0">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">Write</prov:type>
</prov:activity>
<prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:entity prov:ref="e1"/>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a0"/>
</prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:wasStartedBy>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a1"/>
<prov:trigger prov:ref="e1"/>
<prov:starter prov:ref="a0"/>
<prov:time>2011-11-16T16:05:00</prov:time>
</prov:wasStartedBy>
<prov:wasStartedBy>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a1"/>
<prov:starter prov:ref="a0"/>
<prov:time>2011-11-16T16:05:00</prov:time>
</prov:wasStartedBy>
</prov:document>
3.1.7 End
End is when an activity is deemed to have been ended by an entity, known as trigger. The activity no longer exists after its end. Any usage, generation, or invalidation involving an activity precedes the activity's end. An end may refer to a trigger entity that terminated the activity, or to an activity, known as ender that generated the trigger.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="End">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:element name="trigger" type="prov:EntityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="ender" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="time" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="wasEndedBy" ype="prov:End"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:entity prov:id="e1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:string">approval document</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:activity prov:id="a1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">Editing</prov:type>
</prov:activity>
<prov:wasEndedBy>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a1"/>
<prov:trigger prov:ref="e1"/>
</prov:wasEndedBy>
</prov:document>
3.1.8 Invalidation
Invalidation is the start of the destruction, cessation, or expiry of an existing entity by an activity. The entity is no longer available for use (or further invalidation) after invalidation. Any generation or usage of an entity precedes its invalidation.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Invalidation">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="time" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="wasInvalidatedBy" type="prov:Invalidation"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#"
xmlns:bbc="http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/">
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:The-Painter"/>
<prov:agent prov:id="ex:Picasso"/>
<prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:entity prov:ref="ex:The-Painter" />
<prov:agent prov:ref="ex:Picasso" />
</prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:activity prov:id="ex:crash"/>
<prov:wasInvalidatedBy>
<prov:entity prov:ref="ex:The-Painter"/>
<prov:activity prov:ref="ex:crash"/>
<prov:time>1998-09-03T01:31:00</prov:time>
<ex:circumstances>plane accident</ex:circumstances>
</prov:wasInvalidatedBy>
</prov:document>
3.2 Component 2: Derivations
The second component of PROV-DM is concerned with: derivations of entities from other entities and derivation subtypes WasRevisionOf (Revision), WasQuotedFrom (Quotation), and HasPrimarySource (Primary Source).
3.2.1 Derivation
A derivation is a transformation of an entity into another, an update of an entity resulting in a new one, or the construction of a new entity based on a pre-existing entity.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Derivation">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="generatedEntity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="usedEntity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="generation" type="prov:GenerationRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="usage" type="prov:UsageRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="wasDerivedFrom" type="prov:Derivation"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#">
<prov:entity prov:id="e1"/>
<prov:entity prov:id="e2"/>
<prov:wasDerivedFrom>
<prov:generatedEntity prov:ref="e2"/>
<prov:usedEntity prov:ref="e1"/>
</prov:wasDerivedFrom>
<prov:wasDerivedFrom>
<prov:generatedEntity prov:ref="e2"/>
<prov:usedEntity prov:ref="e1"/>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:string">physical transform</prov:type>
</prov:wasDerivedFrom>
</prov:document>
3.2.2 Revision
A revision is a derivation for which the resulting entity is a revised version of some original.
To specialize a Derivation relationship as a Revision relationship, include a prov:type with the value "prov:Revision".
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:rec54="http://www.w3.org/2001/02pd/rec54#"
xmlns:tr="http://example.com/ns/tr#">
<prov:entity prov:id="tr:WD-prov-dm-20111215">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">rec54:WD</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:entity prov:id="tr:WD-prov-dm-20111018">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">rec54:WD</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:wasDerivedFrom>
<prov:generatedEntity prov:ref="tr:WD-prov-dm-20111215"/>
<prov:usedEntity prov:ref="tr:WD-prov-dm-20111018"/>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Revision</prov:type>
</prov:wasDerivedFrom>
</prov:document>
The modeling of Revision is currently under discussion and is subject to change.
