World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)
"Leading the Web to its full potential"
- Directed by web-inventor Tim Berners-Lee
- International, vendor-neutral consortium
- Multi-stakeholder, consensus process
- Develops open, royalty-free web standards:
- HTML, CSS, XML, SVG, SMIL, ...
- Operates from MIT, ERCIM, and Keio
Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI)
WAI develops strategies, guidelines, resources to make the Web accessible:
- Accessibility support in W3C technologies
- Guidelines for implementing accessibility
- Methods for evaluating accessibility
- Conducting education and outreach
- Coordinating with Research and Development
Relevance of Web Accessibility
The Web has become an essential medium for:
- news, information, commerce, entertainment,
- classroom education, distance learning,
- job searching, workplace interaction,
- civic participation, government services
Access to information has been recognized as human right by the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD)
Accessibility and Innovation
Accessibility is a major driver of innovation and invention:
Braille Code, E-Mail, Headphone, Keyboard, Microphone, Personal Digital Assistant (PDA), Printer, Punchcard, Scanner/OCR, Speech Recognition, Speech Synthesis, Spectogram, Subtitling, Talking Books, Telephone, Teletype, Transistor, Voice Indexing, ...
Source: Accessibility and Disability - A History of Innovation by Artur Ortega, Yahoo!
Accessibility and Technology
People with disabilities are early adopters of technology:
- Speech Synthesis (text-to-speech)
- Speech Recognition (speech-to-text)
- Eye-tracking and gesture recognition
- Alternate pointing and input methods
- Internet, Web, and other ICT systems
People with Disabilities
Web accessibility is people with disabilities:
- Vision - blind, partial sight, color, ...
- Hearing - deaf, hard of hearing, ...
- Physical - missing limbs, paralysis, ...
- Cognitive - dyslexia, intellectual, ...
- Neurological - seizures, sclerosis, ...
- People with ageing-related impairments
Web Accessibility Barriers
Examples of barriers on the Web include:
- Images, videos, audio with no alternative text
- Layout and font do not expand and shrink well
- Forms and controls can not be used by keyboard
- Inconsistent and/or overly complex navigation
- Script events are device and browser dependent
- User control, natural language, ...
Accessibility for Everyone
Web accessibility benefits many users:
- Low literacy or computer skills
- Temporal functional limitations
- Situation or external influence
- Limited bandwidth connectivity
- Legacy hardware and software
- Mobile and ambient technologies
Up to 65% benefit from accessibility (Microsoft, 2005)
Benefits for Businesses
Web accessibility has business benefits:
- Increase audience reach and market share
- Increase search engine ranking (SEO)
- More usability and customer satisfaction
- Reduce maintenance and redesign costs
- Improve the access for mobile Web users
- Increase server and bandwidth efficiency
- Support older and newer technologies
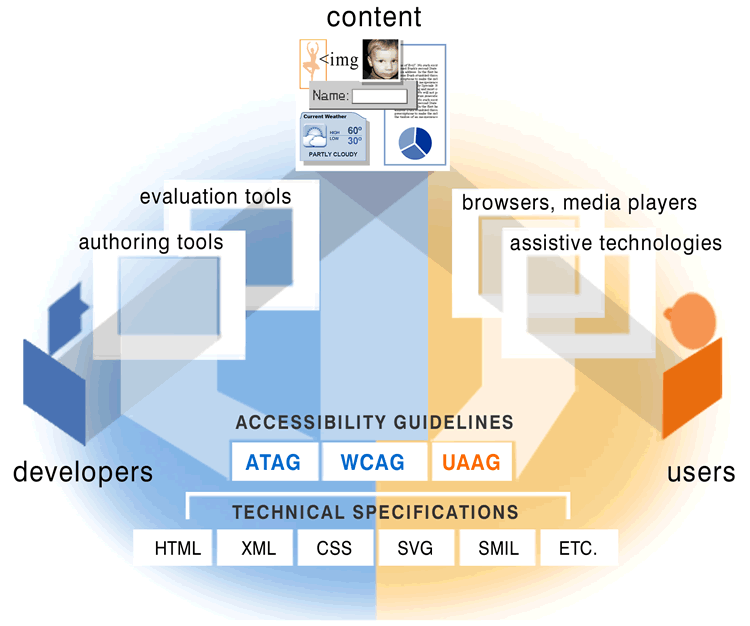
Scope of Web Accessibility
Web accessibility is supported by several key components:
- Base Format - technologies such as (X)HTML, CSS, SVG, SMIL, PDF, Flash, Silverlight, ...
