1. Document Object Model Events
- Editors:
- Philippe Le Hégaret, W3C
- Tom Pixley, Netscape Communications Corporation (until July 2002)
1.1 Introduction
DOM Events is designed with two main goals. The first goal is the design of an event system which allows registration of event listeners and describes event flow through a tree structure. Additionally, the specification will provide standard modules of events for user interface control and document mutation notifications, including defined contextual information for each of these event modules.
The second goal of the DOM Events is to provide a common subset of the current event systems used in DOM Level 0 browsers. This is intended to foster interoperability of existing scripts and content. It is not expected that this goal will be met with full backwards compatibility. However, the specification attempts to achieve this when possible.
The following sections of the specification define both the specification for the DOM Event Model and a number of conformant event modules designed for use within the model. The DOM Event Model consists of:
- The DOM event flow, which describe the flow of events in a tree-based structure.
- A set of interfaces to access contextual information on events and to register event listeners.
1.1.1 Event flows
This document specifies an event flow for tree-based structures: DOM event flow. While it is expected that HTML and XML applications will follow this event flow, applications might reuse the interfaces defined in this document for non tree-based structures. In that case, it is the responsibility of such applications to define their event flow and how it relates to the DOM event flow. An example of such use can be found in [DOM Level 3 Load and Save].
1.1.2 Conformance
An implementation is DOM Level 3 Events conformant if it
supports the Core module defined in [DOM Level 2 Core],
the DOM event flow and the interfaces with their
associated semantics defined in Basic interfaces. An implementation conforms to a DOM
Level 3 Events module if it conforms to DOM Level 3 Events and
the event types defined in the module. An implementation
conforms to an event type if it conforms to its associated
semantics and DOM interfaces. For example, an implementation
conforms to the DOM Level 3 User Interface Events module (see
User Interface event types) if it conforms
to DOM Level 3 Events (i.e. implements all the basic
interfaces), can generate the event types
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMActivate"}
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMFocusIn"}
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMFocusOut"} accordingly to
their semantics, supports the UIEvent interface,
and conforms to the DOM Level 2 Core module.
Note:
An implementation which does not conform to an event module
can still implement the DOM interfaces associated with it. The
DOM application can then create an event object using the
DocumentEvent.createEvent() method and dispatch an
event type associated with this interface using the
EventTarget.dispatchEvent() method.
A DOM application may use the hasFeature(feature,
version) method of the DOMImplementation
interface with parameter values "Events" and
"3.0" (respectively) to determine whether or not
DOM Level 3 Events is supported by the implementation. In order
to fully support DOM Level 3 Events, an implementation must also
support the "Core" feature defined in the DOM Level 2 Core
specification [DOM Level 2 Core] and use the DOM event flow. For additional information
about conformance,
please see the DOM Level 3 Core specification [DOM Level 3 Core]. DOM Level 3 Events is built on top of DOM Level
2 Events [DOM Level 2 Events], i.e. a DOM Level 3 Events
implementation where hasFeature("Events", "3.0")
returns true must also return true
when the version number is "2.0",
"" or, null.
Each event module describes its own feature string in the event module listing.
1.2 DOM event flow
The DOM event flow is the process through which the event originates from the DOM Events implementation and is dispatched into a tree. Each event has an event target, a targeted node in the case of the DOM Event flow, toward which the event is dispatched by the DOM Events implementation.
1.2.1 Phases
The event is dispatched following a path from the root of the tree to this target node. It can then be handled locally at the target node level or from any target's ancestors higher in the tree. The event dispatching (also called event propagation) occurs in three phases and the following order:
- The capture phase: the event is dispatched to the target's ancestors from the root of the tree to the direct parent of the target node.
- The target phase: the event is dispatched to the target node.
- The bubbling phase: the event is dispatched to the target's ancestors from the direct parent of the target node to the root of the tree.
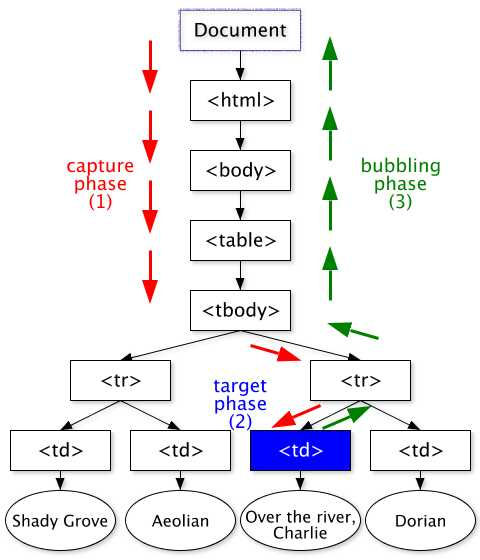
Figure: graphical representation of an event dispatched in a DOM tree using the DOM event flow [SVG 1.0 version]
Note: An SVG 1.0 version of the representation above is also available.
The target's ancestors are determined before the initial dispatch of the event. If the target node is removed during the dispatching, or a target's ancestor is added or removed, the event propagation will always be based on the target node and the target's ancestors determined before the dispatch.
Some events may not necessarily accomplish the three phases of
the DOM event flow, e.g. the event could only be defined for one
or two phases. As an example, events defined in this
specification will always accomplish the capture and target
phases but some will not accomplish the bubbling phase
("bubbling events" versus "non-bubbling events", see also the
Event.bubbles attribute).
1.2.2 Event listeners
Each node encountered during the dispatch of the event may contain event listeners.
1.2.2.1 Registration of event listeners
Event listeners can be registered on all nodes in the tree for a specific type of event (Event types) or event category (Event types and event categories), phase, and group (Event groups).
If the event listener is being registered on a node while an event gets processed on this node, the event listener will not be triggered during the current phase but may be triggered during a later phase in the event flow, i.e. the bubbling phase.
1.2.2.2 Event groups
An event listener is always part of a group. It is either explicitly in a group if a group has been specified at the registration or implicitly in the default group if no group has been specified. Within a group, event listeners are ordered in their order of registration. If two event listeners {A1, A2}, which are part of the same group, are registered one after the other (A1, then A2) for the same phase, the DOM event flow guarantees their triggering order (A1, then A2). If the two listeners are not part of the same group, no specification is made as to the order in which they will be triggered.
In general, a DOM application does not need to define and use a separate group unless other event listeners, external to the DOM application, may change the event propagation (e.g. from a concurrent DOM application, from imported functionalities that rely on the event system, etc.).
Note: While this specification does not specify a full ordering (i.e. groups are still unordered), it does specify ordering within a group. This implies that if the event listeners {A1, A2, B1, B2}, with A and B being two different groups, are registered for the same phase in the order A1, A2, B1, and B2, the following triggering orders are possible and conform to the DOM event flow: {A1, A2, B1, B2}, {A1, B1, A2, B2}, {B1, A1, A2, B2}, {A1, B1, B2, A2}, {B1, A1, B2, A2}, {B1, B2, A1, A2}. DOM Events implementations may impose priorities on groups but DOM applications must not rely on it. Unlike this specification, [DOM Level 2 Events] did not specify any triggering order for event listeners.
1.2.2.3 Triggering an event listener
When the event is dispatched through the tree, from node to node, event listeners registered on the node are triggered if the following three conditions are all met:
- they were registered for the same type of event, or the same category.
- they were registered for the same phase;
- the event propagation has not been stopped for the group.
1.2.2.4 Removing an event listener
If an event listener is removed from a node while an event is being processed on the node, it will not be triggered by the current actions. Once removed, the event listener is never invoked again (unless registered again for future processing).
1.2.2.5 Reentrance
It is expected that actions taken by an event listener may
cause additional events to be dispatched. Additional events
should be handled in a synchronous manner and may cause
reentrance into the event model. If an event listener fires a
new event using EventTarget.dispatchEvent(), the
event propagation that causes the event listener to be
triggered will resume only after the event propagation of the
new event is completed.
Since implementations may have restrictions such as stack-usage or other memory requirements, applications should not depend on how many synchronous events may be triggered.
1.2.2.6 Event propagation and event groups
All event listeners are part of a group (see Registration of event listeners). An event listener may prevent event listeners that are part of a same group from being triggered. The effect can be:
-
immediate: no more event listeners from the same group
will be triggered by the event object (see
Event.stopImmediatePropagation()); -
deferred until all event listeners from the same group
have been triggered on the current node, i.e. the event
listeners of the same group attached on other nodes will
not be triggered (see
Event.stopPropagation()).
If two event listeners are registered for two different groups, one cannot prevent the other from being triggered.
1.3 Default actions and cancelable events
Implementations may have a default action associated with an event
type. An example is the [HTML 4.01]
form element. When the user submits the form (e.g. by pressing on
a submit button), the event {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"submit"} is dispatched to the element and the default
action for this event type is generally to send a request to a Web
server with the parameters from the form.
The default actions are not part of the DOM Event flow. Before invoking a default action, the implementation must first dispatch the event as described in the DOM event flow.
A cancelable event is an event associated with a default action which is allowed to be canceled during the DOM event flow. At any phase during the event flow, the triggered event listeners have the option of canceling the default action or allowing the default action to proceed. In the case of the hyperlink in the browser, canceling the action would have the result of not activating the hyperlink. Not all events defined in this specification are cancelable events.
Different implementations will specify their own default actions, if any, associated with each event. The DOM Events specification does not attempt to specify these actions.
This specification does not provide mechanisms for accessing default actions or adding new ones.
Note:
Some implementations also provide default actions
before the dispatch of the event. It is not
possible to cancel those default actions and this specification
does not address them. An example of such default actions can be
found in [DOM Level 2 HTML] on the
HTMLInputElement.checked attribute.
1.4 Event types
Each event is associated with a type, called event
type. The event type is composed of a local name and a namespace URI as used in [DOM Level 3 Core]. All events defined in this specification use the
namespace URI "http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events".
1.4.1 Event types and event categories
An event type could be part of one or more categories. A category is represented using a local name and a namespace URI as defined in [XML Namespaces]. The event types defined in this specification are not associated with one or more event categories and this specification does not provide methods to associate them. Other specifications may create and associate event categories with event listeners but in such case would need to inform the dispatch mechanism of those event categories. An example of the use of categories is given at Using VoiceXML Events.
1.4.2 Complete list of event types
Depending on the level of DOM support, or the devices used for
display (e.g. screen) or interaction (e.g. mouse, keyboard,
touch screen, voice, ...), these event types can be generated by
the implementation. When used with an [XML 1.0] or [HTML 4.01] application, the specifications of those
languages may restrict the semantics and scope (in particular the
possible target nodes) associated with an event type. For
example, {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "click"} can be targeted to all
[XHTML 1.0] elements except applet,
base, basefont, bdo, br, font, frame, frameset, head, html,
iframe, isindex, meta, param, script, style, and title. Refer to
the specification defining the language used in order to find
those restrictions or to find event types that are not defined
in this document.
