This document details and deepens some of the most important
conformance-related concepts evoked in the QA Specification Guidelines,
developing some of the analysis axes that need to be considered while designing a specification and providing advanced techniques, particularly for
dealing with conformance variability and complexity
This section describes the status of this document at the time of its publication. Other documents may supersede this document. A list of current W3C publications and the latest revision of this technical report can be found in the W3C technical reports index at http://www.w3.org/TR/.
This document is a First Public Working Draft made available by
the W3C Quality Assurance (QA) Activity for discussion by W3C members and
other interested parties. For more information about the QA Activity, please
see the QA Activity
statement.
It essentially contains Concepts section of the November 2003 version of the Specification Guidelines, which the Working Group found useful to maintain and develop, but independently from the main document of the Specification Guidelines in consequence of the decision to make the Specification Guidelines lighter to read. There are a few open issues, marked with a capitalized ISSUE
keyword.
Publication as a Working Draft does not imply endorsement by
the W3C Membership. This is a draft document and may be updated, replaced or
obsoleted by other documents at any time. It is inappropriate to cite this
document as other than work in progress.
The QA Working Group does not expect this document to become a Recommendation. Rather, after further development, review and refinement, it will be published and maintained as a WG Note.
You may email comments on this document to www-qa@w3.org, the publicly archived list
of the QA Interest Group. Please note
that comments that you make will be publicly archived and
available, do not send information you would not want to see distributed,
such as private data.
-
Introduction
- Dimensions of
Variability (DoV)
- Specification category and class of
product
- Profiles, Modules, Levels
- Acknowledgments
- References
This document analyzes how design decisions of the conformance model of a specification may affect its implementability and the interoperability of its implementations. To do so, it introduces the concept of variability - how much implementations conforming to a given specification may vary among themselves - and presents a set of well-known dimensions of variability.
Its goal is to raise awareness of the potential cost that some benign-looking decisions may have on interoperability and to provide guidance on how to avoid these pitfalls by better understanding the mechanisms induced by variability.
It completes and deepens the concepts evoked in the Specification Guidelines.
Like the Specification Guidelines, the primary audience of this document is editors and authors, however, it
is applicable to a broader audience including:
- those who review specifications during their development
- implementers of specifications
- builders of test materials, including conformance test suites and
tools.
This document first introduces the concept of dimensions of variability, and then analyzes the specific aspects related to some of these dimensions, more specifically the classes of products, and the subdividing dimensions profiles, modules and levels.
Several principles of the Specification Guidelines address a way in which the
conformance model of a specification might allow variation among
conforming implementations. For example, a specification might allow
implementations to choose between one of two well defined behaviors for a
given functionality, thus two conforming implementations might vary on that
aspect.
The QA Working Group has identified
seven ways in which a specification can allow variability, that
are referred to as dimensions of variability (DoV).
The seven dimensions of variability recognized by this document
are:
- classes of product - the generic name for the group of products that would implement, for the same purpose, the specification,
- profiles - a subset of a technology that is tailored to meet specific functional requirements of a particular application community,
- modules - a collection of semantically-related features that represents a unit of functionality,
- levels - a technology subset that is one of a hierarchy of nested subsets, ranging from minimal or core functionality to full or complete functionally ,
- deprecation - the process of marking certain features as outdated and being phased out,
- discretionary items - deliberate and explicit grants of discretion by the specification to the implementations, that describe or allow optionality of behavior, functionality, parameter values, error handling, etc.,
- extensibility - a mechanism allowing any party to create extensions.
The above are not necessarily all orthogonal to one another. There are
many possible associations, dependencies, and interrelationships. As a
general policy, this document and the Specification Guidelines do not attempt to legislate
correct or proper relationships among the DoV. Rather, they try to clarify
the nature of each dimension and suggest that specifications designers make deliberate
and well documented choices.
The dimensions of variability are one of the principal concepts in the Specification Guidelines to help organize, classify and assess the conformance
characteristics of W3C specifications. The seven DoV get special attention because
they are at the core of the definition of a specification's conformance
model, and thus there is significant potential for negative interoperability
impacts if they are handled carelessly or without careful deliberation.
As a general principle, variability complicates
interoperability. In theory, interoperability is best when there are
numerous identical, complete, correct implementations. However, in
practice, the net effect of conformance variability is not necessarily
negative in all cases, when compared to the alternatives. For example
profiles — subdivisions of the technology targeted at specific
applications communities — introduce variability among
implementations. Some will implement Profile ABC, some will implement Profile
XYZ, and the two might not intercommunicate well if ABC and XYZ are fairly
different. However, if ABC and XYZ are subsets of a large monolithic
specification — too large for many implementors to tackle in total --
and if they are well targeted at actual application sectors, then subdivision
by profiles may actually enhance interoperability.
Different sorts of variability have different negative and positive
impacts. The principal danger is "excessive" variability -
variability which goes beyond that needed for a positive interoperability
trade-off, and which unnecessarily complicates the conformance landscape.
