Semantic Web Specification at W3C
...
<foaf:Person>
<foaf:name>Takashi OTA</foaf:name>
<foaf:name xml:lang="ja">太田尚志</foaf:name>
<foaf:title>Mr</foaf:title>
<foaf:firstName xml:lang="ja">尚志</foaf...
<foaf:firstName>Takashi</foaf...
<foaf:surname xml:lang="ja">太田</foaf:s...
<foaf:surname>OTA</foaf:surname>
<foaf:nick>takot, Takashi</foaf:nick>
<foaf:nick xml:lang="ja">たこちー</foaf:n...
<foaf:knows>
<foaf:Person>
<foaf:name>SHIMIZU Noritada</foaf...
<foaf:firstname>Noritada</foaf:fi...
<foaf:firstname xml:lang="ja">智公...
<foaf:surname>SHIMIZU</foaf:surname>
<foaf:surname xml:lang="ja">清水<...
</foaf:Person>
</foaf:knows>
</foaf:Person>
...
Eric Prud'hommeaux
19 March, 2004
$Revision: 1.1 $ $Date: 2004/03/19 01:21:40 $
Available at http://www.w3.org/2004/Talks/0319-RDF-WGs/.
These slide contain many pointers -- intended to be used as a resource after the talk is complete.
RDF and other W3C Technology
- Data in RDF
- Acquired by HTTP
- Layout defined in SVG, XSLT, CSS
- Presented in XHTML
Imagine SQL with:
- standard transport
- a presentation language
- device independence
- global scope
- standard self description
W3C specifies a set of semantic web specifications to standardize the publication and description of data.
Other W3C specifications provide a "web" framework for distribution and consumption of this data.
What motivates us to work in RDF?
- URI's leverage existing social system to create unambiguous terms
- URI's provide dereferencing system for acquiring latent semantics
- coincides with industry interest in process process integration
- coincides with world enthusiasm for the world wide web
Semantic Web "Layer Cake"
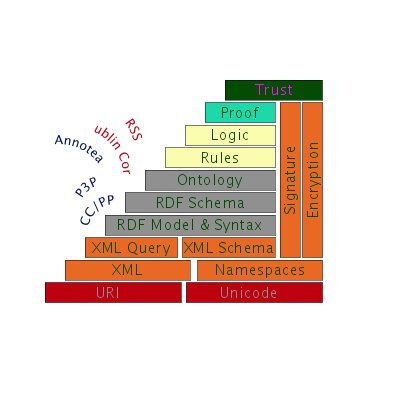
TimBL presents the stack of semantic technologies as a series of strata.
Publication History
- 1997-1998 Pre-RDF ground work ...
- Feb 1999 original RDF Model and Syntax Recommendation
- March 1999 RDF Schema Proposed Recommendation
- 1999-2003 RDF infrastructure and protocol notes
- 2000-2004 RDF application vocabularies (PICS, P3P, CC/PP...)
- Feb 2004 suite of RDF Recommendations (syntax, concepts, semantics, primer, test cases)
- Feb 2004 Rdf Schema Recommendation
- Feb 2004 suite of OWL Recommendations (overview, language Guide, reference, semantics, test cases)
- replaced by later publication
- W3C Recommendation
- W3C Note
Specifying the "Layer Cake"
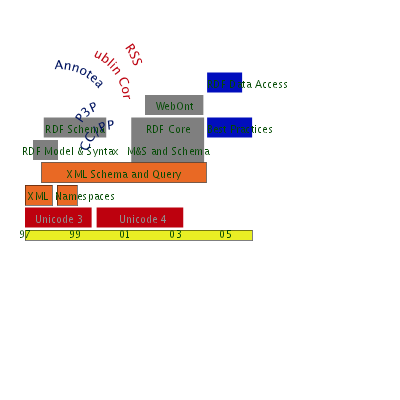
What we've specified so far, what we're doing now, and what we have left to do...
W3C Standardizes RDF, RDF Schema, and OWL
What do these standards give us?
- common model for data
- data model shared with metadata
- excellent opportunity for data re-use
- opportunity to unify the world's databases
What we are doing now
Two working groups underway:
The RDF Interest Group met March 1-2. topics included:
- Data Access Working Group
- Best Practices Working Group
The BPWG met March 4-5.