The following list defines all event types (with the exception
of two event types preserved for backward compatibility with
[HTML 4.01], see HTML Events) provided in this
specification. All event types defined in this specification are
bound to the namespace URI "http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events" and the
following list only enumerates the local name of the event type.
- DOMActivate
-
An element is activated, for instance, using a mouse
device, a keyboard device, or a voice command.
Note: The activation of an element is device dependent but is also application dependent, e.g. a link in a document can be activated using a mouse click or a mouse double click.
- DOMFocusIn
- An event target receives focus, for instance via a pointing device being moved onto an element or using keyboard navigation. The focus is given to the element before the dispatch of this event type.
- DOMFocusOut
- A event target loses focus, for instance via a pointing device being moved out of an element or by tabbing navigation out of the element. The focus is taken from the element before the dispatch of this event type.
- textInput
- One or more characters have been entered. The characters can originate from a variety of sources. For example, it could be characters resulting from a key being pressed or released on a keyboard device, characters resulting from the processing of an input method editor, or resulting from a voice command. Where a "paste" operation generates a simple sequence of characters, i.e. a text without any structure or style information, this event type should be generated as well.
- click
-
A pointing device button is clicked over an element. The
definition of a click depends on the environment
configuration; i.e. may depend on the screen location or
the delay between the press and release of the pointing
device button. In any case, the target node must be the
same between the mousedown, mouseup, and click. The
sequence of these events is:
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mousedown"},{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mouseup"}, and{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "click"}. Note that, given the definition of a click, If one or more of the event types{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mouseover"},{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mousemove"}, and{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mouseout"}occur between the press and release of the pointing device button, the event type{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "click"}cannot occur. In the case of nested elements, this event type is always targeted at the most deeply nested element. - mousedown
- A pointing device button is pressed over an element. In the case of nested elements, this event type is always targeted at the most deeply nested element.
- mouseup
- A pointing device button is released over an element. In the case of nested elements, this event type is always targeted at the most deeply nested element.
- mouseover
- A pointing device is moved onto an element. In the case of nested elements, this event type is always targeted at the most deeply nested element.
- mousemove
- A pointing device is moved while it is over an element. In the case of nested elements, this event type is always targeted at the most deeply nested element.
- mouseout
- A pointing device is moved away from an element. In the case of nested elements, this event type is always targeted at the most deeply nested element.
- keydown
-
A key is pressed down. This event type is device dependent
and relies on the capabilities of the input devices and
how they are mapped in the operating system. This event
type is generated after the keyboard mapping but before
the processing of an input method
editor. This event should logically happen
before the event
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "keyup"}is produced. Whether a keydown contributes or not to the generation of a text event is implementation dependent. - keyup
-
A key is released. This event type is device dependent and
relies on the capabilities of the input devices and how
they are mapped in the operating system. This event type
is generated after the keyboard mapping but before the
processing of an input method
editor. This event should logically happen after
the event
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "keydown"}is produced. Whether a keyup contributes or not to the generation of a text event is implementation dependent. - DOMSubtreeModified
- This is a general event for notification of all changes to the document. It can be used instead of the more specific events listed below. It may be dispatched after a single modification to the document or, at the implementation's discretion, after multiple changes have occurred. The latter use should generally be used to accommodate multiple changes which occur either simultaneously or in rapid succession. The target of this event is the lowest common parent of the changes which have taken place. This event is dispatched after any other events caused by the mutation(s) have occurred.
- DOMNodeInserted
- A node has been added as a child of another node. This event is dispatched after the insertion has taken place. The target node of this event is the node being inserted.
- DOMNodeRemoved
- A node is being removed from its parent node. This event is dispatched before the node is removed from the tree. The target node of this event is the node being removed.
- DOMNodeRemovedFromDocument
-
A node is being removed from a document, either through
direct removal of the node or removal of a subtree in
which it is contained. This event is dispatched before the
removal takes place. The target node of this event
type is the node being removed. If the node is being
directly removed, the event type
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMNodeRemoved"}will fire before this event type. - DOMNodeInsertedIntoDocument
-
A node is being inserted into a document, either through
direct insertion of the node or insertion of a subtree in
which it is contained. This event is dispatched after the
insertion has taken place. The target node of this event
is the node being inserted. If the node is being directly
inserted, the event type
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMNodeInserted"}will fire before this event type. - DOMAttrModified
-
Occurs after an
Attrhas been modified on a node. The target node of this event is the parentElementnode whoseAttrchanged. It is expected that string based replacement of anAttrvalue will be viewed as a modification of theAttrsince its identity does not change. Subsequently replacement of theAttrnode with a differentAttrnode is viewed as the removal of the firstAttrnode and the addition of the second. - DOMCharacterDataModified
-
Occurs after
CharacterData.dataorProcessingInstruction.datahave been modified but the node itself has not been inserted or deleted. The target node of this event is theCharacterDatanode or theProcessingInstructionnode. - DOMElementNameChanged
-
Occurs after the
namespaceURIand/or thenodeNameof anElementnode have been modified (e.g., the element was renamed usingDocument.renameNode()). The target of this event is the renamedElementnode. - DOMAttributeNameChanged
-
Occurs after the
namespaceURIand/or thenodeNameof aAttrnode have been modified (e.g., the attribute was renamed usingDocument.renameNode). The target of this event is the parentElementnode whoseAttrhas been renamed. - load
-
The DOM Implementation finishes loading the resource (such
as the document) and any dependent resources (such as
images, style sheets, or scripts). Dependent resources
that fail to load will not prevent this event from firing
if the resource that loaded them is still accessible via
the DOM. If this event type is dispatched, implementations
are required to dispatch this event at least on the
Documentnode. - unload
-
The DOM implementation removes from the environment the
resource (such as the document) or any dependent resources
(such as images, style sheets, scripts). The document is
unloaded after the dispatch of this event type. If this
event type is dispatched, implementations are required to
dispatch this event at least on the
Documentnode. - abort
- The loading of the document, or a resource linked from it, is stopped before being entirely loaded.
- error
- The document, or a resource linked from it, has been loaded but cannot be interpreted according to its semantic, such as an invalid image, a script execution error, or non-well-formed XML.
- select
- A user selects some text. DOM Level 3 Events does not provide contextual information to access the selected text. The selection occured before the dispatch of this event type.
- change
- A control loses the input focus and its value has been modified since gaining focus.
- submit
- A form, such as [HTML 4.01], [XHTML 1.0], or [XForms 1.0] form, is submitted.
- reset
- A form, such as [HTML 4.01], [XHTML 1.0], or [XForms 1.0] form, is reset.
- resize
- A document view or an element has been resized. The resize occured before the dispatch of this event type.
- scroll
- A document view or an element has been scrolled. The scroll occured before the dispatch of this event type.
The following table provides additional information on the event types. All events will accomplish the capture and target phases, but not all of them will accomplish the bubbling phase (see also DOM event flow). Some events are not cancelable (see Default actions and cancelable events). Some events will only be dispatched to a specific set of possible targets, specified using node types. Contextual information related to the event type is accessible using DOM interfaces.
| type | Bubbling phase | Cancelable | Target node types | DOM interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOMActivate | Yes | Yes |
Element |
UIEvent |
| DOMFocusIn | Yes | No |
Element |
UIEvent |
| DOMFocusOut | Yes | No |
Element |
UIEvent |
| textInput | Yes | Yes |
Element |
TextEvent |
| click | Yes | Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
| mousedown | Yes | Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
| mouseup | Yes | Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
| mouseover | Yes | Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
| mousemove | Yes | Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
| mouseout | Yes | Yes |
Element |
MouseEvent |
| keydown | Yes | Yes |
Element |
KeyboardEvent |
| keyup | Yes | Yes |
Element |
KeyboardEvent |
| DOMSubtreeModified | Yes | No |
Document, DocumentFragment,
Element, Attr
|
MutationEvent |
| DOMNodeInserted | Yes | No |
Element, Attr,
Text, Comment,
CDATASection, DocumentType,
EntityReference, ProcessingInstruction |
MutationEvent |
| DOMNodeRemoved | Yes | No |
Element, Attr,
Text, Comment,
CDATASection, DocumentType,
EntityReference, ProcessingInstruction |
MutationEvent |
| DOMNodeRemovedFromDocument | No | No |
Element, Attr,
Text, Comment,
CDATASection, DocumentType,
EntityReference, ProcessingInstruction |
MutationEvent |
| DOMNodeInsertedIntoDocument | No | No |
Element, Attr,
Text, Comment,
CDATASection, DocumentType,
EntityReference, ProcessingInstruction |
MutationEvent |
| DOMAttrModified | Yes | No |
Element |
MutationEvent |
| DOMCharacterDataModified | Yes | No |
Text, Comment,
CDATASection,
ProcessingInstruction
|
MutationEvent |
| DOMElementNameChanged | Yes | No |
Element
|
MutationNameEvent |
| DOMAttributeNameChanged | Yes | No |
Element
|
MutationNameEvent |
| load | No | No |
Document, Element
|
Event |
| unload | No | No |
Document, Element
|
Event |
| abort | Yes | No |
Element
|
Event |
| error | Yes | No |
Element
|
Event |
| select | Yes | No |
Element
|
Event |
| change | Yes | No |
Element
|
Event |
| submit | Yes | Yes |
Element
|
Event |
| reset | Yes | Yes |
Element
|
Event |
| resize | Yes | No |
Document, Element
|
UIEvent |
| scroll | Yes | No |
Document, Element
|
UIEvent |
As an example, the event {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "load"}
will trigger event listeners attached on Element
nodes for that event and on the capture and target phases. This
event cannot be cancelled. If an event listener for the load
event is attached to a node other than Element
nodes, or if it is attached to the bubbling phase only, this
event listener cannot be triggered.
The event objects associated with the event types described above may contain context information. Refer to the description of the DOM interfaces for further information.
1.4.3 Compatibility with DOM Level 2 Events
Namespace URIs were
only introduced in DOM Level 3 Events and were not part of DOM
Level 2 Events. DOM Level 2 Events methods are namespace
ignorant and the event type is only represented by an XML name, specified in the
Event.type attribute.
