SOAP 1.2
Message Exchange Patterns (MEPs)
Glen Daniels
Jean-Jacques Moreau
SOAP 1.1
- HTTP specific
- Although less so
than prior versions
- Uses
HTTP POST
- Mainly
used for RPCs
- RPC request
mapped to HTTP request
- RPC response
mapped to HTTP response
SOAP 1.2
- No longer limited to HTTP
- Binding framework
- Shields SOAP from underlying protocol
- Model
for plugging-in other protocols
- Not
limited to request-response either
- Features not supported by a given protocol can be
implemented via extensions to SOAP processing model
SOAP 1.2 MEPs
- Describe message exchanges, such as
request-response
- Described by state machine for each participating
node
- Independent of underlying protocol
- Named by URI
- E.g.
http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/request-response/
- Two MEPs in latest ed-copy
- SOAP request-response (stable)
- SOAP response (work in progress, no consensus, subject
to TAG feedback)
Request-Response MEP
- Exchange of a single SOAP request and a SOAP response
between two adjacent SOAP nodes
- No intermediary in between
- Assumption time-limited exchange, not long-lived
transactions
- Both requests and responses
are SOAP messages
- Both are processed according
to SOAP processing model
- For HTTP binding, maps to HTTP POST
Request-Response MEP
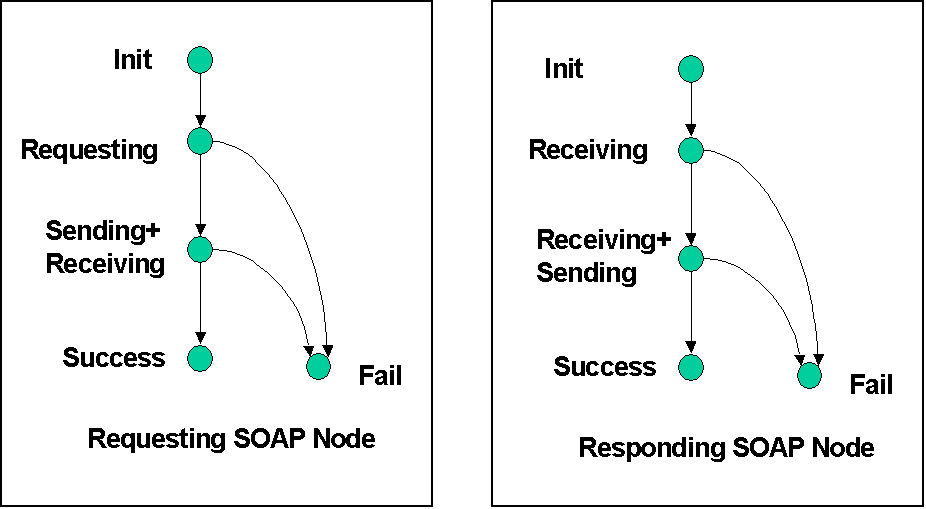
Request-Response MEP
MEP properties:
- context:ExchangePatternName
- context:FailureReason
- reqres:Role
- reqres:State
- reqres:OutboundMessage
- reqres:InboundMessage
- reqres:ImmediateDestination
- reqres:ImmediateSender
SOAP MEP = WSDL MEP ?
Does it
make sense to replace hard-coded <input> and <output>
elements with dynamic syntax using SOAP message and feature
names?
Example
<operation name="foo" mep="…/request-response">
<message name="…OutboundMessage" element="foo:req" />
<message name="…InboundMessage" element="foo:resp" />
</operation>