3.2.3 Quotation
A quotation is the repeat of (some or all of) an entity, such as text or image, by someone who may or may not be its original author.
To specialize a Derivation relationship as a Quotation relationship, include a prov:type with the value "prov:Quotation".
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:wp="http://thinklinks.wordpress.com/2012/03/07/"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#"
xmlns:dm="http://dvcs.w3.org/hg/prov/raw-file/default/model/prov-dm.html#">
<prov:entity prov:id="wp:thoughts-from-the-dagstuhl-principles-of-provenance-workshop"/>
<prov:entity prov:id="dm:bl-dagstuhl"/>
<prov:agent prov:id="ex:Luc"/>
<prov:agent prov:id="ex:Paul"/>
<prov:wasDerivedFrom>
<prov:generatedEntity prov:ref="dm:gl-dagstuhl"/>
<prov:usedEntity prov:ref="wp:thoughts-from-the-dagstuhl-principles-of-provenance-workshop"/>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Quotation</prov:type>
</prov:wasDerivedFrom>
<prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:entity prov:ref="dm:bl-dagstuhl"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ex:Luc"/>
</prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:entity prov:ref="wp:thoughts-from-the-dagstuhl-principles-of-provenance-workshop"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ex:Paul"/>
</prov:wasAttributedTo>
</prov:document>
The modeling of Quotation is currently under discussion and is subject to change.
3.2.4 Primary Source
A primary source for a topic refers to something produced by some agent with direct experience and knowledge about the topic, at the time of the topic's study, without benefit from hindsight.
To specialize a Derivation relationship as a Primary Source relationship, include a prov:type with the value "prov:PrimarySource".
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:la-campagne-de-Russie-1812-1813">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">map</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:revue-d-Histoire-de-la-Pharmacie-t-XVIII">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">journal</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:wasDerivedFrom>
<prov:generatedEntity prov:ref="ex:la-campagne-de-Russie-1812-1813"/>
<prov:usedEntity prov:ref="ex:revue-d-Histoire-de-la-Pharmacie-t-XVIII"/>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:PrimarySource</prov:type>
</prov:wasDerivedFrom>
</prov:document>
The modeling of PrimarySource is currently under discussion and is subject to change.
3.3 Component 3: Agents, Responsibility, and Influence
The third component of PROV-DM is concerned with agents and the relations WasAttributedTo
(Attribution), WasAssociatedWith (Association), ActedOnBehalfOf (Delegation), relating agents to entities, activities, and agents, respectively.
3.3.1 Agent
An agent is something that bears some form of responsibility for an activity taking place, for the existence of an entity, or for another agent's activity.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Agent">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="agent" type="prov:Agent"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:agent prov:id="e1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Person</prov:type>
<ex:name>Alice</ex:name>
<ex:employee>1234</ex:employee>
</prov:agent>
</prov:document>
3.3.2 Attribution
Attribution is the ascribing of an entity to an agent.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Attribution">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="agent" type="prov:AgentRef"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="wasAttributedTo" type="prov:Attribution"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#"
xmlns:tr="http://example.com/ns/tr#"
xmlns:rec54="http://example.com/ns/rec54#">
<prov:agent prov:id="ex:Paolo">
<prov:typexsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Person</prov:type>
</prov:agent>
<prov:agent prov:id="ex:Simon">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Person</prov:type>
</prov:agent>
<prov:entity prov:id="tr:WD-prov-dm-20111215">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">rec54:WD</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:entity prov:ref="rec54:WD"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ex:Paolo"/>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">editorship</prov:type>
</prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:entity prov:ref="rec54:WD"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ex:Simon"/>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">authorship</prov:type>
</prov:wasAttributedTo>
</prov:document>
3.3.3 Association