Therefore, while it is safe to use these methods when not
dealing with namespaces, using them and the new ones at the same
time should be avoided. DOM Level 2 Events methods solely
identify events by their Event.type. On the
contrary, the namespaces aware DOM Level 3 Events methods,
identify attribute nodes by their
Event.namespaceURI and
Event.type. Because of this fundamental difference,
mixing both sets of methods can lead to unpredictable
results. For example, using
EventTarget.addEventListenerNS(namespaceURI, type,
listener, ...), two event listeners (or more) could be
registered using the same type and same
useCapture values, but different
namespaceURIs. Calling
EventTarget.removeEventListener(type, listener,
...) with that type and
useCapture could then remove any or none of those
event listeners. The result depends on the implementation. The
only guarantee in such cases is that all methods which access an
event listener by its namespaceURI and
type will access the same event listener. For
instance, EventTarget.removeEventListenerNS(namespaceURI,
type, listener, ...) removes the event that
EventTarget.addEventListenerNS(namespaceURI, type,
listener, ...) added.
For compatibility reasons, the dispatching of an event will
ignore namespace URIs if either the event or the event listener
has a null namespace URI. If a DOM Level 2 event
(i.e. with a null namespace URI) is dispatched in
the DOM tree, all event listeners that match the
type will be triggered as described in the DOM event flow. If a DOM Level 3 event (i.e. with a
namespace URI) is dispatched in the DOM tree, all event listeners
with the same type and the same or null namespace
URI will be triggered as described in the DOM event flow.
1.5 Event listener registration
Note: This section is informative.
There are mainly two ways to associate an event listener to a node in the tree:
-
at the programming level using the
EventTargetmethods. - at the document level using [XML Events] or an ad-hoc syntax, as the ones provided in [XHTML 1.0] or [SVG 1.1].
1.5.1
Using the EventTarget methods
The user can attach an event listener using the methods on the
EventTarget interface:
myCircle.addEventListenerNS("http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMActivate",
myListener,
true,
null);
The methods do not provide the ability to register the same event listener more than once for the same event type and the same phase. It is not possible to register an event listener:
- for only one of the target and bubbling phases since those phases are coupled during the registration (but the listener itself could ignore events during one of these phases if desired).
- for a specific event category.
To register an event listener, DOM applications must use the
methods EventTarget.addEventListener() and
EventTarget.addEventListenerNS().
An EventListener being registered on an
EventTarget may choose to have that
EventListener triggered during the capture phase by
specifying the useCapture parameter of the
EventTarget.addEventListener() or
EventTarget.addEventListenerNS() methods to be
true. If false, the
EventListener will be triggered during the target
and bubbling phases.
1.5.2 Using XML Events
In [XML Events], event listeners are attached using elements and attributes:
<listener event="DOMActivate" observer="myCircle" handler="#myListener"
phase="capture" propagate="stop"/>
Event listeners can only be registered on Element
nodes, i.e. other Node types are not addressable,
and cannot be registered for a specific group either, i.e. they
are always attached to the default group. The target phase and the bubbling phase are coupled
during the registration. [XML Events] does not address namespaces in event types. If
the value of the event attribute of the
listener element contains a colon (':'), it should
be interpreted as a QName as defined in [XML Schema Part 2].
1.5.3 Using VoiceXML Events
In [VoiceXML 2.0], event listeners are attached using elements:
<form>
<field>
<prompt>Please say something</prompt>
<catch event="error.noauthorization">
<prompt>You don't have the authorization!</prompt>
</catch>
<catch event="connection.disconnect.hangup">
<prompt>Connection error</prompt>
</catch>
<catch event="connection.disconnect">
<prompt>Connection error</prompt>
</catch>
</field>
<catch event="error">
<prompt>Unknown error</prompt>
</catch>
</form>
Event listeners can only be registered on Element
nodes, i.e. other Node types are not addressable,
and cannot be registered for a specific group either, i.e. they
are always attached to the default group. The target phase and the bubbling phase are coupled
during the registration. [VoiceXML 2.0] does not address namespaces in event types but
uses the notion of event categories. The event type
"connection.disconnect.hangup" could be associated to
the event categories
{"http://www.example.org/2003/voicexml", "connection"}
and {"http://www.example.org/2003/voicexml",
"connection.disconnect"}.
1.5.4 Using XML or HTML attributes
In languages such as [HTML 4.01], [XHTML 1.0], or [SVG 1.1], event listeners are specified as attributes:
<circle id="myCircle" onactivate="myListener(evt)"
cx="300" cy="225" r="100" fill="red"/>
Since only one attribute with the same name can appear on an
element, it is therefore not possible to register more than one
event listener on a single EventTarget for the
event type. Also, event listeners can only be registered on
Element nodes for the target phase and bubbling phase, i.e. other
Node types and the capture phase are not
addressable with these languages. Event listeners cannot be
registered for a specific group either, i.e. they are always
attached to the default group.
In order to achieve compatibility with those languages,
implementors may view the setting of attributes which represent
event handlers as the creation and registration of an
EventListener on the EventTarget. The value
of useCapture defaults to false. This
EventListener behaves in the same manner as any
other EventListeners which may be registered on the
EventTarget. If the attribute representing the
event listener is changed, this may be viewed as the removal of
the previously registered EventListener and the
registration of a new one. Furthermore, no specification is made
as to the order in which event attributes will receive the event
with regards to the other EventListeners on the
EventTarget.
1.6 Basic interfaces
The interfaces described in this section are fundamental to DOM Level 3 Events and must always be supported by the implementation.
- Interface Event (introduced in DOM Level 2)
-
The
Eventinterface is used to provide contextual information about an event to the listener processing the event. An object which implements theEventinterface is passed as the parameter to anEventListener. More specific context information is passed to event listeners by deriving additional interfaces fromEventwhich contain information directly relating to the type of event they represent. These derived interfaces are also implemented by the object passed to the event listener.To create an instance of the
Eventinterface, use theDocumentEvent.createEvent("Event")method call.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 2: interface Event { // PhaseType const unsigned short CAPTURING_PHASE = 1; const unsigned short AT_TARGET = 2; const unsigned short BUBBLING_PHASE = 3; readonly attribute DOMString type; readonly attribute EventTarget target; readonly attribute EventTarget currentTarget; readonly attribute unsigned short eventPhase; readonly attribute boolean bubbles; readonly attribute boolean cancelable; readonly attribute DOMTimeStamp timeStamp; void stopPropagation(); void preventDefault(); void initEvent(in DOMString eventTypeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: readonly attribute DOMString namespaceURI; // Introduced in DOM Level 3: boolean isCustom(); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: void stopImmediatePropagation(); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: boolean isDefaultPrevented(); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: void initEventNS(in DOMString namespaceURIArg, in DOMString eventTypeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg); };
- Definition group PhaseType
An integer indicating which phase of the event flow is being processed as defined in DOM event flow.
- Defined Constants
AT_TARGET- The current event is in the target phase, i.e. it is being evaluated at the event target.
BUBBLING_PHASE- The current event phase is the bubbling phase.
CAPTURING_PHASE- The current event phase is the capture phase.
- Attributes
bubblesof typeboolean, readonly-
Used to indicate whether or not an event is a bubbling event.
If the event can bubble the value is
true, otherwise the value isfalse.
cancelableof typeboolean, readonly-
Used to indicate whether or not an event can have its default
action prevented (see also Default actions and cancelable events). If the default action can be
prevented the value is
true, otherwise the value isfalse.
currentTargetof typeEventTarget, readonly-
Used to indicate the
EventTargetwhoseEventListenersare currently being processed. This is particularly useful during the capture and bubbling phases. This attribute could contain the target node or a target ancestor when used with the DOM event flow.
eventPhaseof typeunsigned short, readonly-
Used to indicate which phase of event flow is currently being
accomplished.
namespaceURIof typeDOMString, readonly, introduced in DOM Level 3-
The namespace URI
associated with this event at creation time, or
nullif it is unspecified.
For events initialized with a DOM Level 2 Events method, such asEvent.initEvent(), this is alwaysnull.
targetof typeEventTarget, readonly-
Used to indicate the event
target. This attribute contains the target node when used with the
DOM event flow.
timeStampof typeDOMTimeStamp, readonly-
Used to specify the time (in milliseconds relative to the epoch)
at which the event was created. Due to the fact that some
systems may not provide this information the value of
timeStampmay be not available for all events. When not available, a value of0will be returned. Examples of epoch time are the time of the system start or 0:0:0 UTC 1st January 1970.
typeof typeDOMString, readonly-
The name should be an NCName
as defined in [XML Namespaces] and is
case-sensitive.
If the attributeEvent.namespaceURIis different fromnull, this attribute represents a local name.
- Methods
initEvent-
The
initEventmethod is used to initialize the value of anEventcreated through theDocumentEvent.createEventmethod. This method may only be called before theEventhas been dispatched via theEventTarget.dispatchEvent()method. If the method is called several times before invokingEventTarget.dispatchEvent, only the final invocation takes precedence. This method has no effect if called after the event has been dispatched. If called from a subclass of theEventinterface only the values specified in this method are modified, all other attributes are left unchanged.
This method sets theEvent.typeattribute toeventTypeArg, andEvent.namespaceURItonull. To initialize an event with a namespace URI, use theEvent.initEventNS(namespaceURIArg, eventTypeArg, ...)method.ParameterseventTypeArgof typeDOMString-
Specifies
Event.type.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Specifies
Event.bubbles. This parameter overrides the intrinsic bubbling behavior of the event.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Specifies
Event.cancelable. This parameter overrides the intrinsic cancelable behavior of the event.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions initEventNSintroduced in DOM Level 3-
The
initEventNSmethod is used to initialize the value of anEventobject and has the same behavior asEvent.initEvent().ParametersnamespaceURIArgof typeDOMString-
Specifies
Event.namespaceuRI, the namespace URI associated with this event, ornullif no namespace.
