Policies shaping the Web in Europe
Gilles Kahn
W3C10 Europe
3 June 2004
Policies shaping the Web in Europe
Eric Velleman (Bartimeus) - Web Accessibility
perspective
Isabelle Falque-Pierrotin (Internet Rights Forum) - Internet Policy: Overcoming Contradictions
Peter Brown (European Parliament) - Policies shaping the
Web in EuropeStandards, the Public Sector and the Web
Moderator: Gilles Kahn (INRIA)
Web Accessibility perspective
eInclusion, Europe and WAI, Netherlands best-practice and
harmonization

Eric Velleman, Director, Bartimeus Accessibility Foundation
Demographics for Accessibility
- Total 730 M people in Europe in 2005
- 80 mobiles/100p
- Domain names: 52,914,393
- 37 M persons with disability, excluding RSI and cognitive
disability.
- By 2020: 25% population over 60 (largest increase in 75+)
Source: Internet World
Stats
People use the Web
|
People on the Internet (xM) |
| Asia |
302 |
| Europe |
259 |
| North America |
221 |
What are they all looking for?
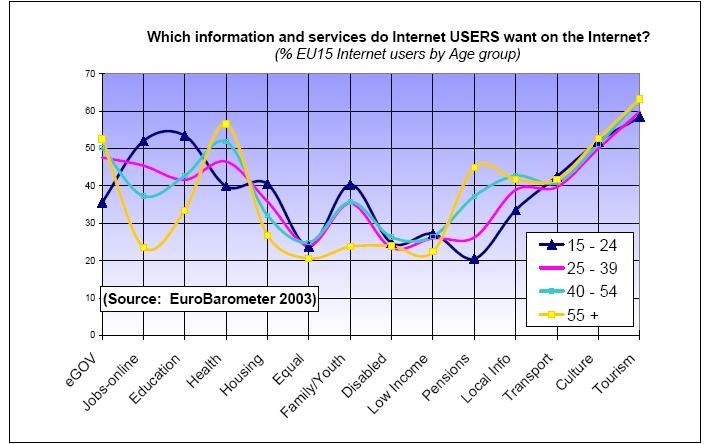
Shopping online
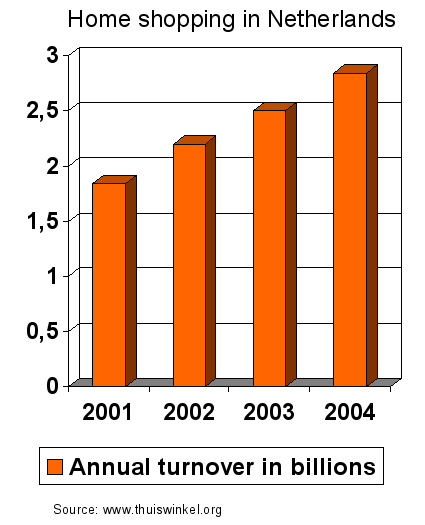
2004 Netherlands:
- 174 Euros per inhabitant
- Increased participation of elderly and disabled
- 30% of shopping was outside own country
- Total for Europe: 67,7 Billion Euros
But is it accessible??
Online government
- 93% of EU member states have a website
- 90% of all countries online offer information, databanks, legislation
online
- 30% offers online services
But are they accessible??
Google WAI impact *)
- 142,000,000 for guidelines web
- 14,100,000 for guidelines web accessibility
- 7,270,000 Web Content Accessibility
Guidelines
- 5,700,000 for Web Accessibility
Initiative
- 215,000 for User Agent Accessibility Guidelines
- 144,000 for Authoring Tool Accessibility Guidelines
Note: Google estimates
Note: relative inpact of UAAG and ATAG, althought smaller in number can be
greater.