The HTML WG discussed RDF in HTML.
The Device Independence WG discussed RDF query and annotations.
Semanic Web Best Practices and Deployment Working Group
"...provide hands-on support for developers of Semantic Web applications." -- SWBP charter
Focus areas:
- Supporting initiatives for publishing ontologies / vocabularies
- FAQs and how-to-do-it guidelines
- Repository of tools and demo applications
- Links to related techniques
RDF Data Access Working Group
"...reduce redundancy and enhance interoperability as SQL did for relational databases." -- DAWG charter
Benefits of standardization:
- will provide applications with uniform access to RDF data.
- will enable standard a query language service.
Expressivity
Commonality:
- Conjuntive query with variable bindings.
RDF Query Issues
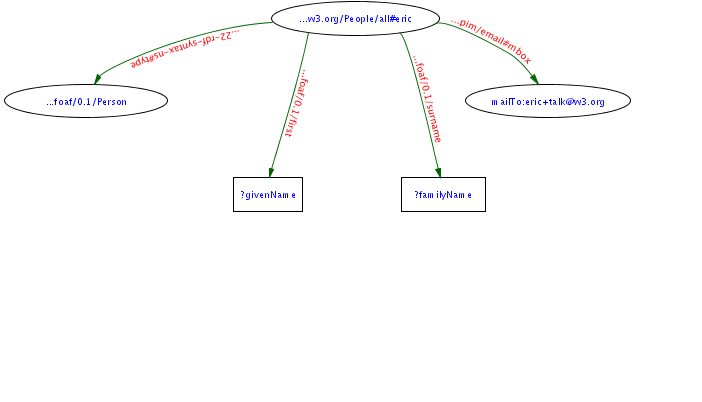
ns foaf=<http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
ns pim=<http://www.w3.org/2000/10/swap/pim/>
ask (
?who swap:pim <mailto:eric+talk@w3.org>.
?who foaf:firstName ?givenName.
?who foaf:surname ?familyName)
collect (?givenName ?familyName)
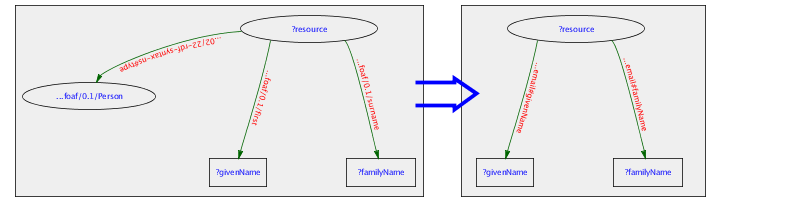
- express query comonents in XML
- between a lot and too many angle brackets
- RDF
- express the query as an RDF graph
- leads to reificiation (or misleading assertions)
- other (ASCII)
- SQL-like
- XPath/XQuery-like
- Templating -- express results XML
- can re-use XQuery syntax (maybe some implementation?)
What we have left to do...
... (that we know of)
- Trust -- discovering and modeling social practice
- Proof -- bookkeeping
- Rules -- already vast implementation experience
RDF Rules
RDFS and OWL have semantics that must be interpreted by a programmer.
A standard expression of rules allows the machine to assume that step.
- Inventor of the term defines the rules.
- User of the term imports the rules and benefits from their inferences.
Research Issues
Such a large arena, hard to select.
Here are a few recurring issues:
Context, Attribution, Provenance...
Most information management systems imply some "paper trail", information about where the information comes from.
Databases, RDF included, tend to push this information in the application layer.
There is no current standard way to describe the relationship between an assertion and the document where that assertion was found. cwm uses logInclude. Most DBs keep the information "out of the model".
Interaction with Conventional Databases
efficiency -- flexibility of RDF with the efficiency of relational DBs:
- store data efficiently in relational databases
- give semantic web access to data in relational databases
This provides access to much of the data now used within organizations.
- use RDF to add flexibility to relational data.
Database manufacturers can provide this view of data:
- Oracle Network Data Model -- store and query RDF graphs.
Conclusions:
- Knowledge Representation is a well-explored field.
- W3C provides expertise in scalable web technology.
- W3C provides a forum for industry consensus.
- RDF promotes balance between chaotic freedom and standardized interoperability
More Topics