eventTypeArgof typeDOMString-
Specifies
Event.type, the local name of the event type.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
Event.initEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
Event.initEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions isCustomintroduced in DOM Level 3-
This method will always return
false, unless the event implements theCustomEventinterface.Return Valuebooleanfalse, unless the event object implements theCustomEventinterface.No ParametersNo Exceptions isDefaultPreventedintroduced in DOM Level 3-
This method will return
trueif the methodEvent.preventDefault()has been called for this event,falseotherwise.Return ValuebooleantrueifEvent.preventDefault()has been called for this event.No ParametersNo Exceptions preventDefault-
If an event is cancelable, the
preventDefaultmethod is used to signify that the event is to be canceled, meaning any default action normally taken by the implementation as a result of the event will not occur (see also Default actions and cancelable events), and thus independently of event groups. Calling this method for a non-cancelable event has no effect.Note: This method does not stop the event propagation; use
stopPropagationorstopImmediatePropagationfor that effect.No ParametersNo Return ValueNo Exceptions stopImmediatePropagationintroduced in DOM Level 3-
This method is used to prevent event listeners of the same group to be triggered and, unlike
stopPropagationits effect is immediate (see Event propagation and event groups). Once it has been called, further calls to that method have no additional effect.Note: This method does not prevent the default action from being invoked; use
Event.preventDefault()for that effect.No ParametersNo Return ValueNo Exceptions stopPropagation-
This method is used to prevent event listeners of the same group to be triggered but its effect is deferred until all event listeners attached on the
currentTargethave been triggered (see Event propagation and event groups). Once it has been called, further calls to that method have no additional effect.Note: This method does not prevent the default action from being invoked; use
preventDefaultfor that effect.No ParametersNo Return ValueNo Exceptions
- Interface EventTarget (introduced in DOM Level 2)
-
The
EventTargetinterface is implemented by all the objects which could be event targets in an implementation which supports the Event flows. The interface allows registration, removal or query of event listeners, and dispatch of events to an event target.When used with DOM event flow, this interface is implemented by all target nodes and target ancestors, i.e. all DOM
Nodesof the tree support this interface when the implementation conforms to DOM Level 3 Events and, therefore, this interface can be obtained by using binding-specific casting methods on an instance of theNodeinterface.Invoking
addEventListeneroraddEventListenerNSmultiple times on the sameEventTargetwith the same parameters (namespaceURI,type,listener, anduseCapture) is considered to be a no-op and thus independently of the event group. They do not cause theEventListenerto be called more than once and do not cause a change in the triggering order. In order to guarantee that an event listener will be added to the event target for the specified event group, one needs to invokeremoveEventListenerorremoveEventListenerNSfirst.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 2: interface EventTarget { void addEventListener(in DOMString type, in EventListener listener, in boolean useCapture); void removeEventListener(in DOMString type, in EventListener listener, in boolean useCapture); // Modified in DOM Level 3: boolean dispatchEvent(in Event evt) raises(EventException); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: void addEventListenerNS(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString type, in EventListener listener, in boolean useCapture, in DOMObject evtGroup); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: void removeEventListenerNS(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString type, in EventListener listener, in boolean useCapture); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: boolean willTriggerNS(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString type); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: boolean hasEventListenerNS(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString type); };
- Methods
addEventListener-
This method allows the registration of an event listener in the default group and, depending on the
useCaptureparameter, on the capture phase of the DOM event flow or its target and bubbling phases.Parameterstypeof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.typeassociated with the event for which the user is registering.
listenerof typeEventListener-
The
listenerparameter takes an object implemented by the user which implements theEventListenerinterface and contains the method to be called when the event occurs.
useCaptureof typeboolean-
If true,
useCaptureindicates that the user wishes to add the event listener for the capture phase only, i.e. this event listener will not be triggered during the target and bubbling phases. Iffalse, the event listener will only be triggered during the target and bubbling phases.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions addEventListenerNSintroduced in DOM Level 3-
This method allows the registration of an event listener in a specified group or the default group and, depending on the
useCaptureparameter, on the capture phase of the DOM event flow or its target and bubbling phases.ParametersnamespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.namespaceURIassociated with the event for which the user is registering.
typeof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.typeassociated with the event for which the user is registering.
listenerof typeEventListener-
The
listenerparameter takes an object implemented by the user which implements theEventListenerinterface and contains the method to be called when the event occurs.
useCaptureof typeboolean-
If true,
useCaptureindicates that the user wishes to add the event listener for the capture phase only, i.e. this event listener will not be triggered during the target and bubbling phases. Iffalse, the event listener will only be triggered during the target and bubbling phases.
evtGroupof typeDOMObject-
The object that represents the event group to associate with
the
EventListener(see also Event propagation and event groups). Usenullto attach the event listener to the default group.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions dispatchEventmodified in DOM Level 3-
This method allows the dispatch of events into the implementation's event model. The event target of the event is the
EventTargetobject on whichdispatchEventis called.Parametersevtof typeEvent-
The event to be dispatched.
Return ValuebooleanIndicates whether any of the listeners which handled the event called
Event.preventDefault(). IfEvent.preventDefault()was called the returned value isfalse, else it istrue.ExceptionsUNSPECIFIED_EVENT_TYPE_ERR: Raised if the
Event.typewas not specified by initializing the event beforedispatchEventwas called. Specification of theEvent.typeasnullor an empty string will also trigger this exception.DISPATCH_REQUEST_ERR: Raised if the
Eventobject is already being dispatched in the tree.NOT_SUPPORTED_ERR: Raised if the
Eventobject has not been created usingDocumentEvent.createEvent()or does not support the interfaceCustomEvent. hasEventListenerNSintroduced in DOM Level 3-
This method allows the DOM application to know if this
EventTargetcontains an event listener registered for the specified event type. This is useful for determining at which nodes within a hierarchy altered handling of specific event types has been introduced, but should not be used to determine whether the specified event type triggers an event listener (seeEventTarget.willTriggerNS()).ParametersnamespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.namespaceURIassociated with the event.
typeof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.typeassociated with the event.
Return Valuebooleantrueif an event listener is registered on thisEventTargetfor the specified event type,falseotherwise.No Exceptions removeEventListener-
This method allows the removal of event listeners from the default group.
CallingremoveEventListenerwith arguments which do not identify any currently registeredEventListeneron theEventTargethas no effect.Parameterstypeof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.typefor which the user registered the event listener.
listenerof typeEventListener-
The
EventListenerto be removed.
useCaptureof typeboolean-
Specifies whether the
EventListenerbeing removed was registered for the capture phase or not. If a listener was registered twice, once for the capture phase and once for the target and bubbling phases, each must be removed separately. Removal of an event listener registered for the capture phase does not affect the same event listener registered for the target and bubbling phases, and vice versa.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions removeEventListenerNSintroduced in DOM Level 3-
This method allows the removal of an event listener, independently of the associated event group.
CallingremoveEventListenerNSwith arguments which do not identify any currently registeredEventListeneron theEventTargethas no effect.ParametersnamespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.namespaceURIassociated with the event for which the user registered the event listener.
typeof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.typeassociated with the event for which the user registered the event listener.
listenerof typeEventListener-
The
EventListenerparameter indicates theEventListenerto be removed.
useCaptureof typeboolean-
Specifies whether the
EventListenerbeing removed was registered for the capture phase or not. If a listener was registered twice, once for the capture phase and once for the target and bubbling phases, each must be removed separately. Removal of an event listener registered for the capture phase does not affect the same event listener registered for the target and bubbling phases, and vice versa.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions willTriggerNSintroduced in DOM Level 3-
This method allows the DOM application to know if an event listener, attached to this
EventTargetor one of its ancestors, will be triggered by the specified event type during the dispatch of the event to this event target or one of its descendants.ParametersnamespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.namespaceURIassociated with the event.
typeof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.typeassociated with the event.
Return Valuebooleantrueif an event listener will be triggered on theEventTargetwith the specified event type,falseotherwise.No Exceptions
- Interface EventListener (introduced in DOM Level 2)
-
The
EventListenerinterface is the primary way for handling events. Users implement theEventListenerinterface and register their event listener on anEventTarget. The users should also remove theirEventListenerfrom itsEventTargetafter they have completed using the listener.Copying a
Node, with methods such asNode.cloneNodeorRange.cloneContents, does not copy the event listeners attached to it. Event listeners must be attached to the newly createdNodeafterwards if so desired.Moving a
Node, with methodsDocument.adoptNode,Node.appendChild, orRange.extractContents, does not affect the event listeners attached to it.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 2: interface EventListener { void handleEvent(in Event evt); };
- Methods
- Exception EventException introduced in DOM Level 2
-
Event operations may throw an
EventExceptionas specified in their method descriptions.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 2: exception EventException { unsigned short code; }; // EventExceptionCode const unsigned short UNSPECIFIED_EVENT_TYPE_ERR = 0; // Introduced in DOM Level 3: const unsigned short DISPATCH_REQUEST_ERR = 1;
- Definition group EventExceptionCode
An integer indicating the type of error generated.
- Defined Constants
DISPATCH_REQUEST_ERR, introduced in DOM Level 3.-
If the
Eventobject is already dispatched in the tree. UNSPECIFIED_EVENT_TYPE_ERR-
If the
Event.typewas not specified by initializing the event before the method was called. Specification of theEvent.typeasnullor an empty string will also trigger this exception.
1.6.1 Event creation
In most cases, the events dispatched by the DOM Events
implementation are also created by the implementation. It is
however possible to simulate events such as mouse events by
creating the Event objects and dispatch them using
the DOM Events implementation.
DOM Events provides two ways for creating Event
objects. An application can either create Event
objects that are known to the implementation, or create its own
objects and have them dispatched by the DOM Events
implementation.
Creating Event objects that are known to the DOM
Events implementation is done using
DocumentEvent.createEvent(). The application must
then initialize the object by calling the appropriate
initialization method before invoking
EventTarget.dispatchEvent(). The Event
objects created must be known by the DOM Events implementation;
otherwise an event exception is thrown.
The DOM application might want to create its own
Event objects, in order to change the default
Event implementation provided by the DOM Events
implementation or to generate new event types with specific
contextual information. In any case, the application is
responsible for creating and initializing the Event
object. The application can then dispatch the event using the
DOM Events implementation by using
EventTarget.dispatchEvent().
However, the DOM Events implementation requires to have access
to two attributes in the Event object in order to
accomplish the dispatch appropriately:
Event.currentTarget and
Event.eventPhase. Those attributes are defined as
readonly in the Event interface since
event listeners must not change them and it is the
responsibility of the DOM Events implementation to update them
during the event flow. Therefore, implementing the
Event interface when creating its own events is not
enough for an application since the DOM Events implementation
will not be able to update the current phase and the current
node during the dispatch, unless the event object also
implements the CustomEvent interface to give access
to the relevant attributes.
- Interface DocumentEvent (introduced in DOM Level 2)
-
The
DocumentEventinterface provides a mechanism by which the user can create anEventobject of a type supported by the implementation. If the feature "Events" is supported by theDocumentobject, theDocumentEventinterface must be implemented on the same object. If the feature "+Events" is supported by theDocumentobject, an object that supports theDocumentEventinterface must be returned by invoking the methodNode.getFeature("+Events", "3.0")on theDocumentobject.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 2: interface DocumentEvent { Event createEvent(in DOMString eventType) raises(DOMException); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: boolean canDispatch(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString type); };
- Methods
canDispatchintroduced in DOM Level 3-
Test if the implementation can generate events of a specified type.Parameters
namespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.namespaceURIof the event.
typeof typeDOMString-
Specifies the
Event.typeof the event.
