Amaya Overview
Amaya is a complete web browsing and authoring environment.
- Amaya lets users both browse and author Web pages
Using Amaya you can create Web pages and upload them onto a server. Authors can create a document from scratch, they can browse the web and find the information they need, copy and paste it to their pages, and create links to other Web sites. All this is done in a straightforward and simple manner, and actions are performed in a single consistent environment. Editing and browsing functions are integrated seamlessly in a single tool.
- Amaya maintains a consistent internal document model adhering to the
DTD
Amaya always represents the document internally in a structured way consistent with the Document Type Definition (DTD). A properly structured document enables other tools to further process the data safely.
Amaya allows you to display the document structure at the same time as the formatted view, which is portrayed diagrammatically on the screen. - Amaya is able to work on several documents at a time
Several (X)HTML, native MathML (.mml) and SVG (.svg) documents can be displayed and edited at a time.
- Amaya helps authors create hypertext links
The editor helps you create and text out links to other documents on the Web from the document you currently are working on. You can view the links and get a feel for how the information is interconnected. This feature is not limited to HTML anchors. With XLink, any MathML and SVG element can be a link too.
- Amaya includes a collaborative annotation application
Annotations are external comments, notes, remarks that can be attached to any Web document or a selected part of the document.
You can find a more detailed description of Amaya and of its features in the W3C Note "An Introduction to Amaya."
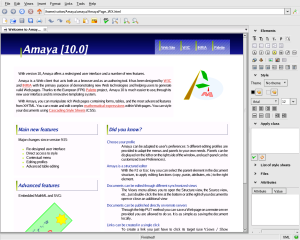
The image shows the Amaya main view. Along the top are a number of buttons associated with browsing. The panel at the right proposes a set of editing tools. At any time, the user can select any part of a document and assign to it an HTML type (H1, LI, EM, etc.), by means of the XHTML palette, or of the shortcut buttons. Such a command transforms the selected part into an element of the chosen type.
Transport protocols
Amaya accesses remote sites by means of HTTP/1.1. Implementation of this protocol is provided by the W3C libwww. Amaya takes advantage of the most advanced features of HTTP, such as content negotiation to retrieve the most appropriate picture format, keep alive connections to save bandwidth and authentication to allow secure remote publishing.
Support for CSS
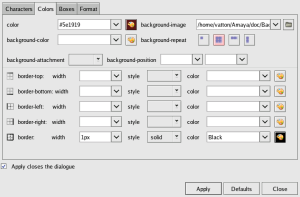
Amaya has support for the W3C style sheet language CSS although this is not yet complete. For a large set of properties like foreground color, background color, background image, alignment, etc. the user can interact on the formatted document by using style specific tools. In this case it's not necessary to well know about the CSS syntax. At the same time Amaya provides an efficient mechanism to test and associate external style sheets with HTML documents. Users can also use Amaya to download, edit and publish CSS style sheets as well as HTML pages.
Support for MathML
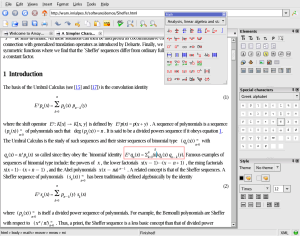
Amaya provides a support for MathML presentation markup which allows users to browse and edit Web pages containing mathematical expressions (see some examples). Like the rest of the document, these expressions are manipulated through specific editing tools proposed in the Amaya panel (palettes of constructors and special characters).
When a character string is typed in a MathML element, Amaya parses the string and automatically generates the elements mo (operator), mn (number), and mi (identifier).
Amaya uses namespaces to integrate MathML expressions within XHTML documents, i.e. HTML documents written in XML syntax. This mechanism is also used to mix graphics in SVG and mathematics in MathML within XHTML documents (see an example).
Support for SVG
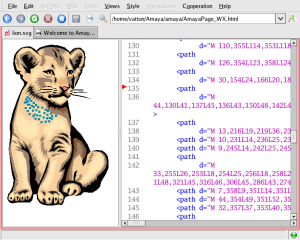
Amaya supports a subset of the Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) format, namely basic shapes, text, images, and foreignObject (the latter is useful to include HTML fragments or MathML expressions in drawings).
Alpha transparency, transformations, and animations are supported and the SVG source can be inspected and manipulated at any time.
The graphics are written in XML and may be mixed freely with HTML and MathML. It also has annotation capabilities.
Support for RDF and XPointer
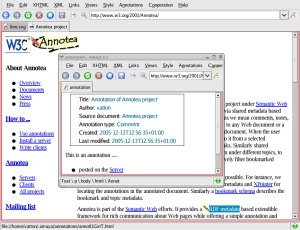
Amaya includes a collaborative annotation application based on Resource Description Framework (RDF), XLink, and XPointer. From the technical point of view, annotations are usually seen as metadata, as they give additional information about an existing piece of data. In this project, we use a special RDF annotation schema for describing annotations.
Annotations can be stored locally or in one or more annotation
servers. When a document is browsed, Amaya queries each of these
servers, requesting the annotations related to that document.. Amaya uses
XPointer to describe where an
annotation should be attached to a document. With this technique, it is
possible to annotate any Web document independently, without needing to edit
that document. Finally Amaya presents annotations with pencil annotation icons
 . and attaches XLink
attributes to these icons. If the user single-clicks on an annotation icon, the
text that was annotated is highlighted. If the user double-clicks on this icon,
the annotation text and other metadata are presented in a separate window.
. and attaches XLink
attributes to these icons. If the user single-clicks on an annotation icon, the
text that was annotated is highlighted. If the user double-clicks on this icon,
the annotation text and other metadata are presented in a separate window.