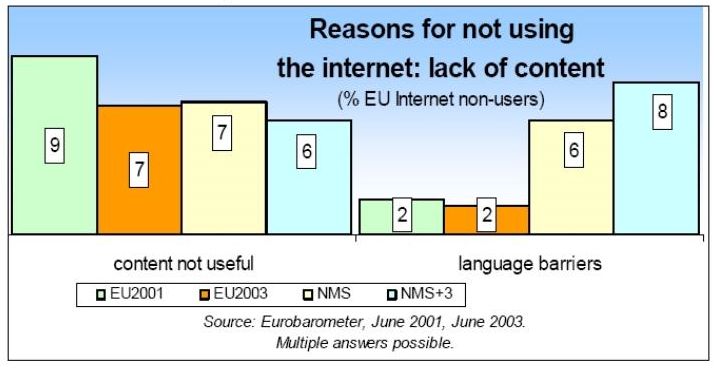
Useful content
Reasons for not using the Internet: lack of content
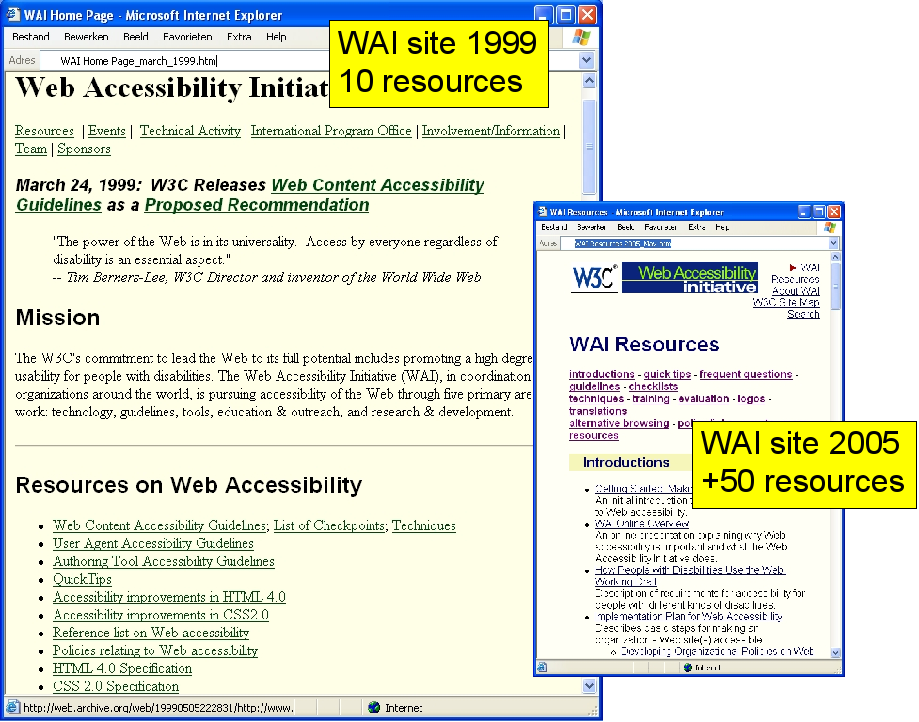
The archive.org
Why Use W3C Accessibility Guidelines (and Valid Code)
Lessons learnt in the Netherlands
Accessibility is good news (1/2)
- No need for text only sites, everyone gets the full experience of your
site including images and multimedia
- Easily changable 'Look-and-feel‘
- Up to 60% decr.pagesize possible *)
- Optimized for Search engines
- Futureproof: Conforms to standards
*) Actual decrease in size of main website of
ministry of Health Netherlands.
IBM saved up to 50 percent with their main graphic site.…
Accessibility is good news (2/2)
- Works better in old and future browsers
- Ready for possible legislation and certification
- More ready for your mobile devices
- One site for multiple platforms is easier
- Faster loading time
- Sites available in case of calamities
Web Accessibility Harmonization in Europe
Logos Related to Web Accessibility

Google: 778,000 hits for quality mark web
accessibility
European Answers for an Inclusive Future
Adoption and harmonization of W3C/WAI standards
European information Society i2010
- Promoting a borderless EU information space
- Internet, tv and telephone over the same infrastructure
- Action plan for general framework for the digital services economy
(guidelines and best-practice–3jrs)
- Stimulating innovation by investment in research
- Doubling IST funding for FP7
- Making the European Information Society as inclusive and accessible as
possible
Source: Speech: i2010: How to make Europe’s
Information Society competitive. Viviane Reding. Brussels, 22 February
2005
EC eAccessibility for 2005
Objective: achieving an information Society for all
- Three pillars:
- Accessibility requirements in public procurement
- Certification and assessment (self declaration, 3rd party,
voluntary, mandatory, etc.)
- Explore legal measures
- Instruments:
- Harmonisation (voluntary)
- Help self-regulation
- Review situation in 2006
- Possibly other measures including legislation.
Source: Results of online consultation: Mrs.
Viviane Reding
EC eAccessibility for 2005
- Complementary actions:
- Foster standardisation/ Increase skills/ Design for all/ Raise
awareness/ Benchmark and monitor/ Research and technological
development
- Web accessibility: Need to assess and certify accessibility of
public web sites
- Member states websites accessible by end of 2001/2003 ?
Source: Results of online consultation: Mrs.
Viviane Reding and Source: 25 September 2001agreed by European Parliament
The WAB Cluster


FP6/IST project (2003-2006) on eInclusion:
- WAB Cluster - Web Accessibility Benchmarking (WAB) Cluster, with a
close coordination with WAI. The cluster goal is to define a unified web
evaluation methodology (UWEM) for conformance to the WCAG guidelines.