Specification writers need to carefully consider and justify any conformance
variability allowed, do so by reference to the project requirements and use
cases, and explicitly document the choices made.
It is even more important to take
into account the multiplicative effect on variability created by combining
several dimensions of variability; each pair of dimensions of variability used in a specification needs to be
assessed with regard to the variability it creates; the writers should
document the limited ways an implementation can combine two dimensions. For
instance, deprecated features in HTML 4.01 [HTML4] are allowed in the Transitional profile and
forbidden in the Strict profile.
Note that the variability addressed by the so called
dimensions of variability is only considered with regard to conformance to a
well-defined specification. As such, the changes introduced in the
conformance requirements between two versions or two editions of the
specification are not considered as dimensions of variability.
The most visible dimension of variability is the the classes of products, which separate the different kind of implementations a specification may have; for instance, SVG 1.1 [SVG11] defines conformance for 6 classes of product: SVG document fragments, SVG stand-alone files, SVG included documents fragments, SVG generators, SVG interpreters, SVG viewiers.
Defining these classes of products is thus one of the most important step in the design of a conformance model for a specification; this section tries and gives advices on how to do this design, introducing to do so the concept of specification categories.
ISSUE: needs to explain the different categories, how to actually make a specification category analysis
To answer the question "what needs to conform?" it helps to first look at the nature of the specification and categorize it and then look at
the types of products that would implement the
specification. Categorizing the specification provides a basis for
classifying the software that may be affected by the specification.
The specification category is the generic
name for the type of specification and the technology it describes.
The following is a list of some of the most common specification
categories:
- foundation or abstract (e.g., Infoset),
- content/data (e.g., MathML, SVG),
- protocols (e.g., SOAP),
- processors (e.g., XSLT,
XML Query),
- APIs (e.g.,
DOM),
- notation/syntax (e.g., XPath),
- set of events (e.g., one part of XForms),
- rules for deriving profiles (e.g., part of SMIL),
- guidelines (e.g., WCAG, QA Operational Guidelines).
The categories indicate what the specification describes. One
specification could potentially fall into more than one category. This
list does not exhaust all possibilities. Specifications may have to define
their own specification category if none of these fits.
From this categorization of specifications, a Working Group can identify the class of
products that are affected by the specification. Classes of products
can be generalized as either producers or consumers, or as
content itself.
For example, identifying which are producers and consumers is clear for a
protocol-type specification: the two parties to the dialog are the targets.
For a processor-type specification, the processor is the consumer of an
XML vocabulary defined
in the specification. For content-type specifications, there may be one or
more consumers that take the content and 'play' or 'read' it in some way.
The following is a list of the
most common classes of products for W3C
specifications:
- content (of type, meaning, and format as defined in the
specification),
- producer of content (may be divided into initiators and modifiers),
- player (read-only consumer, conveys content in non- XML way),
- consumer in a one-way pipeline,
- responding agent (e.g., server) of API (consumer and
producer),
- processor (consumer of its vocabulary/instructions),
- module that hosts the processor,
- producer of instructions/commands to processor,
- profile derived from the specification's Rules for Profiles,
- specification (guidelines).
This list does not exhaust all possibilities. Specifications may have
to define their own classes of product if none of these fits.
Profiles, modules and levels are three ways to
subdivide a specification into related groups of conformance requirements.
Because these three dimensions of variability define subsets of a technology,
they share some characteristics in the way they affect conformance and
interoperability.
A profile is a subset of the technology that
supports a particular functional objective or a subset of a set of
technologies defining how they are required to operate together (e.g., XHTML
plus MathML plus
SVG).
Profiles can be based on hardware considerations associated with target
product classes — for example, SVG Tiny is aimed at mobile phones
— or they may be driven by other functional requirements of their
target constituencies — for example, a graphical profile tailored for
technical illustrations in aircraft maintenance manuals.
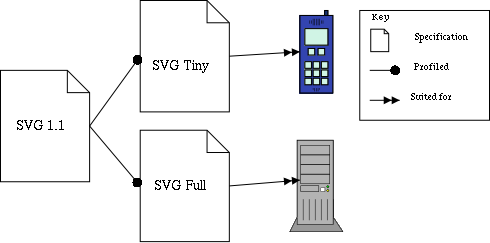
Diagram illustrating profiles used to adapt the SVG Technology to different
platforms.
The use of profiles to divide the technology is described in the
specification, and may or may not be reflected and paralleled by the
structure and organization of the specification.
Specifications may define individual profiles, or may define rules for
profiles, or both. An individual profile defines the requirements
for classes of products that conform to that profile. Rules for
profiles define validity criteria for profiles themselves —
i.e., if others (users, applications, or other standards) define their own
profiles of the standard (called derived profiles of the
specification), then rules for profiles define the constraints that
those derived profiles must
satisfy in order to be considered valid profiles of the specification.