An activity association is an assignment of responsibility to an agent for an activity, indicating that the agent had a role in the activity. It further allows for a plan to be specified, which is the plan intended by the agent to achieve some goals in the context of this activity.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Association">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:element name="agent" type="prov:AgentRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="plan" type="prov:EntityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="wasAssociatedWith" type="prov:Association"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:activity prov:id="a">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:string">workflow execution</prov:type>
</prov:activity>
<prov:agent prov:id="ag1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">operator</prov:type>
</prov:agent>
<prov:agent prov:id="ag2">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">designator</prov:type>
</prov:agent>
<prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ag1"/>
<prov:role xsi:type="xsd:QName">loggedInUser</prov:role>
<ex:how>webapp</ex:how>
</prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ag2"/>
<prov:plan prov:ref="ex:wf"/>
<prov:role xsi:type="xsd:QName">designer</prov:role>
<ex:content>project1</ex:content>
</prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:wf">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Plan</prov:type>
<ex:label>Workflow 1</ex:label>
<prov:location xsi:type="xsd:anyURI">http://example.org/workflow1.bpel</prov:location>
</prov:entity>
</prov:document>
3.3.4 Delegation
Delegation is the assignment of authority and responsibility to an agent (by itself or by another agent) to carry out a specific activity as a delegate or representative, while the agent it acts on behalf of retains some responsibility for the outcome of the delegated work.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Delegation">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="delegate" type="prov:AgentRef"/>
<xs:element name="responsible" type="prov:AgentRef"/>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="actedOnBehalfOf" type="prov:Delegation"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#">
<prov:activity prov:id="a">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">workflow</prov:type>
</prov:activity>
<prov:agent prov:id="ag1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">programmer</prov:type>
</prov:agent>
<prov:agent prov:id="ag2">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">researcher</prov:type>
</prov:agent>
<prov:agent prov:id="ag3">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">funder</prov:type>
</prov:agent>
<prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ag1"/>
<prov:role xsi:type="xsd:QName">loggedInUser</prov:role>
</prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ag2"/>
</prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ag3"/>
</prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:actedOnBehalfOf>
<prov:delegate prov:ref="ag1"/>
<prov:responsible prov:ref="ag2"/>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">line-management</prov:type>
</prov:actedOnBehalfOf>
<prov:actedOnBehalfOf>
<prov:delegate prov:ref="ag2"/>
<prov:responsible prov:ref="ag3"/>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">contract</prov:type>
</prov:actedOnBehalfOf>
</prov:document>
3.3.5 Influence
Influence is the capacity of an entity, activity, or agent to have an effect on the character, development, or behavior of another by means of usage, start, end, generation, invalidation, communication, derivation, attribution, association, or delegation.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Influence">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="influencee" type="prov:AnyRef"/>
<xs:element name="influencer" type="prov:AnyRef"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="wasInfluencedBy" type="prov:Influence"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:tr="http://example.com/ns/tr#"
xmlns:w3="http://w3.org/">
<prov:entity prov:id="tr:WD-prov-dm-20111215"/>
<prov:agent prov:id="w3:Consortium"/>
<prov:wasInfluencedBy>
<prov:influencee prov:ref="tr:WD-prov-dm-20111215"/>
<prov:influencer prov:ref="w3:Consortium"/>
</prov:wasInfluencedBy>
</prov:document>
3.4 Component 4: Bundles
The fourth component is concerned with bundles, a mechanism to support provenance of provenance.
Content in this section is still under discussion and may be subject to change.
3.4.1 Bundle
A bundle is a named set of provenance descriptions, and is itself an entity, so allowing provenance of provenance to be expressed.
A Bundle is an entity that can contain nested provenance statements.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Bundle">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:group ref="prov:documentElements"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
To specialize an Entity as a Bundle, include a prov:type with the value "prov:Bundle". The bundle element with nested provenance statements is declared separately from the bundle's entity.