- European Internet Accessibility Observatory (EIAO), in relation to
the 2002 Council's request for obtaining comparable data across
Member States;
- Supporting the creation of an eAccessibility Mark (Support-EAM), in
relation with the 2002 Council's request to investigate such a
labelling - the project has triggered a CEN Workshop for discussing
the approaches;
- Benchmarking Tools for the Web (BenToWeb)
Example of a Quality Mark and evaluation scheme Netherlands
Quality Mark drempelvrij.nl

- Priority 1
- Ensuring representation from all stakeholders
- TV attention, and umbrella orgs advertising
Identifying experts: Accessible builders/design companies
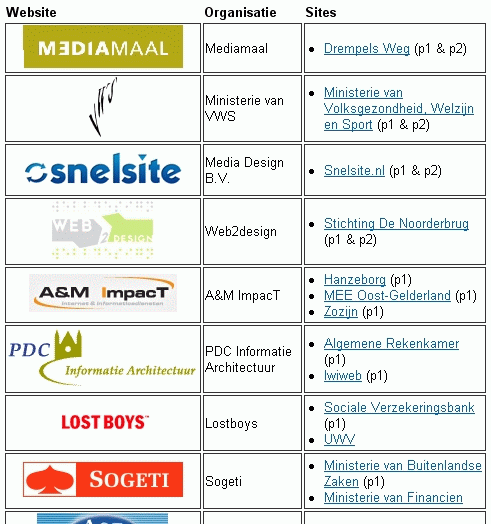
Organizations: Mediamaal, Ministerie van VWS,
Media Design B.V., Web2design, A&M ImpacT, PDF Informatie Architectuur,
Lostboys, Sogeti
Identifying Experts: Accessible Web sites/best practice
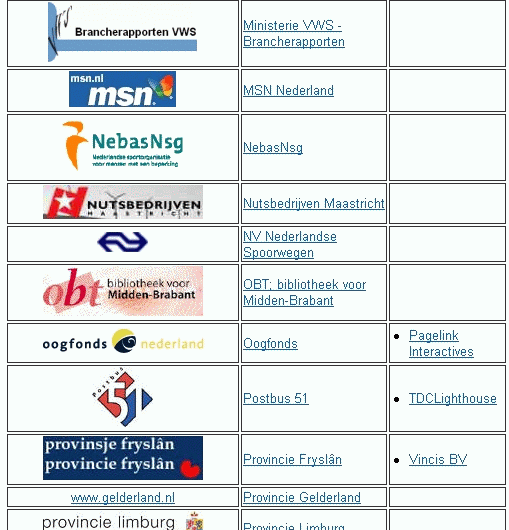
Organizations: Ministerie WVS-Brancherapporten,
MSN Nederland, NebasNsg, Nutsbedrijven Maastricht, NV Nederlandse Spoorwegen,
OBT: bibliotheek voor Midden-Brabant, Oogfonds, Postbus 51, Provincie
Fryslân, Provincie Gelderland, Provincie Limburg
Identify best practice examples
Summary of years of evaluation and raising awareness
Current state in most countries
Percentage of total Dutch Web sites
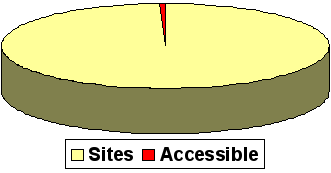
Percentage of government sites
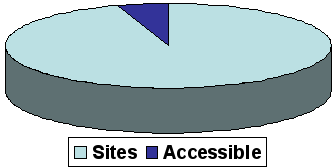
Percentage of accessible Web sites
In the Netherlands:
- 1.000.000 websites
- 33 accessible
- Of 1000 websites researched, 2 valid code (education necessary)
Conformance: the magic tool
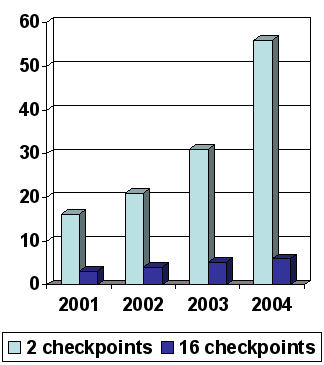
Dutch situation:
- 2 checkpoints: designers ‘please the test’
- 4 government websites had the Quality Mark (less than 0,4 percent of
the total. Dec.2004)
- Monitor 2004 shows 2 of the 100 sites accessible
Action: Results of ‘WAI’ campaign in the Netherlands
- Awareness (85% population, 67% companies)
- 33% of participants are accessible
- 101 paying participants for quality mark
- Participants include multinational companies
- Significant increase in accessibility of websites
- 350 Declarations of Intent
- List of preferred suppliers
- Increasing demand for usability testing protocols
General conclusions (1/2)
- Positive role of WAI has been and is important
- Accessibility recommended by Council and Parliament not yet
achieved.