Return Valuebooleantrueif the implementation can generate and dispatch this event type,falseotherwise.No Exceptions createEvent-
Parameters
eventTypeof typeDOMString-
The
eventTypeparameter specifies the name of the DOM Events interface to be supported by the created event object, e.g."Event","MouseEvent","MutationEvent"and so on. If theEventis to be dispatched via theEventTarget.dispatchEvent()method the appropriate event init method must be called after creation in order to initialize theEvent's values.
As an example, a user wishing to synthesize some kind ofUIEventwould invokeDocumentEvent.createEvent("UIEvent"). TheUIEvent.initUIEventNS()method could then be called on the newly createdUIEventobject to set the specific type of user interface event to be dispatched,{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMActivate"}for example, and set its context information, e.g.UIEvent.detailin this example.
ThecreateEventmethod is used in creatingEvents when it is either inconvenient or unnecessary for the user to create anEventthemselves. In cases where the implementation providedEventis insufficient, users may supply their ownEventimplementations for use with theEventTarget.dispatchEvent()method. However, the DOM implementation needs access to the attributesEvent.currentTargetandEvent.eventPhaseto appropriately propagate the event in the DOM tree. Therefore users'Eventimplementations might need to support theCustomEventinterface for that effect.Note: For backward compatibility reason, "UIEvents", "MouseEvents", "MutationEvents", and "HTMLEvents" feature names are valid values for the parameter
eventTypeand represent respectively the interfaces "UIEvent", "MouseEvent", "MutationEvent", and "Event".
Return ValueThe newly created event object.
ExceptionsDOMExceptionNOT_SUPPORTED_ERR: Raised if the implementation does not support the
Eventinterface requested.
- Interface CustomEvent (introduced in DOM Level 3)
-
The
CustomEventinterface gives access to the attributesEvent.currentTargetandEvent.eventPhase. It is intended to be used by the DOM Events implementation to access the underlying current target and event phase while dispatching a customEventin the tree; it is also intended to be implemented, and not used, by DOM applications.The methods contained in this interface are not intended to be used by a DOM application, especially during the dispatch on the
Eventobject. Changing the current target or the current phase may result in unpredictable results of the event flow. The DOM Events implementation should ensure that both methods return the appropriate current target and phase before invoking each event listener on the current target to protect DOM applications from malicious event listeners.Note: If this interface is supported by the event object,
Event.isCustom()must returntrue.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 3: interface CustomEvent : Event { void setDispatchState(in EventTarget target, in unsigned short phase); boolean isPropagationStopped(); boolean isImmediatePropagationStopped(); };
- Methods
isImmediatePropagationStopped-
The
isImmediatePropagationStoppedmethod is used by the DOM Events implementation to know if the methodstopImmediatePropagation()has been called for this event. It returnstrueif the method has been called,falseotherwise.Return Valuebooleantrueif the event propagation has been stopped immediately in the current group.No ParametersNo Exceptions isPropagationStopped-
This method will return
trueif the methodstopPropagation()has been called for this event,falsein any other cases.Return Valuebooleantrueif the event propagation has been stopped in the current group.No ParametersNo Exceptions setDispatchState-
The
setDispatchStatemethod is used by the DOM Events implementation to set the values ofEvent.currentTargetandEvent.eventPhase. It also reset the states ofisPropagationStoppedandisImmediatePropagationStopped.Parameterstargetof typeEventTarget-
Specifies the new value for the
Event.currentTargetattribute.
phaseof typeunsigned short-
Specifies the new value for the
Event.eventPhaseattribute.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions
1.7 Event module definitions
The DOM Event Model allows a DOM implementation to support multiple modules of events. The model has been designed to allow addition of new event modules if required. The DOM will not attempt to define all possible events. For purposes of interoperability, the DOM defines a module of user interface events including lower level device dependent events and a module of document mutation events.
1.7.1 User Interface event types
The User Interface event module contains basic event types associated with user interfaces.
- Interface UIEvent (introduced in DOM Level 2)
-
The
UIEventinterface provides specific contextual information associated with User Interface events.To create an instance of the
UIEventinterface, use theDocumentEvent.createEvent("UIEvent")method call.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 2: interface UIEvent : Event { readonly attribute views::AbstractView view; readonly attribute long detail; void initUIEvent(in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in views::AbstractView viewArg, in long detailArg); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: void initUIEventNS(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in views::AbstractView viewArg, in long detailArg); };
- Attributes
- Methods
initUIEvent-
The
initUIEventmethod is used to initialize the value of aUIEventobject and has the same behavior asEvent.initEvent().ParameterstypeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
Event.initEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
Event.initEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
Event.initEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
viewArgof typeviews::AbstractView-
Specifies
UIEvent.view.
detailArgof typelong-
Specifies
UIEvent.detail.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions initUIEventNSintroduced in DOM Level 3-
The
initUIEventNSmethod is used to initialize the value of aUIEventobject and has the same behavior asEvent.initEventNS().ParametersnamespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
Event.initEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
typeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
Event.initEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
Event.initEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
Event.initEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
viewArgof typeviews::AbstractView-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
detailArgof typelong-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions
The User Interface event types are listed below. For a full
description of the semantics associated with these event types,
refer to the Complete list of event types. A DOM
application may use the hasFeature(feature,
version) method of the DOMImplementation
interface with parameter values "UIEvents" and "3.0"
(respectively) to determine whether or not the DOM Level 3 User
Interface event types are supported by the implementation. In
order to fully support this module, an implementation must also
support the "Events" feature defined in this specification and
the "Views" feature defined in the DOM Level 2 Views
specification [DOM Level 2 Views]. For
additional information about conformance,
please see the DOM Level 3 Core specification [DOM Level 3 Core]. The DOM Level 3 User Interface Events module is
built on top of the DOM Level 2 User Interface Events [DOM Level 2 Events] module, i.e. a DOM Level 3 User Interface
Events implementation where hasFeature("UIEvents",
"3.0") returns true must also return
true when the version number is
"2.0", "" or, null.
| type | Context information |
|---|---|
| DOMActivate |
UIEvent.view is in use.
|
| DOMFocusIn | (same as above) |
| DOMFocusOut | (same as above) |
1.7.2 Text events types
The text event module originates from the [HTML 4.01] onkeypress attribute. Unlike
this attribute, the event type {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"textInput"} applies only to characters and is designed
for use with any text input devices, not just keyboards. Refer
to Appendix A, "Keyboard events and key identifiers", for examples on how
text events are used in combination with keyboard events.
- Interface TextEvent (introduced in DOM Level 3)
-
The
TextEventinterface provides specific contextual information associated with Text Events.To create an instance of the
TextEventinterface, use theDocumentEvent.createEvent("TextEvent")method call.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 3: interface TextEvent : UIEvent { readonly attribute DOMString data; void initTextEvent(in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in views::AbstractView viewArg, in DOMString dataArg); void initTextEventNS(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString type, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in views::AbstractView viewArg, in DOMString dataArg); };
- Attributes
dataof typeDOMString, readonly-
dataholds the value of the characters generated by the character device. This may be a single Unicode character or a non-empty sequence of Unicode characters [Unicode]. Characters should be normalized as defined by the Unicode normalization form NFC, defined in [UTR #15]. This attribute cannot be null or contain the empty string.
- Methods
initTextEvent-
The
initTextEventmethod is used to initialize the value of aTextEventobject and has the same behavior asUIEvent.initUIEvent(). The value ofUIEvent.detailremains undefined.ParameterstypeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
viewArgof typeviews::AbstractView-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
dataArgof typeDOMString-
Specifies
TextEvent.data.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions initTextEventNS-
The
initTextEventNSmethod is used to initialize the value of aTextEventobject and has the same behavior asUIEvent.initUIEventNS(). The value ofUIEvent.detailremains undefined.ParametersnamespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
typeof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
viewArgof typeviews::AbstractView-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
dataArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
TextEvent.initTextEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions
The text event type is listed below. For a full description of
the semantics associated with this event type, refer to the
Complete list of event types. A DOM application
may use the hasFeature(feature, version) method of
the DOMImplementation interface with parameter
values "TextEvents" and "3.0"
(respectively) to determine whether or not the Text event module
is supported by the implementation. In order to fully support
this module, an implementation must also support the
"UIEvents" feature defined in this
specification. For additional information about conformance,
please see the DOM Level 3 Core specification [DOM Level 3 Core].
| type | Context information |
|---|---|
| textInput |
UIEvent.view and TextEvent.data are
in use.
|
1.7.3 Mouse event types
The Mouse event module originates from the [HTML 4.01] onclick,
ondblclick, onmousedown,
onmouseup, onmouseover,
onmousemove, and onmouseout
attributes. This event module is specifically designed for use
with pointing input devices, such as a mouse or a trackball.
- Interface MouseEvent (introduced in DOM Level 2)
-
The
MouseEventinterface provides specific contextual information associated with Mouse events.In the case of nested elements mouse events are always targeted at the most deeply nested element. Ancestors of the targeted element may use bubbling to obtain notification of mouse events which occur within theirs descendent elements.
To create an instance of the
MouseEventinterface, use theDocumentEvent.createEvent("MouseEvent")method call.Note: When initializing
MouseEventobjects usinginitMouseEventorinitMouseEventNS, implementations should use the client coordinatesclientXandclientYfor calculation of other coordinates (such as target coordinates exposed by DOM Level 0 implementations).