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="document" type="prov:Document" />
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Document">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:group ref="prov:documentElements"/>
<xs:element name="bundle" type="prov:Bundle"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#"
xmlns:bob="http://example.com/ns/bob#"
xmlns:alice="http://example.com/ns/alice#"
xmlns:agg="http://example.com/ns/agg#">
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:report1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">report</prov:type>
<ex:version>1</ex:version>
</prov:entity>
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:report2">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">report</prov:type>
<ex:version>2</ex:version>
</prov:entity>
<prov:bundle prov:id="bob:bundle1">
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:report1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">report</prov:type>
<ex:version>1</ex:version>
</prov:entity>
<prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:entity prov:ref="ex:report1"/>
<prov:time>2012-05-24T10:00:01</prov:time>
</prov:wasGeneratedBy>
</prov:bundle>
<prov:bundle prov:id="alice:bundle2">
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:report1"/>
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:report2">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">report</prov:type>
<ex:version>2</ex:version>
</prov:entity>
<prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:entity prov:ref="ex:report2"/>
<prov:time>2012-05-25T11:00:01</prov:time>
</prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:wasDerivedFrom>
<prov:generatedEntity prov:ref="ex:report2"/>
<prov:usedEntity prov:ref="ex:report1"/>
</prov:wasDerivedFrom>
</prov:bundle>b>
<prov:entity prov:id="bob:bundle1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Bundle</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:entity prov:ref="bob:bundle1"/>
<prov:time>2012-05-24T10:30:00</prov:time>
</prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:entity prov:ref="bob:bundle1"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ex:Bob"/>
</prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:entity prov:id="alice:bundle2">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Bundle</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:entity prov:ref="alice:bundle2"/>
<prov:time>2012-05-25T11:15:00</prov:time>
</prov:wasGeneratedBy>
<prov:wasAttributedTo>
<prov:entity prov:ref="alice:bundle2"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ex:Alice"/>
</prov:wasAttributedTo>
</prov:document>
3.5 Component 5: Alternate Entities
The fifth component of PROV-DM is concerned with
relations SpecializationOf (specialization) and AlternateOf (alternate) between entities.
3.5.1 Specialization
An entity that is a specialization of another shares all aspects of the latter, and additionally presents more specific aspects of the same thing as the latter. In particular, the lifetime of the entity being specialized contains that of any specialization.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Specialization">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="specificEntity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="generalEntity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="specializationOf" type="prov:Specialization"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#"
xmlns:bbc="http://www.bbc.co.uk/">
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:bbcNews2012-03-23"/>
<prov:entity prov:id="bbc:news"/>
<prov:specializationOf>
<prov:specificEntity prov:ref="ex:bbcNews2012-03-23"/>
<prov:generalEntity prov:ref="bbc:news"/>
</prov:specializationOf>
</prov:document>
3.5.2 Alternate
Two alternate entities present aspects of the same thing. These aspects may be the same or different, and the alternate entities may or may not overlap in time.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Alternate">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="alternate1" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="alternate2" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="alternateOf" type="prov:Alternate"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:bbc="http://www.bbc.co.uk/news"
xmlns:bbcmobile="http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/mobile">
<prov:entity prov:id="bbc:science-environment-17526723">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:string">a news item for desktop</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:entity prov:id="bbcmobile:science-environment-17526723">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:string">a news item for mobile devices</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:alternateOf>
<prov:alternate1 prov:ref="bbcmobile:science-environment-17526723"/>
<prov:alternate2 prov:ref="bbc:science-environment-17526723"/>
</prov:alternateOf>
</prov:document>
3.6 Component 6: Collections
The sixth component of PROV-DM is concerned with the notion of collections.
A collection is an entity that has some members. The members are themselves entities, and therefore their provenance can be expressed. Some applications need to be able to express the provenance of the collection itself: e.g. who maintains the collection (attribution), which members it contains as it evolves, and how it was assembled. The purpose of Component 6 is to define the types and relations that are useful to express the provenance of collections.
3.6.1 Collection
A collection is an entity that provides a structure to some constituents that must themselves be entities. These constituents are said to be member of the collections.
To specialize an Entity as a Collection, include a prov:type with the value "prov:Collection".
An EmptyCollection is asserted with the prov:type "prov:EmptyCollection" and denotes a Collection with no members.
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<!-- c0 is an empty collection -->
<prov:entity prov:id="c0">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:EmptyCollection</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<!-- c1 is a collection, with unknown content -->
<prov:entity prov:id="c1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Collection</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
</prov:document>
The modeling of Collection is currently under discussion and is subject to change.
3.6.2 Membership
Membership is the belonging of an entity to a collection.
