The Semantic Web
- What is the Semantic Web?
- Where did it come from?
- PICS, or Where has it been?
- RDF, DAML/OIL or Where is it up to?
- What does it do? Example - Accessibility
Charles McCN - charles@w3.org
The Semantic Web??
Using metadata to add (and extract) meaning
Part of the original design ideas of the Web
Now a W3C Activity in its own right
Let the computer do the work!
Some Key Technologies:
- RDF
- RDF, RDF
Schema, EARL, Dublin
Core, OIL, DAML
- XML architecture
- XML, Namespaces, XLink, Xpath, XML Schema
- XML languages
- XSLT, XHTML, SVG, SMIL
- As well as
- Annotea,
CC/PP, PICS, implementation
information that makes sense to people...
can be given semantics...
to let the computer add meaning for us.
Metadata...
What is it?
In Principio (of the Web)...
From HTML - IETF draft
1.2 of 1993
element link - this document links to that one
- Attribute
rel="X"
- The link to that document is of type X
- E.g.
<a href="gloss"
rel="glossary">xxx</a.>
- xxx is linked to something that is a glossary.
rel, rev are literal text values, for documents
or hypertext
old technology: PICS
level is 0, health is
9, colour is 27
often but not always gives a "minimum or maximum"
Works easily in major browsers
Includes a trust mechanism...
PICS is useful...
- Traditional uses
- Rating for censorship
- Local interest
- Education level/value
Ratings bureaus allow third parties to add metadata
... but PICS is limited
name = value pairs
Hard to describe relationships
Schemes become very complex
RDF has (a bit) more power
In RDF we can...
Relate anything that can have a URI
Have literal values (for the 3rd term of a triple)
Use anonymous nodes or first-class objects
Take some information...
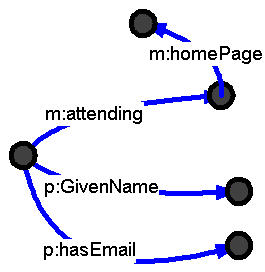
...and add to it
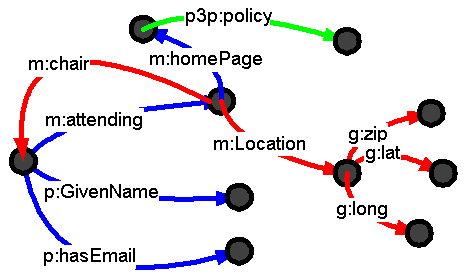
Architecture
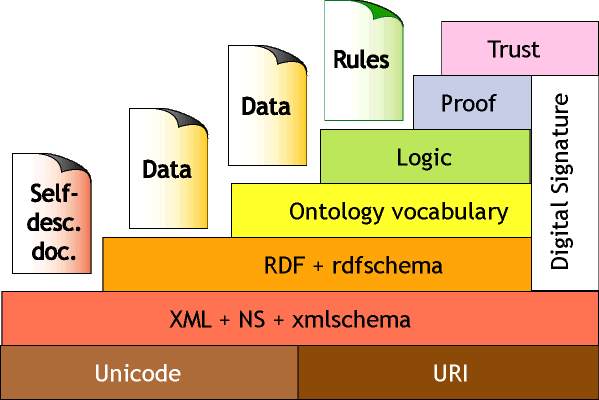
RDF+Schema layer
- Minimalist model - (thing), Class, Property
- Subproperty, Subclass
- Domain & Range
- Comments & labels
Very wide interoperability of RDF data
"Ontology" layer
- More metainformation, such as
- equivalence
- Unique, Cardinality, etc
- Ontology community exists
- Huge extra usage for extra functionality
Wide interoperability & interconversion
What is Accessibility?
Making the Web useful to all people
- Multiple devices
- Sign languages
- Text-rich or text-poor
- Motion, or motion free
"Transform Gracefully"
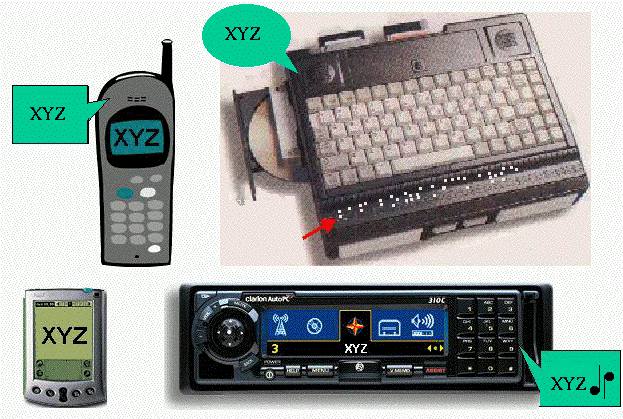

Different input or output
CC/PP - an RDF framework for multiple devices
Equivalent alternatives, and metadata, to specify related pieces
Assistive technology to render to the users
Conversion of languages
PICS helps access...