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 2: interface MouseEvent : UIEvent { readonly attribute long screenX; readonly attribute long screenY; readonly attribute long clientX; readonly attribute long clientY; readonly attribute boolean ctrlKey; readonly attribute boolean shiftKey; readonly attribute boolean altKey; readonly attribute boolean metaKey; readonly attribute unsigned short button; readonly attribute EventTarget relatedTarget; void initMouseEvent(in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in views::AbstractView viewArg, in long detailArg, in long screenXArg, in long screenYArg, in long clientXArg, in long clientYArg, in boolean ctrlKeyArg, in boolean altKeyArg, in boolean shiftKeyArg, in boolean metaKeyArg, in unsigned short buttonArg, in EventTarget relatedTargetArg); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: boolean getModifierState(in DOMString keyIdentifierArg); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: void initMouseEventNS(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in views::AbstractView viewArg, in long detailArg, in long screenXArg, in long screenYArg, in long clientXArg, in long clientYArg, in unsigned short buttonArg, in EventTarget relatedTargetArg, in DOMString modifiersList); };
- Attributes
altKeyof typeboolean, readonly-
trueif the alt (alternative) key modifier is activated.Note: The Option key modifier on Macintosh systems must be represented using this key modifier.
buttonof typeunsigned short, readonly-
During mouse events caused by the depression or release of a
mouse button,
buttonis used to indicate which mouse button changed state.0indicates the normal button of the mouse (in general on the left or the one button on Macintosh mice, used to activate a button or select text).2indicates the contextual property (in general on the right, used to display a context menu) button of the mouse if present.1indicates the extra (in general in the middle and often combined with the mouse wheel) button. Some mice may provide or simulate more buttons, and values higher than2can be used to represent such buttons.
clientXof typelong, readonly- The horizontal coordinate at which the
event occurred relative to the DOM implementation's client area.
clientYof typelong, readonly- The vertical coordinate at which the
event occurred relative to the DOM implementation's client area.
ctrlKeyof typeboolean, readonly-
trueif the control (Ctrl) key modifier is activated.
metaKeyof typeboolean, readonly-
trueif the meta (Meta) key modifier is activated.Note: The Command key modifier on Macintosh system must be represented using this meta key.
relatedTargetof typeEventTarget, readonly-
Used to identify a secondary
EventTargetrelated to a UI event. Currently this attribute is used with the mouseover event to indicate theEventTargetwhich the pointing device exited and with the mouseout event to indicate theEventTargetwhich the pointing device entered.
screenXof typelong, readonly- The horizontal coordinate at which the
event occurred relative to the origin of the screen coordinate
system.
screenYof typelong, readonly- The vertical coordinate at which the
event occurred relative to the origin of the screen coordinate
system.
shiftKeyof typeboolean, readonly-
trueif the shift (Shift) key modifier is activated.
- Methods
getModifierStateintroduced in DOM Level 3-
This methods queries the state of a modifier using a key identifier. See also Modifier keys.Parameters
keyIdentifierArgof typeDOMString-
A modifier key identifier, as defined by the
KeyboardEvent.keyIdentifierattribute. Common modifier keys are"Alt","AltGraph","CapsLock","Control","Meta","NumLock","Scroll", or"Shift".Note: If an application wishes to distinguish between right and left modifiers, this information could be deduced using keyboard events and
KeyboardEvent.keyLocation.
Return Valuebooleantrueif it is modifier key and the modifier is activated,falseotherwise.No Exceptions initMouseEvent-
The
initMouseEventmethod is used to initialize the value of aMouseEventobject and has the same behavior asUIEvent.initUIEvent().ParameterstypeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
viewArgof typeviews::AbstractView-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
detailArgof typelong-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
screenXArgof typelong-
Specifies
MouseEvent.screenX.
screenYArgof typelong-
Specifies
MouseEvent.screenY.
clientXArgof typelong-
Specifies
MouseEvent.clientX.
clientYArgof typelong-
Specifies
MouseEvent.clientY.
ctrlKeyArgof typeboolean-
Specifies
MouseEvent.ctrlKey.
altKeyArgof typeboolean-
Specifies
MouseEvent.altKey.
shiftKeyArgof typeboolean-
Specifies
MouseEvent.shiftKey.
metaKeyArgof typeboolean-
Specifies
MouseEvent.metaKey.
buttonArgof typeunsigned short-
Specifies
MouseEvent.button.
relatedTargetArgof typeEventTarget-
Specifies
MouseEvent.relatedTarget.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions initMouseEventNSintroduced in DOM Level 3-
The
initMouseEventNSmethod is used to initialize the value of aMouseEventobject and has the same behavior asUIEvent.initUIEventNS().ParametersnamespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
typeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
viewArgof typeviews::AbstractView-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
detailArgof typelong-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
screenXArgof typelong-
Refer to the
MouseEvent.initMouseEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
screenYArgof typelong-
Refer to the
MouseEvent.initMouseEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
clientXArgof typelong-
Refer to the
MouseEvent.initMouseEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
clientYArgof typelong-
Refer to the
MouseEvent.initMouseEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
buttonArgof typeunsigned short-
Refer to the
MouseEvent.initMouseEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
relatedTargetArgof typeEventTarget-
Refer to the
MouseEvent.initMouseEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
modifiersListof typeDOMString-
A white
space separated list of modifier key identifiers
to be activated on this object. As an example,
"Control Alt"will activated the control and alt modifiers.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions
The Mouse event types are listed below. For a full description of the semantics associated with these event types, refer to the Complete list of event types. In the case of nested elements, mouse event types are always targeted at the most deeply nested element. Ancestors of the targeted element may use bubbling to obtain notification of mouse events which occur within its descendent elements.
A DOM application may use the hasFeature(feature,
version) method of the DOMImplementation
interface with parameter values "MouseEvents" and
"3.0" (respectively) to determine whether or not
the Mouse event module is supported by the implementation. In
order to fully support this module, an implementation must also
support the "UIEvents" feature defined in this
specification. For additional information about conformance,
please see the DOM Level 3 Core specification [DOM Level 3 Core]. The DOM Level 3 Mouse Events
module is built on top of the DOM Level 2 Mouse Events [DOM Level 2 Events] module, i.e. a DOM Level 3 Mouse Events
implementation where hasFeature("MouseEvents",
"3.0") returns true must also return
true when the version number is
"2.0", "" or, null.
| type | Context information |
|---|---|
| click |
MouseEvent.screenX,
MouseEvent.screenY,
MouseEvent.clientX,
MouseEvent.clientY,
MouseEvent.altKey,
MouseEvent.ctrlKey,
MouseEvent.shiftKey,
MouseEvent.metaKey,
MouseEvent.altGraphKey,
MouseEvent.button, and
UIEvent.view are in use. The
UIEvent.detail attribute indicates the number
of consecutive clicks of a pointing device button during
a user action. The attribute value is 1 when
the user begins this action and increments by
1 for each click. The notion of consecutive
clicks depends on the environment configuration. For
example, a "double click" will not happen if there is a
long delay between the two clicks, even if the pointing
device did not move.
|
| mousedown |
MouseEvent.screenX,
MouseEvent.screenY,
MouseEvent.clientX,
MouseEvent.clientY,
MouseEvent.altKey,
MouseEvent.ctrlKey,
MouseEvent.shiftKey,
MouseEvent.metaKey,
MouseEvent.altGraphKey,
MouseEvent.button, and
UIEvent.view are in use. The
UIEvent.detail attribute indicates the number
of consecutive clicks, incremented by one, of a pointing
device button during a user action. For example, if no click
happened before the mousedown, UIEvent.detail
will contain the value 1.
|
| mouseup |
MouseEvent.screenX,
MouseEvent.screenY,
MouseEvent.clientX,
MouseEvent.clientY,
MouseEvent.altKey,
MouseEvent.ctrlKey,
MouseEvent.shiftKey,
MouseEvent.metaKey,
MouseEvent.altGraphKey,
MouseEvent.button, and
UIEvent.view are in use. The
UIEvent.detail attribute indicates the number
of consecutive clicks, incremented by one, of a pointing
device button during a user action.
|
| mouseover |
MouseEvent.screenX,
MouseEvent.screenY,
MouseEvent.clientX,
MouseEvent.clientY,
MouseEvent.altKey,
MouseEvent.ctrlKey,
MouseEvent.shiftKey,
MouseEvent.metaKey,
MouseEvent.altGraphKey, and
UIEvent.view are in
use. MouseEvent.relatedTarget indicates the
event target a
pointing device is exiting.
|
| mousemove |
MouseEvent.screenX,
MouseEvent.screenY,
MouseEvent.clientX,
MouseEvent.clientY,
MouseEvent.altKey,
MouseEvent.ctrlKey,
MouseEvent.shiftKey,
MouseEvent.metaKey,
MouseEvent.altGraphKey, and
UIEvent.view are in use.
|
| mouseout |
MouseEvent.screenX,
MouseEvent.screenY,
MouseEvent.clientX,
MouseEvent.clientY,
MouseEvent.altKey,
MouseEvent.ctrlKey,
MouseEvent.shiftKey,
MouseEvent.metaKey,
MouseEvent.altGraphKey, and
UIEvent.view are in
use. MouseEvent.relatedTarget indicates the
event target a
pointing device is entering.
|
As an example, a "double-click" on a mouse device will produce
the following events (the value of UIEvent.detail
is indicated in parenthesis):
-
{
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mousedown"} (1) -
{
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mouseup"} (1) -
{
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "click"} (1) -
{
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mousedown"} (2) -
{
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "mouseup"} (2) -
{
"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "click"} (2)
1.7.4 Keyboard event types
Keyboard events are device dependent, i.e. they rely on the capabilities of the input devices and how they are mapped in the operating systems. It is therefore highly recommended to rely on Text events types when dealing with character input.
- Interface KeyboardEvent (introduced in DOM Level 3)
-
The
KeyboardEventinterface provides specific contextual information associated with keyboard devices. Each keyboard event references a key using an identifier. Keyboard events are commonly directed at the element that has the focus.The
KeyboardEventinterface provides convenient attributes for some common modifiers keys:KeyboardEvent.ctrlKey,KeyboardEvent.shiftKey,KeyboardEvent.altKey,KeyboardEvent.metaKey. These attributes are equivalent to use the methodKeyboardEvent.getModifierState(keyIdentifierArg)with "Control", "Shift", "Alt", or "Meta" respectively.To create an instance of the
KeyboardEventinterface, use theDocumentEvent.createEvent("KeyboardEvent")method call.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 3: interface KeyboardEvent : UIEvent { // KeyLocationCode const unsigned long DOM_KEY_LOCATION_STANDARD = 0x00; const unsigned long DOM_KEY_LOCATION_LEFT = 0x01; const unsigned long DOM_KEY_LOCATION_RIGHT = 0x02; const unsigned long DOM_KEY_LOCATION_NUMPAD = 0x03; readonly attribute DOMString keyIdentifier; readonly attribute unsigned long keyLocation; readonly attribute boolean ctrlKey; readonly attribute boolean shiftKey; readonly attribute boolean altKey; readonly attribute boolean metaKey; boolean getModifierState(in DOMString keyIdentifierArg); void initKeyboardEvent(in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in views::AbstractView viewArg, in DOMString keyIdentifierArg, in unsigned long keyLocationArg, in DOMString modifiersList); void initKeyboardEventNS(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in views::AbstractView viewArg, in DOMString keyIdentifierArg, in unsigned long keyLocationArg, in DOMString modifiersList); };
- Definition group KeyLocationCode
This set of constants is used to indicate the location of a key on the device. In case a DOM implementation wishes to provide a new location information, a value different from the following constant values must be used.
- Defined Constants
DOM_KEY_LOCATION_LEFT- The key activated is in the left key location (there is more than one possible location for this key). Example: the left Shift key on a PC 101 Key US keyboard.
DOM_KEY_LOCATION_NUMPAD- The key activation originated on the numeric keypad or with a virtual key corresponding to the numeric keypad. Example: the '1' key on a PC 101 Key US keyboard located on the numeric pad.