Type definition in XML Schema:
<xs:complexType xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="Membership">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="collection" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:EntityRef" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="hadMember" type="prov:Membership"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#">
<prov:entity prov:id="e0"/>
<prov:entity prov:id="e1"/>
<prov:entity prov:id="e2"/>
<prov:entity prov:id="c">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Collection</prov:type>
</prov:entity>
<prov:hadMember>
<prov:collection prov:ref="c"/>
<prov:entity prov:ref="e0"/>
<prov:entity prov:ref="e1"/>
<prov:entity prov:ref="e2"/>
</prov:hadMember>
</prov:document>
3.7 Further Elements of PROV
This section introduces further elements of PROV.
3.7.1 Identifier
The identifier attribute is used to identify instances of PROV types or relations.
Usage in XML:
<xs:attribute xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="id" type="xs:QName"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#"
xmlns:tr="http://example.com/ns/tr#">
<prov:entity prov:id="tr:WD-prov-dm-20111215">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:Qname">document</prov:type>
<ex:version>2</ex:version>
</prov:entity>
</prov:document>
REVIEW QUESTION:
The Identifier type is currently still under discussion. We intend to use an identifier type that makes sense for XML conventions and current XML tooling. The PROV-XML group is currently seeking feedback on recommended type ranges for the id attribute.
3.7.2 Attributes
The PROV-DM defined PROV attributes are represented in XML as elements.
3.7.2.1 Label
The attribute prov:label provides a human-readable representation of an instance of a PROV-DM type or relation.
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="label" type="prov:InternationalizedString"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:e1">
<prov:label>This is a human-readable label</prov:label>
</prov:entity>
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:car01">
<prov:label xml:lang="fr">Voiture 01</prov:label>
<prov:label xml:lang="en">Car 01</prov:label>
</prov:entity>
</prov:document>
3.7.2.2 Location
A location can be an identifiable geographic place (ISO 19112), but it can also be a non-geographic place such as a directory, row, or column.
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="location" type="xs:anySimpleType"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:MonaLisa">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">StillImage</prov:type>
<prov:location xsi:type="xsd:string">Le Louvre, Paris</prov:location>
</prov:entity>
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:cell">
<prov:location xsi:type="xsd:string">(5,5)</prov:location>
<prov:value xsi:type="xsd:integer">10</prov:value>
</prov:entity>
</prov:document>
3.7.2.3 Role
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="role" type="xs:anySimpleType"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ag1"/>
<prov:role xsi:type="xsd:QName">loggedInUser</prov:role>
<ex:how>webapp</ex:how>
</prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:wasAssociatedWith>
<prov:activity prov:ref="a"/>
<prov:agent prov:ref="ag2"/>
<prov:plan prov:ref="ex:wf"/>
<prov:role xsi:type="xsd:QName">designer</prov:role>
<ex:content>project1</ex:content>
</prov:wasAssociatedWith>
</prov:document>
3.7.2.4 Type
The attribute prov:type provides further typing information for any construct with an optional set of attribute-value pairs.
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="type" type="xs:anySimpleType"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#"
xmlns:tr="http://example.com/ns/tr#">
<prov:entity prov:id="tr:WD-prov-dm-20111215">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">document</prov:type>
<ex:version>2</ex:version>
</prov:entity>
<prov:agent prov:id="e1">
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">prov:Person</prov:type>
<ex:name>Alice</ex:name>
<ex:employee>1234</ex:employee>
</prov:agent>
<prov:activity prov:id="a1">
<prov:startTime>2011-11-16T16:05:00</prov:startTime>
<prov:endTime>2011-11-16T16:06:00</prov:endTime>
<prov:type xsi:type="xsd:QName">ex:edit</prov:type>
<ex:host>server.example.org</ex:host>
</prov:activity>
</prov:document>
3.7.2.5 Value
The attribute
prov:value provides a value that is a direct representation of an entity as a PROV-DM
Value.
Usage in XML:
<xs:element xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" name="value" type="xs:anySimpleType"/>
<prov:document
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:ex="http://example.com/ns/ex#">
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:in">
<prov:value xsi:type="xsd:string">abcd</prov:value>
</prov:entity>
<prov:entity prov:id="ex:out">
<prov:value xsi:type="xsd:integer">4</prov:value>
</prov:entity>
</prov:document>
3.7.3 Value
A value is a constant such as a string, number, time, qualified name, IRI, and encoded binary data, whose interpretation is outside the scope of PROV.