- Authoring Tools - code editors, CMS, blog, wiki, save-as tools, conversion tools, ...
- User Agents - Web browsers, media players, browser plug-ins, assisitive technology, ...
- Web Content - text, images, audio, video, code, markup, structure, presentation, ...
Components of Web Accessibility
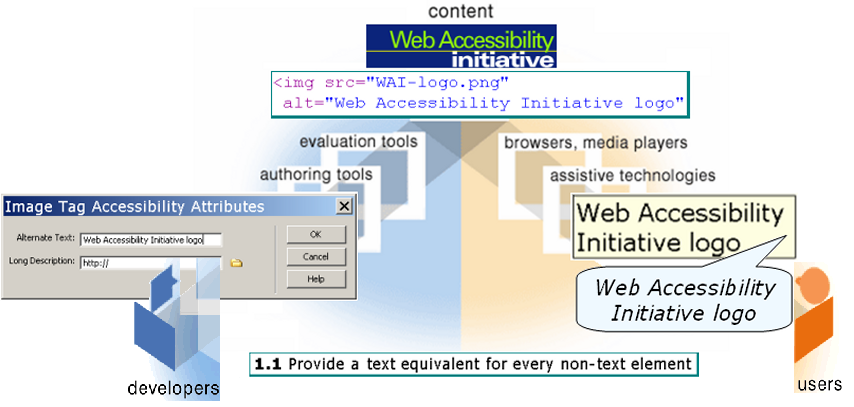
Example of Accessibility
WAI Accessibility Guidelines
W3C Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) develops and maintains:
Also: WAI-ARIA for accessible web applications.
Web Accessibility Evaluation
For optimal web accessibility evaluation, developers need to:
- Combine different skills and expertise
- Combine different types of support tools
- Integrate into the development process
Skills for Evaluation
Web accessibility evaluation can be done by people with different skills:
- Few aspects can be checked automatically
- Some aspects can be checked by anyone
- Some aspects need technical expertise
- Some aspects need knowledge of users
- Some aspects need usability expertise
Motivations for Evaluation
Evaluation should be carried out throughout the development process:
- Get a quick, rough idea of the website
- Learn about certain types of issues
- Investigate particular design aspects
- Testing of features during development
- Get objective opinion on conformance
- Get comprehensive feedback analysis
- Monitor on-going accessibility progress
Sampling Web Pages
Representative samples should include pages developed by different people and that include different features (such as lists, tables, forms, etc.); in particular:
- Templates, style sheets, snippets
- Home page, other important pages
- Frequently-used, high traffic pages
- Critical paths and full processes
Prioritizing Repairs
After evaluation, prioritization becomes a key question:
- Impact on accessibility
- Frequently accessed pages
- Pages with significance
- Logically related pages
- Logically related repairs
Note on Evaluation Tools
Web accessibility evaluation tools can:
- Reduce time and effort for evaluation
- Automatically check some requirements
- Assist during the evaluation process
Types of Evaluation Tools
There are many different types of web accessibility evaluation tools:
- Fully automated
- Semi-automated
- In-page feedback
- Wizzard interface
- Developer tools
List of Web Accessibility Evaluation Tools
Limitation of Tools
Web accessibility evaluation tools have substantial limitations:
- Only few requirements are automatable
- Tools may be misleading or imprecise
- Prone to false positives or negatives
Selecting Web Accessibility Evaluation Tools
Conclusions
- Access to information is a human right
- Accessibility is a source of innovation
- Benefits for many users and businesses
- Mature and recognized standards exist
- Research opportunities in evaluation