DOM_KEY_LOCATION_RIGHT- The key activation is in the right key location (there is more than one possible location for this key). Example: the right Shift key on a PC 101 Key US keyboard.
DOM_KEY_LOCATION_STANDARD- The key activation is not distinguished as the left or right version of the key, and did not originate from the numeric keypad (or did not originate with a virtual key corresponding to the numeric keypad). Example: the 'Q' key on a PC 101 Key US keyboard.
- Attributes
altKeyof typeboolean, readonly-
trueif the alternative (Alt) key modifier is activated.Note: The Option key modifier on Macintosh systems must be represented using this key modifier.
ctrlKeyof typeboolean, readonly-
trueif the control (Ctrl) key modifier is activated.
keyIdentifierof typeDOMString, readonly-
keyIdentifierholds the identifier of the key. The key identifiers are defined in Appendix A.2 "Key identifiers set". Implementations that are unable to identify a key must use the key identifier"Unidentified".
keyLocationof typeunsigned long, readonly-
The
keyLocationattribute contains an indication of the location of they key on the device, as described in Keyboard event types.
metaKeyof typeboolean, readonly-
trueif the meta (Meta) key modifier is activated.Note: The Command key modifier on Macintosh systems must be represented using this key modifier.
shiftKeyof typeboolean, readonly-
trueif the shift (Shift) key modifier is activated.
- Methods
getModifierState-
This methods queries the state of a modifier using a key identifier. See also Modifier keys.Parameters
keyIdentifierArgof typeDOMString-
A modifier key identifier. Common modifier keys are
"Alt","AltGraph","CapsLock","Control","Meta","NumLock","Scroll", or"Shift".Note: If an application wishes to distinguish between right and left modifiers, this information could be deduced using keyboard events and
KeyboardEvent.keyLocation.
Return Valuebooleantrueif it is modifier key and the modifier is activated,falseotherwise.No Exceptions initKeyboardEvent-
The
initKeyboardEventmethod is used to initialize the value of aKeyboardEventobject and has the same behavior asUIEvent.initUIEvent(). The value ofUIEvent.detailremains undefined.ParameterstypeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
viewArgof typeviews::AbstractView-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
keyIdentifierArgof typeDOMString-
Specifies
KeyboardEvent.keyIdentifier.
keyLocationArgof typeunsigned long-
Specifies
KeyboardEvent.keyLocation.
modifiersListof typeDOMString-
A white
space separated list of modifier key identifiers
to be activated on this object.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions initKeyboardEventNS-
The
initKeyboardEventNSmethod is used to initialize the value of aKeyboardEventobject and has the same behavior asUIEvent.initUIEventNS(). The value ofUIEvent.detailremains undefined.ParametersnamespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
typeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
viewArgof typeviews::AbstractView-
Refer to the
UIEvent.initUIEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
keyIdentifierArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
KeyboardEvent.initKeyboardEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
keyLocationArgof typeunsigned long-
Refer to the
KeyboardEvent.initKeyboardEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
modifiersListof typeDOMString-
A white
space separated list of modifier key identifiers
to be activated on this object. As an example,
"Control Alt"will activated the control and alt modifiers.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions
Depending on the character generation device, keyboard events may or may not be generated.
The keyboard event types are listed below. For a full
description of the semantics associated with these event types,
refer to the Complete list of event types. A DOM
application may use the hasFeature(feature,
version) method of the DOMImplementation
interface with parameter values "KeyboardEvents"
and "3.0" (respectively) to determine whether or
not the Keyboard event module is supported by the
implementation. In order to fully support this module, an
implementation must also support the "UIEvents"
feature defined in this specification. For additional
information about conformance,
please see the DOM Level 3 Core specification [DOM Level 3 Core].
| type | Context information |
|---|---|
| keydown |
UIEvent.view,
KeyboardEvent.keyIdentifier,
KeyboardEvent.location,
KeyboardEvent.altKey,
KeyboardEvent.altGraphKey,
KeyboardEvent.shiftKey,
KeyboardEvent.ctrlKey, and
KeyboardEvent.metaKey are in use.
|
| keyup |
UIEvent.view,
KeyboardEvent.keyIdentifier, and
KeyboardEvent.location are in use.
KeyboardEvent.altKey,
KeyboardEvent.altGraphKey,
KeyboardEvent.shiftKey,
KeyboardEvent.ctrlKey, and
KeyboardEvent.metaKey are in use unless the
Keyboard.keyIdentifier corresponds to the key
modifier itself.
|
1.7.5 Mutation and mutation name event types
The mutation and mutation name event modules are designed to allow notification of any changes to the structure of a document, including attribute, text, or name modifications. It may be noted that none of the event types associated with the modules are designated as cancelable. This stems from the fact that it is very difficult to make use of existing DOM interfaces which cause document modifications if any change to the document might or might not take place due to cancelation of the resulting event. Although this is still a desired capability, it was decided that it would be better left until the addition of transactions into the DOM.
Many single modifications of the tree can cause multiple mutation events to be dispatched. Rather than attempt to specify the ordering of mutation events due to every possible modification of the tree, the ordering of these events is left to the implementation.
- Interface MutationEvent (introduced in DOM Level 2)
-
The
MutationEventinterface provides specific contextual information associated with Mutation events.To create an instance of the
MutationEventinterface, use theDocumentEvent.createEvent("MutationEvent")method call.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 2: interface MutationEvent : Event { // attrChangeType const unsigned short MODIFICATION = 1; const unsigned short ADDITION = 2; const unsigned short REMOVAL = 3; readonly attribute Node relatedNode; readonly attribute DOMString prevValue; readonly attribute DOMString newValue; readonly attribute DOMString attrName; readonly attribute unsigned short attrChange; void initMutationEvent(in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in Node relatedNodeArg, in DOMString prevValueArg, in DOMString newValueArg, in DOMString attrNameArg, in unsigned short attrChangeArg); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: void initMutationEventNS(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in Node relatedNodeArg, in DOMString prevValueArg, in DOMString newValueArg, in DOMString attrNameArg, in unsigned short attrChangeArg); };
- Definition group attrChangeType
An integer indicating in which way the
Attrwas changed.- Defined Constants
ADDITION-
The
Attrwas just added. MODIFICATION-
The
Attrwas modified in place. REMOVAL-
The
Attrwas just removed.
- Attributes
attrChangeof typeunsigned short, readonly-
attrChangeindicates the type of change which triggered the{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMAttrModified"}event. The values can beMODIFICATION,ADDITION, orREMOVAL.
attrNameof typeDOMString, readonly-
attrNameindicates the name of the changedAttrnode in a{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMAttrModified"}event.
newValueof typeDOMString, readonly-
newValueindicates the new value of theAttrnode in{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMAttrModified"}events, and of theCharacterDatanode in{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMCharacterDataModified"}events.
prevValueof typeDOMString, readonly-
prevValueindicates the previous value of theAttrnode in{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMAttrModified"}events, and of theCharacterDatanode in{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMCharacterDataModified"}events.
relatedNodeof typeNode, readonly-
relatedNodeis used to identify a secondary node related to a mutation event. For example, if a mutation event is dispatched to a node indicating that its parent has changed, therelatedNodeis the changed parent. If an event is instead dispatched to a subtree indicating a node was changed within it, therelatedNodeis the changed node. In the case of the{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMAttrModified"}event it indicates theAttrnode which was modified, added, or removed.
- Methods
initMutationEvent-
The
initMutationEventmethod is used to initialize the value of aMutationEventobject and has the same behavior asEvent.initEvent().ParameterstypeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
Event.initEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
Event.initEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
Event.initEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
relatedNodeArgof typeNode-
Specifies
MutationEvent.relatedNode.
prevValueArgof typeDOMString-
Specifies
MutationEvent.prevValue. This value may be null.
newValueArgof typeDOMString-
Specifies
MutationEvent.newValue. This value may be null.
attrNameArgof typeDOMString-
Specifies
MutationEvent.attrname. This value may be null.
attrChangeArgof typeunsigned short-
Specifies
MutationEvent.attrChange. This value may be null.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions initMutationEventNSintroduced in DOM Level 3-
The
initMutationEventNSmethod is used to initialize the value of aMutationEventobject and has the same behavior asEvent.initEventNS().ParametersnamespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
Event.initEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
typeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
Event.initEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
Event.initEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
Event.initEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
relatedNodeArgof typeNode-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
prevValueArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
newValueArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
attrNameArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
attrChangeArgof typeunsigned short-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions
The mutation event types are listed below. For a full
description of the semantics associated with these event types,
refer to the Complete list of event types. A DOM
application may use the hasFeature(feature,
version) method of the DOMImplementation
interface with parameter values "MutationEvents"
and "3.0" (respectively) to determine whether or
not the MutationEvent is supported by the
implementation. In order to fully support this module, an
implementation must also support the "Events"
feature defined in this specification. For additional
information about conformance,
please see the DOM Level 3 Core specification [DOM Level 3 Core]. This
MutationEvent interface is built on top of the DOM
Level 2 Mutation Events [DOM Level 2 Events] module,
i.e. a DOM Level 3 MutationEvent interface
implementation where
hasFeature("MutationEvents","3.0") returns
true must also return true when the
version number is "2.0",
"" or, null.
| type | Context information |
|---|---|
| DOMSubtreeModified | None |
| DOMNodeInserted |
MutationEvent.relatedNode holds the parent
node of the node being inserted.
|
| DOMNodeRemoved |
MutationEvent.relatedNode holds the parent
node of the node being removed.
|
| DOMNodeRemovedFromDocument | None |
| DOMNodeInsertedIntoDocument | None |
| DOMAttrModified |
MutationEvent.attrName is in use. The value
of MutationEvent.relatedNode indicates the
Attr node whose value has been affected. The
value of MutationEvent.attrChange indicates
whether the Attr was modified, added, or
removed. If the Attr node is being added,
MutationEvent.newValue is in use. If the
Attr node is being removed,
MutationEvent.prevValue is in value. If the
Attr node is being modified,
MutationEvent.newValue and
MutationEvent.prevValue are in use.
|
| DOMCharacterDataModified |
MutationEvent.prevValue, and
MutationEvent.newValue are in use.
|
- Interface MutationNameEvent (introduced in DOM Level 3)
-
The
MutationNameEventinterface provides specific contextual information associated with Mutation name event types.To create an instance of the
MutationNameEventinterface, use theDocument.createEvent("MutationNameEvent")method call.