Relations defined by the PROV-DM to have type Value have type xs:anySimpleType in PROV-XML unless otherwise specified.
A. Full XML Schema
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:prov="http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#"
xmlns:cu="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/datatypes/"
xmlns:xml="http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:import namespace="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml/datatypes/" />
<xs:import namespace="http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace"
schemaLocation="http://www.w3.org/2001/xml.xsd"/>
<!-- Component 1 -->
<xs:complexType name="Entity">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:value"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Activity">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="startTime" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="endTime" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Generation">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="time" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Usage">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:EntityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="time" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Communication">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="informed" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:element name="informant" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Start">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:element name="trigger" type="prov:EntityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="starter" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="time" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="End">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:element name="trigger" type="prov:EntityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="ender" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="time" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Invalidation">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="time" type="xs:dateTime" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<!-- Component 2 -->
<xs:complexType name="Derivation">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="generatedEntity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="usedEntity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="generation" type="prov:GenerationRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="usage" type="prov:UsageRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<!-- Component 3 -->
<xs:complexType name="Agent">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:location"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Attribution">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="agent" type="prov:AgentRef"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Association">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef"/>
<xs:element name="agent" type="prov:AgentRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="plan" type="prov:EntityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:role"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Delegation">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="delegate" type="prov:AgentRef"/>
<xs:element name="responsible" type="prov:AgentRef"/>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:ActivityRef" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Influence">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="influencee" type="prov:AnyRef"/>
<xs:element name="influencer" type="prov:AnyRef"/>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:label"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:type"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
<!-- Component 4 -->
<!-- Component 5 -->
<xs:complexType name="Specialization">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="specificEntity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="generalEntity" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Alternate">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="alternate1" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="alternate2" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<!-- Component 6 -->
<xs:complexType name="Membership">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="collection" type="prov:EntityRef"/>
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:EntityRef" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="InternationalizedString">
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="xs:string">
<xs:attribute ref="xml:lang" use="optional"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
<!--
Typed literals are encoded by means
of xsi:type that represent the prov:datatype.
-->
<xs:element name="label" type="prov:InternationalizedString"/>
<xs:element name="role" type="xs:anySimpleType"/>
<xs:element name="type" type="xs:anySimpleType"/>
<xs:element name="location" type="xs:anySimpleType"/>
<xs:element name="value" type="xs:anySimpleType"/>
<!-- See comment in preamble.
These should be prov:QualifiedName
but instead are xsd:QName for tools to process them -->
<xs:attribute name="id" type="xs:QName"/>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:QName"/>
<xs:complexType name="ActivityRef">
<xs:attribute ref="prov:ref" use="required" />
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="EntityRef">
<xs:attribute ref="prov:ref" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="AgentRef">
<xs:attribute ref="prov:ref" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="UsageRef">
<xs:attribute ref="prov:ref" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="GenerationRef">
<xs:attribute ref="prov:ref" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="AnyRef">
<xs:attribute ref="prov:ref" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
<!--
top-level definition of elements following the salami slice XSD design pattern
to encourage integration within existing non-prov XML documents.
