Scenario B: The XML source has encrypted elements and content accessible by a number of applications. When one of these applications queries an encrypted element, that app needs to decrypt the element but MUST NOT modify the source.
Scenario A: SOAP msg w/ encrypted data
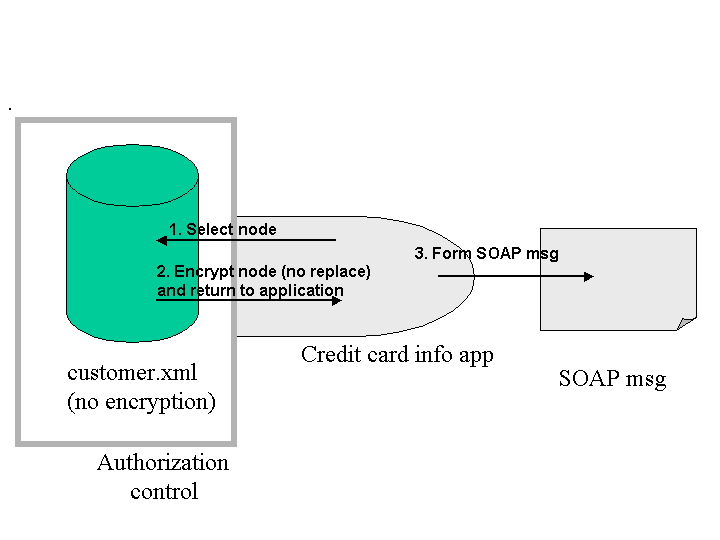
Scenario A: SOAP message
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Envelope xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/06/soap-envelope">
<Body>
<VerifyCreditCardRequest xmlns="http://…/actions">
<EncryptedData Type="NodeList“ xmlns="http://…/xmlenc">
<EncryptionMethod Algorithm="urn:nist-gov:tripledes…">
<IV>adCwS3wowQ8=</IV>
</EncryptionMethod>
…<CipherData>Ynj…M1f</CipherData>…
</EncryptedData>
</VerifyCreditCardRequest>
</Body>
</Envelope>
Scenario A code
Encrypting
// Encrypt the content of the 2nd/ element nodeToBeEncrypted = XPathAPI.selectSingleNode(doc, "//Customer[2]/CreditCard/Number"); // Encrypt the nodes (whole elements are encrypted) Element elemEncryptedData = xmlencEncryptor.encrypt((Element)nodeToBeEncrypted, false, getEncryptedDataTemplate(desKey, false), desKey); Document docSoap = new DocumentImpl(); Element elemEnvelope = docSoap.createElement("Envelope"); Element elemBody = docSoap.createElement("Body"); Element elemBodyChild = docSoap.createElement("VerifyCreditCardRequest"); Node nodeImported = docSoap.importNode(elemEncryptedData, true); elemBodyChild.appendChild(nodeImported); elemBody.appendChild(elemBodyChild); elemEnvelope.appendChild(elemBody); docSoap.appendChild(elemEnvelope);
Scenario A code…
Note: The preceding code works (uses IBM’s XSS4J) but, according to the spec, its illegal because the XML source is not being replaced.
Scenario B: Encrypted customer DB
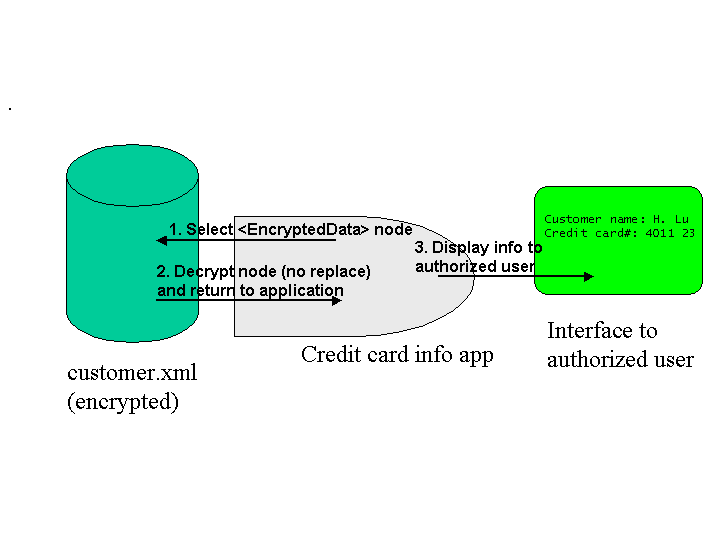
Scenario B code
Decrypting
// Get the nodes to be decrypted
Element elemEncryptedDataToDecrypt = (Element)
DOMUtil.getElementsByTagNameNS(doc, XEncryption.XMLENC_NS,
"EncryptedData").item(5);
Element elemIV = (Element)
elemEncryptedDataToDecrypt.getElementsByTagName("IV").item(0);
String strIV = elemIV.getFirstChild().getNodeValue();
Element elemCipherData = (Element)
elemEncryptedDataToDecrypt.getElementsByTagName("CipherText").item(0);
String strCipherData = elemCipherData.getFirstChild().getNodeValue();
javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec ivparmspec = new
javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec(com.ibm.xml.dsig.Base64.decode(strIV));
Cipher desCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
desCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, desKey, ivparmspec);
byte[] bytesPlainData = desCipher.doFinal(com.ibm.xml.dsig.Base64.decode(strCipherData));
String strCreditCardNumber = new String(bytesPlainData);
Scenario B code…
Don’t want to use decryptAndReplace() because I don’t want to modify the XML source.
But XML Encryption doesn’t allow Toolkits to give me an alternative so I have to use low-level security APIs instead!
Rather, XML Encryption should allow Toolkits to return the decrypted XML element or content without requiring replacement in the source.
QAQ (Quietly Anticipated Questions)
Question: Why not create a dummy document before and/or after encrypting?
Answer: Yes, one could create a dummy document and copy in the relevant elements before encrypting or decrypting and still conform to the XML Encryption spec as it currently stands. However, this would be inefficient and often inelegant.
Question: The example code you showed doesn’t deal with more complex context situations such as inherited namespaces, default attributes, etc.. How will those artifacts affect the no-replacement processing of <EncryptedData> elements?
Answer: I think this question will only be answered through more coding and application experience. There could be some issues that arise.