- Need for methodologies to evaluate (and repair) public web sites.
- Cluster all efforts for accessible web sites around the W3C/WAI
- Harmonize standards for web accessibility in Europe.
- Awareness has considerably increased since 1997/9.
- Accessibility claims do not always show really accessible sites.
General conclusions (2/2)
- Accessibility has ROI
- Experienced designers and appropriate training are necessary.
- There is a need for accessibility support in web authoring and CMS
tools to ease the development of accessible web sites.
- There is a need for official translations and formal recognition of the
WAI guidelines as standard for use in national legislation (by
Standardisation organisations with W3C)
- We need a mechanism to follow up, monitor and respond to requests and
complaints from citizens with disabilities.
- We need research on different certification models (Wab cluster)
Brochure

Internet Policy: Overcoming Contradictions

Isabelle Falque-Pierrotin, Chair – Internet Rights Forum
Outline
- A Bit of
History
- The Rise of Regulatory Initiatives
- Co-Regulation and the Internet Rights Forum
- A Universal Approach to Complex Social Issues?
A Bit of History
From a small community to the digital avatar of our globalized
societies
- Originally a community of specialists, expanding fast
- 130 websites in 1993
- 23,500 in 1995
- 230,000 in 1996 (MIT)
- 1996 : Trouble ahead as Net usage booms (The end of innocence?)
- France: Gubler case fires regulatory concerns
- USA: Communication Decency Act as a failed attempt to regulate the
Internet
Outline
- A Bit of History
- The Rise of
Regulatory Initiatives
- Co-Regulation and the Internet Rights Forum
- A Universal Approach to Complex Social Issues?
The Rise of Regulatory Initiatives
From strict self-regulation …
- Climax in 1997?
- FTC strongly endorses self-regulation on data protection …
- … but finally notices a lack of uniformity in data protection
practices
- Limits : self-regulation sometimes fails to satisfy objectives of
common interest
- FTC finally asked Congress for new laws
- Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act of 1998
The Rise of Regulatory Initiatives
… to governmental intervention
- From 1998 onwards: an upsurge in legislation
- USA: DMCA (1998), COPPA (1998), Can Spam Act (2003), …
- EU: More than 15 directives in a few years
- France: Laws on electronic signature and cryptography (2000), data
retention (2001), electronic voting (2004), e-commerce (2004), data
protection (2004), …
- Limits: Governmental intervention having little impact of some major
issues
- Spamming
- Copyright enforcement issues …
Outline
- A Bit of History
- The Rise of Regulatory Initiatives
- Co-Regulation and the
Internet Rights Forum
- A Universal Approach to Complex Social Issues?
Co-Regulation and the Internet Rights Forum
Co-regulation : 3 beliefs
- Internet as global social space / marketplace needs a form of
regulation
- Complexity of the Internet challenges traditional modes of regulation,
notably by the State
- A principle of shared responsibility
Co-Regulation and the Internet Rights Forum
The Internet Rights Forum
- A dedicated para-governmental organization, open to membership
- Organizes a permanent dialogue between all members of the Internet
community on an equal basis
- 16 policy recommendations (IP, e-voting, child protection,
tele-working…) adopted by consensus
- To the Government as well as to business and users
- Legislation, codes of conduct, technical recommendations