For example, XHTML Modularization ([XHTML-MOD], section 3) and Synchronized
Multimedia Integration Language (SMIL 2.0), [SMIL20] specifications both define rules for profiles --
what constraints must a profile meet in order to be classified as a "Host
Language Profile" or an "Integration Set Profile." SMIL further defines some
specific profiles, using the modularization. Separate recommendations --
XHTML Basic [XHTML-BASIC] and XHTML 1.1 [XHTML11] — define specific profiles
based on the XHTML modularization.
Modules are
discrete divisions or functional groupings of the technology and
do not necessarily fit in a simple hierarchical structure.
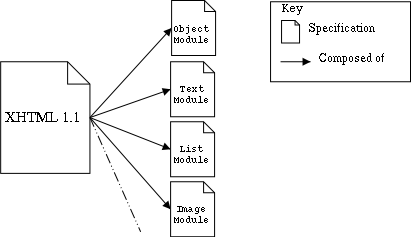
Diagram illustrating modules used to divide XHTML 1.1 in re-usable
components.
Modules generally can be implemented independently of one another —
e.g., audio vs. video module. That notwithstanding, it is possible for one
module's definition (and therefore implementation) to have explicit
dependency upon another module. It is not only possible, but common to
implement multiple modules.
Functional levels — or in common
usage, simply levels — are used to group functionality into
nested subsets, ranging from minimal or core functionality to full or
complete functionally. Level 1 is the minimum or core of the technology.
Level 2 includes all of level 1 plus additional functionality. This nesting
continues until level n, which consists of the entire technology.
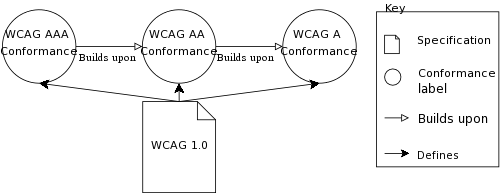
Diagrams illustrating levels of conformance in the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 1.0
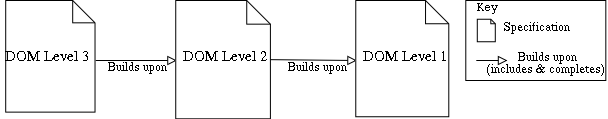
Diagram illustrating levels used to build up the Document Object Model.
Levels may result from progressive historical development and enrichment
of the technology in a series of specifications, as in the case of CSS and DOM. Levels could also be defined
explicitly in a single edition of the specification, as in the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines.
Sometimes, the nesting goal of levels is achieved through profiles. For example, SVG 1.1 [SVG11] together with SVG Mobile [Mobile [SVG-MOBILE] define three nested profiles
— Tiny, Basic, Full — which are each targeted at a specific
graphics hardware community (mobile phone, hand-held computer, desktop
computer).
ISSUE: needs to address discretionary items, and more largely, the remaining DoV.
The following QA Working Group and Interest Group participants have
contributed significantly to the content of this document:
- Patrick Curran (Sun Microsystems)
- Dimitris Dimitriadis (Ontologicon)
- Karl Dubost (W3C)
- Dominique Hazael-Massieux (W3C)
- Lofton Henderson (CGM Open)
- Ian Jacobs (W3C)
- Sandra Martinez (NIST)
- David Marston (IBM Research)
- Lynne Rosenthal (NIST)
- Alex Rousskov (Measurement Factory)
- Mark Skall (NIST)
- Andrew Thackrah (Open Group)
- Olivier Thereaux (W3C)
These references are informative.
- [HTML4]
- HTML 4.01
Specification, W3C Recommendation, 24 December 1999,
available at http://www.w3.org/TR/html401/.
- [SMIL20]
- Synchronized
Multimedia Integration Language
(SMIL 2.0), W3C Recommendation, 07 August 2001, available at
http://www.w3.org/TR/smil20/.
- [SVG11]
- Scalable Vector
Graphics (SVG) 1.1 Specification, D. Jackson, J. Ferraiolo,
J. Fujisawa, Eds., W3C Recommendation 14 January 2003, available at
http://www.w3.org/TR/2003/REC-SVG11-20030114/.
- [SVG-MOBILE]
- Mobile SVG
Profiles: SVG Tiny and SVG Basic, T. Capin, Editor, W3C
Recommendation, 14 January 2003, available at
http://www.w3.org/TR/2003/REC-SVGMobile-20030114/.
- [XHTML-MOD]
- Modularization of
XHTML, M. Altheim, F. Boumphrey, S. Dooley, S. McCarron, S.
Schnitzenbaumer, T. Wugofski,Eds., W3C Recommendation, 10 April 2001,
available at http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml-modularization/.
- [XHTML-BASIC]
- XHTML
Basic, M. Baker, M. Ishikawa, S. Matsui, P. Stark, T.
Wugofski, T. Yamakami, Eds., W3C Recommendation, 19 December 2000,
available at http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml-basic/.
- [XHTML11]
- XHTML 1.1
- Module-based XHTML, M. Altheim, S. McCarron, Eds., W3C
Recommendation, 31 May 2001, available at
http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/.