-->
<!-- Component 1 elements -->
<xs:element name="entity" type="prov:Entity"/>
<xs:element name="activity" type="prov:Activity"/>
<xs:element name="wasGeneratedBy" type="prov:Generation"/>
<xs:element name="used" type="prov:Usage"/>
<xs:element name="wasInformedBy" type="prov:Communication"/>
<xs:element name="wasStartedBy" type="prov:Start"/>
<xs:element name="wasEndedBy" type="prov:End"/>
<xs:element name="wasInvalidatedBy" type="prov:Invalidation"/>
<!-- Component 2 elements -->
<xs:element name="wasDerivedFrom" type="prov:Derivation"/>
<!-- Component 3 elements -->
<xs:element name="agent" type="prov:Agent"/>
<xs:element name="wasAttributedTo" type="prov:Attribution"/>
<xs:element name="wasAssociatedWith" type="prov:Association"/>
<xs:element name="actedOnBehalfOf" type="prov:Delegation"/>
<xs:element name="wasInfluencedBy" type="prov:Influence"/>
<!-- Component 5 elements -->
<xs:element name="specializationOf" type="prov:Specialization"/>
<xs:element name="alternateOf" type="prov:Alternate"/>
<!-- Component 6 elements -->
<xs:element name="hadMember" type="prov:Membership"/>
<xs:group name="documentElements">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="prov:entity"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:activity"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:wasGeneratedBy"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:used"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:wasInformedBy"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:wasStartedBy"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:wasEndedBy"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:wasInvalidatedBy"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:wasDerivedFrom"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:agent"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:wasAttributedTo"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:wasAssociatedWith"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:actedOnBehalfOf"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:wasInfluencedBy"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:specializationOf"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:alternateOf"/>
<xs:element ref="prov:hadMember"/>
<xs:any namespace="##other"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:group>
<xs:element name="document" type="prov:Document" />
<xs:complexType name="Document">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:group ref="prov:documentElements"/>
<xs:element name="bundle" type="prov:Bundle"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="Bundle">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:group ref="prov:documentElements"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="prov:id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
B. Acknowledgements
This document has been produced by the PROV Working Group, and its
contents reflect extensive discussion within the Working Group as a
whole. The editors extend special thanks to Luc Moreau (University of
Southampton), Paul Groth (Vrije Universiteit) and James Cheney
(University of Edinburgh) for their thorough reviews.
Members of the PROV Working Group at the time of publication of this document were:
Ilkay Altintas (Invited expert),
Reza B'Far (Oracle Corporation),
Khalid Belhajjame (University of Manchester),
James Cheney (University of Edinburgh, School of Informatics),
Sam Coppens (IBBT),
David Corsar (University of Aberdeen, Computing Science),
Stephen Cresswell (The National Archives),
Tom De Nies (IBBT),
Helena Deus (DERI Galway at the National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland),
Simon Dobson (Invited expert),
Martin Doerr (Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas(FORTH)),
Kai Eckert (Invited expert),
Jean-Pierre EVAIN (European Broadcasting Union, EBU-UER),
James Frew (Invited expert),
Irini Fundulaki (Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas(FORTH)),
Daniel Garijo (Universidad Politécnica de Madrid),
Yolanda Gil (Invited expert),
Ryan Golden (Oracle Corporation),
Paul Groth (Vrije Universiteit),
Olaf Hartig (Invited expert),
David Hau (National Cancer Institute, NCI),
Sandro Hawke (W3C/MIT),
Jörn Hees (German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI) Gmbh),
Ivan Herman, (W3C/ERCIM),
Ralph Hodgson (TopQuadrant),
Hook Hua (Invited expert),
Trung Dong Huynh (University of Southampton),
Graham Klyne (University of Oxford),
Michael Lang (Revelytix, Inc.),
Timothy Lebo (Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute),
James McCusker (Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute),
Deborah McGuinness (Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute),
Simon Miles (Invited expert),
Paolo Missier (School of Computing Science, Newcastle university),
Luc Moreau (University of Southampton),
James Myers (Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute),
Vinh Nguyen (Wright State University),
Edoardo Pignotti (University of Aberdeen, Computing Science),
Paulo da Silva Pinheiro (Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute),
Carl Reed (Open Geospatial Consortium),
Adam Retter (Invited Expert),
Christine Runnegar (Invited expert),
Satya Sahoo (Invited expert),
David Schaengold (Revelytix, Inc.),
Daniel Schutzer (FSTC, Financial Services Technology Consortium),
Yogesh Simmhan (Invited expert),
Stian Soiland-Reyes (University of Manchester),
Eric Stephan (Pacific Northwest National Laboratory),
Linda Stewart (The National Archives),
Ed Summers (Library of Congress),
Maria Theodoridou (Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas(FORTH)),
Ted Thibodeau (OpenLink Software Inc.),
Curt Tilmes (National Aeronautics and Space Administration),
Craig Trim (IBM Corporation),
Stephan Zednik (Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute),
Jun Zhao (University of Oxford),
Yuting Zhao (University of Aberdeen, Computing Science).