IDL Definition-
// Introduced in DOM Level 3: interface MutationNameEvent : MutationEvent { readonly attribute DOMString prevNamespaceURI; readonly attribute DOMString prevNodeName; // Introduced in DOM Level 3: void initMutationNameEvent(in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in Node relatedNodeArg, in DOMString prevNamespaceURIArg, in DOMString prevNodeNameArg); // Introduced in DOM Level 3: void initMutationNameEventNS(in DOMString namespaceURI, in DOMString typeArg, in boolean canBubbleArg, in boolean cancelableArg, in Node relatedNodeArg, in DOMString prevNamespaceURIArg, in DOMString prevNodeNameArg); };
- Attributes
prevNamespaceURIof typeDOMString, readonly-
The previous value of the
relatedNode'snamespaceURI.
prevNodeNameof typeDOMString, readonly-
The previous value of the
relatedNode'snodeName.
- Methods
initMutationNameEventintroduced in DOM Level 3-
The
initMutationNameEventmethod is used to initialize the value of aMutationNameEventobject and has the same behavior asMutationEvent.initMutationEvent().ParameterstypeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
relatedNodeArgof typeNode-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
prevNamespaceURIArgof typeDOMString-
Specifies
MutationNameEvent.prevNamespaceURI. This value may benull.
prevNodeNameArgof typeDOMString-
Specifies
MutationNameEvent.prevNodeName.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions initMutationNameEventNSintroduced in DOM Level 3-
The
initMutationNameEventNSmethod is used to initialize the value of aMutationNameEventobject and has the same behavior asMutationEvent.initMutationEventNS().ParametersnamespaceURIof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
typeArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
canBubbleArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
cancelableArgof typeboolean-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
relatedNodeArgof typeNode-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEventNS()method for a description of this parameter.
prevNamespaceURIArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
prevNodeNameArgof typeDOMString-
Refer to the
MutationEvent.initMutationEvent()method for a description of this parameter.
No Return ValueNo Exceptions
The mutation name event types are listed below. For a full
description of the semantics associated with these event types,
refer to the Complete list of event types. A DOM
application may use the hasFeature(feature,
version) method of the DOMImplementation
interface with parameter values "MutationNameEvents" and "3.0"
(respectively) to determine whether or not the
MutationNameEvent is supported by the
implementation. In order to fully support this module, an
implementation must also support the
"MutationEvents" feature defined in this
specification and the "Core" feature defined in the
DOM Level 3 Core specification [DOM Level 3 Core]. For additional information about conformance,
please see the DOM Level 3 Core specification [DOM Level 3 Core].
| type | Context information |
|---|---|
| DOMElementNameChanged |
MutationNameEvent.prevNamespaceURI, and
MutationNameEvent.prevNodeName are in use.
|
| DOMAttributeNameChanged |
MutationNameEvent.prevNamespaceURI, and
MutationNameEvent.prevNodeName are in
use. The value of MutationEvent.relatedNode
contains the renamed Attr node.
|
1.7.6 Basic event types
This event module contains basic event types associated with document manipulation.
A DOM application may use the hasFeature(feature,
version) method of the DOMImplementation
interface with parameter values "BasicEvents" and
"3.0" (respectively) to determine whether or not
the basic event module is supported by the implementation. In
order to fully support this module, an implementation must also
support the "Events" feature defined in this
specification. For additional information about conformance,
please see the DOM Level 3 Core specification [DOM Level 3 Core].
The basic event types are listed below. For a full description of the semantics associated with these event types, refer to the Complete list of event types.
The event types {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "resize"} and
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "scroll"} implement the
UIEvent interface. All other HTML event types implement
at least the basic Event interface. However, they
may be generated from a user interface; in that case, the event
objects also implements the UIEvent interface and
UIEvent.view is in use.
| type | Context information |
|---|---|
| load |
UIEvent.view may be in use.
|
| unload | (same as above) |
| abort | (same as above) |
| error | (same as above) |
| select | (same as above) |
| change | (same as above) |
| submit | (same as above) |
| reset | (same as above) |
| resize |
UIEvent.view is in use.
|
| scroll |
UIEvent.view is in use.
|
1.7.7 HTML Events
The HTML event module is composed of events listed in [HTML 4.01] and additional events which
are supported in DOM Level
0 browsers. It refines the semantics and scope of the
basic event types and provides two new event types. This event
module is only applicable if the Document supports
the [DOM Level 2 HTML]
specification. Use Node.isSupported(feature,
version) with the parameter values "HTML" and "2.0"
(respectively) to determine whether or not the
Document node supports the HTML module.
A DOM application may use the hasFeature(feature,
version) method of the DOMImplementation
interface with parameter values "HTMLEvents" and
"3.0" (respectively) to determine whether or not
the HTML event module is supported by the implementation. In
order to fully support this module, an implementation must also
support the "BasicEvents" feature defined in this
specification and the "HTML" feature defined in
[DOM Level 2 HTML]. For additional information about
conformance,
please see the DOM Level 3 Core specification [DOM Level 3 Core]. The DOM Level 3 HTML Events module is built on
top of the DOM Level 2 HTML Events [DOM Level 2 Events]
module, i.e. a DOM Level 3 HTML Events implementation where
hasFeature("HTMLEvents", "3.0") returns
true must also return true when the
version number is "2.0",
"" or, null.
The following descriptions of event types are refinements of the
general descriptions provided in Complete list of event types, with the addition of the
events {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "focus"} and
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "blur"}. All events types are
bound to the namespace URI "http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events" and the
following list only enumerates the local name of the event type.
- load
- The DOM implementation finishes loading all content within the BODY element, all frames within a FRAMESET, or any resource linked from the document.
- unload
- The DOM implementation removes a document from a window or frame. This event is valid for BODY and FRAMESET elements.
- abort
- The page loading is stopped before an image has been allowed to completely load. This event applies to OBJECT elements.
- error
- An image does not load properly or when an error occurs during script execution. This event is valid for OBJECT elements, BODY elements, and FRAMESET element.
- select
- A user selects some text in a text field either via the user interface or via attributes defined in [DOM Level 2 HTML]. This event is valid for INPUT and TEXTAREA elements.
- change
-
A control loses the input focus and its value has been
modified since gaining focus. This event can occur either
via a user interface manipulation or the
focus()methods and the attributes defined in [DOM Level 2 HTML]. This event is valid for INPUT, SELECT, and TEXTAREA element. - submit
-
A form is submitted either via a button. This event only
applies to the FORM element. Note that the
HTMLFormElement.submit()method defined in [DOM Level 2 HTML] does not fire this event type. - reset
-
A form is reset either via a button, or the
HTMLFormElement.reset()method defined in [DOM Level 2 HTML]. This event only applies to the FORM element. - resize
- see resize in Complete list of event types.
- scroll
- see scroll in Complete list of event types.
- focus
-
An element receives focus either via a pointing device,
the
focus()methods defined in [DOM Level 2 HTML], or by tabbing navigation. This event is only valid for the following elements: A, AREA, LABEL, INPUT, SELECT, TEXTAREA, and BUTTON. This event type is dispatched after the event type {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMFocusIn"}. - blur
-
An element loses focus either via a pointing device, the
blur()methods defined in [DOM Level 2 HTML], or by tabbing navigation. This event is only valid for the following elements: A, AREA, LABEL, INPUT, SELECT, TEXTAREA, and BUTTON. This event type is dispatched after the event type {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMFocusOut"}.
The following table provides refinements or additional information on the event types. Some events will only be dispatched to a specific set of possible targets, specified using HTML node types.
| type | Bubbling phase | Cancelable | Target node types | DOM interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| load | [no changes] | [no changes] |
HTMLDocument,
HTMLBodyElement,
HTMLFrameSetElement,
HTMLObjectElement,
HTMLLinkElement,
HTMLMetaElement,
HTMLScriptElement,
HTMLFrameElement,
HTMLIFrameElement,
HTMLImageElement
| [no changes] |
| unload | [no changes] | [no changes] |
HTMLDocument,
HTMLBodyElement,
HTMLFrameSetElement
| [no changes] |
| abort | [no changes] | [no changes] |
HTMLObjectElement
| [no changes] |
| error | [no changes] | [no changes] |
HTMLObjectElement,
HTMLBodyElement,
HTMLFrameSetElement
| [no changes] |
| select | [no changes] | [no changes] |
HTMLInputElement,
HTMLTextAreaElement
| [no changes] |
| change | [no changes] | [no changes] |
HTMLInputElement,
HTMLSelectElement,
HTMLTextAreaElement
| [no changes] |
| submit | [no changes] | [no changes] |
HTMLFormElement
| [no changes] |
| reset | [no changes] | [no changes] |
HTMLFormElement
| [no changes] |
| resize | [no changes] | [no changes] |
HTMLDocument, HTMLElement
| [no changes] |
| scroll | [no changes] | [no changes] |
HTMLDocument, HTMLElement
| [no changes] |
| focus | No | No |
HTMLAnchorElement,
HTMLAreaElement,
HTMLLabelElement,
HTMLInputElement,
HTMLSelectElement,
HTMLtextAreaElement,
HTMLButtonElement.
|
Event |
| blur | No | No |
HTMLAnchorElement,
HTMLAreaElement,
HTMLLabelElement,
HTMLInputElement,
HTMLSelectElement,
HTMLtextAreaElement,
HTMLButtonElement.
|
Event |
The event types {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "focus"} and
{"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "blur"} may be generated from a
user interface; in that case, the event objects also implements
the UIEvent interface and UIEvent.view
is in use.
1.7.7.1 Activation and default actions
The concept of activation ({"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMActivate"}) was introduced in [DOM Level 2 Events] to separate generic actions from the
devices used to activate them. For example, an hyperlink can
be activated using a mouse or a keyboard, and the activation
will force the user agent to follow the link. It is expected
that the action of following the link is done using a default
action attached to the hyperlink element. In such case, the
default action of the device event type is to trigger the
event type {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"DOMActivate"}. Preventing the default action of a
mouse click when the target node is an hyperlink will prevent
the activation. The same approach is made for control
elements.
Implementations could react to an event before dispatching it
and do changes on the display and the DOM tree. In such case,
if a DOM attribute is changed before the event is fired,
cancelling the device event type will also reverse the
change. A good example is the attribute
HTMLInputElement.checked: As described in [DOM Level 2 HTML], the value of this property may be changed
before the dispatch of the event; the user clicks on the radio
button, the radio button is being checked (or unchecked) on
the display, the attribute
HTMLInputElement.checked is changed as well, and
then the device event type {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events",
"click"} is being dispatched. If the default action of
the device event type is prevented, or if the default action
attached to the {"http://www.w3.org/2001/xml-events", "DOMActivate"}
event type is prevented, the property
HTMLInputElement.checked will need to be changed
back to its original value.