
Position Aware Tourist Information Services
A.P. Lenaghan & R Malyan
Networking and Communications Group,
School of Computer Science & Electronic Systems,
Kingston University, Penrhyn Road,
Kingston, Surrey KT1 2EE, UK.
Abstract
We present an analysis of the needs of tourists for positioning information in using mobile multimedia terminals for accessing tourist information on the move. We consider first, a simple framework relating the needs of individuals and groups of tourists to information about a tourist area before going on to develop the concept of layered services for delivering position dependant information to mobile devices.
Introduction
Tourists have an acute need for positional information. A tourist is by definition a person who finds themselves in unfamiliar surroundings. Advances in the development of Personal Digital Assistance's (PDA) coupled with forthcoming 3rd generation wireless technologies offer the possibility of delivering multimedia information to tourists on the move. However, to be of significant use this potentially new mechanism for delivering information must keyed to their current location or planed routes. Truly useful mobile devices for tourists will need to be position-aware and supported by services to select and deliver relevant information.
Framework for Tourist Information Relating to Positioning
A position aware tourist information system would involve, wireless networking, mobile hardware and software implementations of services to assist tourist activities.
In analyzing tourist requirement at its top most level we can leave aside the technological details of how the services will be realized to focus tourist's perspective.
We divide the analysis between the principle components in the tourist scenario we are considering and the relationships between these components (see figure 1 below).

Figure 1 Framework for Positional Information for Tourists
Principle Components (figure 1)
We identify three principle components in our proposed framework for position aware tourist services, which are defines as:
Relationships based on Positioning Information
Focusing on the individuals, we can identify the activities they can perform in relation to the other components that make use of positioning information. The services we outline below are aimed at assisting in these activities.
In this initial analysis we identify 6 activities (stated in italics below) falling into 3 categories that can potentially be supported by services delivered via position aware mobile multimedia devices.
Activities relating Individuals to Tourist-Area
Activities relating Individuals to groups
Activities relating Groups to Tourist area (less relevant to proposal)
We can define services to assist each of the tourist activities an individual performs. The degree of assistance will vary depending on the sources of information that are drawn upon in generating a response to an individual's request. We see this as leading to a layered set of services where information is combined cumulatively to provide progressively richer or more sophisticated versions of a service.
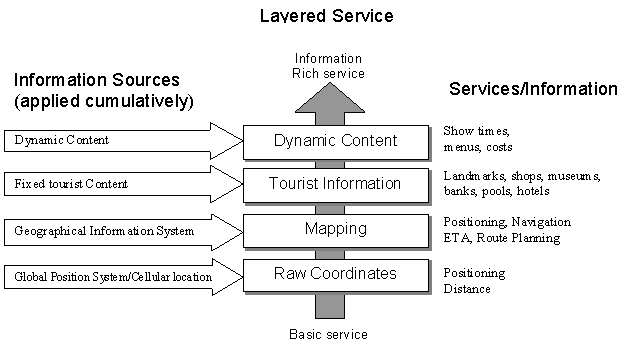 Figure 2: layered services
Figure 2: layered services
We define a service from an individuals perspective as the timely delivery of relevant information to assist in a tourist activity. This encompasses the optimal selection of the format in which to deliver information given the context of the individuals client devices and network connection.
Example of layering
The location and navigation activities relating an individual to a tourist area can be assisted by a basic service that operates solely at the level of the raw coordinate information supplied by the GPS or cellular radio systems. This could provide an individual with their grid reference to assist in locating themselves and a distance and direction to and rendezvous point to assist in navigation.
At a second level raw coordinate information could be combined with the information in a GIS about the tourist area to indicated a uses location on a street map and offer a route to a rendezvous or meeting point.
GIS information would allow basic route planning or suggestion.
At a third level a service could introduce fixed information describing a location in terms of near by landmarks, views, tourist amenities (banks, shops, toilets, beaches, cafes) and it could augment a route to be navigated with local points of interest or via particular amenities.
Finally at a top-level dynamic information could be integrated into the service provided to individuals with information describe changing factors of the tourist environment. For example, to support the exploration activity (relating individuals to tourist areas) with information about museum opening times, cinema show times, restaurant menus and prices.
The principle components in the proposed framework are individuals, groups and tourist-areas. An individual can perform several activities in relation to the other components that require positioning information. These include the location, navigation and exploration of tourist areas and the monitoring and meeting of groups. Each activity can be assisted by a service. Services can be provided at a range of levels of richness depending on the sources of information that are integrated.