Open Web Platform
Accessibility Imperative
The Web has become an essential part of society:
- 15-20% of the population has cognitive, hearing, physical, neurological, speech, or visual disability
- Rapidly growing ageing population also affected
- Benefits for ~57% of the population (Microsoft)
- Business benefits and increased market share
- Legal requirements in many parts of the world
Accessibility Features
Examples of web accessibility features include:
- Text alternatives for images, video, and sound
- Marking-up headings, lists, and other structures
- Labels and instructions for forms and controls
- Consistent labeling, interaction, and behavior
- Adaptable content (text size, color, spacing, ...)
- Understandable instructions, messages, ...
WCAG 2.0
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0:
- Internationally recognized accessibility standard
- Applies to web applications including on mobile
- Authorized W3C translations in 10+ languages
- Also available as ISO/IEC 40500:2012
- Being applied to software (US Section 508, EC Mandate 376) – interpretation in WCAG2ICT
WCAG 2.0 Structure
Structure of the normative WCAG 2.0 standard:
- 4 Principles
- 12 Guidelines
- 25 Level A Success Criteria
- 13 Level AA Success Criteria
- 23 Level AAA Success Criteria
- Conformance Requirements
WCAG 2.0 Principles
Four core principles of WCAG 2.0:
- P - Perceivable
- O - Operable
- U - Understandable
- R - Robust
WCAG 2.0 Guidelines
Examples of WCAG 2.0 Guidelines:
WCAG 2.0 Criteria
Examples of WCAG 2.0 Success Criteria:
- 1.1.1 Non-text Content: All non-text content that is presented to the user has a text alternative that serves the equivalent purpose - Level A
- 2.2.4 Interruptions: Interruptions can be postponed or suppressed by the user, except interruptions involving an emergency - Level AAA
WCAG 2.0 Structure
Structure of the normative WCAG 2.0 standard:
- 4 Principles
- 12 Guidelines
- 25 Level A Success Criteria
- 13 Level AA Success Criteria
- 23 Level AAA Success Criteria
- Conformance Requirements
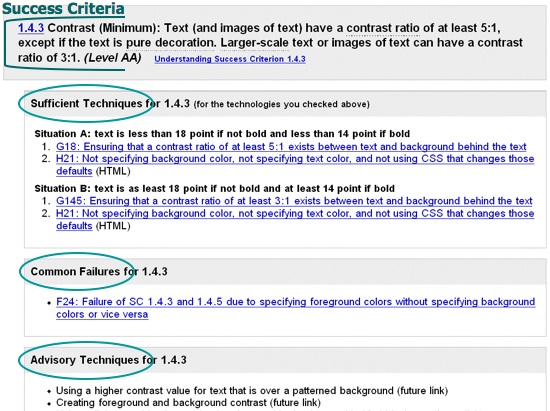
WCAG 2.0 Techniques
Techniques are non-normative, non-exclusive, and non-exhaustive documentation of approaches:
- Sufficient Techniques - minimum requirement
- Advisory Techniques - further improvement
- Common Failures - often encountered issues
Test Procedures
WCAG 2.0 techniques contain test procedures:
Technique H36:
- For all input elements that have a type attribute value of "image", check for the presence of an alt attribute.
- Check that the alt attribute indicates the button's function.
How To Meet WCAG 2.0

Quick Reference
Evaluation Tools
Many tools exist to help testing for WCAG 2.0:
- Automated website crawlers
- In-page and per-page tools
- Focused tools (eg. colors, ...)
- Built into web authoring tools
- Combination of all the above
Participation
Many ways to participate and contribute:
- Uptake and use of W3C/WAI resources
- Translation and promotion of materials
- Review of drafts and providing feedback
- Active participation in Working Groups
- Increased W3C Member organizations
- Opportunities for sponsoring W3C/WAI