Co-Regulation and the Internet Rights Forum
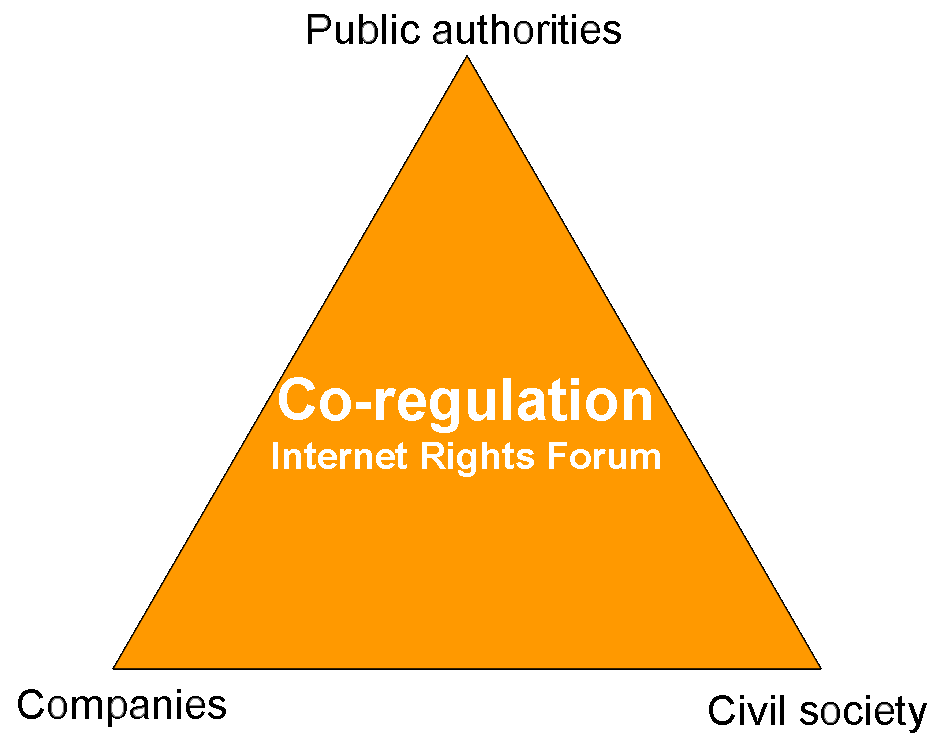
Outline
- A Bit of History
- The Rise of Regulatory Initiatives
- Co-Regulation and the Internet Rights Forum
- A Universal Approach
to Complex Social Issues?
A Universal Approach to Complex Social Issues?
Co-regulation stands out internationally
- The Internet Rights Forum launched the European Internet Co-regulation
Network (EICN) in 2003
- Work by international organizations frequently refers to this
regulatory strategy: WSIS-ITU, EC, Council of Europe…
- Europe a leader of the co-regulatory approach?
A Universal Approach to Complex Social Issues?
Co-regulation calls for cultural changes
- From the Governments
- Accept open dialogue with other stakeholders
- From the private sector
- Commit into real dialogue with all parties involved
- From the civil society / internet users
- Organize themselves to participate constructively
Conclusion
Internet Policy:
Regulation through Open Dialogue
Policies shaping the Web in EuropeStandards, the Public Sector and the
Web

Peter F Brown, Chair, CEN eGovernment Focus Group
Personal Introduction
Official of the European Parliament…
- 2000-2004, Head of service responsible for interoperability and
information architecture
…on secondment to the Austrian Government,…
- Advisor on pan-European eServices and preparation of Austrian
Presidency of EU Council in 2006
Chair of “eGovernment Focus Group”…
- Established by European standards body, CEN
…and individual member of OASIS
- Co-editor of SOA-RM Specification
- Member of eGovernment TC
The “Teenage Web”
The difficult years ahead
“Who am I? What am I?” - identity
“Nobody understands me...” - semantics
“Nobody cares” - trust
Battles with authority and desire/need for independence -
governance
Identity of Web resources
What is a resource? What is a representation?
Problem of conceptual layers
- A “document”
- A “service”
- A “person”
Everything needs identity, but be clear what every “thing”
is...
Taking ownership: value of "Namespaces" to delineate "Unformation
Spaces"
Electronic Identity
Separating concepts of:
- “online identity”
- Electronic ID
Personal data and citizenship
New contribution: “citizen-centred architecture”
- Protecting personal data
- Offering citizens choice
- Federating identity management
- From "DigitalMe" to "Digital I"
"Nobody understands me" - Semantics
Dealing with misunderstandings: concerns about terminology
- Structured domain knowledge vs AI: “I mean this” not “I think
you mean that”
- Semantic interoperability – issue of domain governance - think:
"assets"
- Building bridges between IT/R&D and users
“Semantic Web” or semantic web?
- Who else is involved?
- Keep up the good work of liaisons
Trust
Managing identity
Dealing with abuse
- Recourse and responsibility
Building a web of trust
- “I know who you are, but do you know who I am?”
Governance
Interoperability doesn't just happen
- Domain-based governance and standards
- Acting in loco parentis: is someone responsible?
Not something to fear something to embrace
- Public sector can provide a reference anchor
US and Europe
- We do things differently - reflection of different values?
- Doesn't mean one is right/wrong
- Need to work together
Thank you and Good Luck!
Next Session
Questions and Answers
Thank you all for making this a great celebration.
We look forward to seeing you at the W3C Twentieth Anniversary
Celebration.
All W3C10 Europe Sessions



