- Rate accessibility of content
- Language level
- Colour range
- Document size
... but mostly for rating afterwards
More powerful: RDF
Re-render the RDF...
A beta project: text-only RDF-aware SVG browser
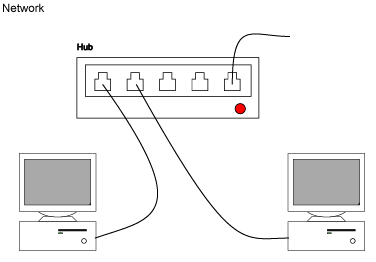
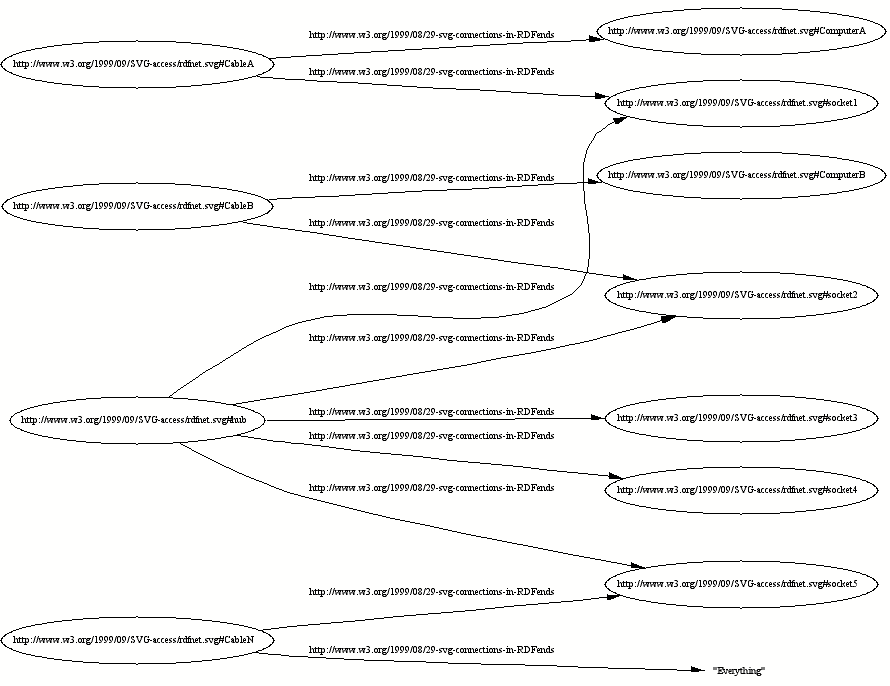
Cable A connects
Computer A and socket 1
Cable B connects
Computer B and socket 2
Cable N connects
external Network and
socket 5
the Hub connects
socket 1 and socket 2 and socket 3 and socket 4 and socket 5
Or re-render the RDF...
Combining technologies
Some XSLT or CSS stylesheet can be used to transform Semantic content
- for a screenreader (to text)
- to make a graphic view of a table
- for braille rendering (low resolution)
- (to work in a mobile phone...)
Text is difficult too...
is a symbol for the idea surprise
 is a symbol for the idea
Available as a video
is a symbol for the idea
Available as a video
The theory of relativity is
(available as a video)  :
: 
EARL - accessible authoring support
Evaluation And Report
Language
Assesment of a particular requirement (Accessibility or not):
Examples:
- Is the text alternative actually equivalent?
- Does the document meet "508 para. (l)"?
- Has the document been approved for publication?
- Are the links and source code valid?
EARL pictured
EARL - use case (authoring)
The content team puts together a news item
- Noted they used a presupplied alternative for an image
- Claimed they meet the QuickTips requirements
Three assessment tools are used, because tool B does some bits well but
not others
EARL - use case (publishing)
The sub-editors' tools check for existing reports
- check presupplied text alternatives
- edit for simpler language
- ...
Each repair is noted and need not be checked again until something
changes
Thank You! Questions?
All W3C presentations are on the
Web: http://www.w3.org/Talks









 is a symbol for the idea
Available as a video
is a symbol for the idea
Available as a video :
: 