 |
 |
 |
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming API for HTML and XML documents. It defines the logical structure of documents and the way a document is accessed and manipulated. In the DOM specification, the term "document" is used in the broad sense - increasingly, XML is being used as a way of representing many different kinds of information that may be stored in diverse systems, and much of this would traditionally be seen as data rather than as documents. Nevertheless, XML presents this data as documents, and the DOM may be used to manage this data.
With the Document Object Model, programmers can create and build documents, navigate their structure, and add, modify, or delete elements and content. Anything found in an HTML or XML document can be accessed, changed, deleted, or added using the Document Object Model, with a few exceptions - in particular, the DOM interfaces for the internal subset and external subset have not yet been specified.
As a W3C specification, one important objective for the Document
Object Model is to provide a standard programming interface that
can be used in a wide variety of environments and applications.
The Document Object Model can be used with any programming
language. In order to provide precise, language-independent specification
of the Document Object Model interfaces, we have chosen to define
the specifications in OMG IDL, as defined in the CORBA 2.2
specification.
In addition to the OMG IDL specification,
we provide language bindings for Java and ECMAScript (an
industry-standard scripting language based on JavaScript and
JScript). Note: OMG IDL is used only as a language-independent and
implementation-neutral way to specify interfaces. Various other
IDLs could have been used; the use of OMG IDL does not imply a
requirement to use a specific object binding runtime.
The Document Object Model is a programming API for documents. The object model itself closely resembles the structure of the documents it models. For instance, consider this table, taken from an HTML document:
<TABLE>
<ROWS>
<TR>
<TD>Shady Grove</TD>
<TD>Aeolian</TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD>Over the River, Charlie</TD>
<TD>Dorian</TD>
</TR>
</ROWS>
</TABLE>
The Document Object Model represents this table like this:
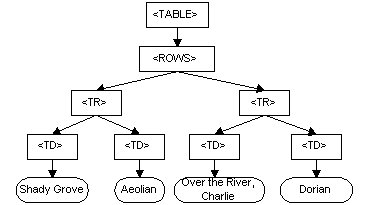
In the Document Object Model, documents have a logical structure which is very much like a tree; to be more precise, it is like a "forest" or "grove" which can contain more than one tree. However, the Document Object Model does not specify that documents be implemented as a tree or a grove , nor does it specify how the relationships among objects be implemented in any way. In other words, the object model specifies the logical model for the programming interface, and this logical model may be implemented in any way that a particular implementation finds convenient. In this specification, we use the term structure model to describe the tree-like representation of a document; we specifically avoid terms like "tree" or "grove" in order to avoid implying a particular implementation. One important property of DOM structure models is structural isomorphism: if any two Document Object Model implementations are used to create a representation of the same document, they will create the same structure model, with precisely the same objects and relationships.
The name "Document Object Model" was chosen because it is an "object model" is used in the traditional object oriented design sense: documents are modeled using objects, and the model encompasses not only the structure of a document, but also the behavior of a document and the objects of which it is composed. In other words, the nodes in the above diagram do not represent a data structure, they represent objects, which have functions and identity. As an object model, the Document Object Model identifies:
The structure of SGML documents has traditionally been represented by an abstract data model, not by an object model. In an abstract data model, the model is centered around the data. In object oriented programming languages, the data itself is encapsulated in objects which hide the data, protecting it from direct external manipulation. The functions associated with these objects determine how the objects may be manipulated, and they are part of the object model.
The Document Object Model currently consists of two parts,
DOM Core and DOM HTML. The DOM Core represents the
functionality used for XML documents, and also serves as the
basis for DOM HTML. All DOM implementations must support the
interfaces listed as "fundamental" in the Core specification;
in addition, XML implementations must support the interfaces
listed as "extended" in the Core specification. The Level 1
DOM HTML specification defines additional functionality
needed for HTML documents.
This section is designed to give a more precise understanding of the Document Object Model by distinguishing it from other systems that may seem to be like it.
The Document Object Model originated as a specification to
allow JavaScript scripts and Java programs to be portable among
web browsers. Dynamic HTML was the immediate ancestor of the
Document Object Model, and it was originally thought of largely
in terms of browsers. However, when the Document Object Model
Working Group was formed, it was also joined by vendors in other
domains, including HTML or XML editors and document
repositories. Several of these vendors had worked with SGML
before XML was developed; as a result, the Document Object Model
has been influenced by SGML Groves and the HyTime standard. Some
of these vendors had also developed their own object models for
documents in order to provide programming APIs for SGML/XML
editors or document repositories, and these object models have
also influenced the Document Object Model.
In the fundamental DOM interfaces, there are no objects representing entities. Numeric character references, and references to the pre-defined entities in HTML and XML, are replaced by the single character that makes up the entity's replacement. For example, in:
the "&" will be replaced by the character "&", and the text in the <p> element will form a single continuous sequence of characters. The representation of general entities, both internal and external, are defined within the extended (XML) interfaces of the Level 1 specification. Note: When a DOM representation of a document is serialized as XML or HTML text, applications will need to check each character in text data to see if it needs to be escaped using a numeric or pre-defined entity. Failing to do so could result in invalid HTML or XML.
<p>This is a dog & a cat</p>
The DOM specifies interfaces which may be used to manage XML or HTML documents. It is important to realize that these interfaces are an abstraction - much like "abstract base classes" in C++, they are a means of specifying a way to access and manipulate an application's internal representation of a document. In particular, interfaces do not imply a particular concrete implementation. Each DOM application is free to maintain documents in any convenient representation, as long as the interfaces shown in this specification are supported. Some DOM implementations will be existing programs that use the DOM interfaces to access software written long before the DOM specification existed. Therefore, the DOM is designed to avoid implementation dependencies; in particular,
The DOM Level 1 specification is intentionally limited to those methods needed to represent and manipulate document structure and content. Future Levels of the DOM specification will provide: